Biol 476 Lab Exam 2 - Vocabulary and Definitions
1/181
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
182 Terms
Femur head
round structure articulates with the acetabulum of the os coxa
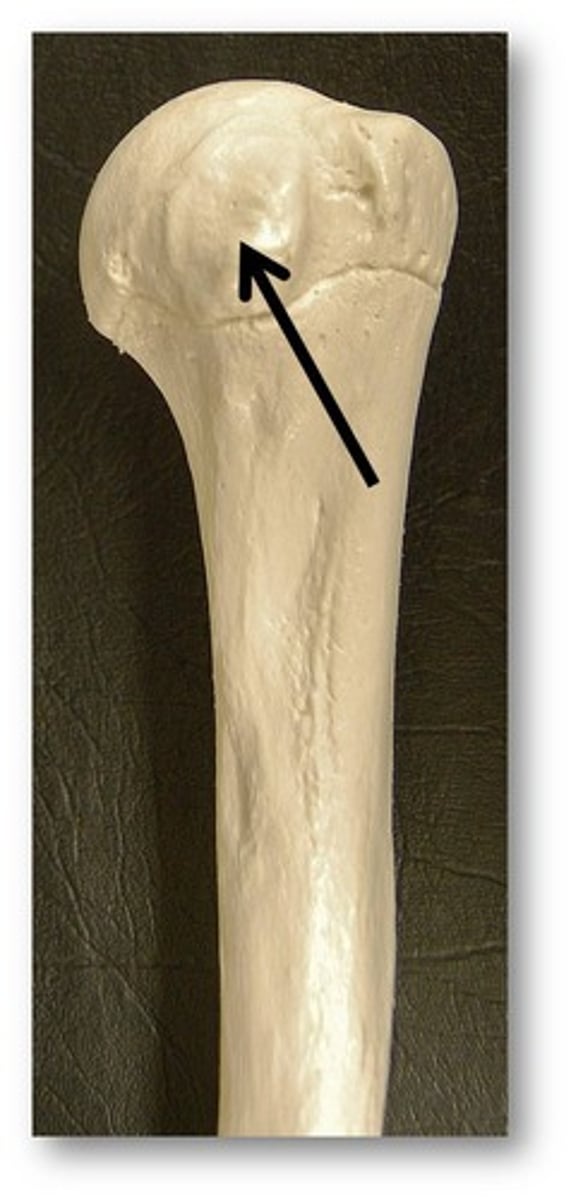
Femur neck
elongated structure connects the head to the main shaft of the bone
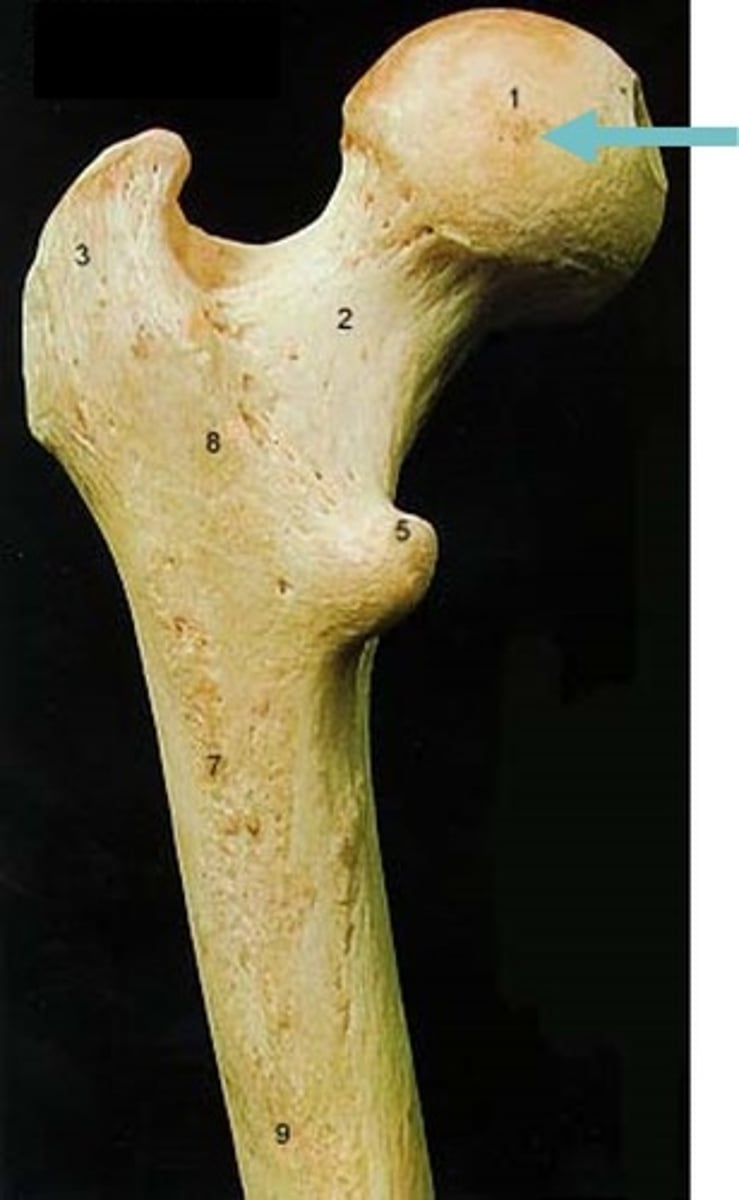
Greater trochanter
large and bumpy muscle attachment point that is lateral to the head
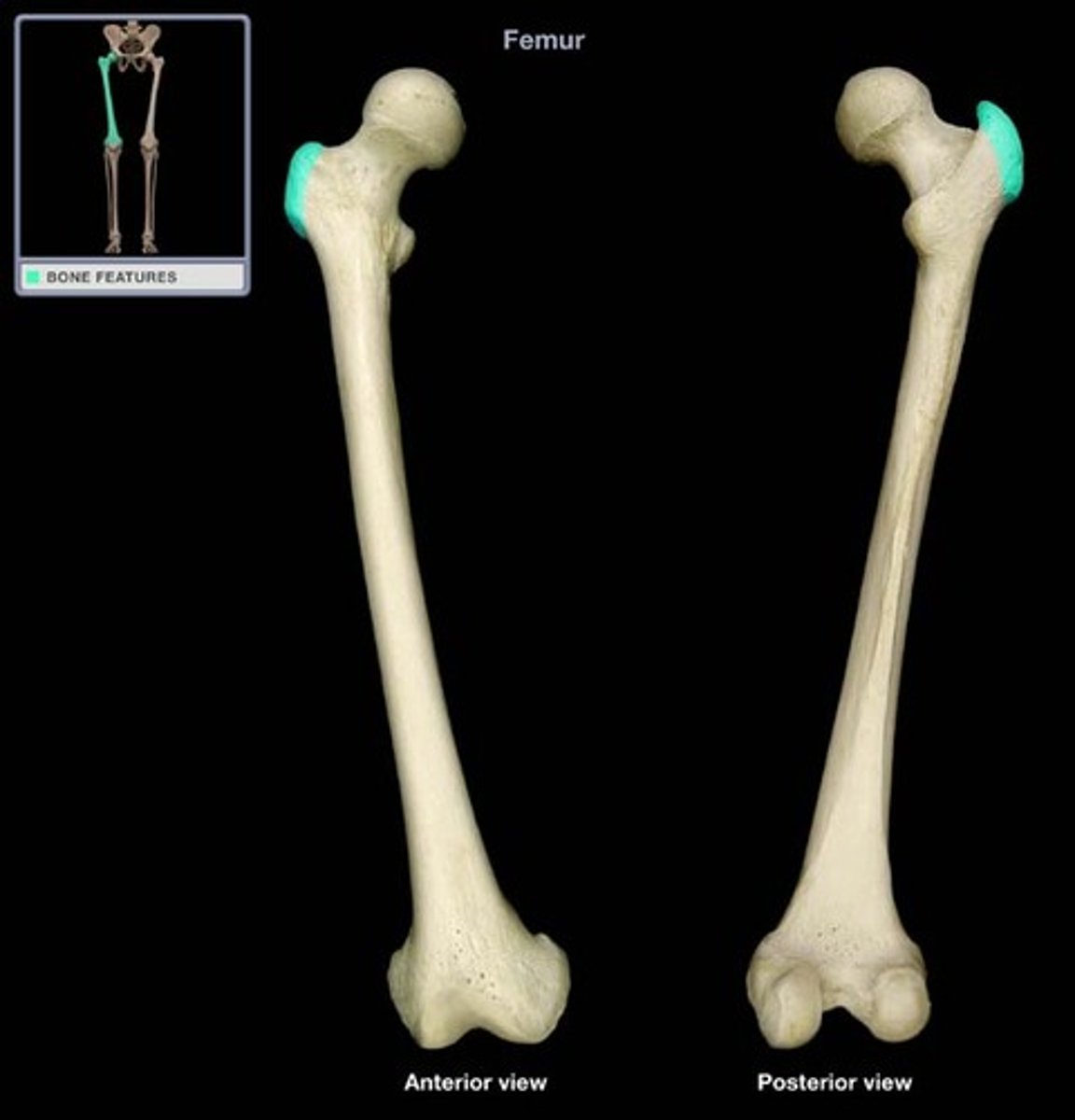
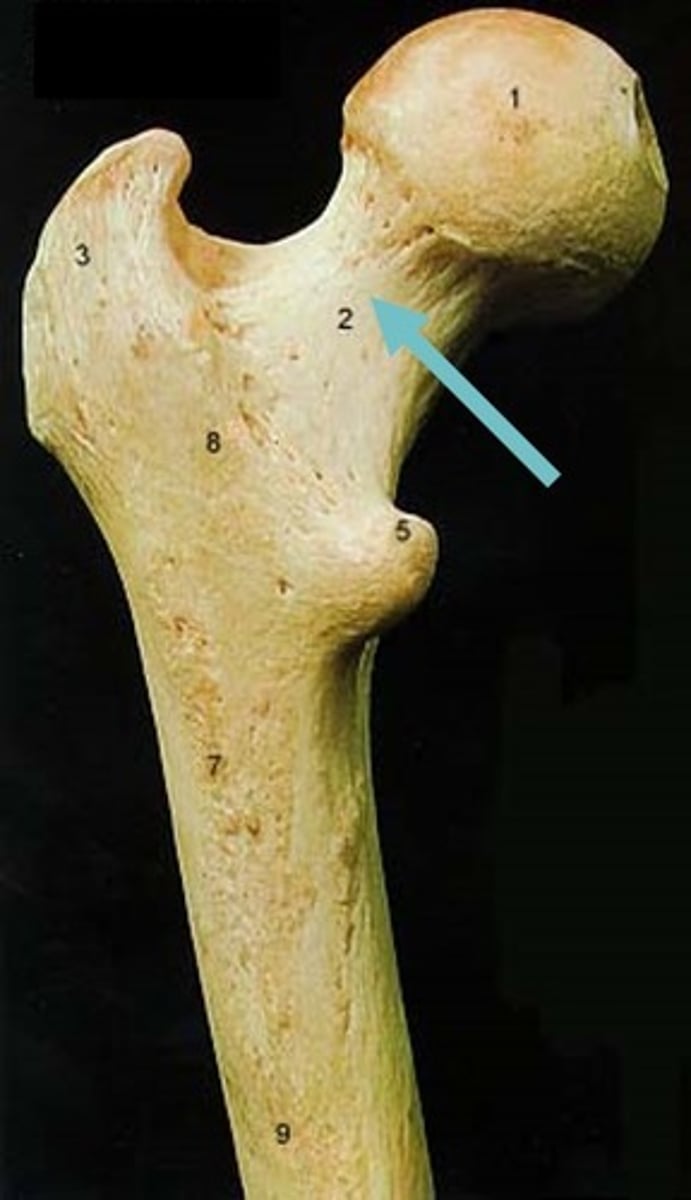
Lesser trochanter
smaller and bumpy muscle attachment point inferior to the greater trochanter
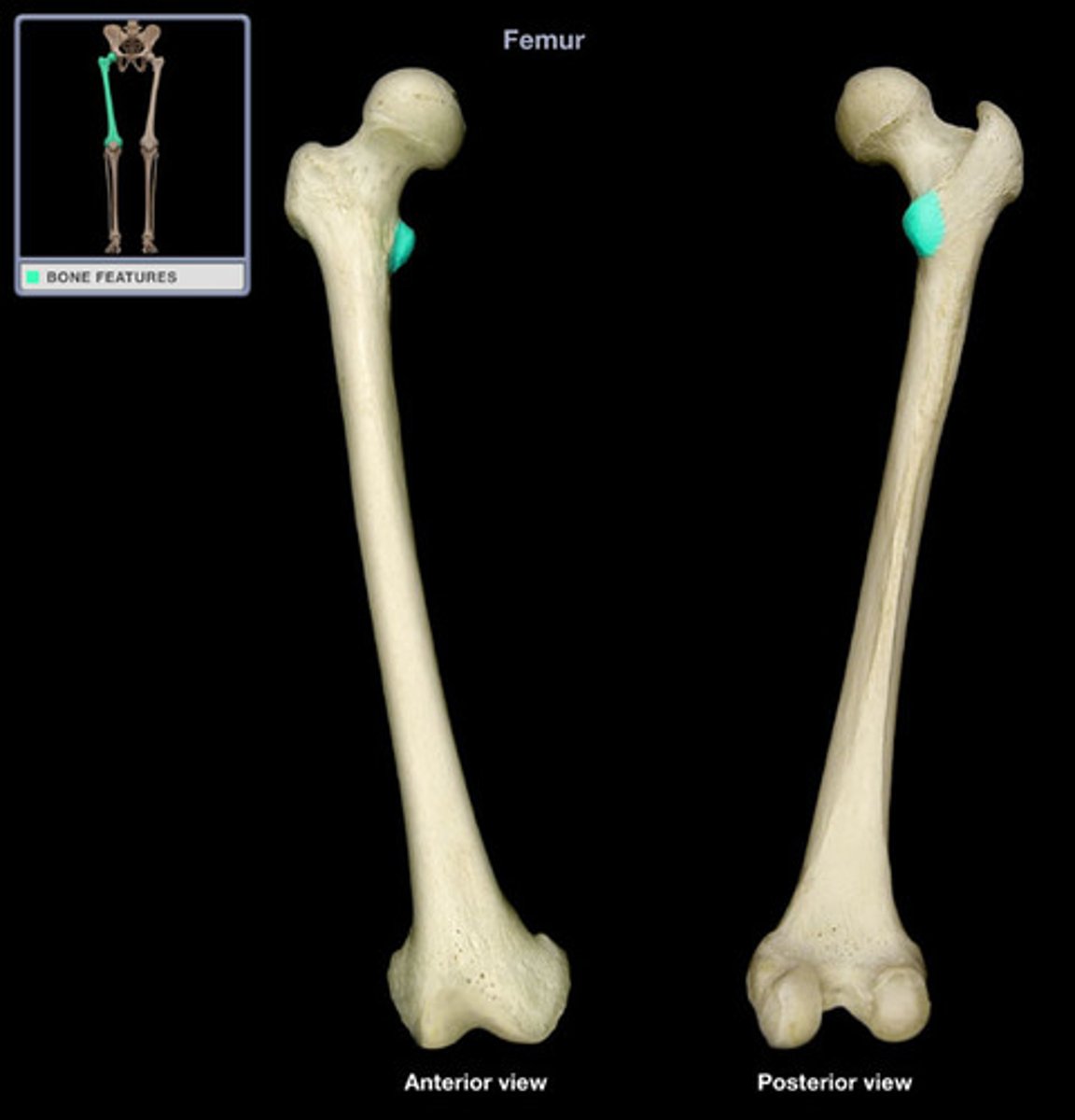
Medial condyle
smooth, round structure on the medial side of the femur also articulates with the tibia distally, and it forms part of the knee joint
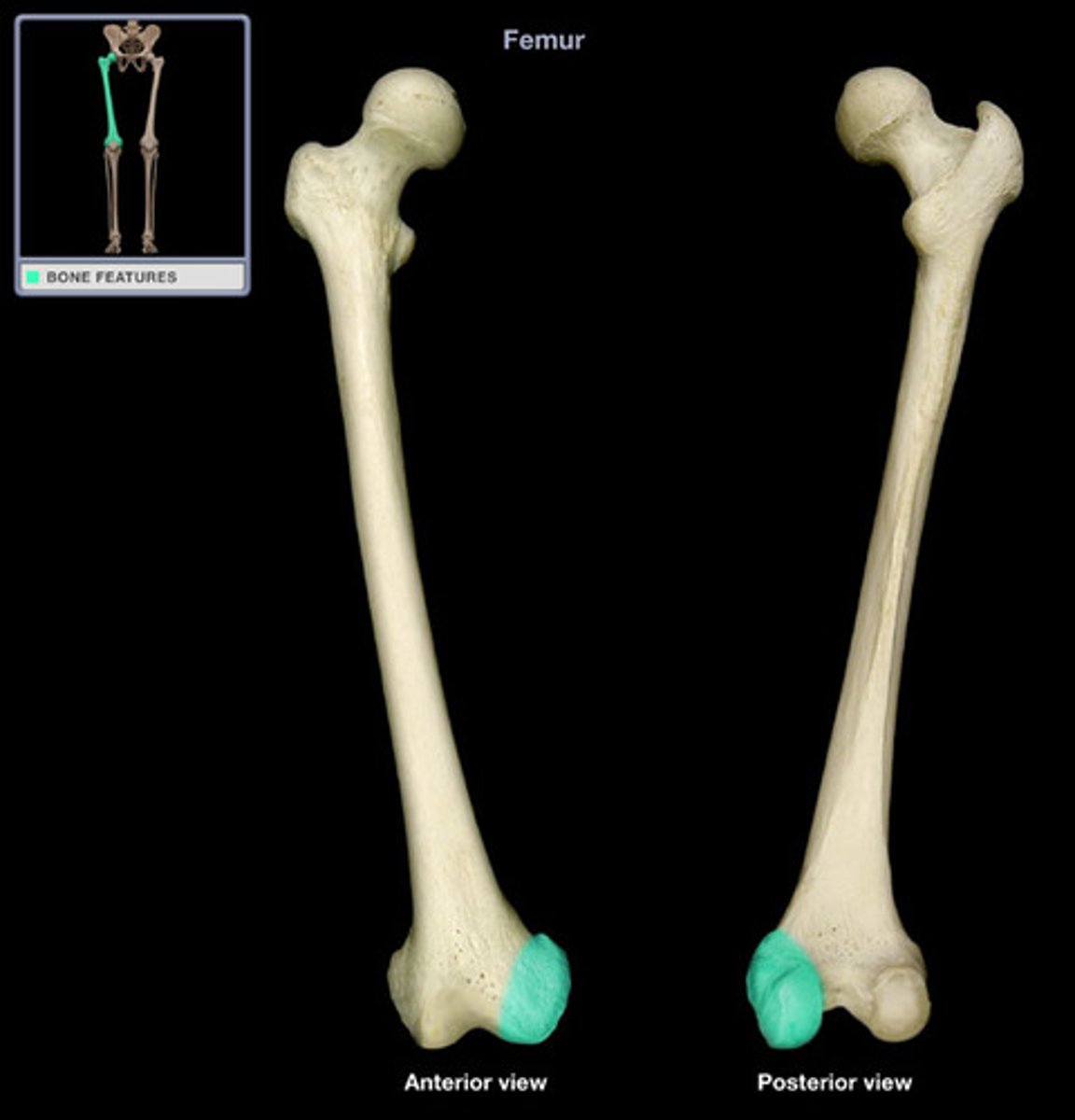
Lateral condyle
smooth, round structure on the lateral side of the femur articulates with the tibia distally, and it forms part of the knee joint
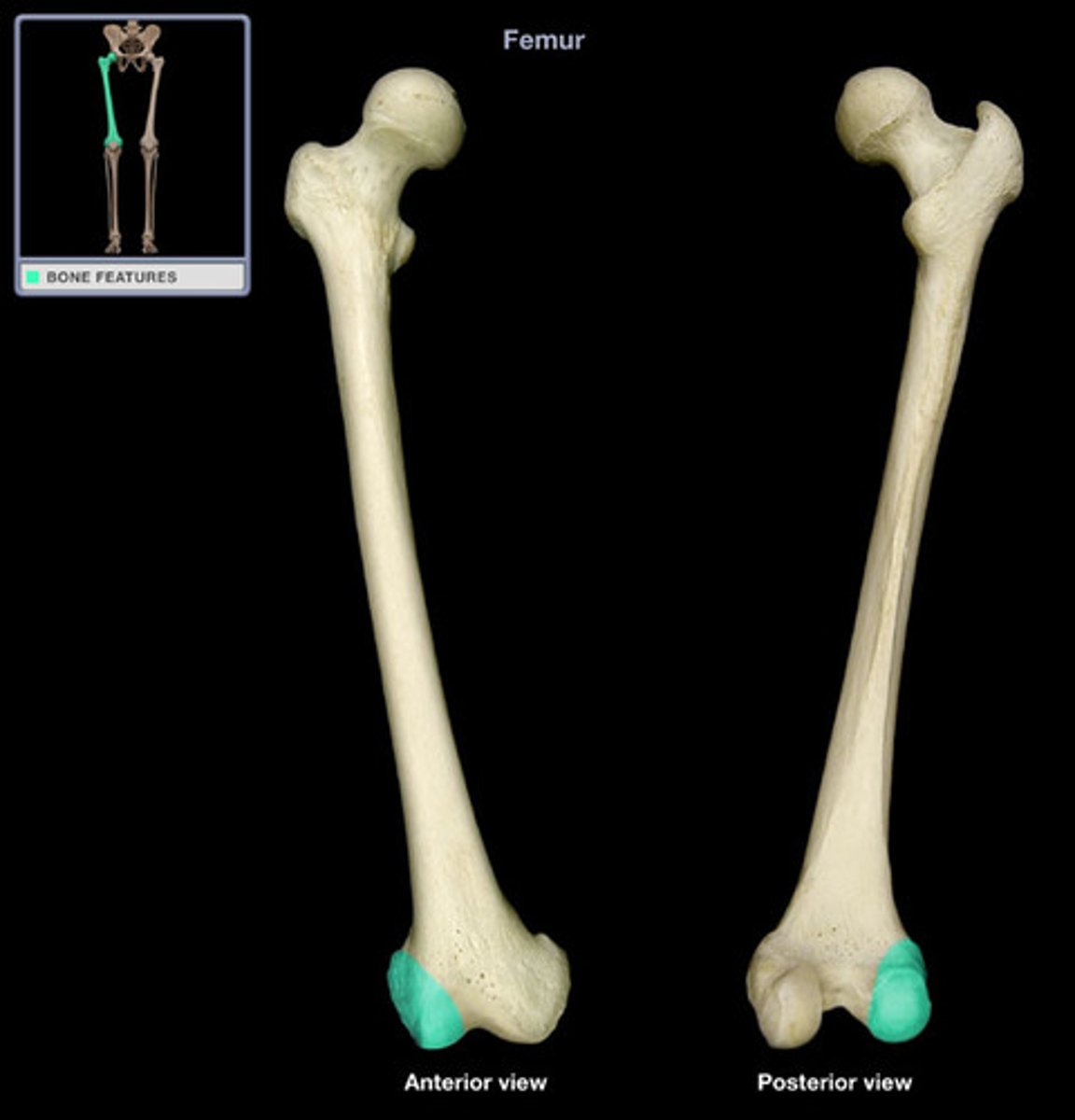
patellar groove
where patella articulates with the femur
Patella
kneecap
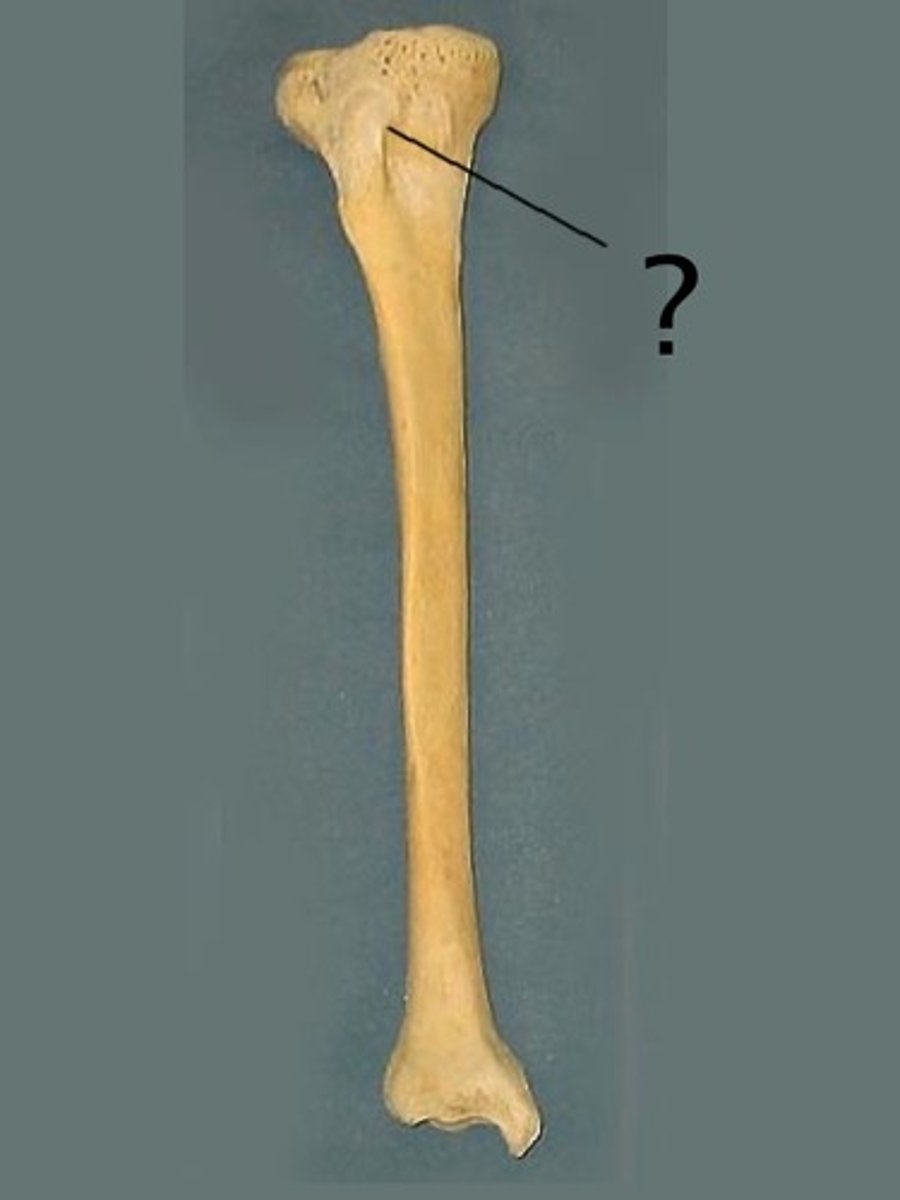
Tibial plateau
flat surface upon which the femoral condyles articulate within the knee joint
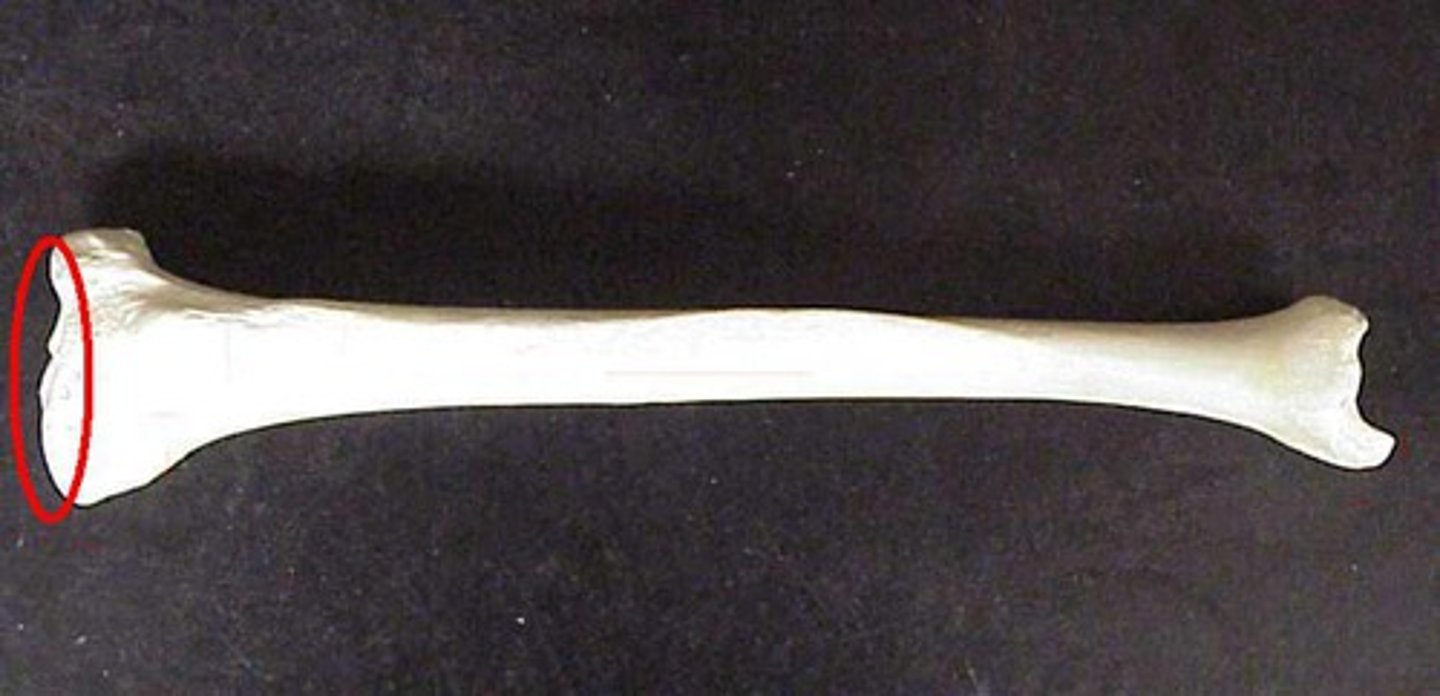

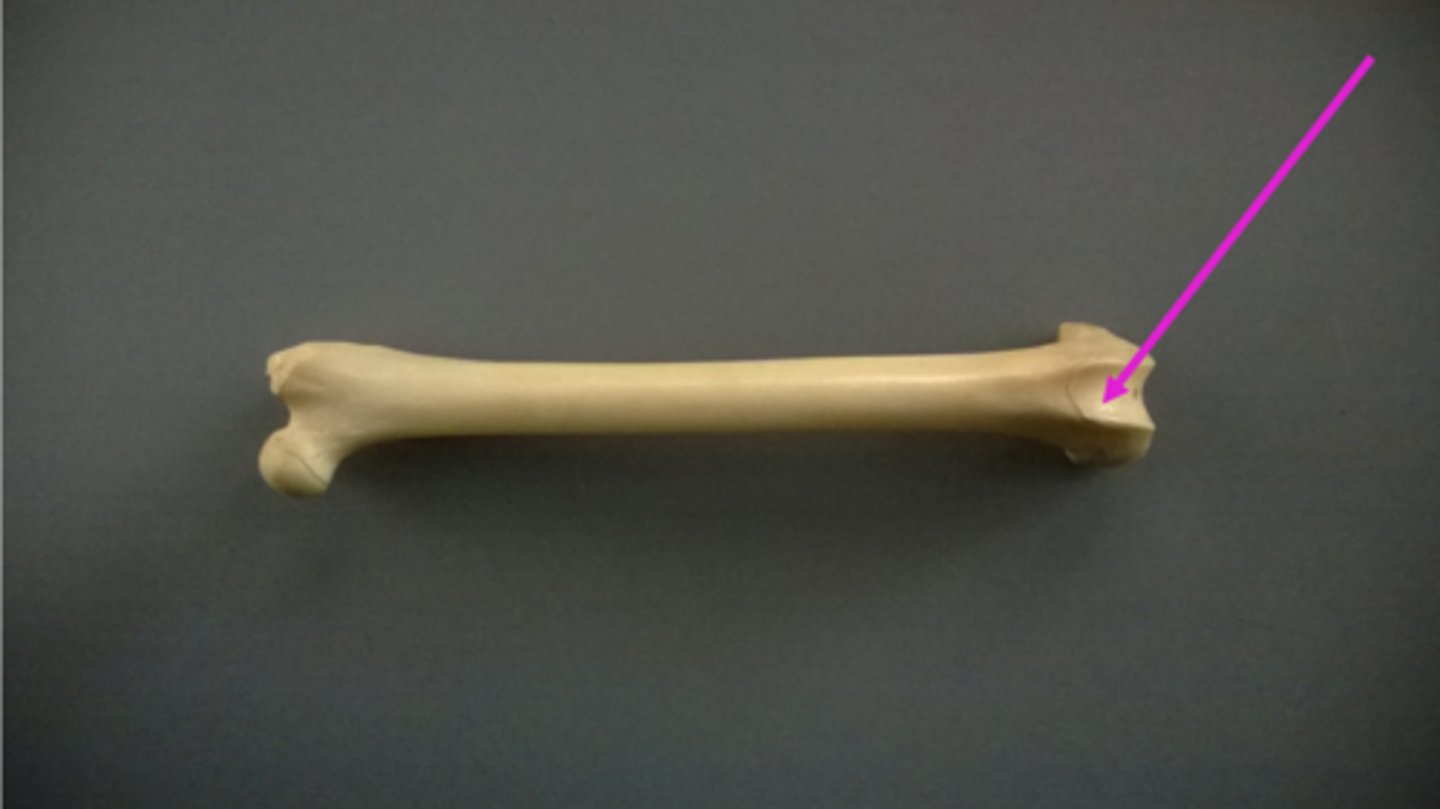
Tibial tuberosity
prominent rough bump on the anterior and proximal end of the tibia that serves as a muscle attachment point
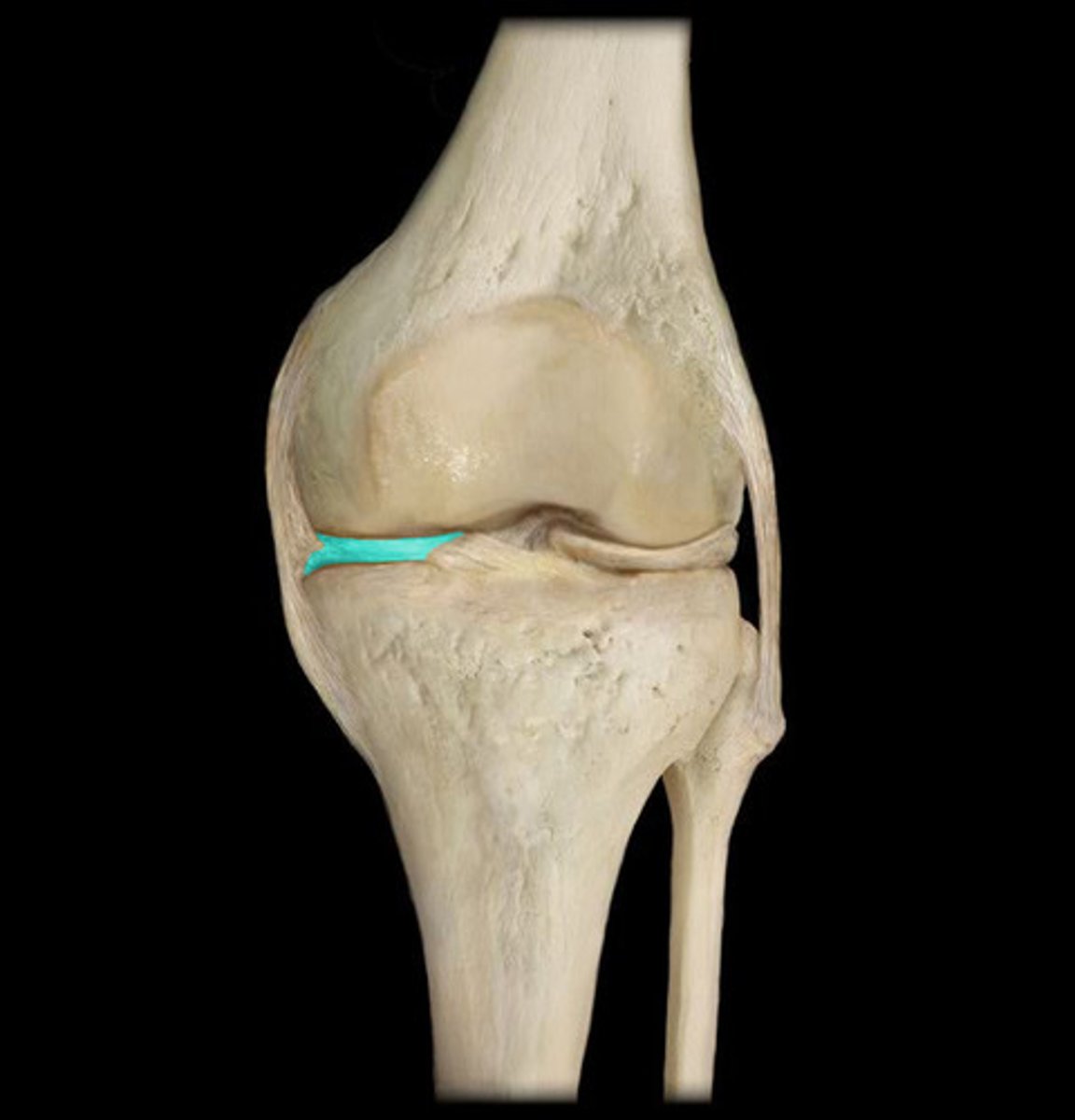
medial meniscus
crescent-shaped pads that sit on the tibial plateau. They allow the condyles of the femur to glide across the tibial plateau
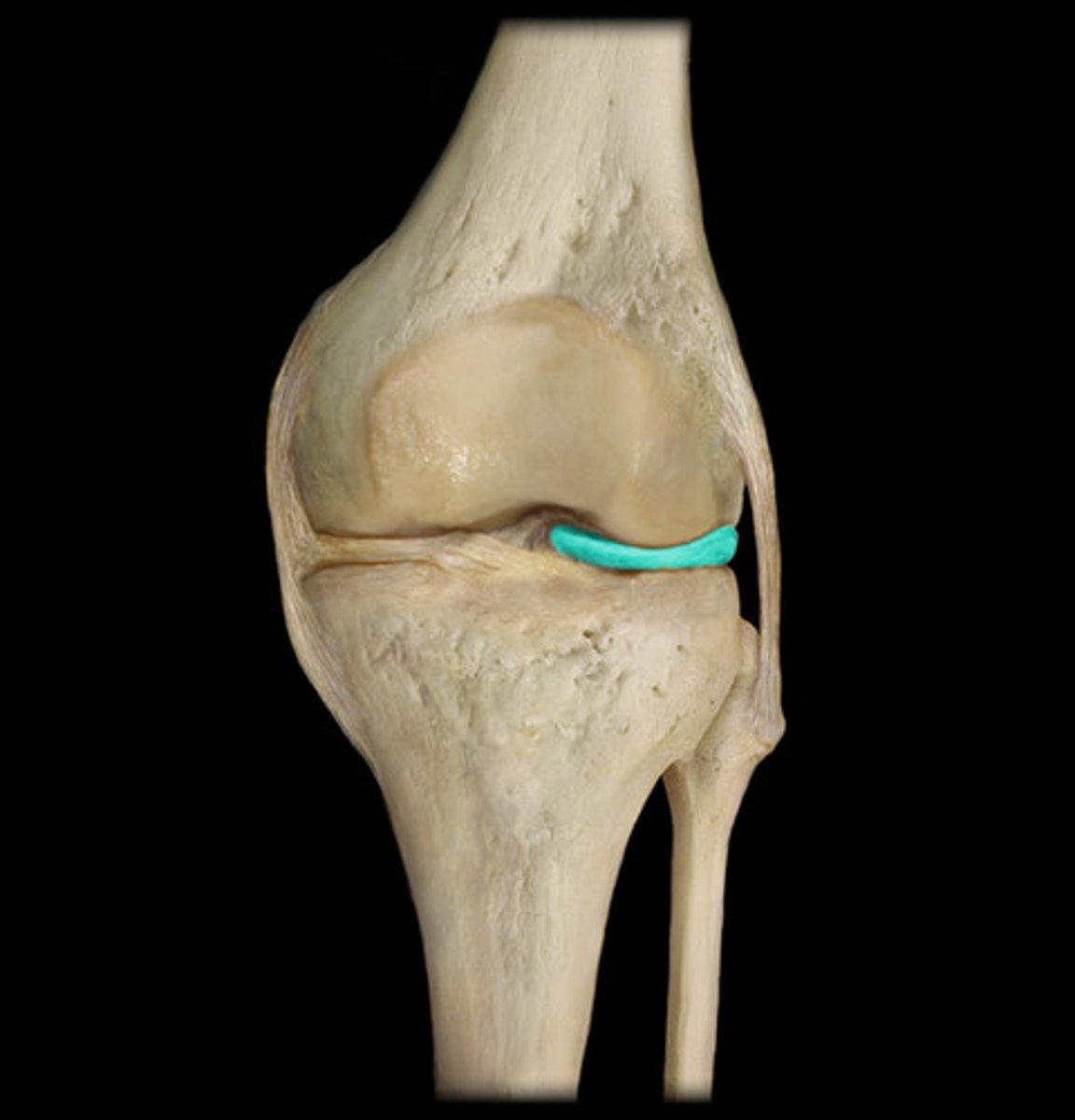
lateral meniscus
crescent-shaped pads that sit on the tibial plateau. They allow the condyles of the femur to glide across the tibial plateau
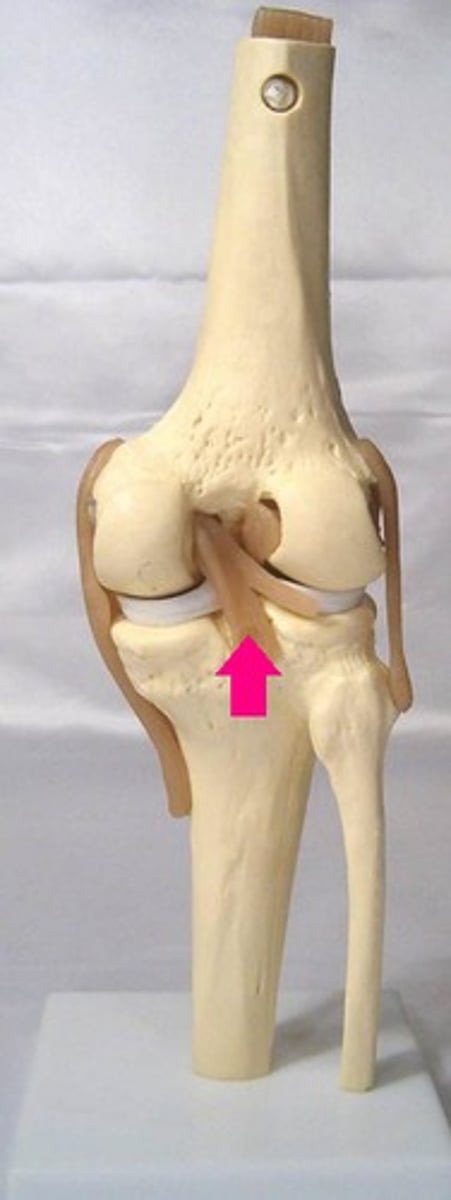
Anterior Cruciate Ligament
This ligament attaches anteriorly on the tibia, between the medial and lateral menisci, and angles posteriorly towards its attachment on the femur near the lateral condyle.
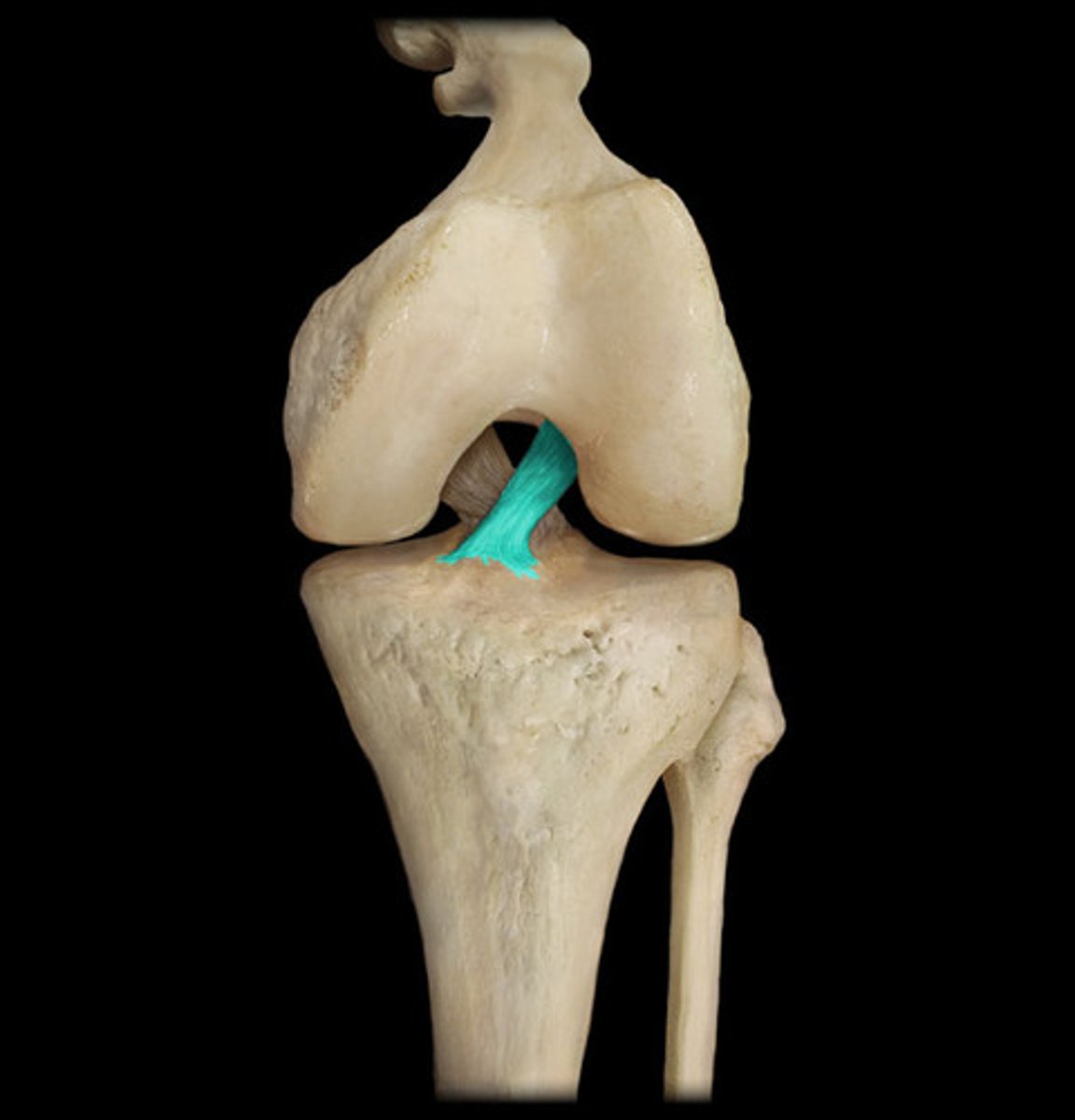
posterior cruciate ligament
ligament attaches posteriorly on the tibia, between the medial and lateral menisci, and angles anteriorly towards its attachment on the femur near the medial condyle
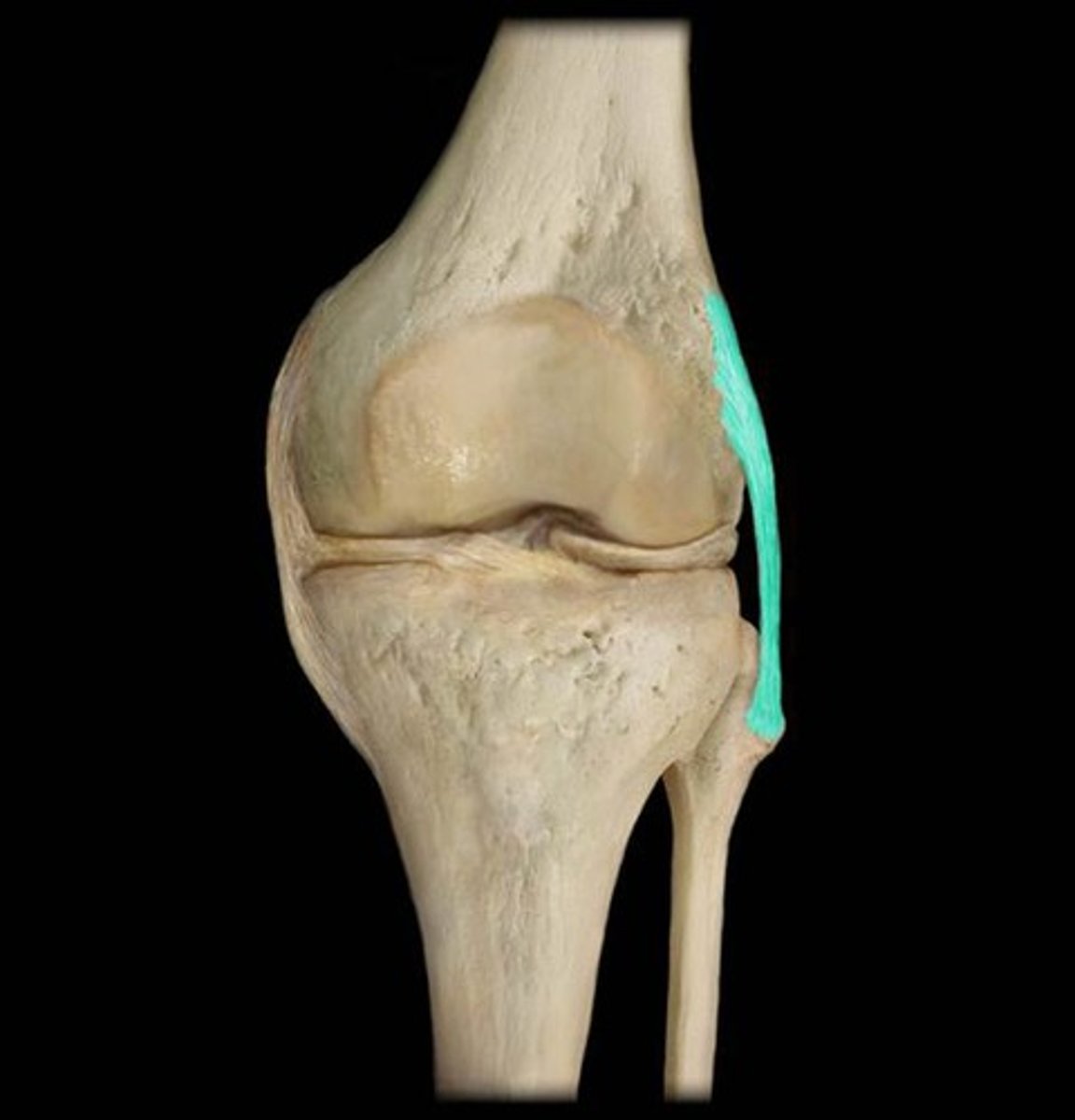
medial collateral ligament
ligament travels superiorly to inferiorly on the medial aspect of the knee
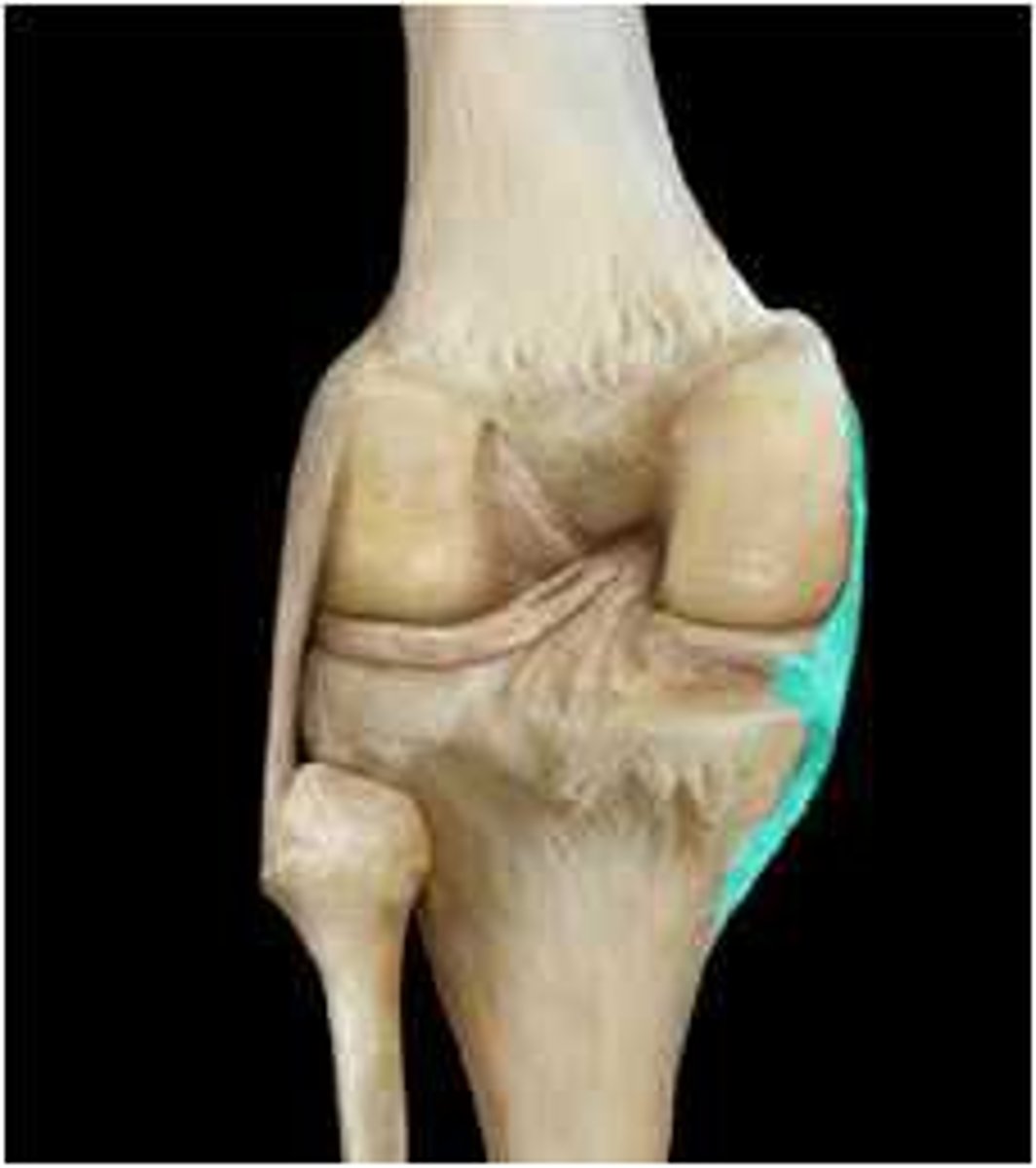
lateral collateral ligament
ligament travels superiorly to inferiorly on the lateral aspect of the knee
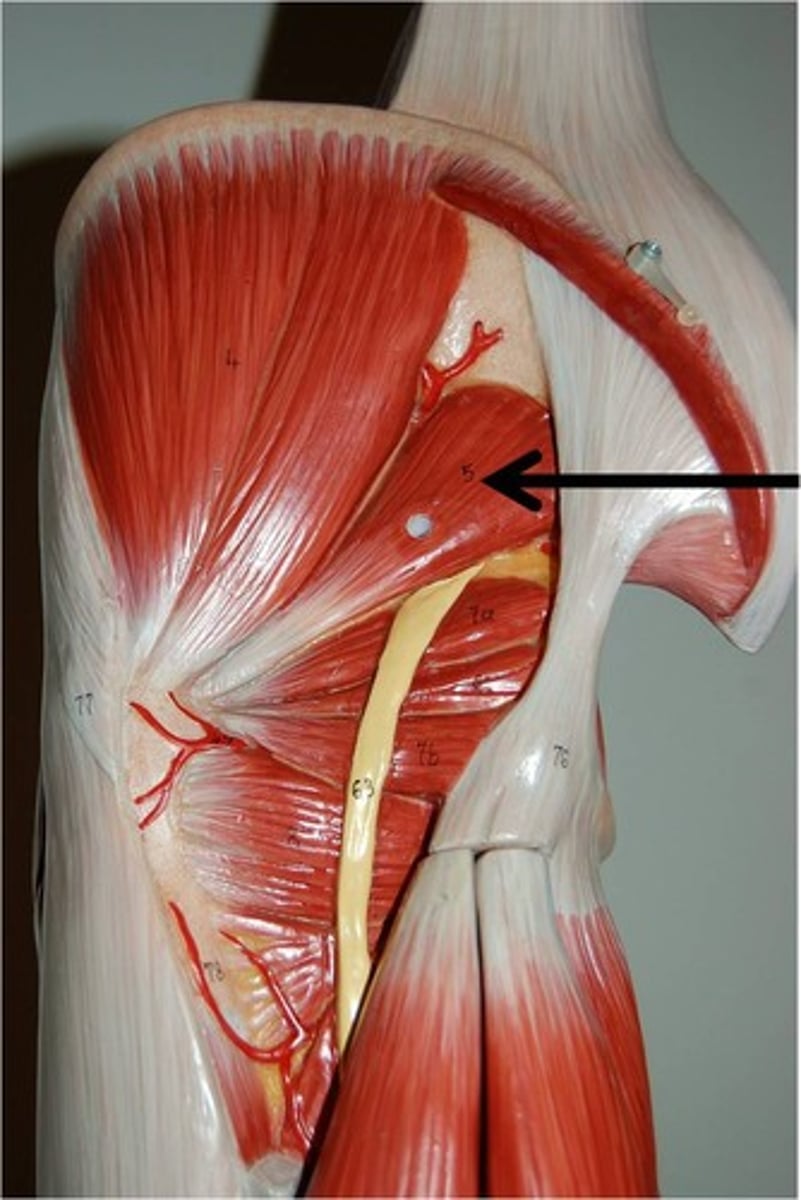
Gluteus minimus
deeper to gluteus maximus and also sequentially smaller in size
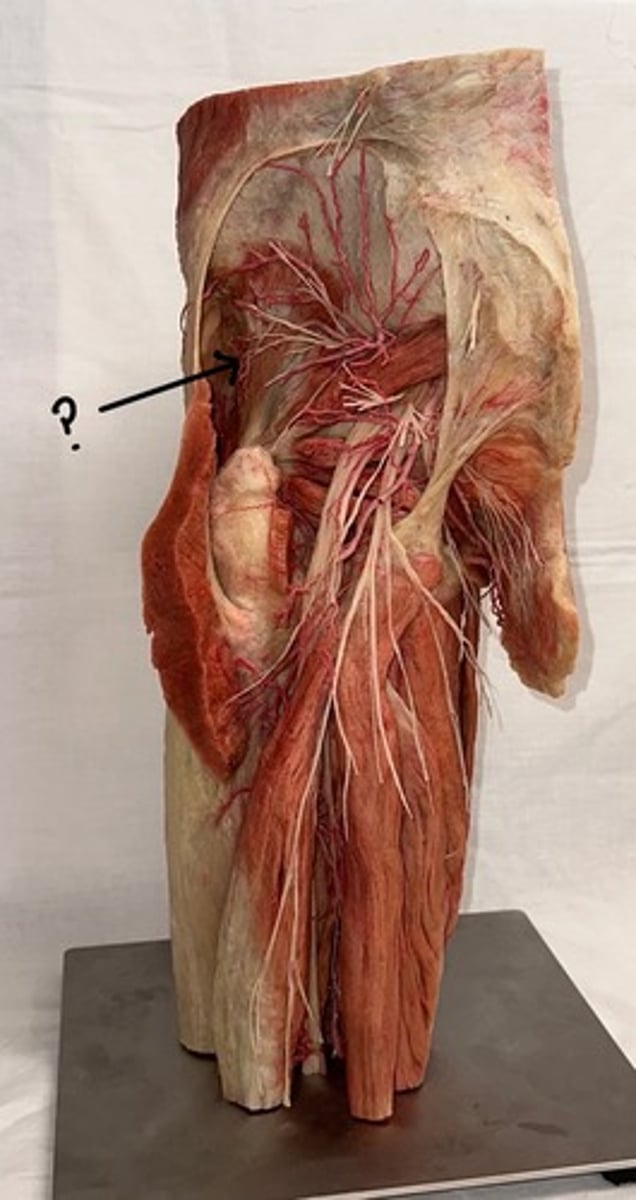
Gluteus maximus
largest and most superficial of these three muscles
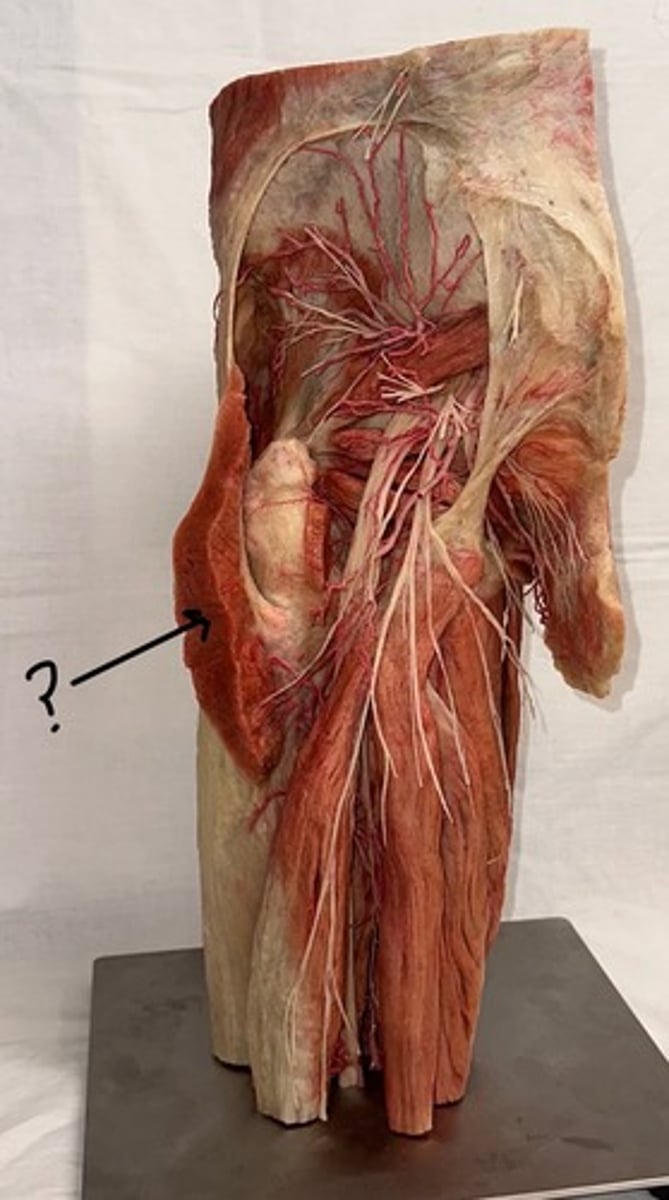
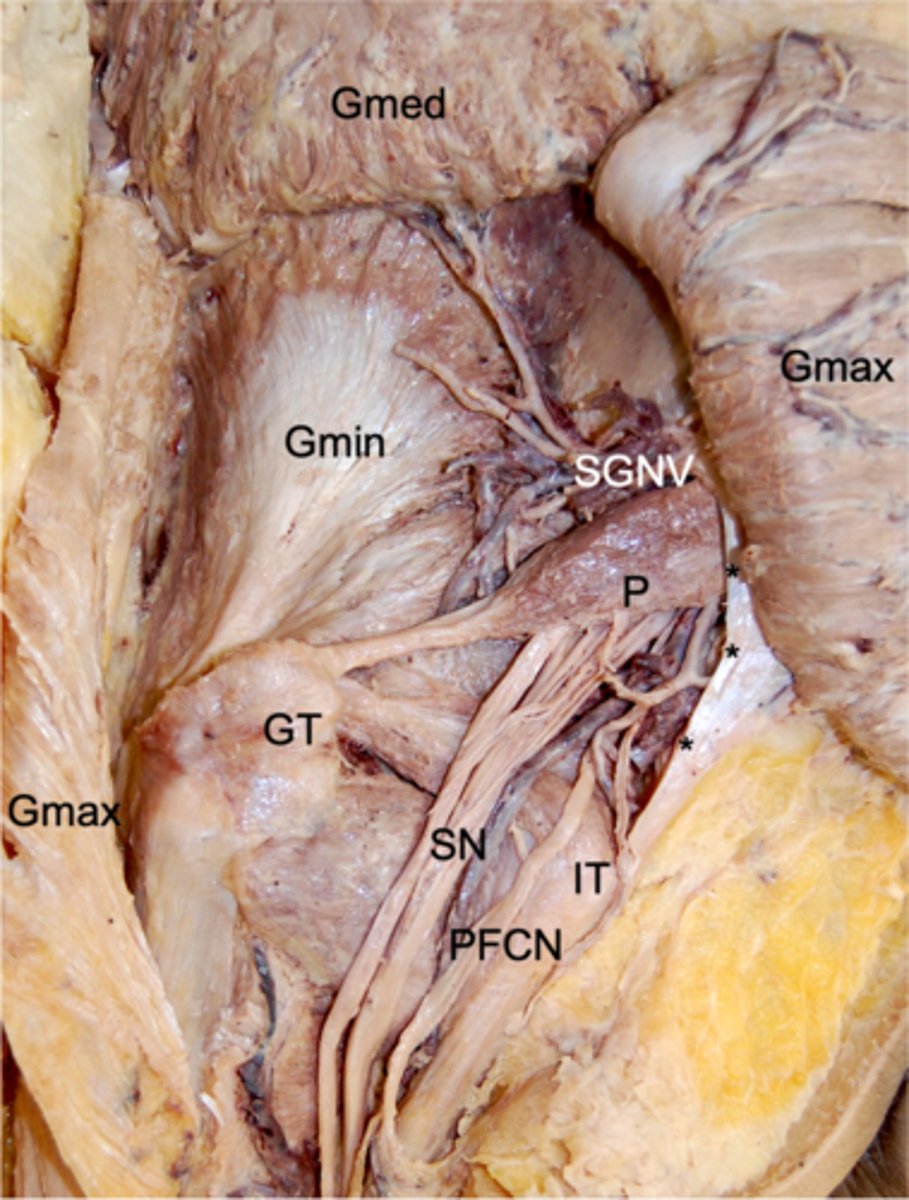
Piriformis
originates at the sacrum and is a pyramid shape
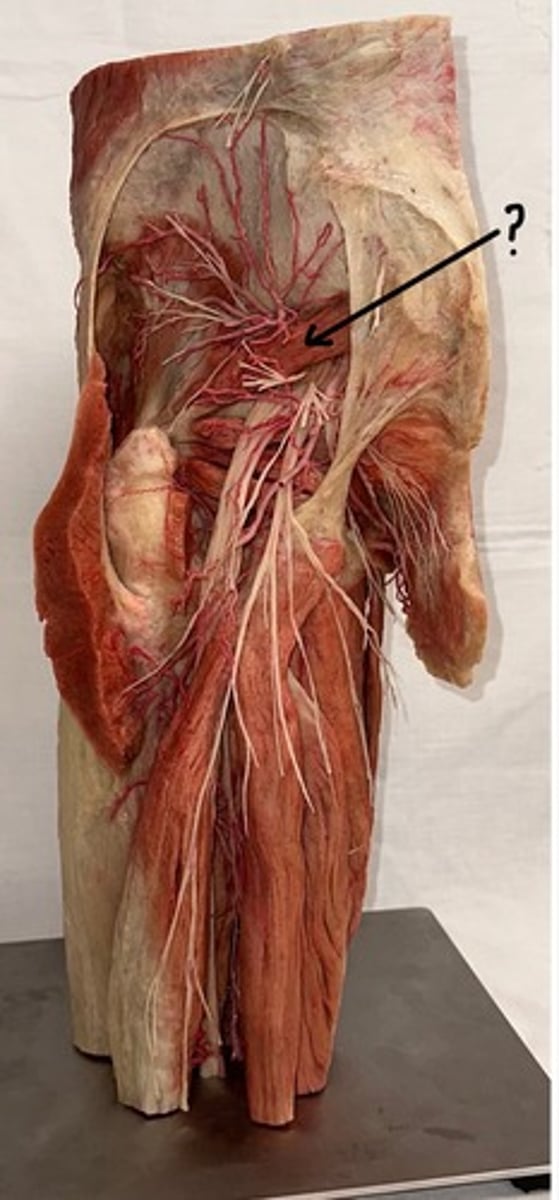
Obturator internus
muscle body covers the posterior (internal) aspect of the obturator foramen in the pelvis
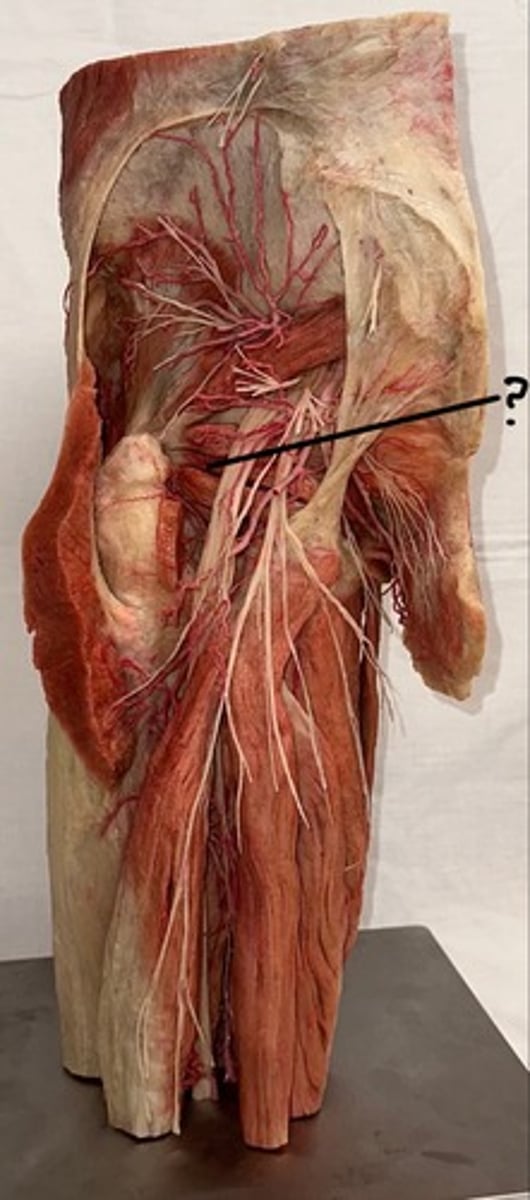
Quadratus femoris
muscle is also square-shaped and attaches to the femur in between the greater and lesser trochanter
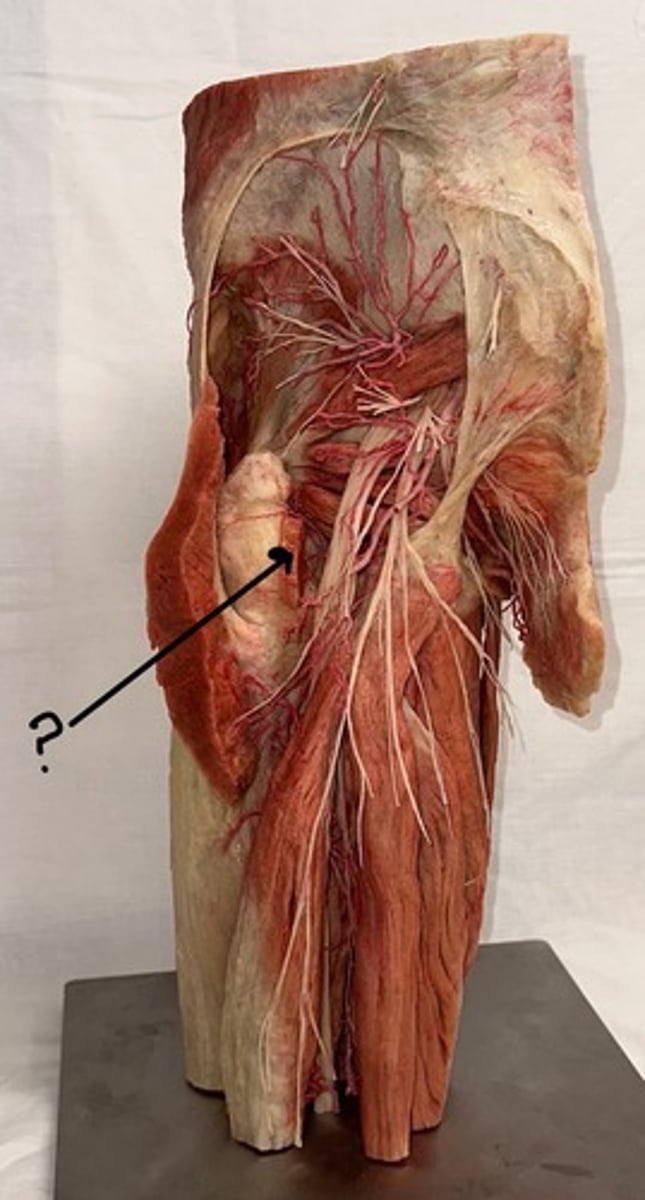
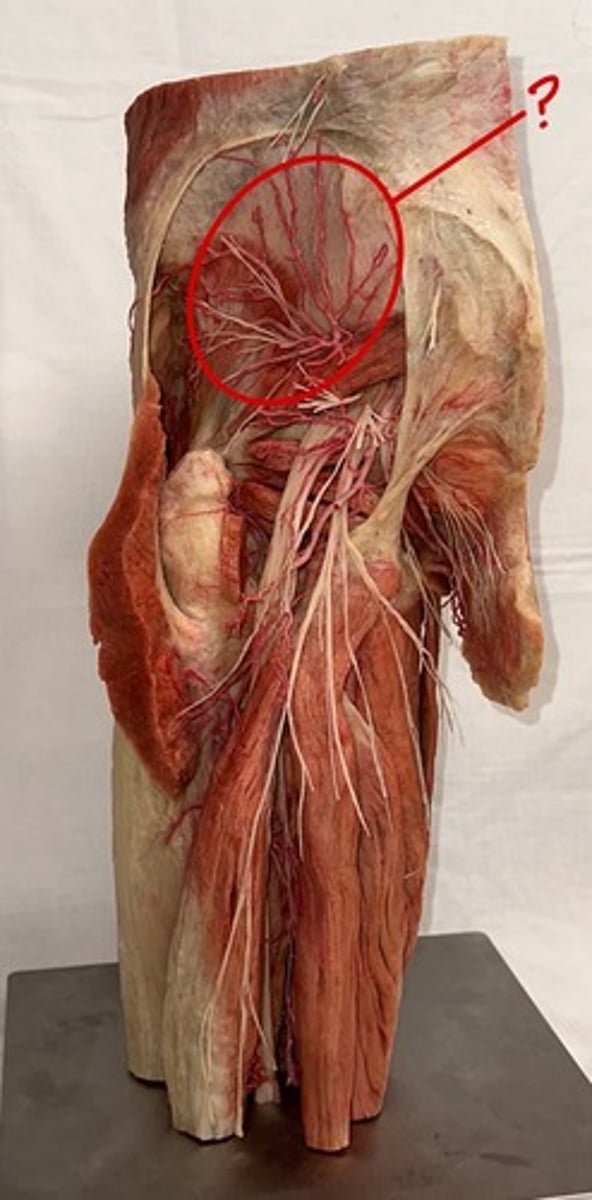
Superior gluteal bundle
This bundle is in between gluteus medius and minimus
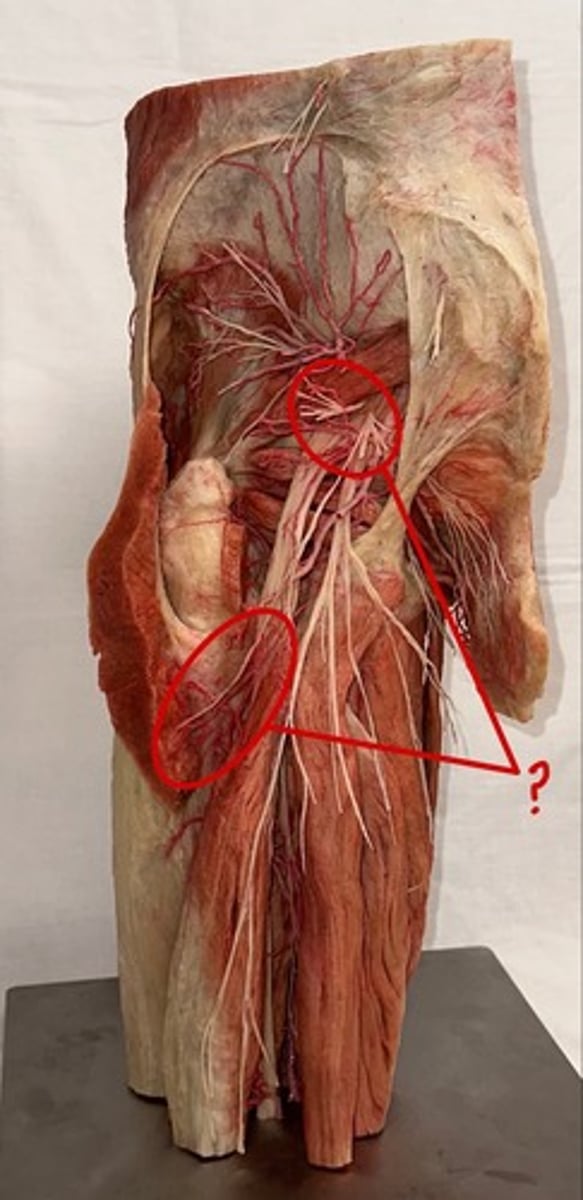
Inferior gluteal bundle
bundle near the gluteus maximus
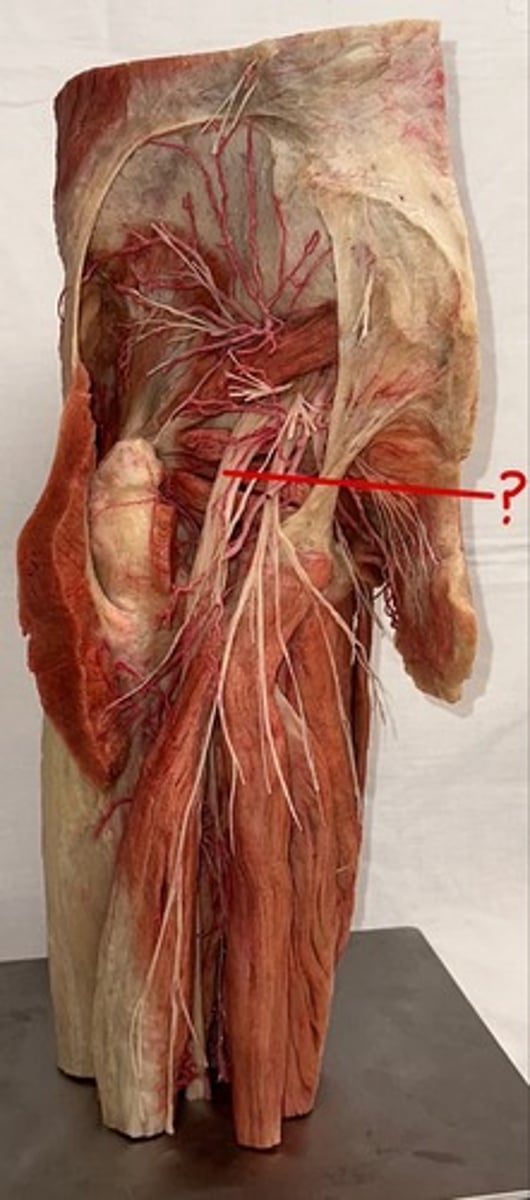
sciatic nerve
nerve is an incredibly thick and significant nerve, and it ultimately branches at the popliteal fossa
sacrotuberous ligament
extends from the sacrum to the ischial tuberosity
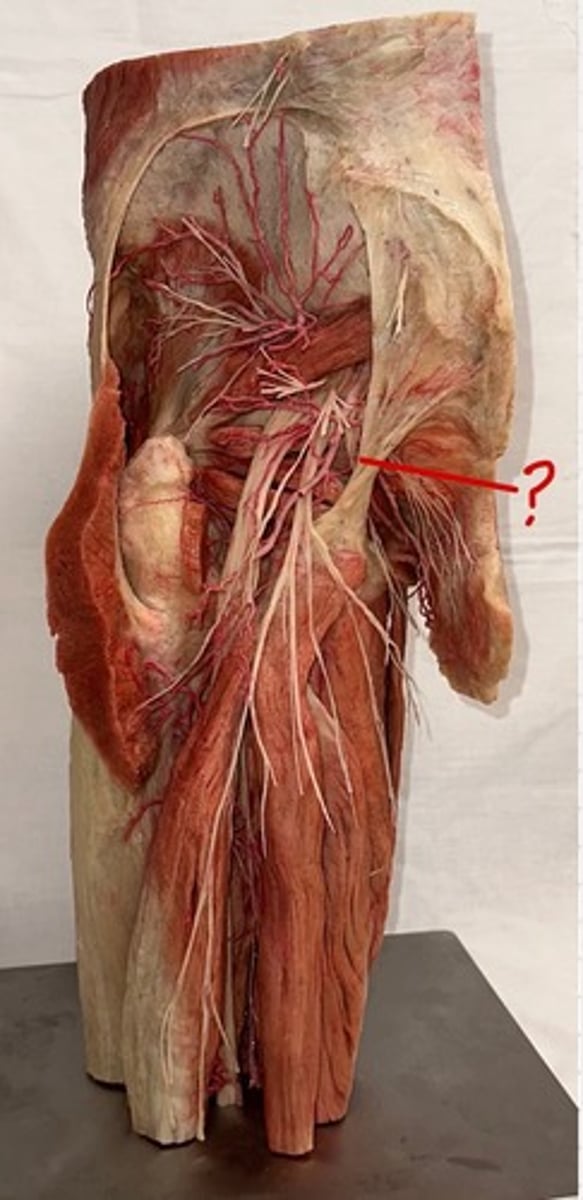
rectus femoris
name of this muscle is based on its appearance ("rectus" means "straight")
pin 3
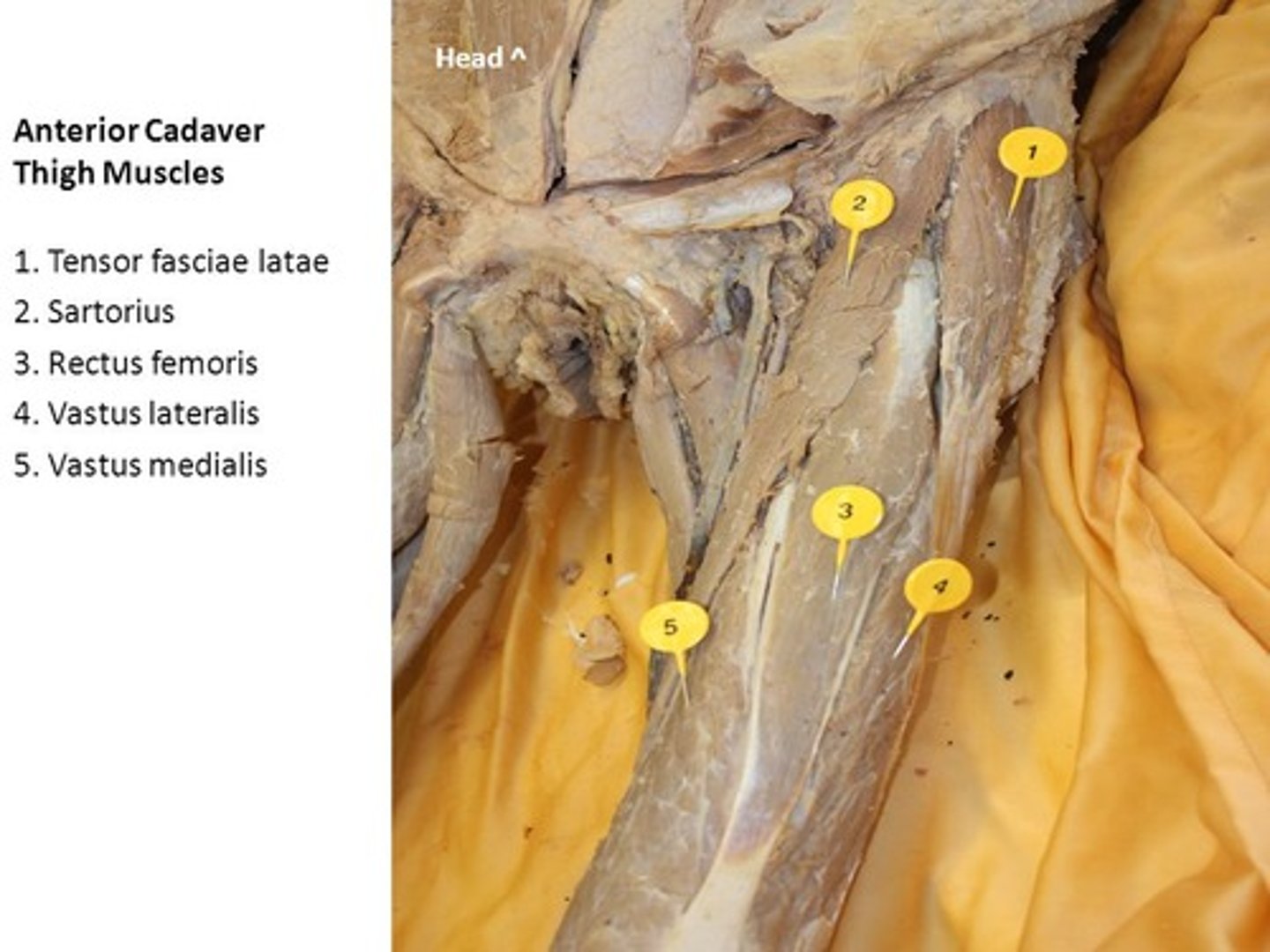
vastus medialis
muscles are lateral and medial, respectively, to the vastus intermedius
pin 5
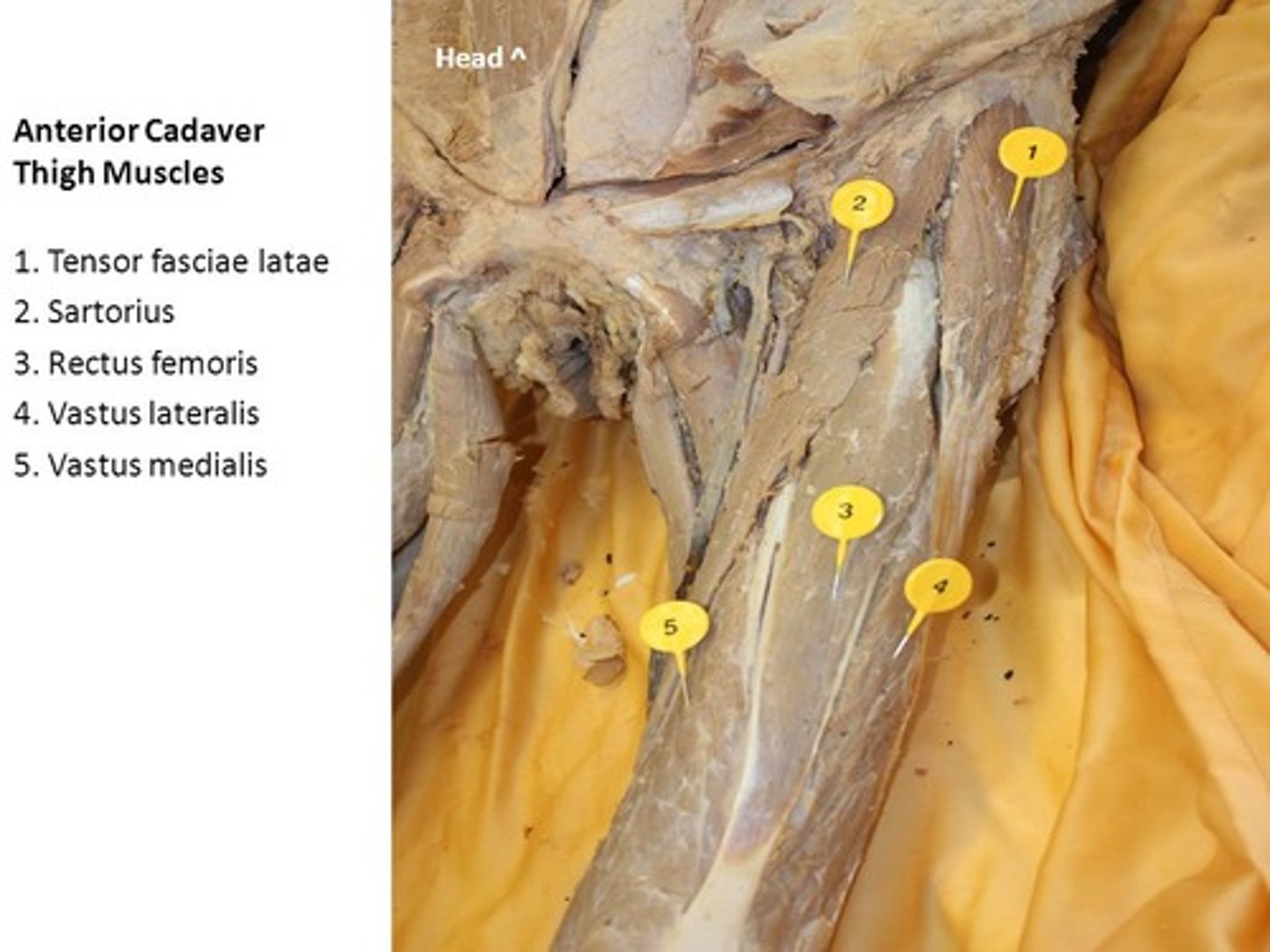
vastus lateralis
muscles are lateral and medial, respectively, to the vastus intermedius
pin 4
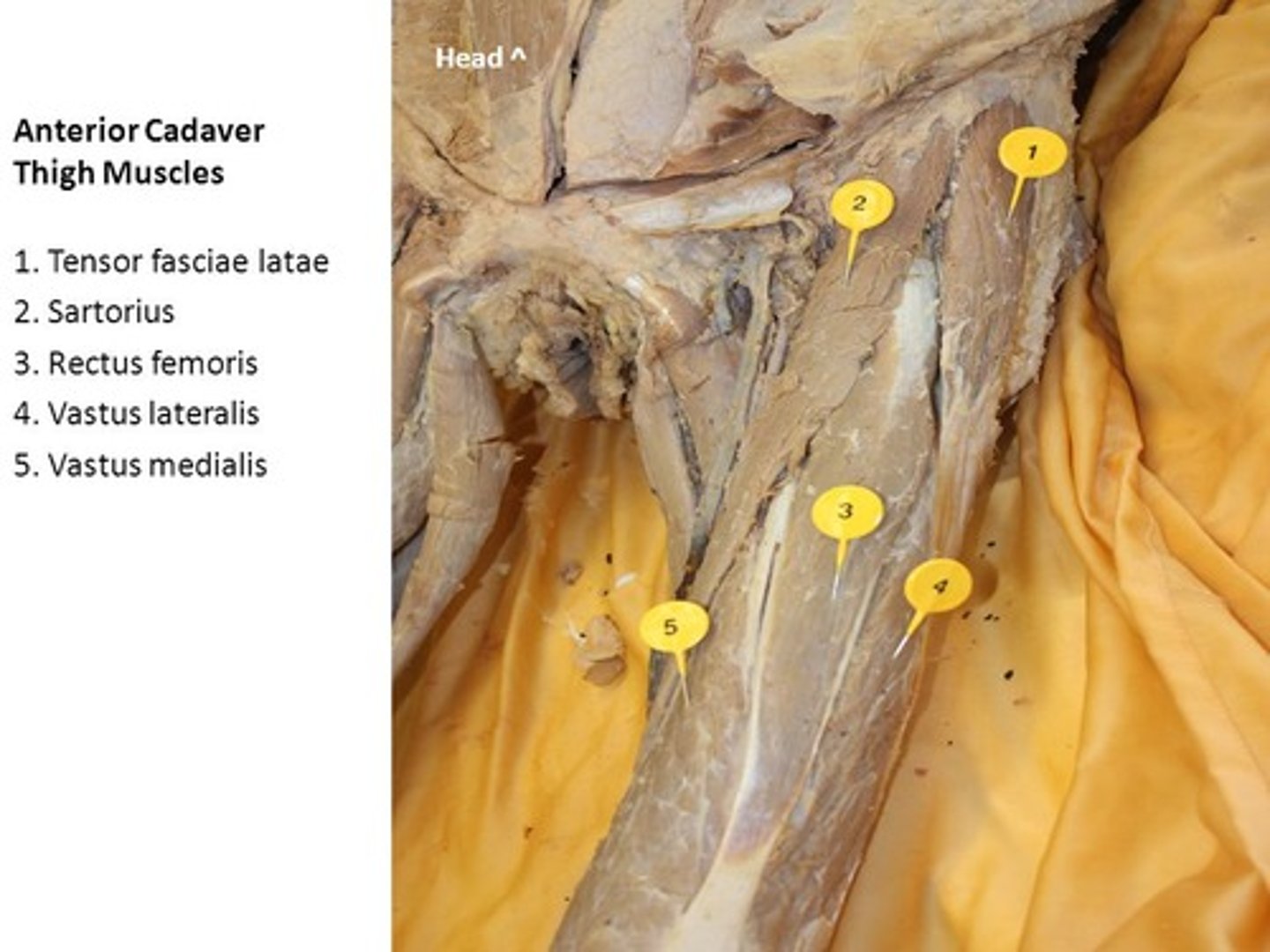
vastus intermedius
muscle is deep to rectus femoris
Sartorius
muscle is an "S"-shaped muscle that attaches laterally at the anterior tip of the iliac crest, travels superficially over the rectus femoris, and attaches to the medial aspect of the tibia
-pin 2
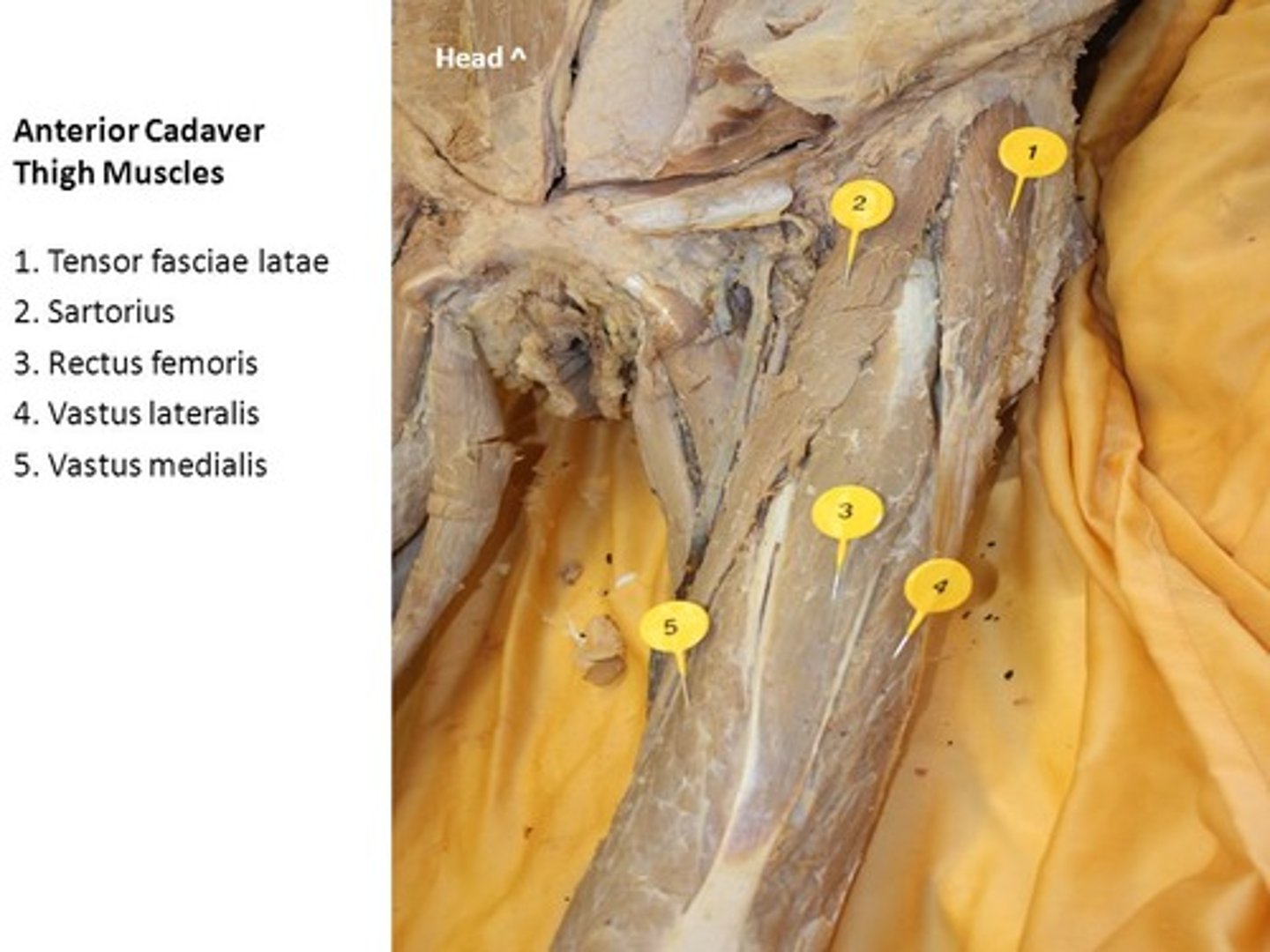
tensor fasciae latae
pin 1

iliopsoas
A small triangle-shape of muscle can be seen lateral to the femoral triangle and pectineus
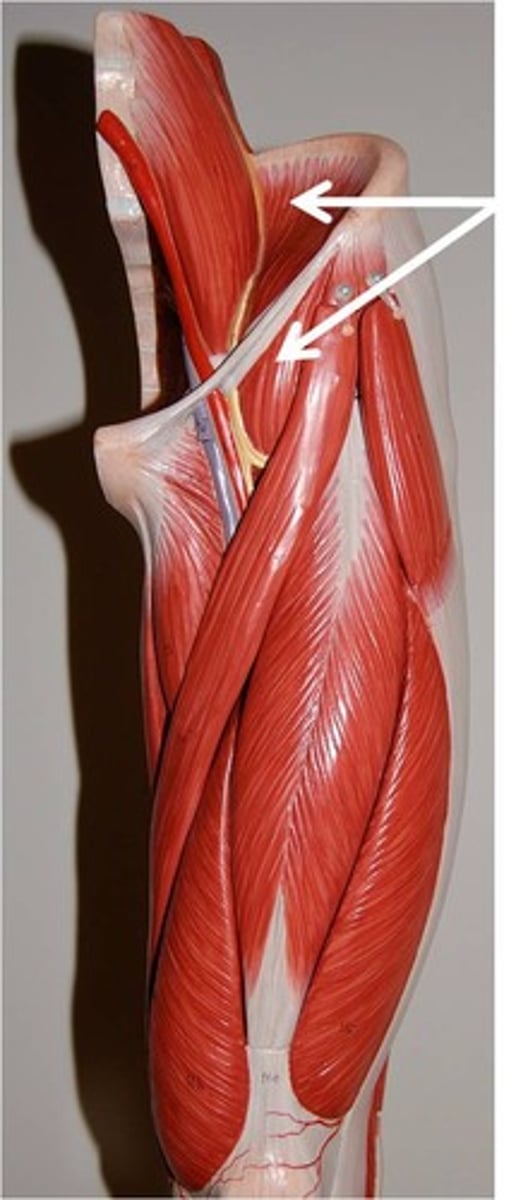
femoral vein, artery, and nerve
they reside in an area referred to as the "femoral triangle."
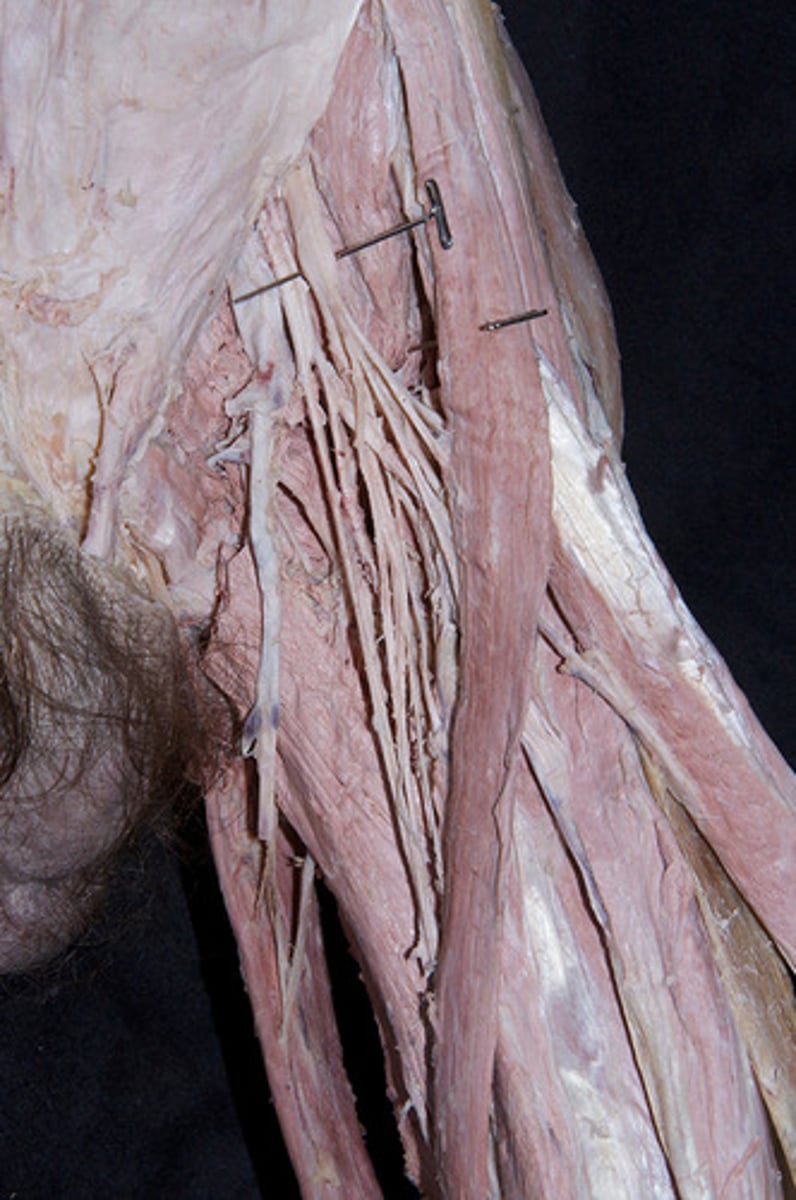
deep artery of thigh
branch of the femoral artery is just inferior to the inguinal canal. Remember when searching for it on a cadaver that it is always more superior than most people expect!

great saphenous vein
longest vein in the human body, branching from the femoral vein medially and traveling inferiorly to the ankle
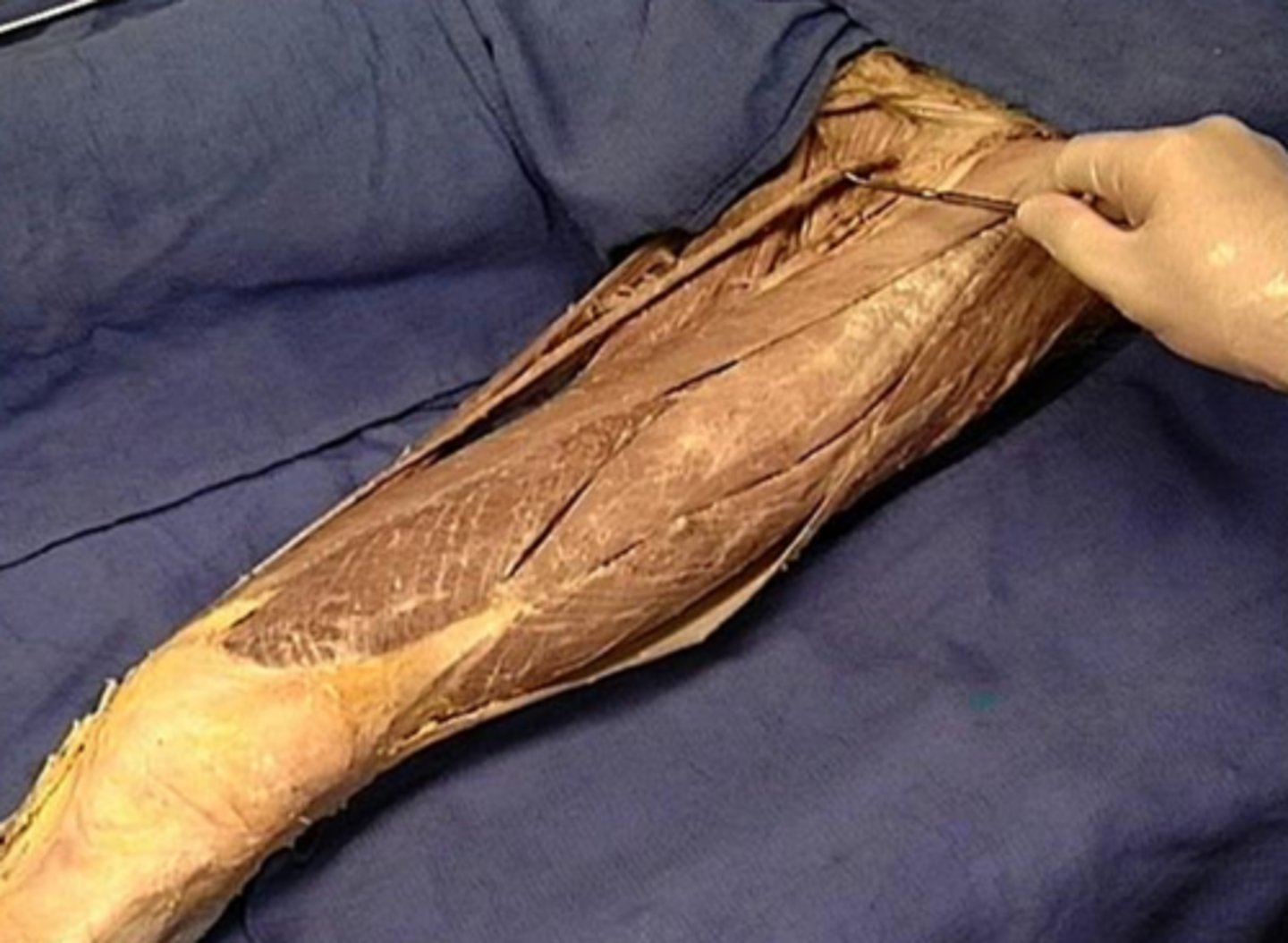
Gracilis
long and cylindrical muscle that is the most medial of the medial thigh muscles
-pin 2

adductor longus
deeper
-pin 4

adductor brevis
more superior than adductor longus
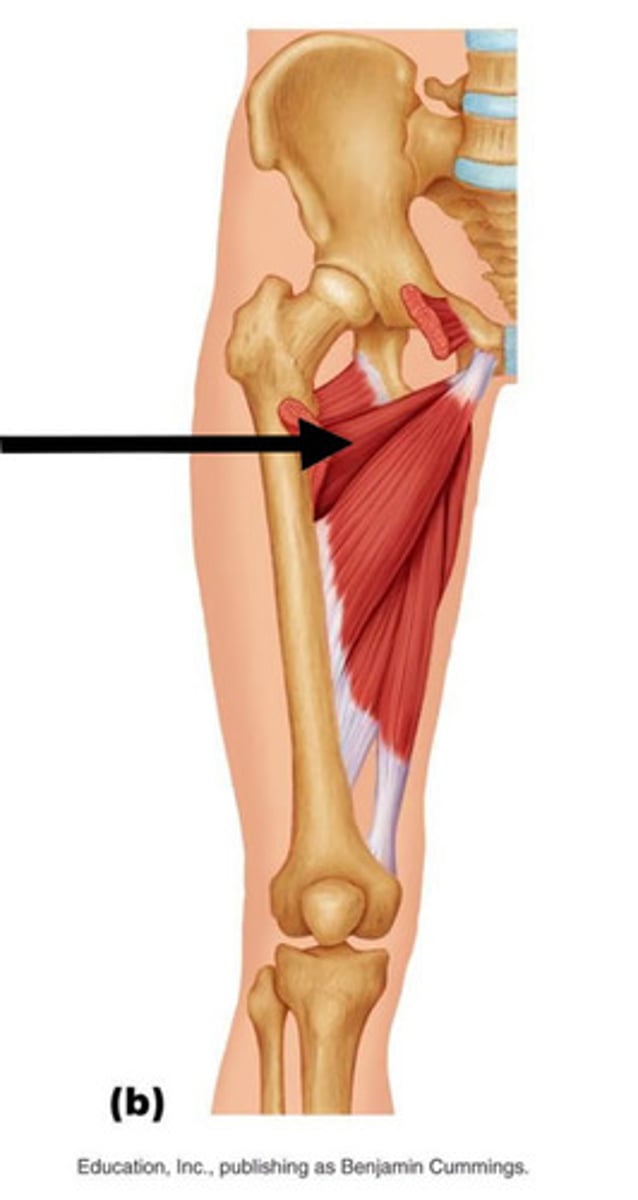
adductor magnus
largest of the three
It is also the deepest, which is why we can only see a small portion of it in the anterior view
pin 3

pectineus
medial to the femoral triangle
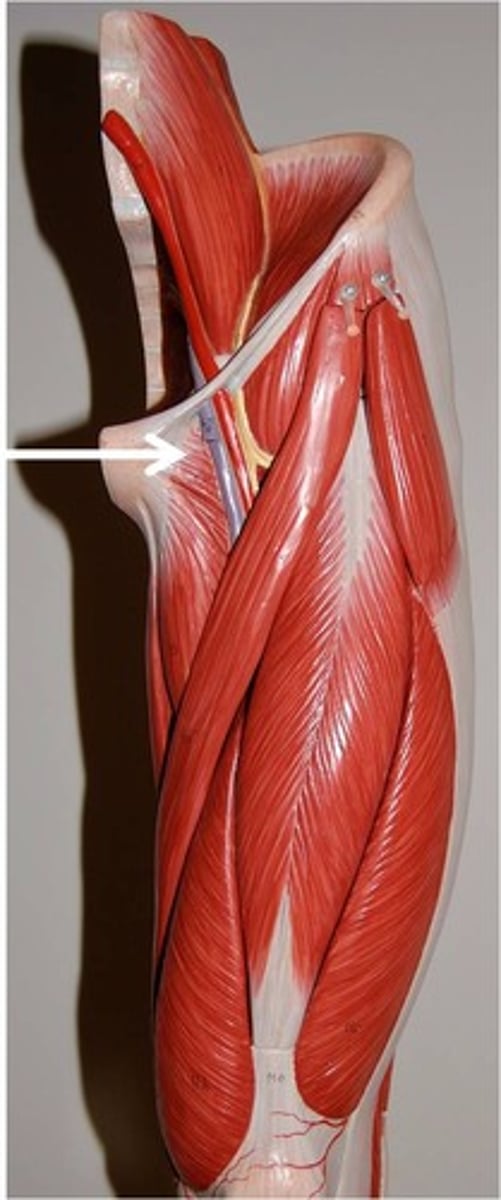
Obturator nerve
you'll find the obturator nerve when you reflect the adductor longus
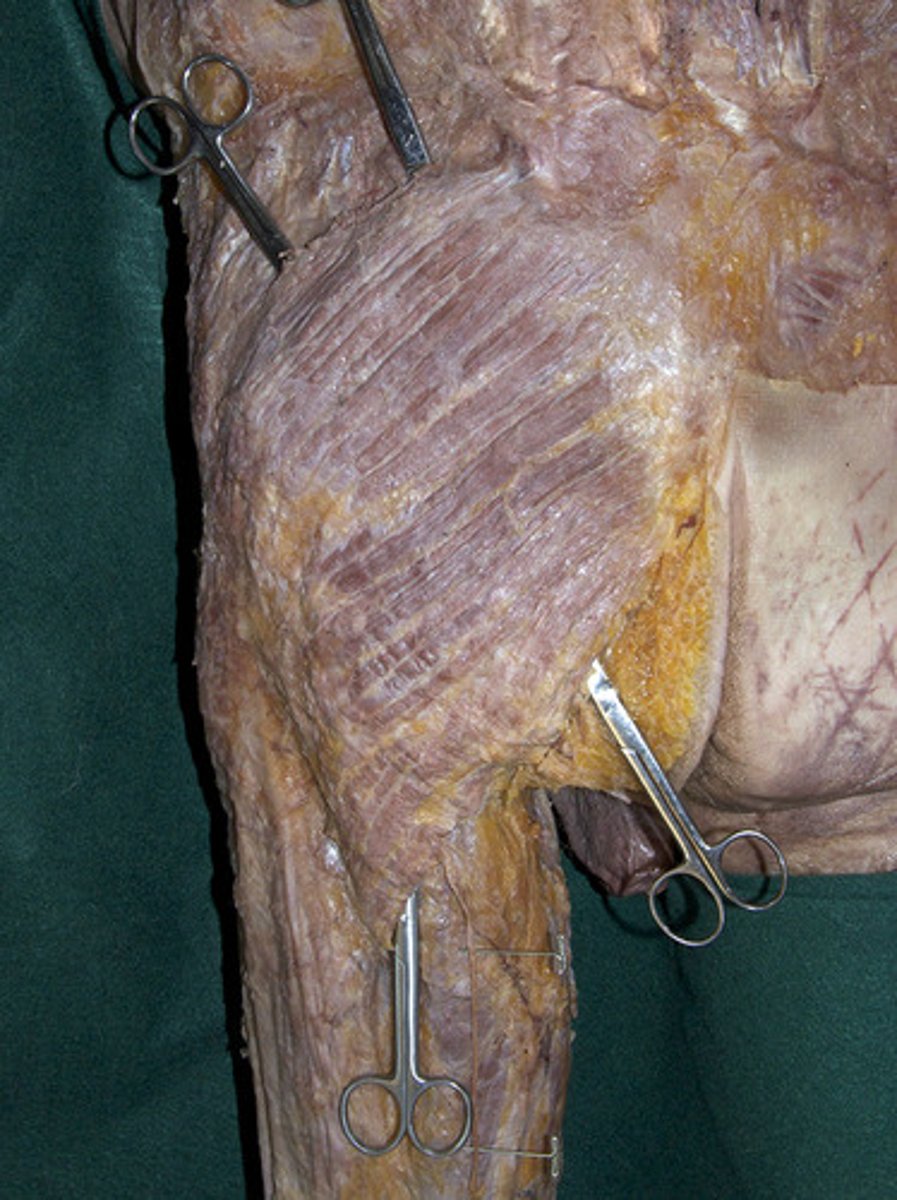
Gluteus maximus
largest and most superficial of these three muscles
gluteus medius
sequentially deeper to gluteus maximus and also sequentially smaller in size
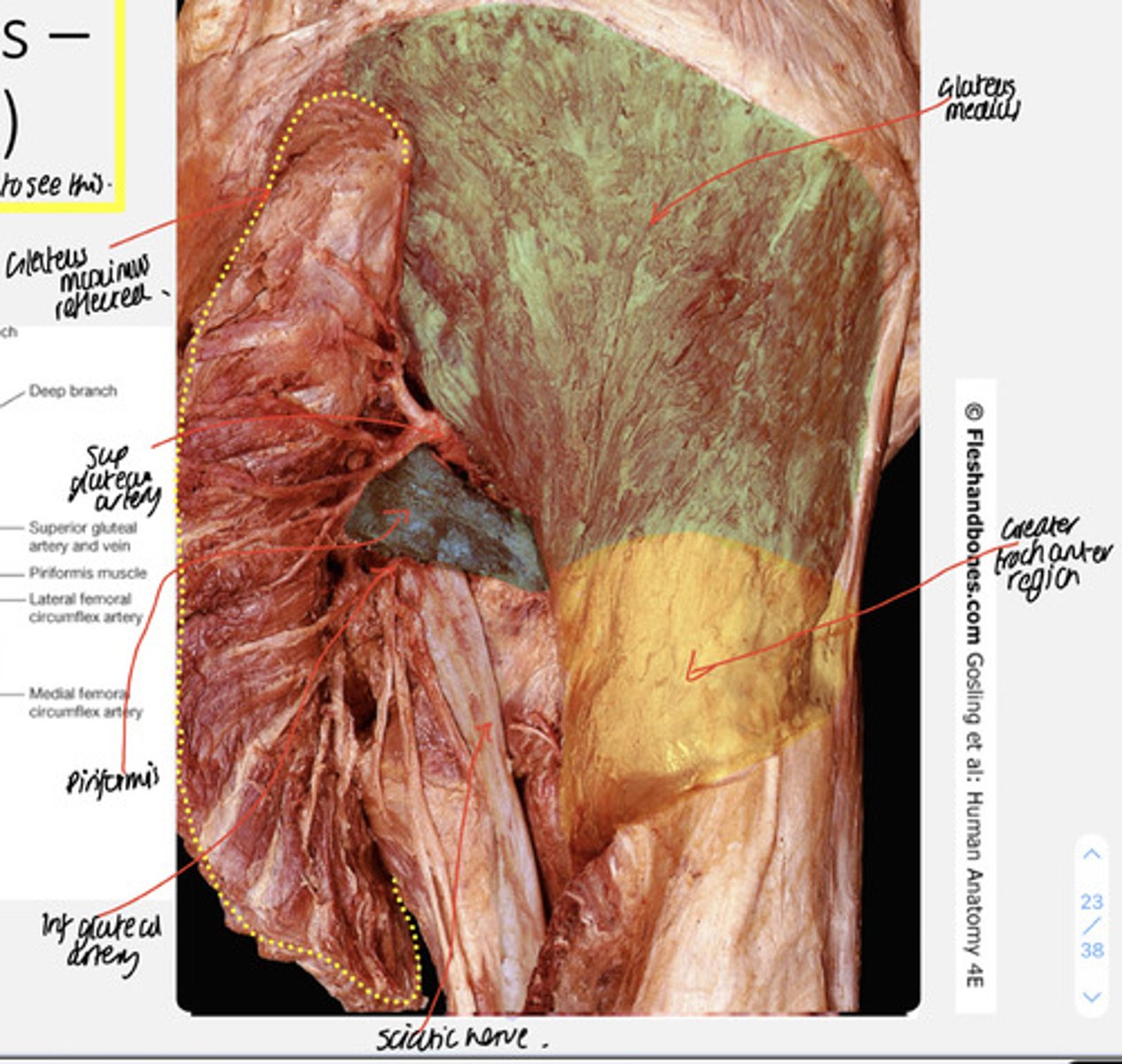
gluteus minimus
sequentially deeper to gluteus maximus and also sequentially smaller in size
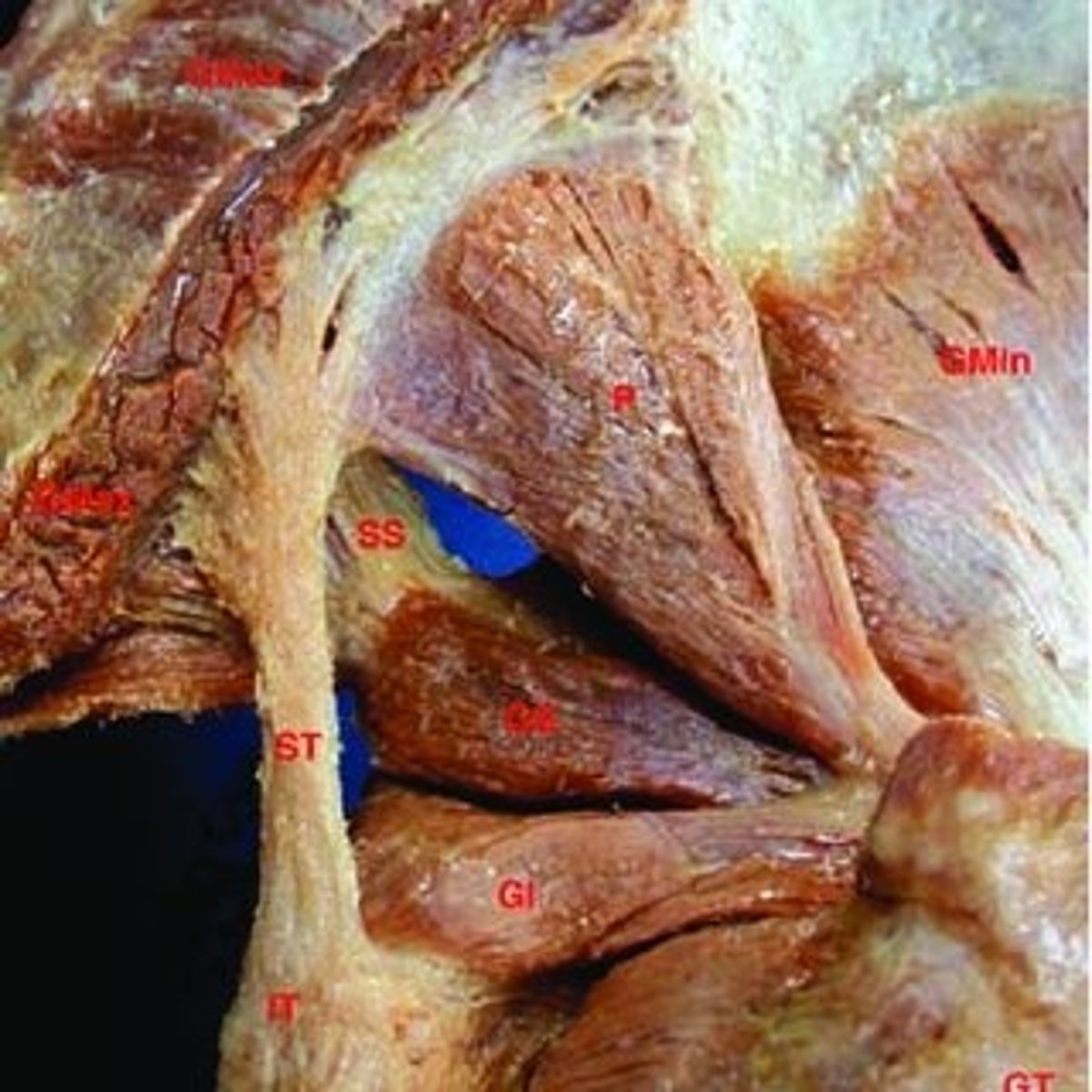
piriformis
piriformis originates at the sacrum and is a pyramid shape. We are now looking at that same muscle but in the posterior view as it travels through the greater sciatic notch to its attachment point on the greater trochanter
obturator internus
its muscle body covers the posterior (internal) aspect of the obturator foramen in the pelvis. It then travels behind the ischium and attaches to the greater trochanter, where we will see it in the gluteal region
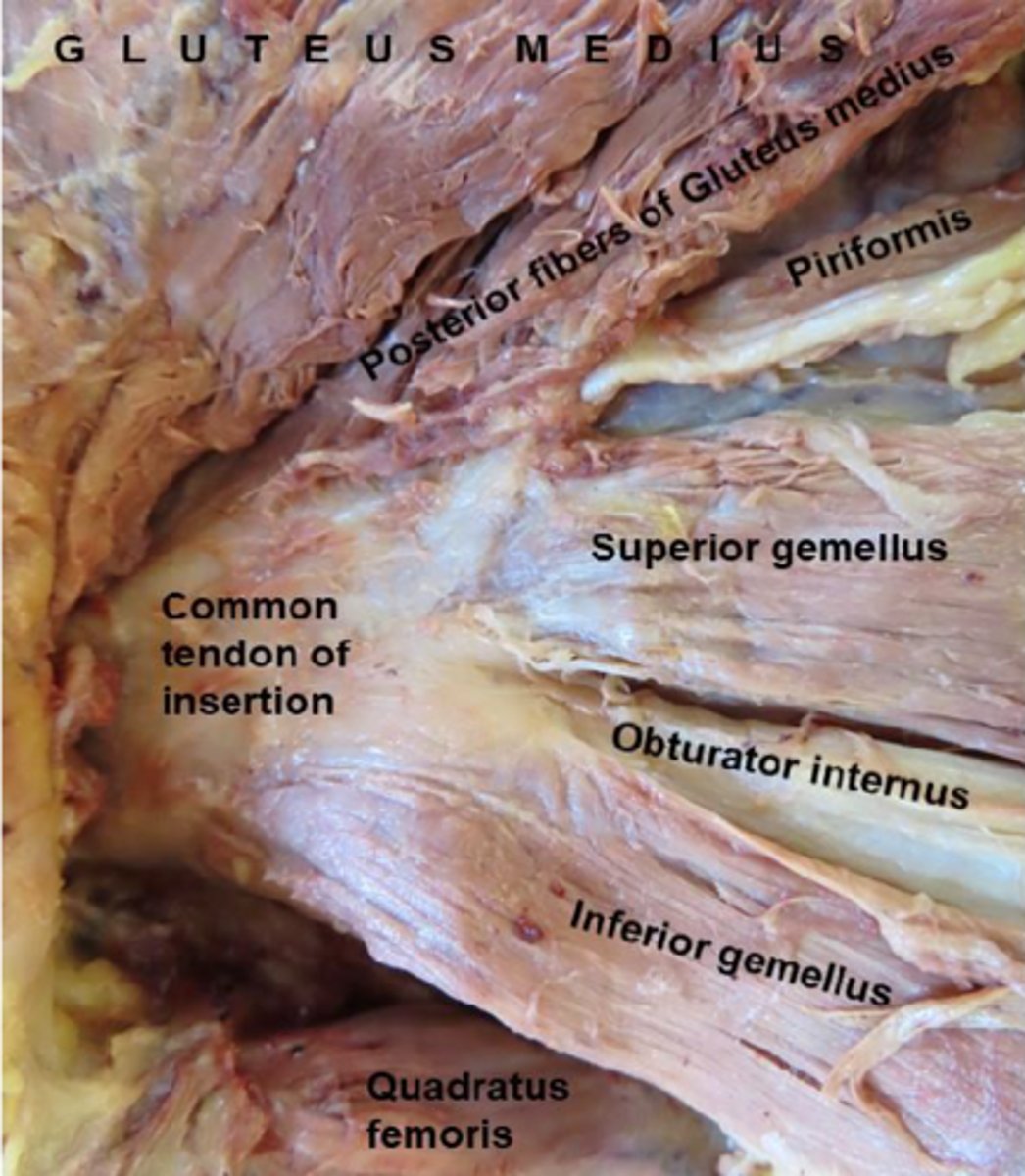
quadratus femoris
muscle is also square-shaped and attaches to the femur in between the greater and lesser trochanter
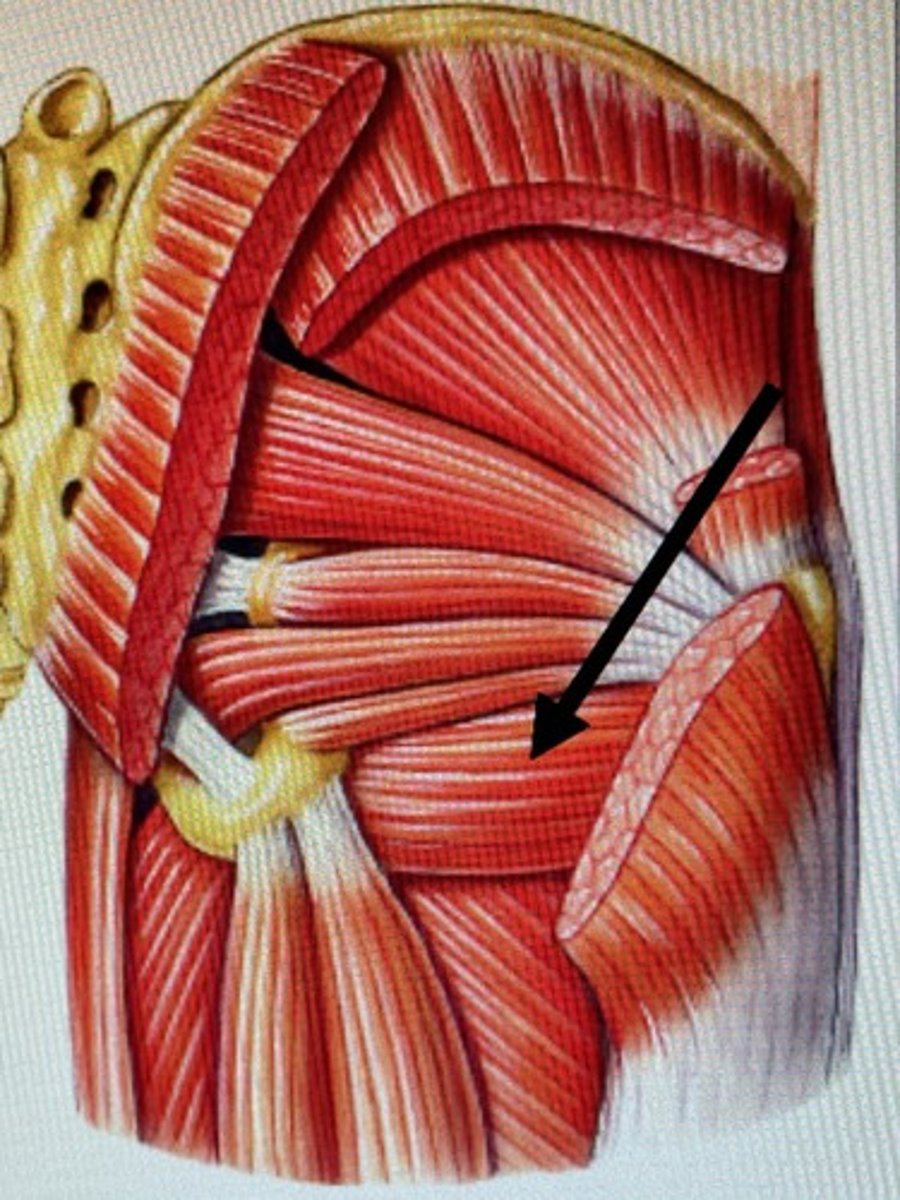
Superior gluteal bundle
supplies the gluteus medius and minimus
Inferior gluteal bundle (gluteal region)
supplies the gluteus maximus
sacrotuberous ligament
name suggests, extends from the sacrum to the ischial tuberosity. You'll find this rigid piece of connective tissue medial to piriformis and obturator internus
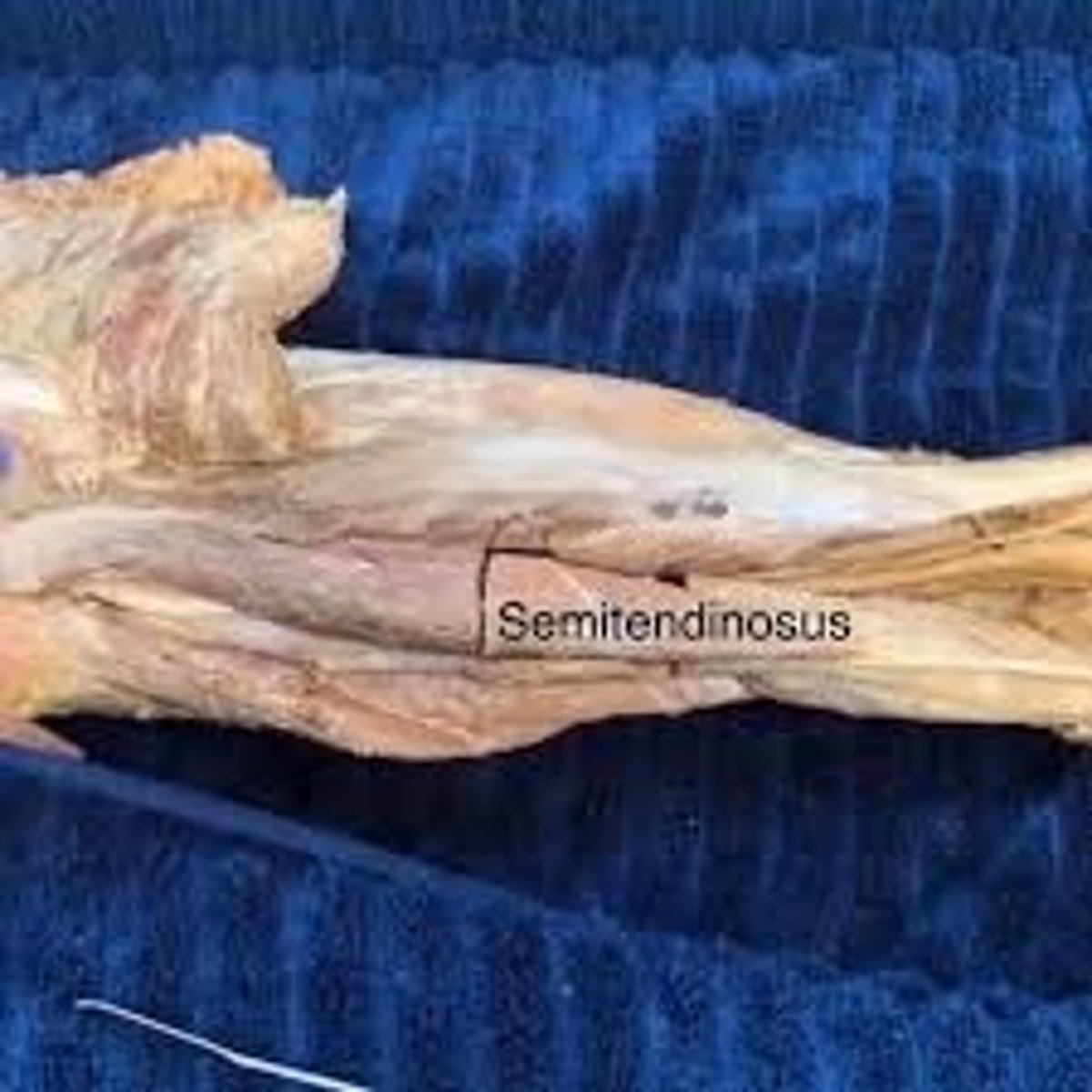
semitendinosus
more superficial and, as its name suggests, has an obvious tendon
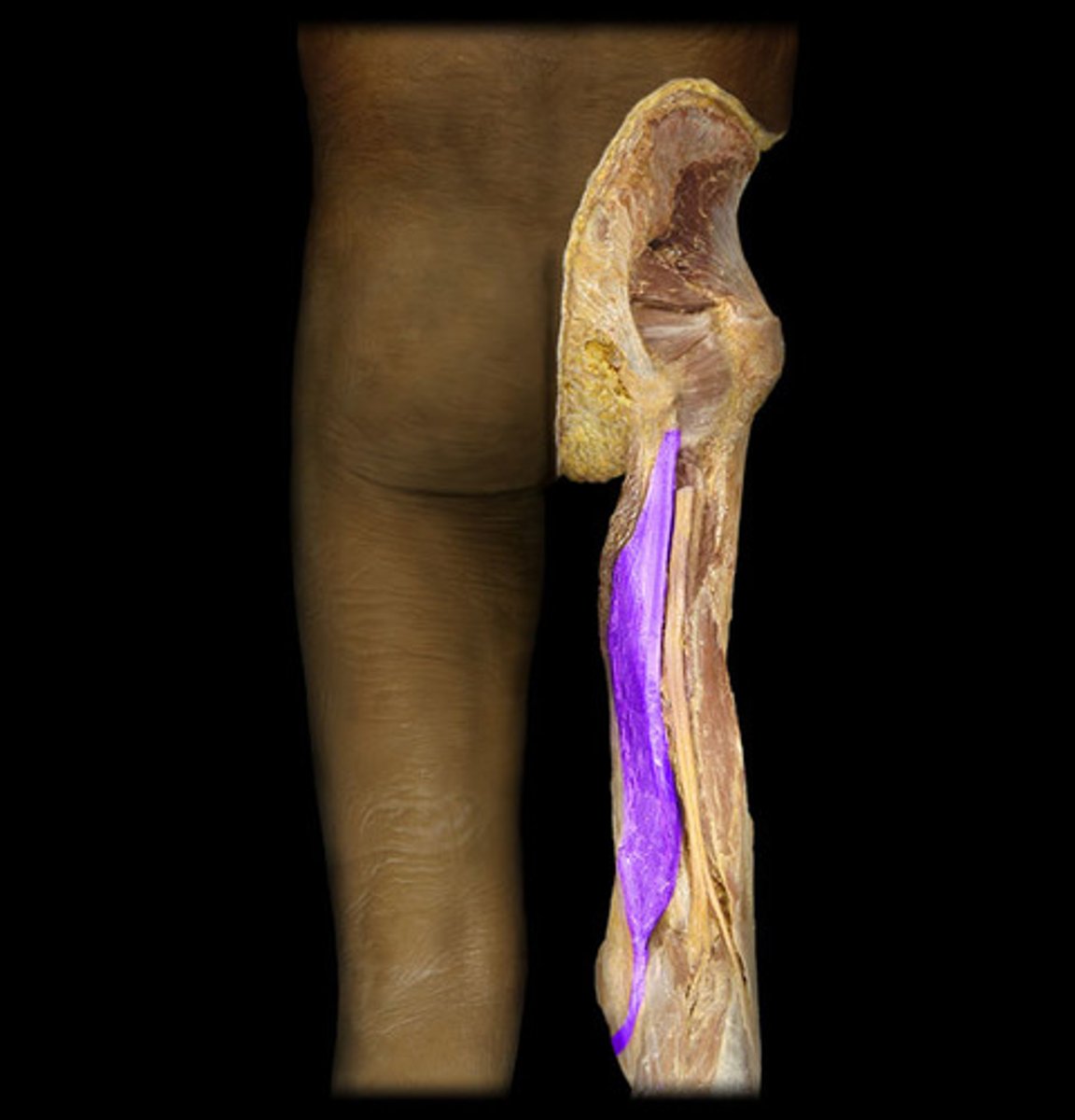
semimembranosus
deep to semitendinosus and its muscle body is slightly larger
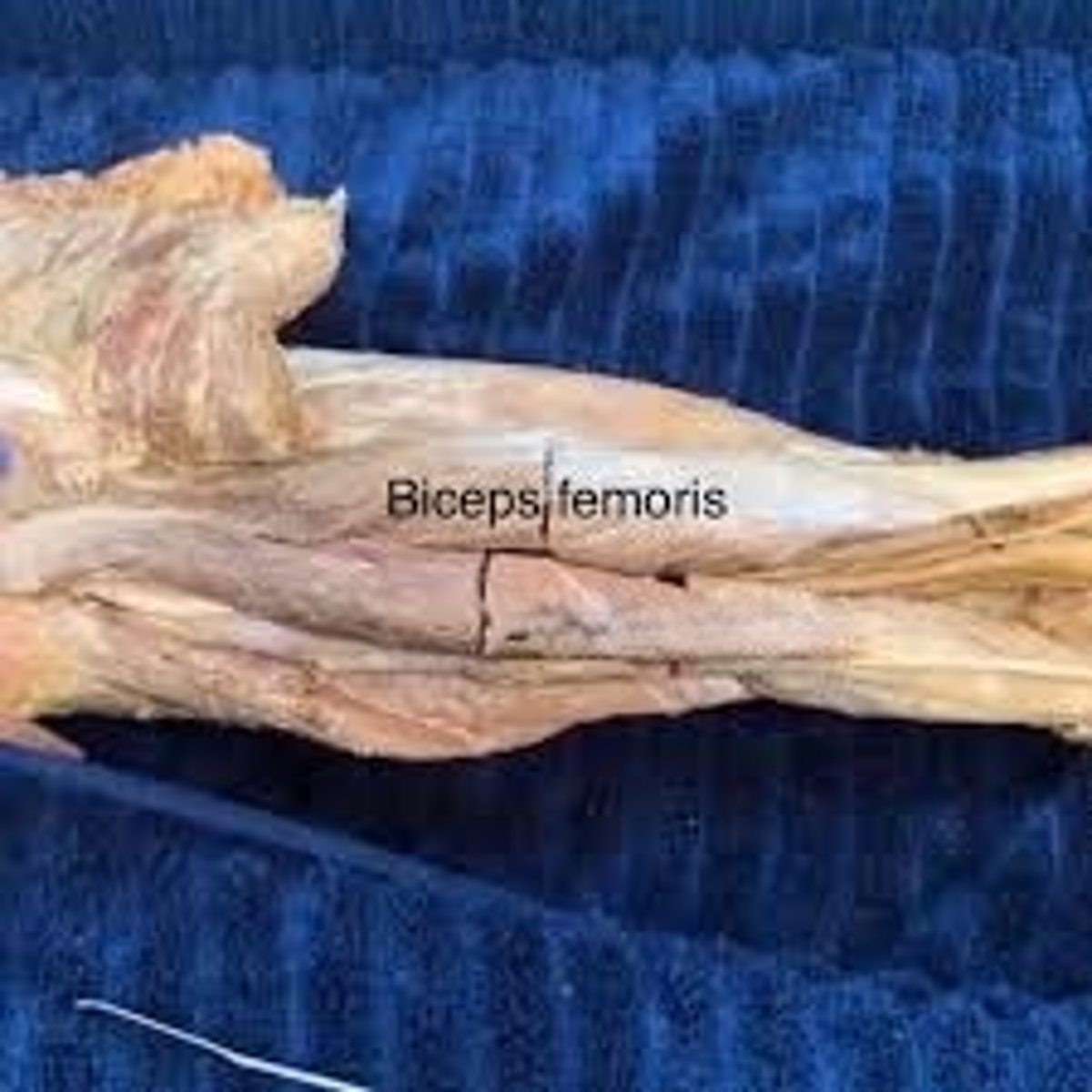
biceps femoris
cylindrical muscle with a short head and a long head, hence "biceps" in the name ("bi" meaning two). This muscle attaches laterally at the head of the fibula
Popliteal artery and vein
continue inferiorly and then wrap medially to the posterior aspect of the thigh. You can see them travel in between semimembranosus and biceps femoris. When they reach the back of the knee (technically called the "popliteal fossa"), the artery and vein are now called the popliteal artery and vein
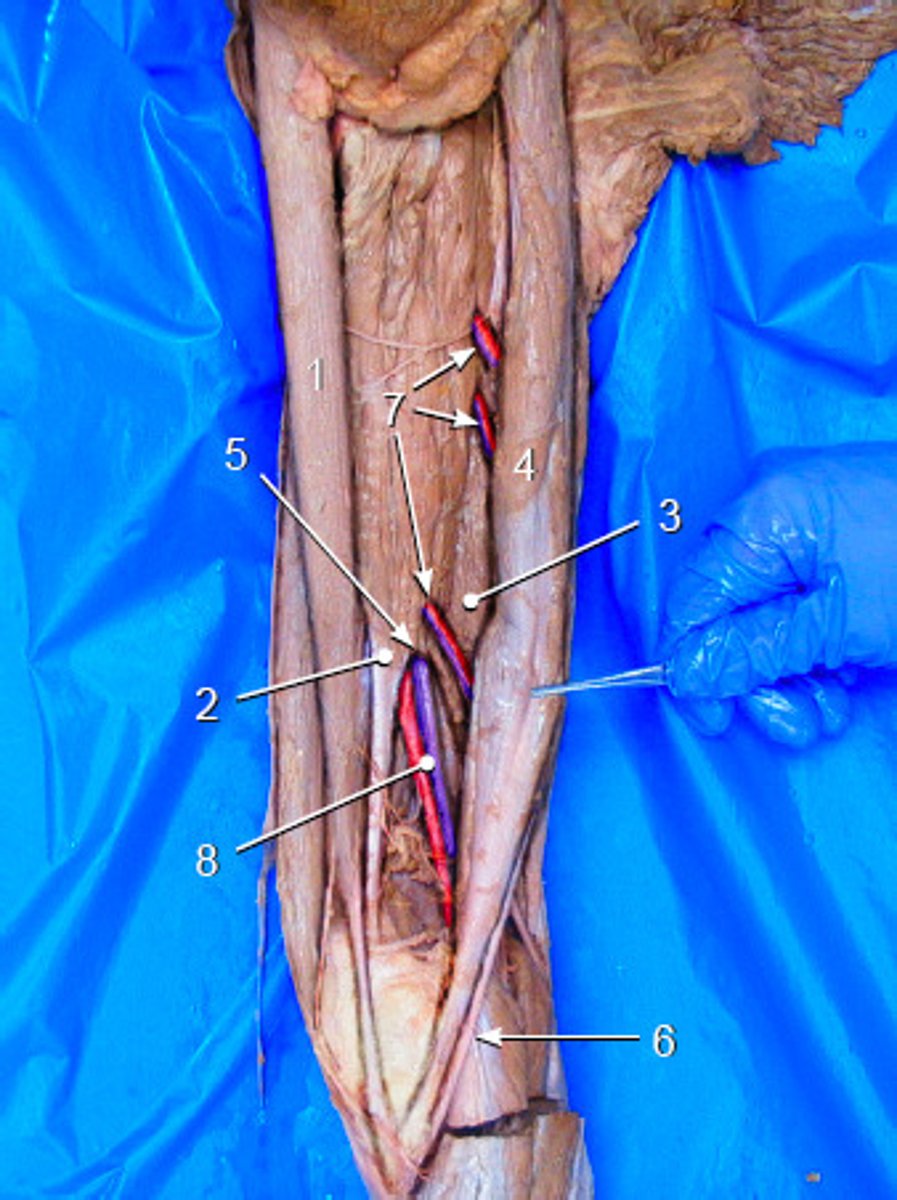
sciatic nerve
It exits through the greater sciatic foramen, travels through the posterior compartment of the thigh, and then alongside the popliteal artery and vein
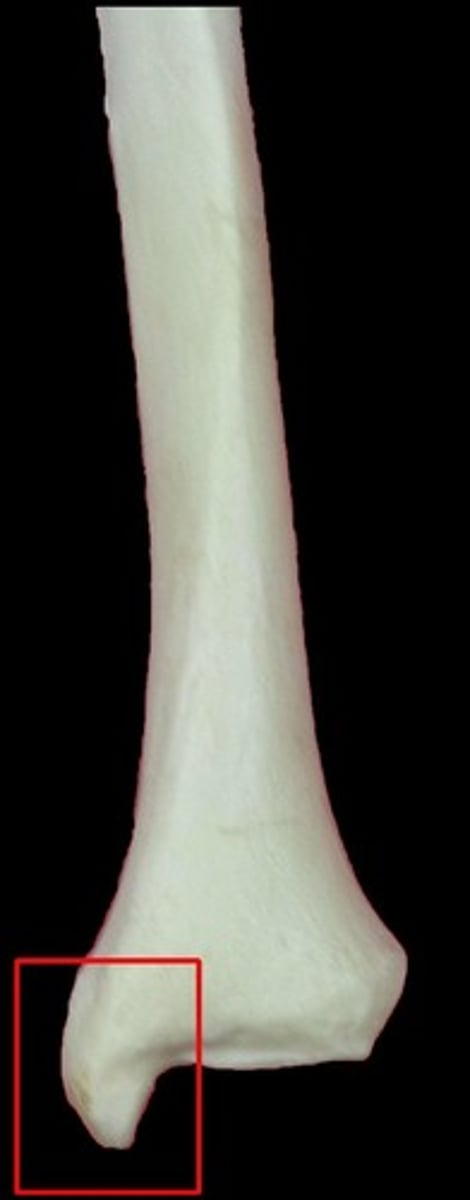
medial malleolus of tibia
large projection from the tibia that is on the medial side. You can feel this chunk of bone under your skin on the inner aspect of your ankle
lateral malleolus of fibula
Opposite the medial malleolus of the tibia
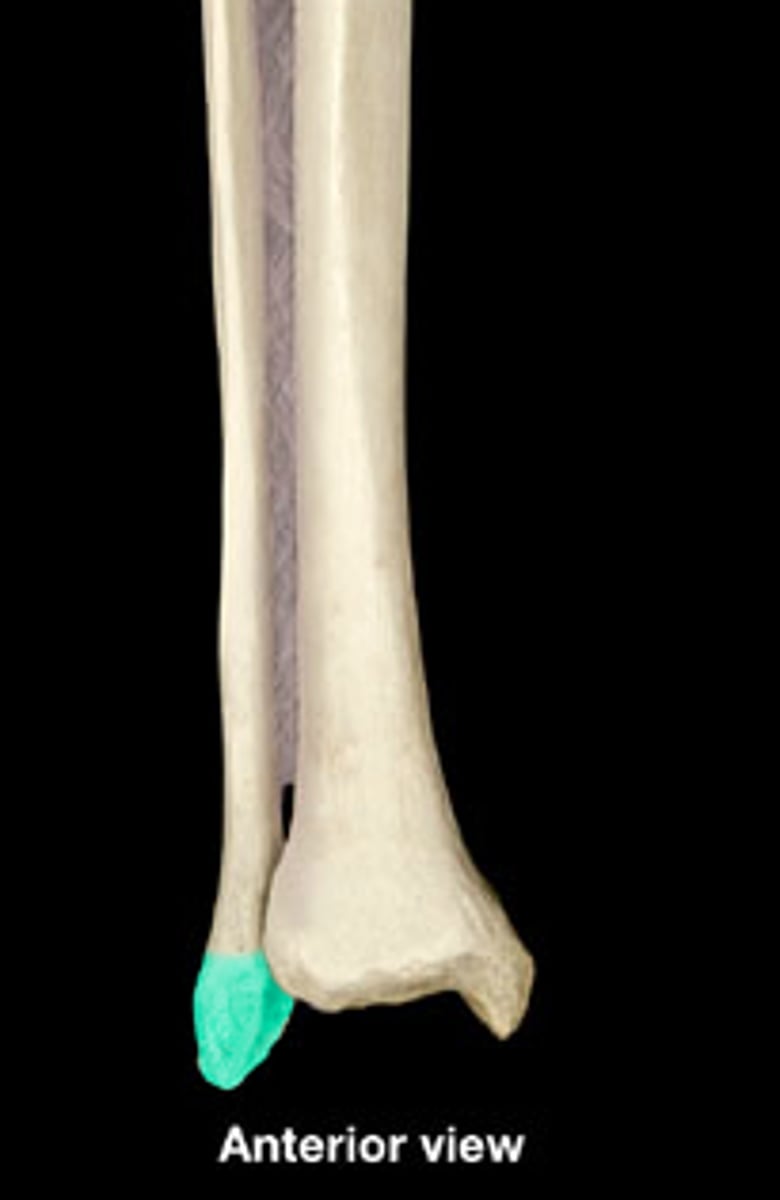
head of fibula
is the square proximal end of the fibula

calcaneus
The bone that makes up your heel
-number 2
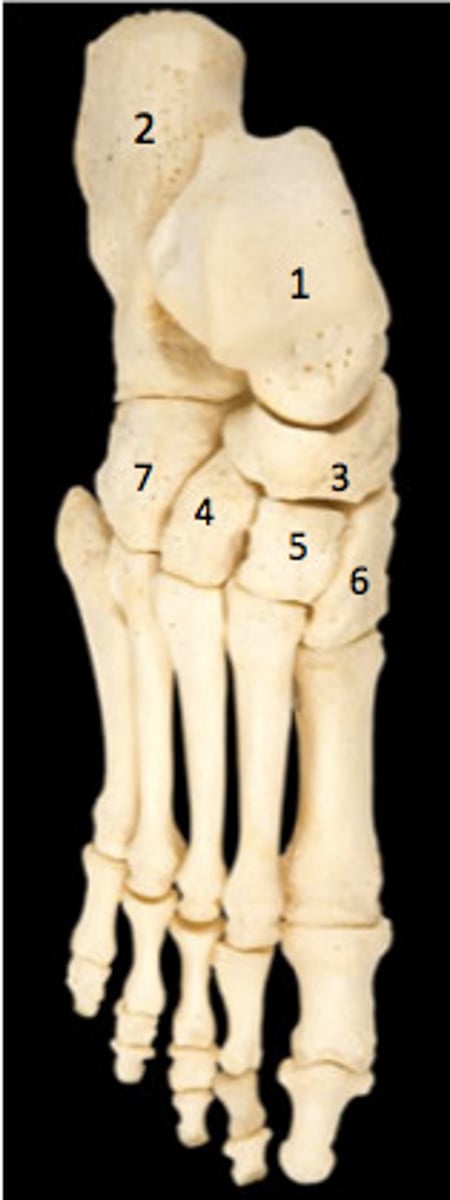
Talus
has a nice round superior surface to interact with the distal end of the tibia in the ankle joint
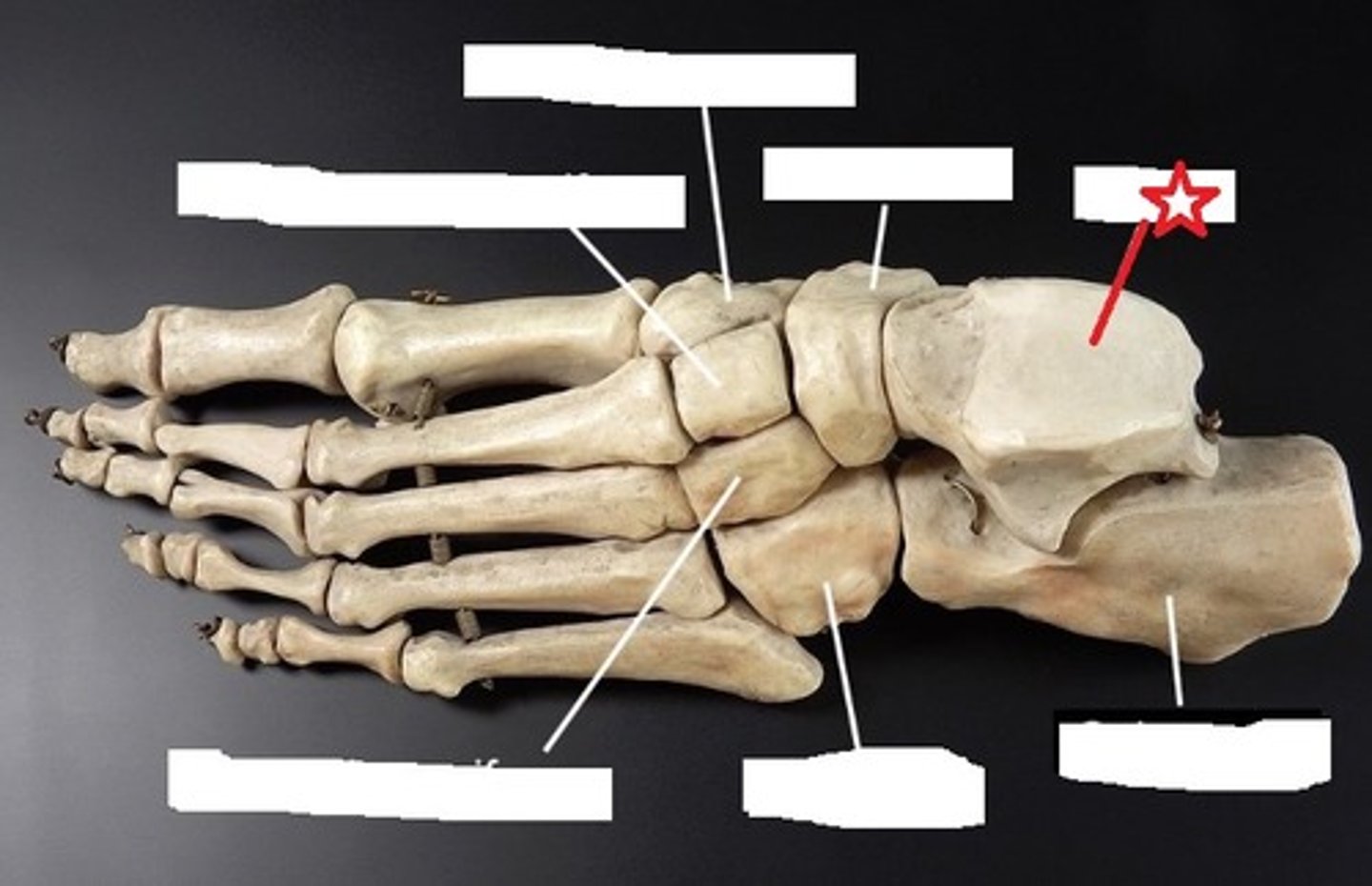
cuboid
Cube-shaped bone
-number 4
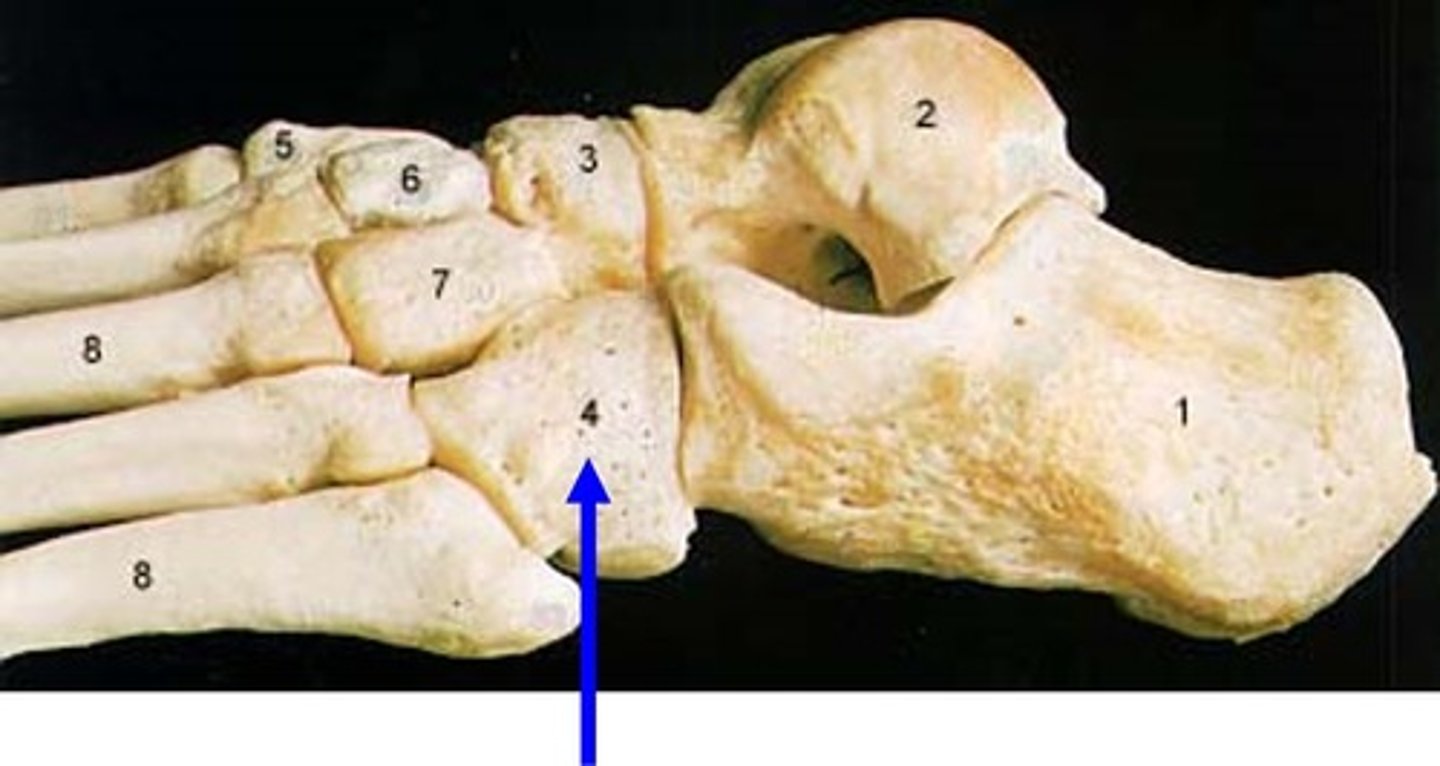
Navicular
crescent-shaped bone that articulates with the talus and cuneiforms. It also kind of looks like a small boat or ship, so you can think of the navy
-number 3
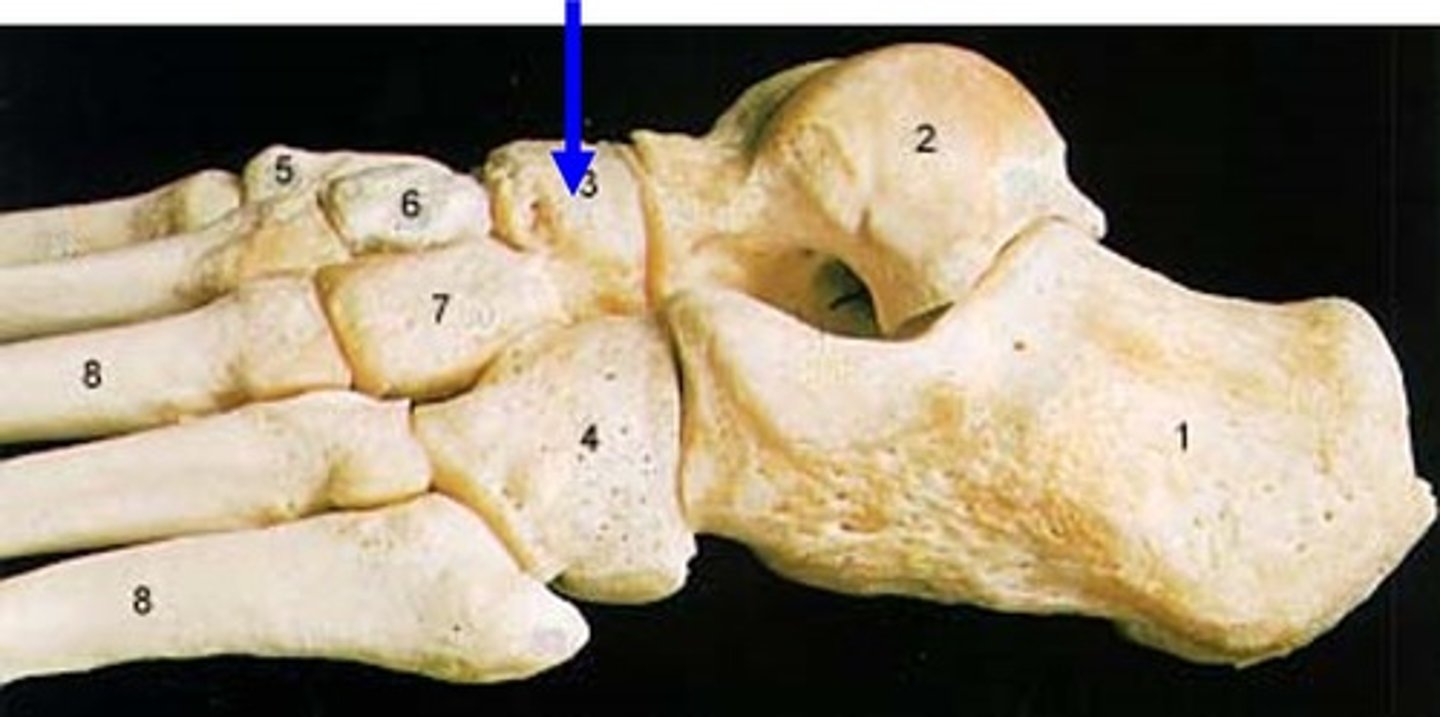
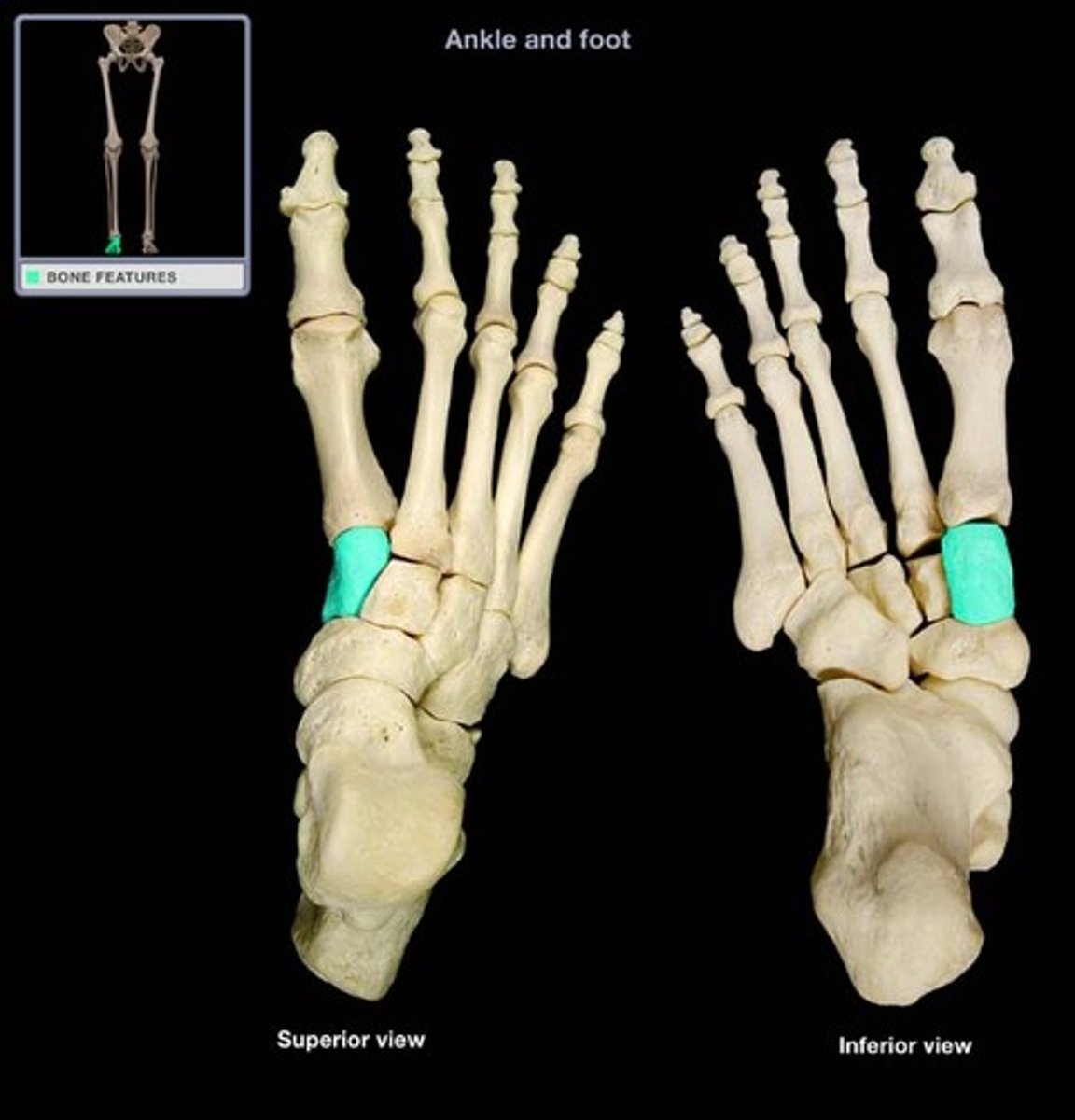
medial cuneiform
Three closely associated bones articulating with the navicular
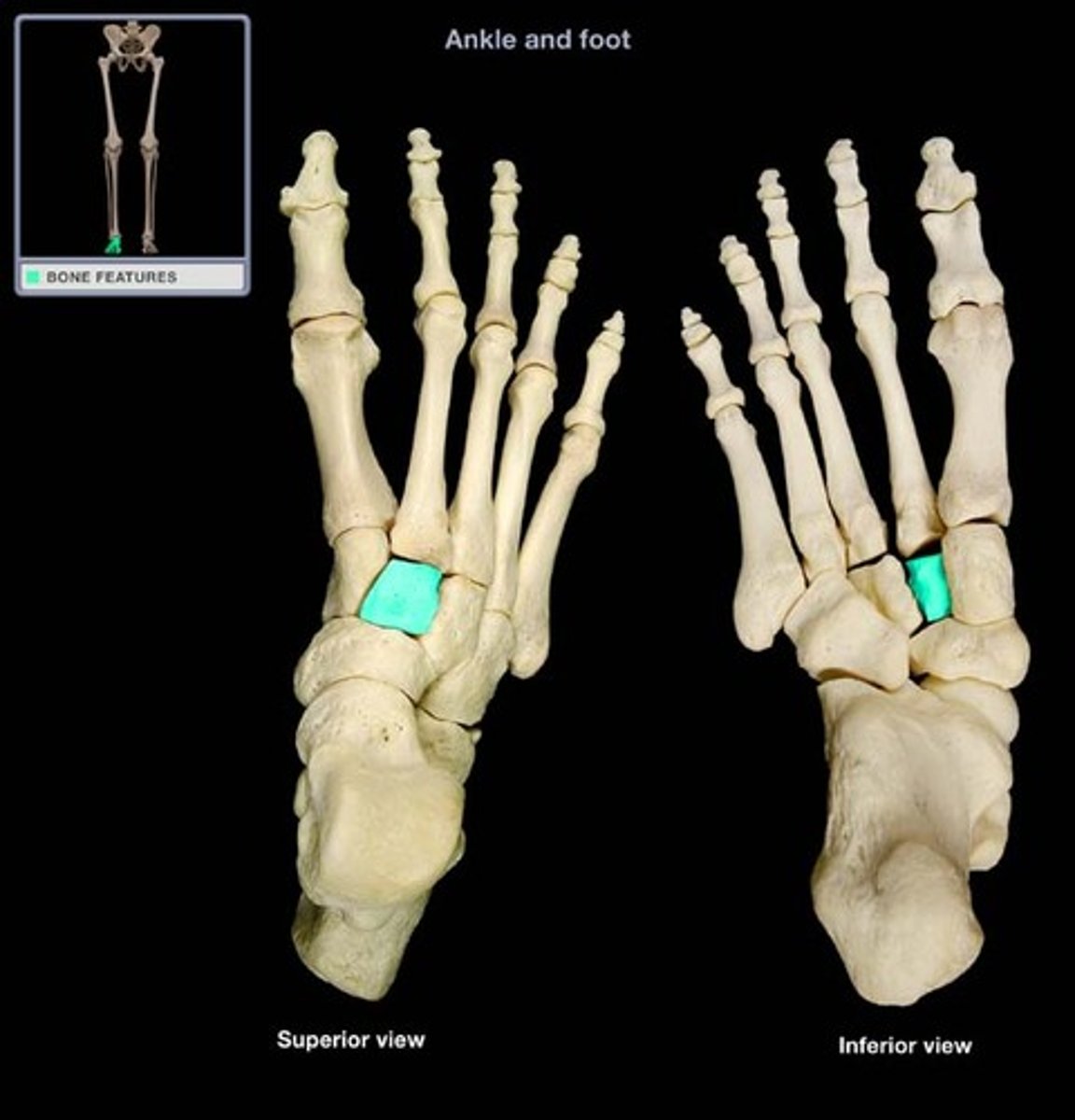
Intermediate cuneiform
Three closely associated bones articulating with the navicular
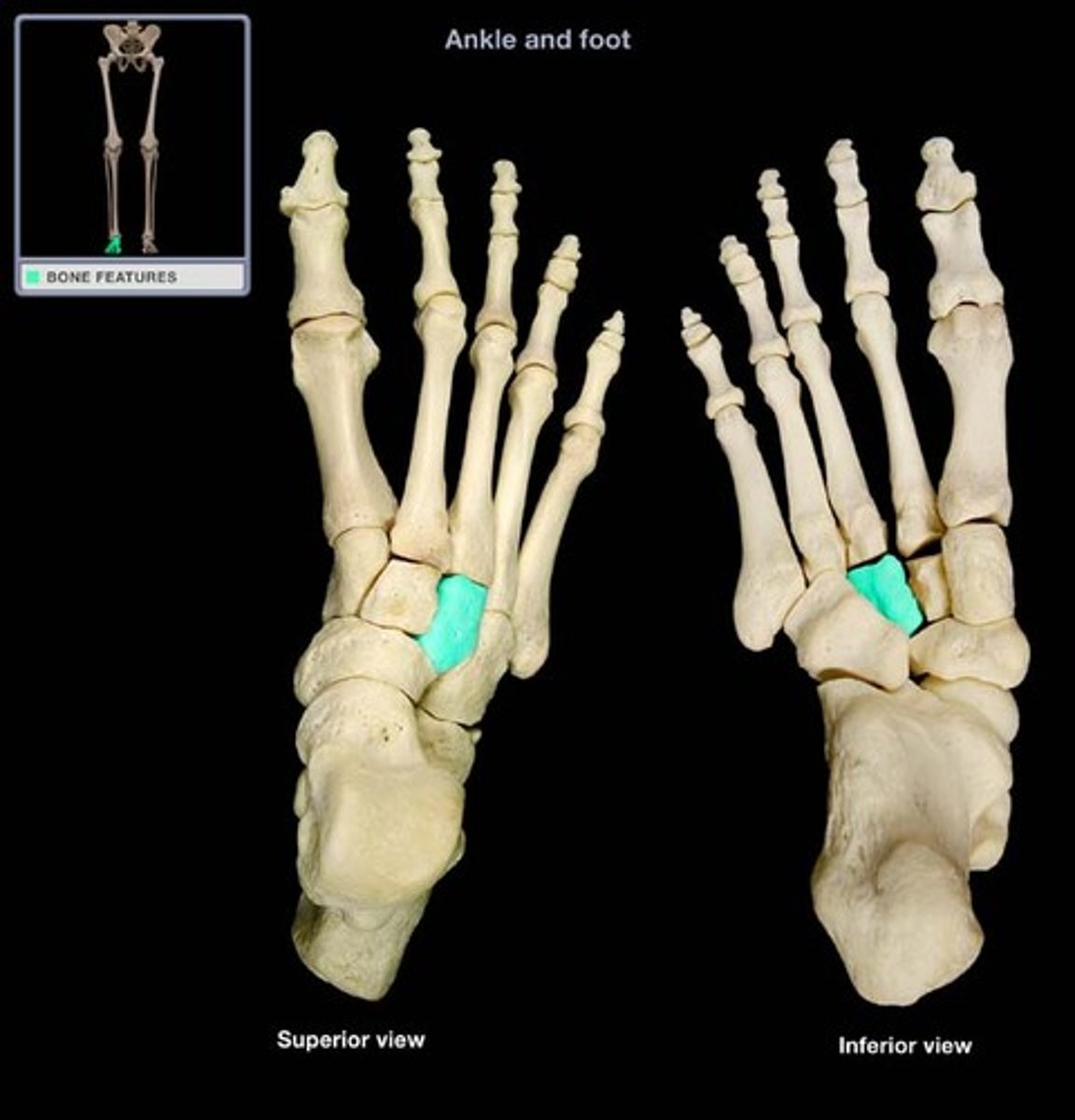
lateral cuneiform
Three closely associated bones articulating with the navicular
first metatarsal
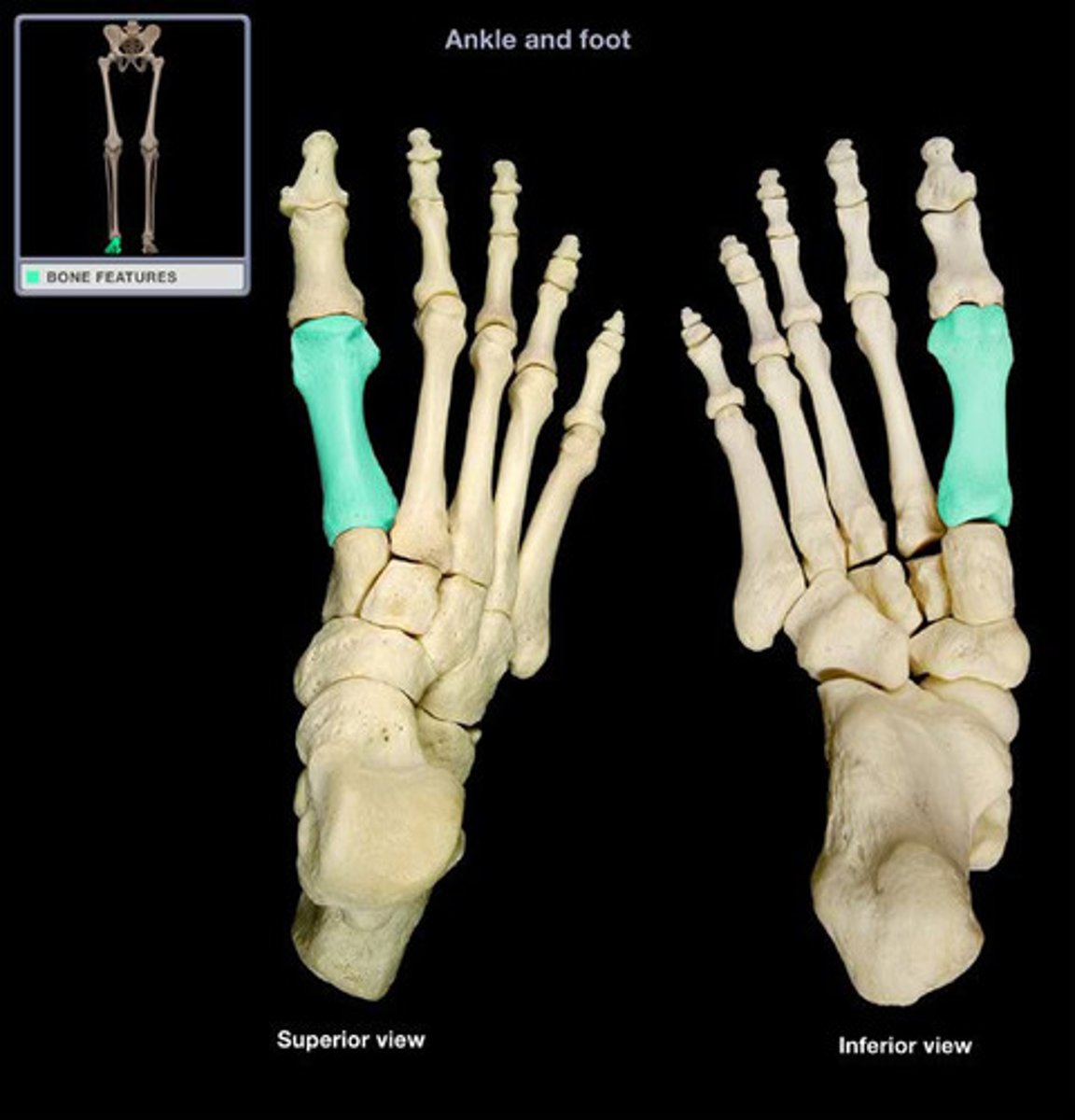
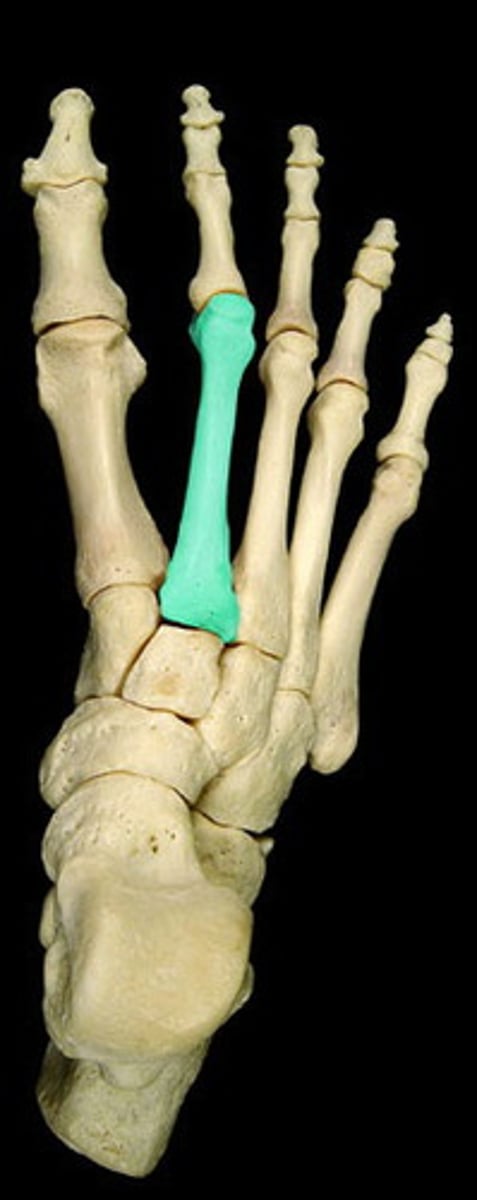
second metatarsal
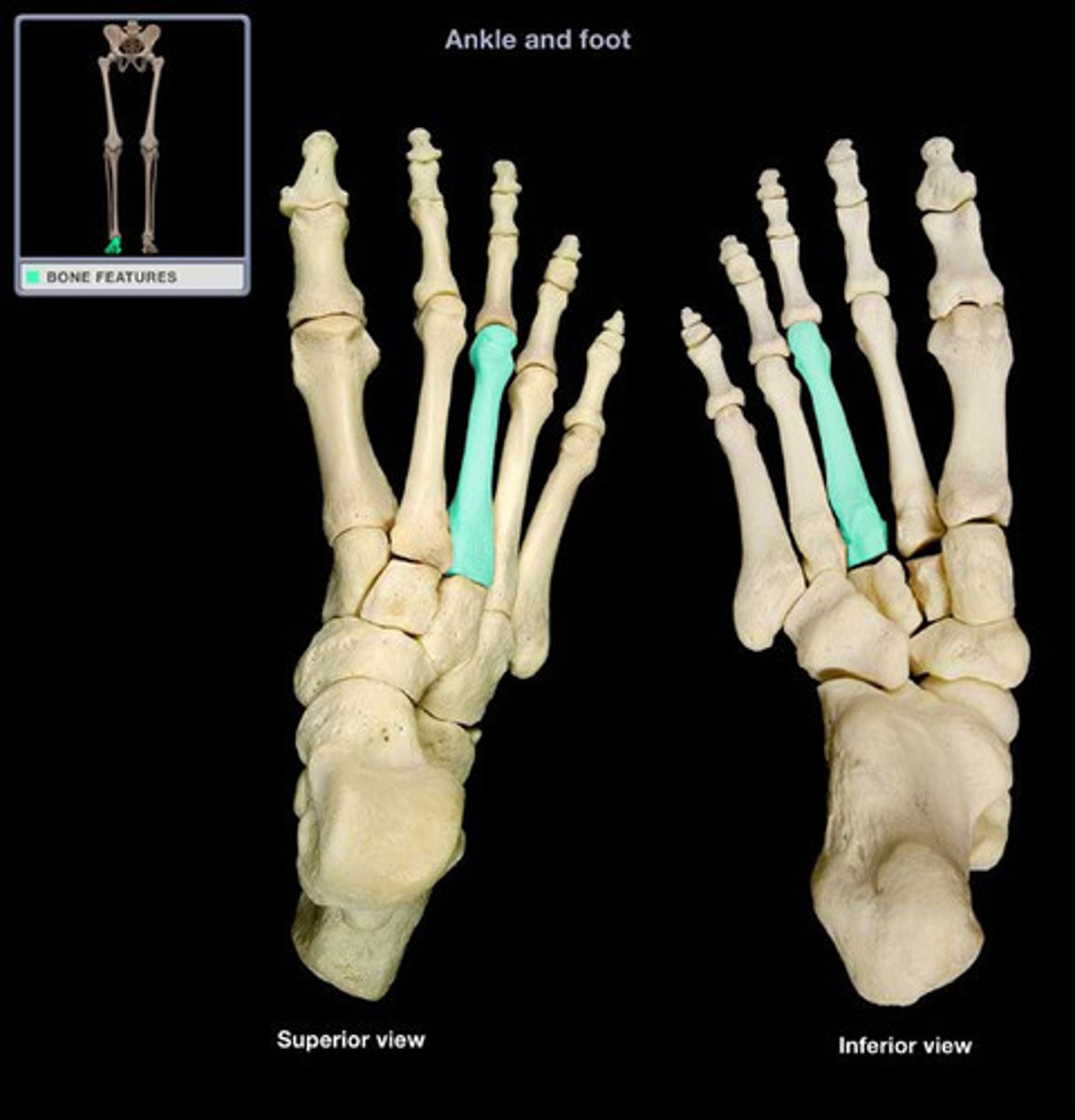
third metatarsal
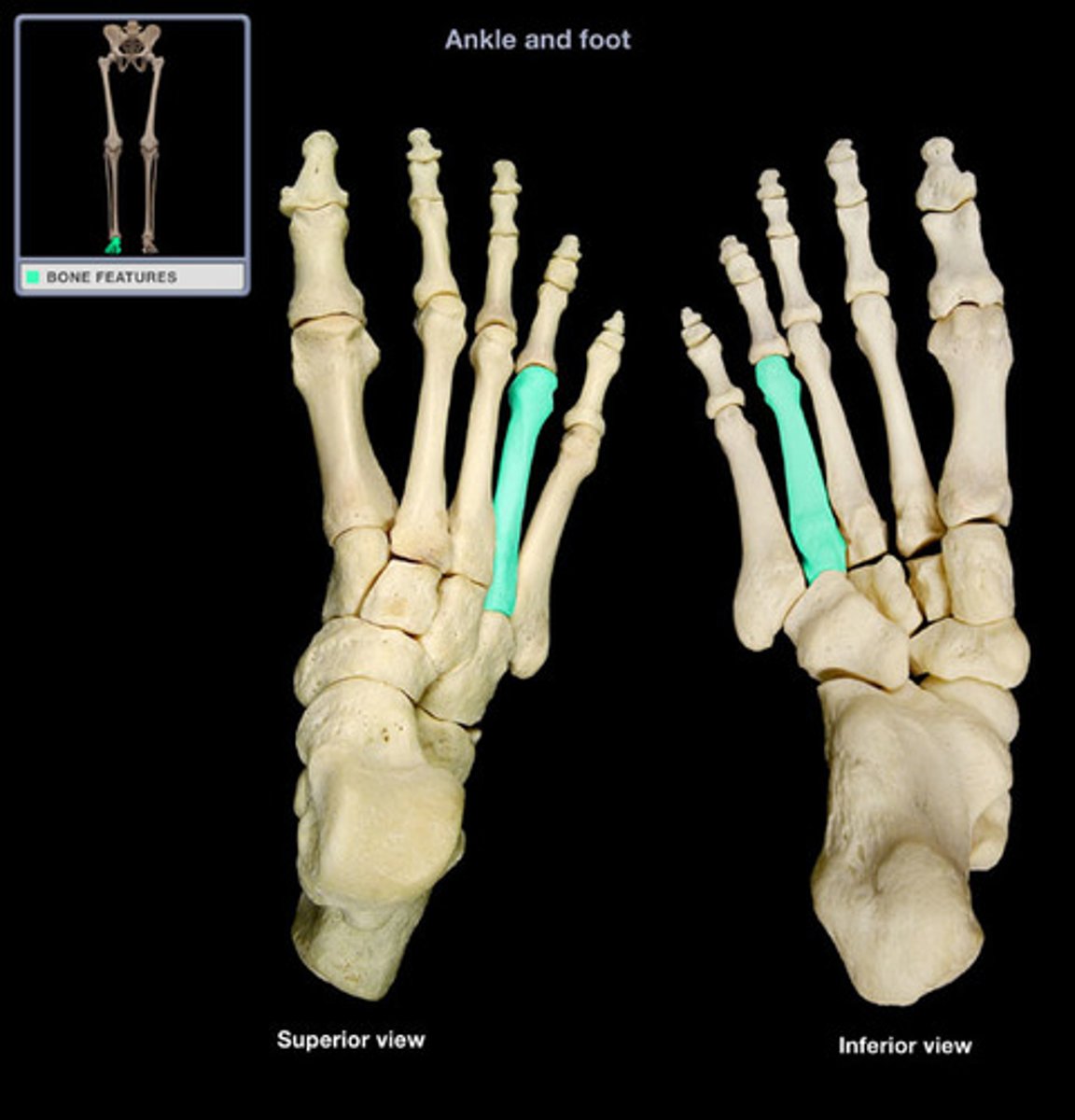
fourth metatarsal
fifth metatarsal
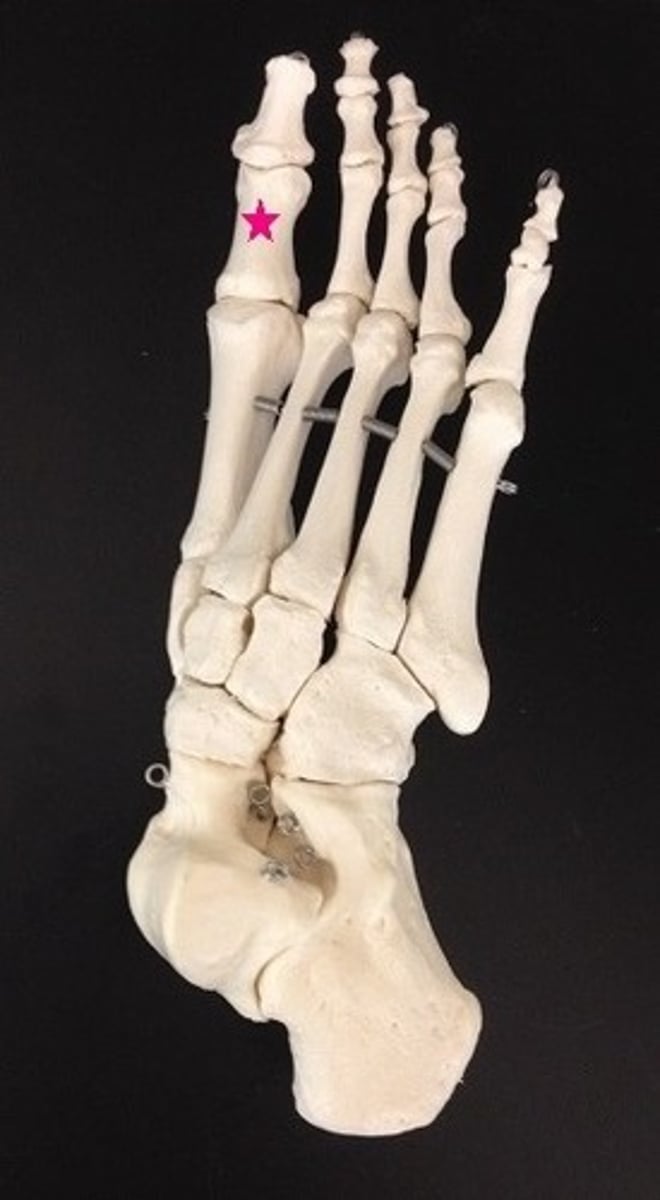
proximal phalanx 1
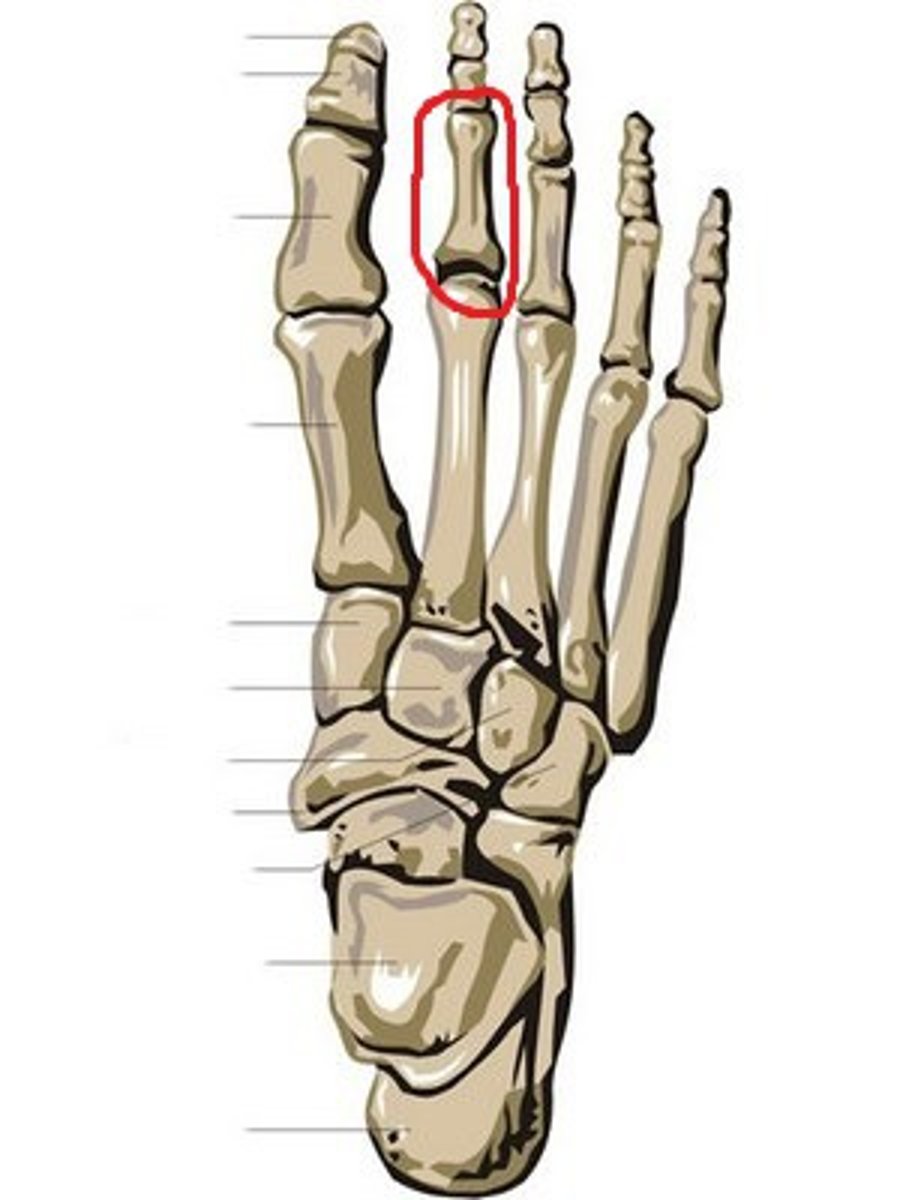
proximal phalanx 2
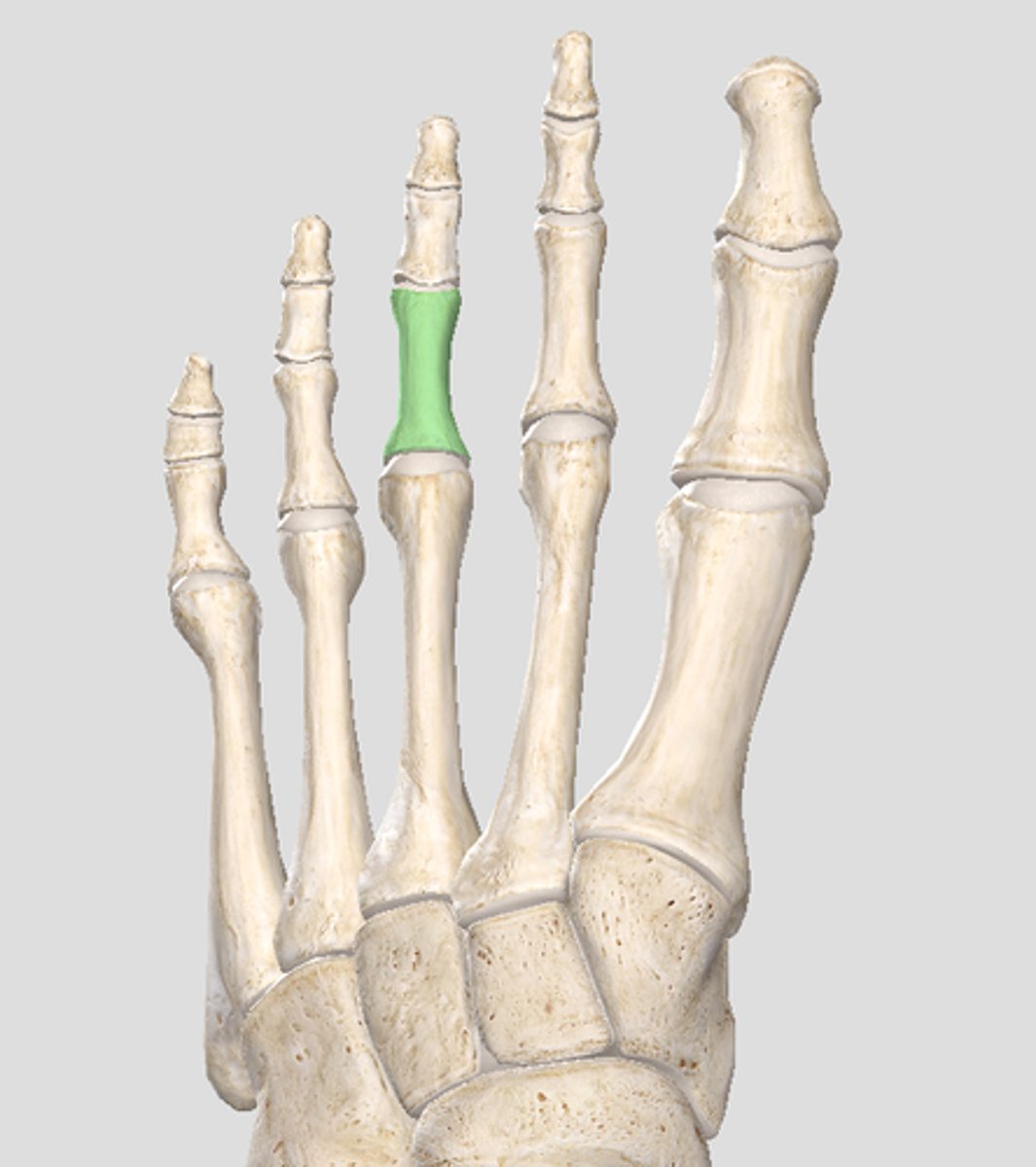
proximal phalanx 3
proximal phalanx 4
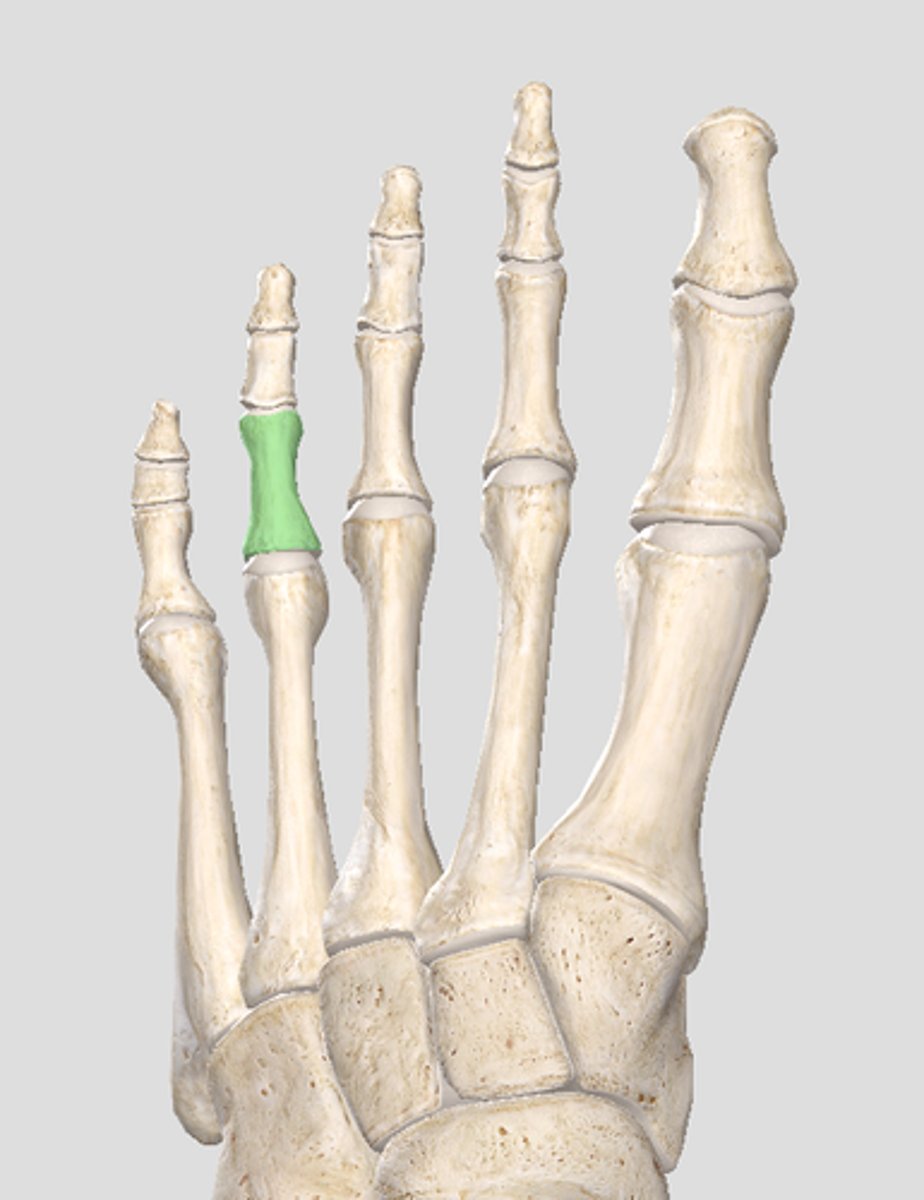
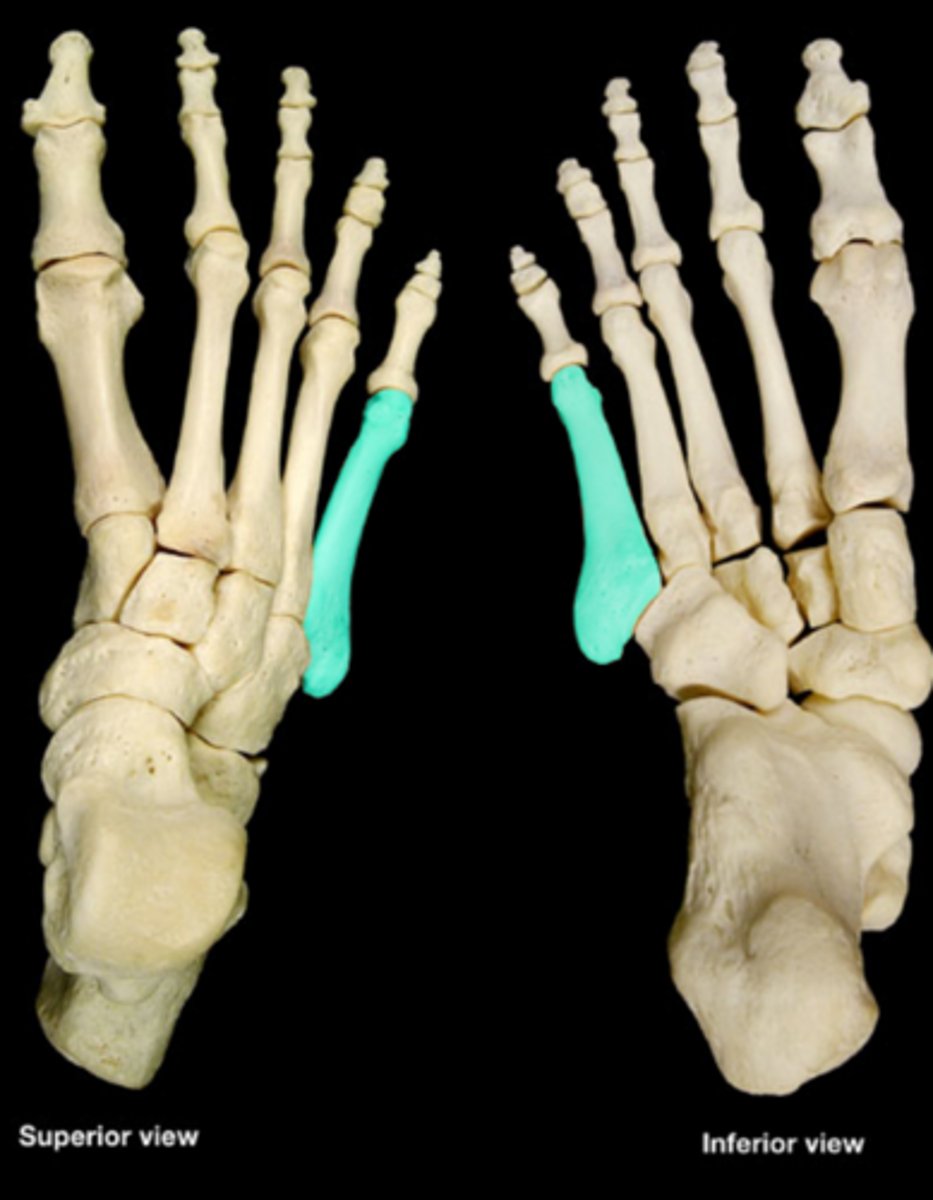
proximal phalanx 5
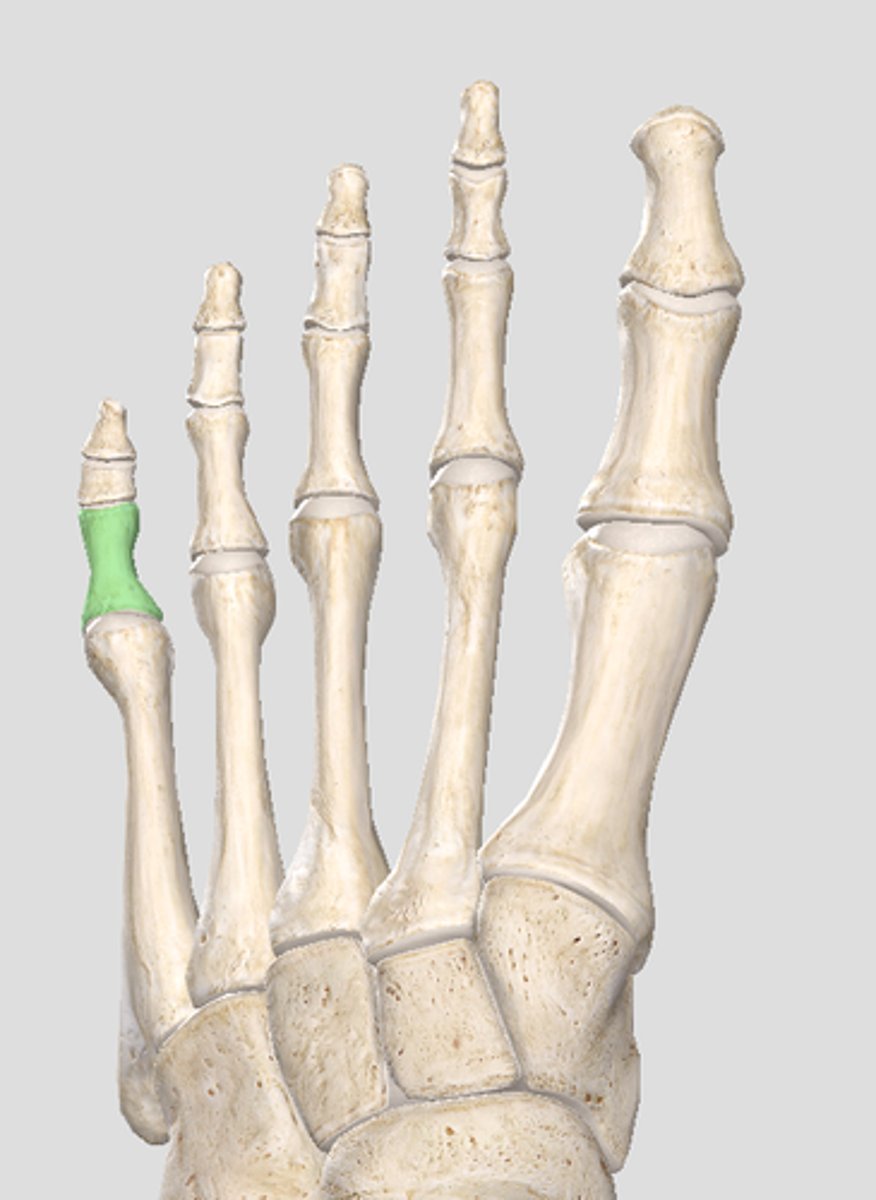
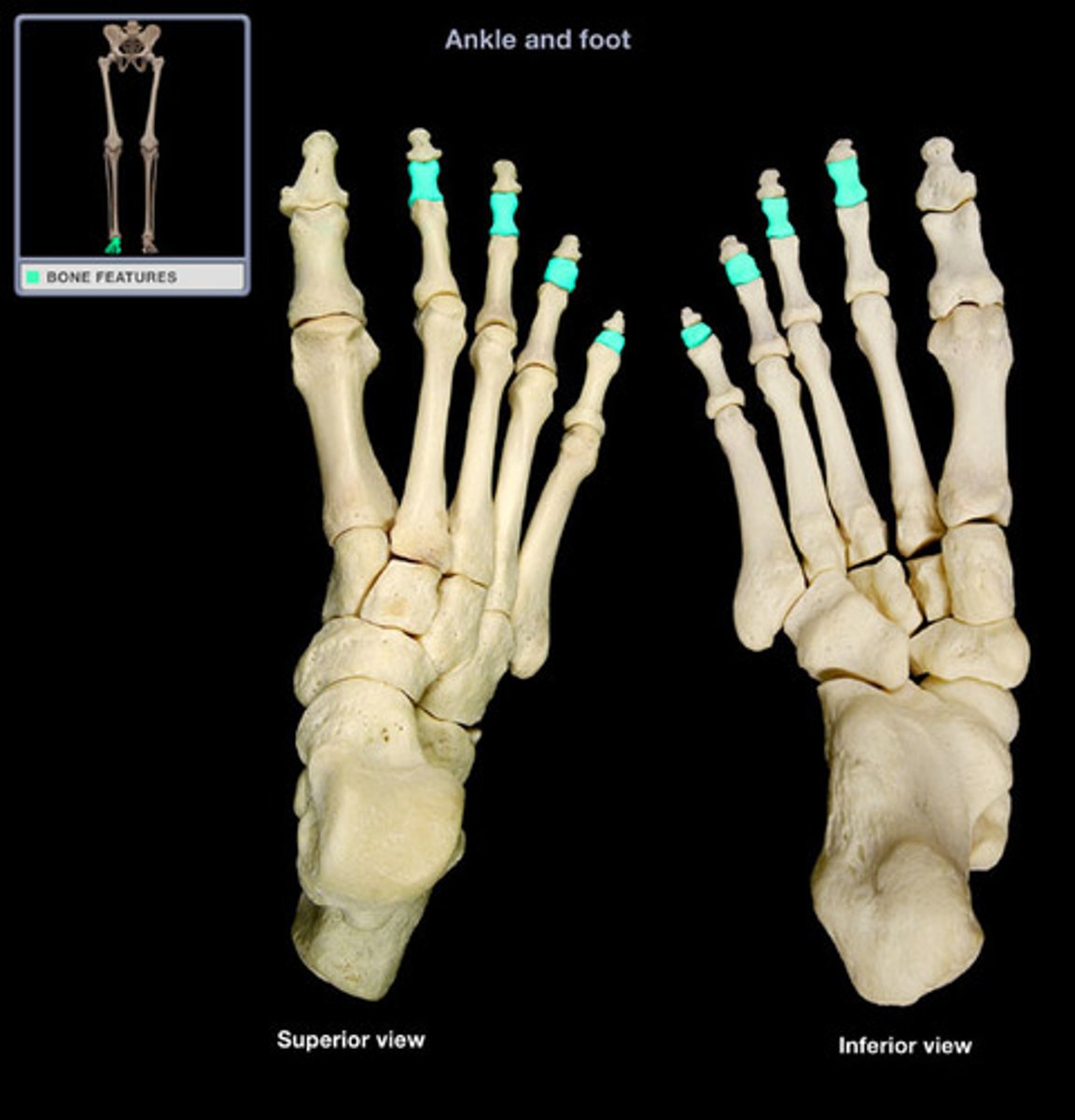
intermediate phalanges
The FOUR phalanges between the Proximal and Distal phalanges.
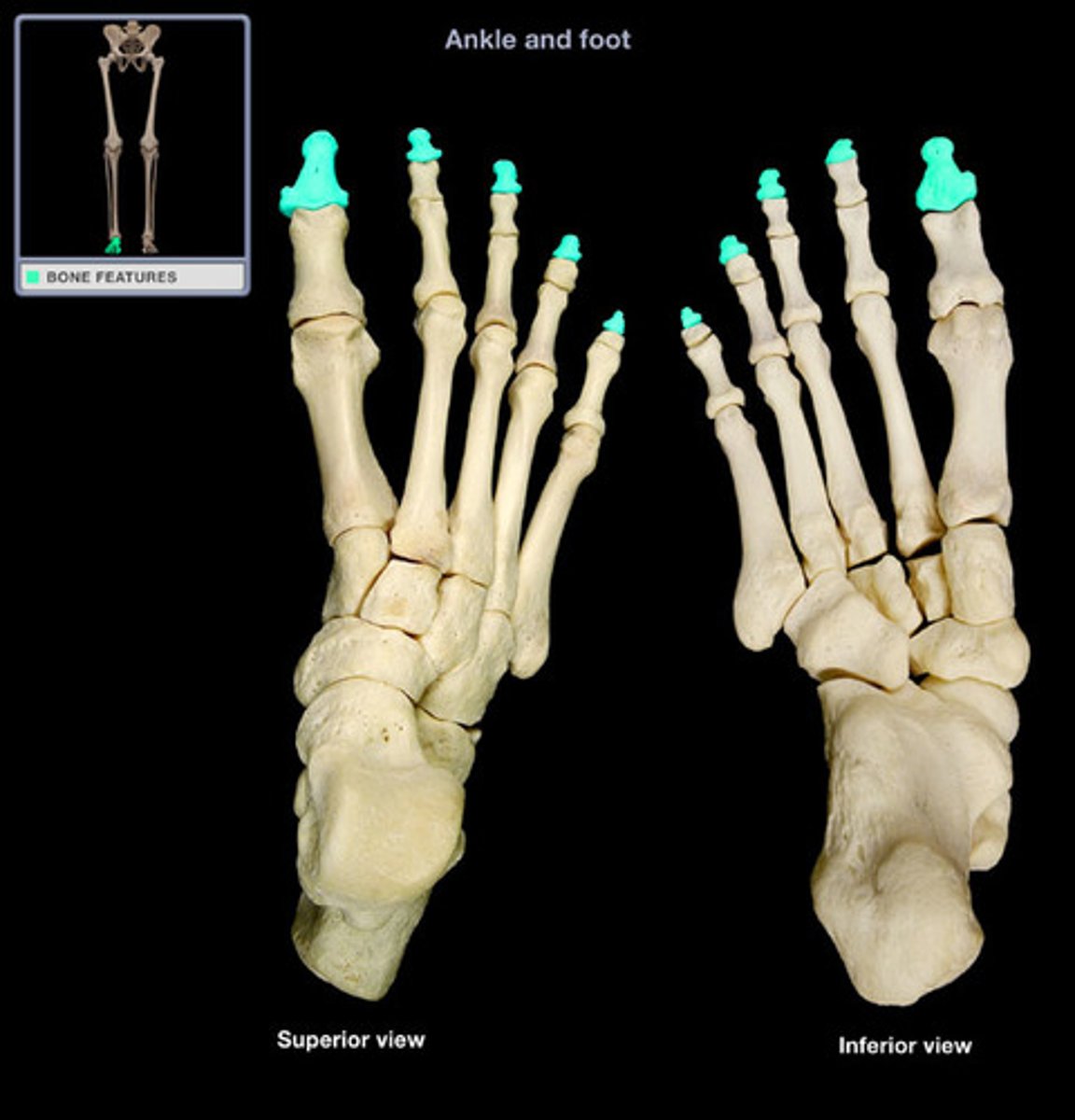
distal phalanges
These bones sit under your toenails
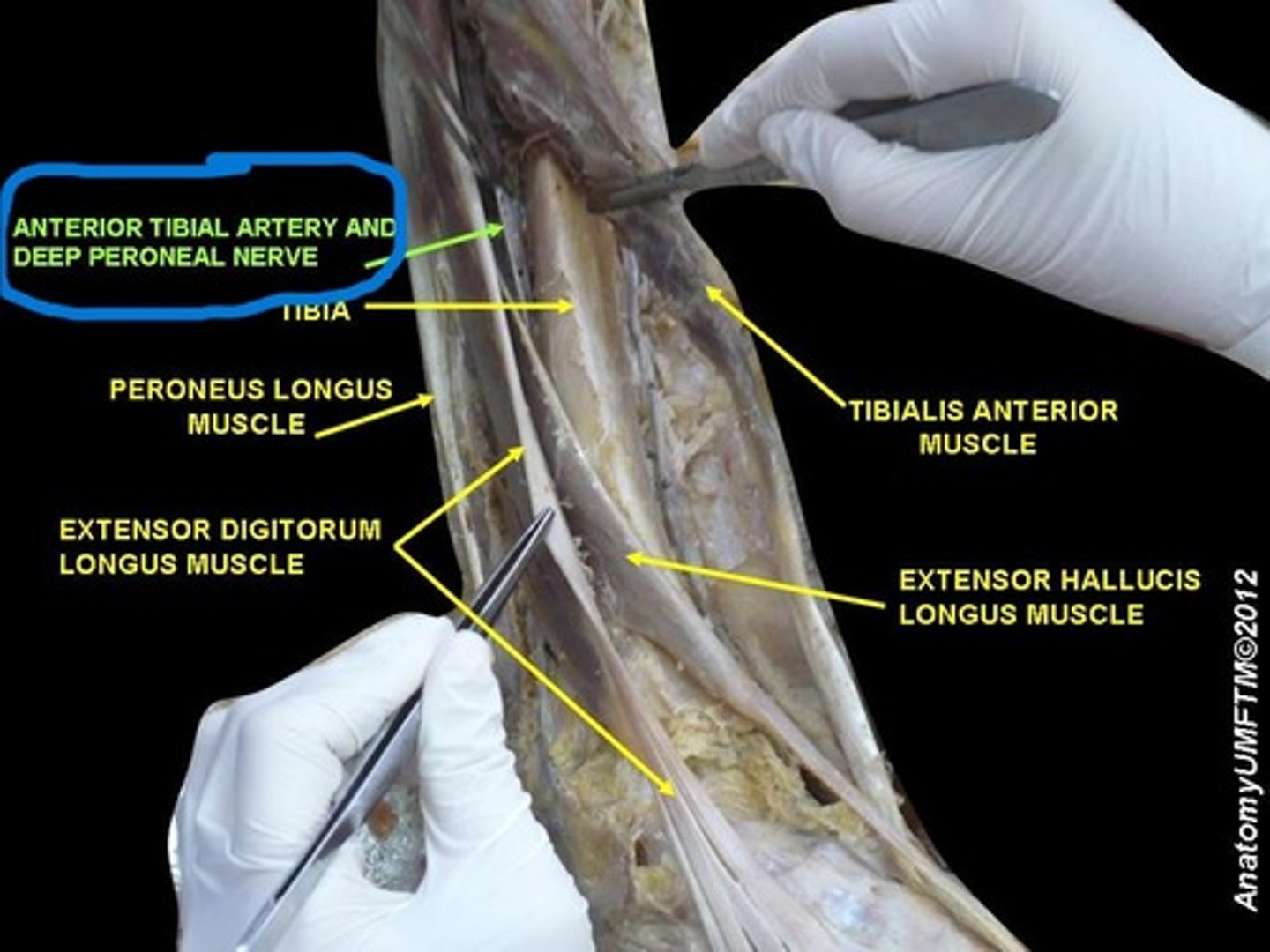
Tibialis anterior
"The Happy Dog" - medial to lateral
muscle is located just lateral to the tibia
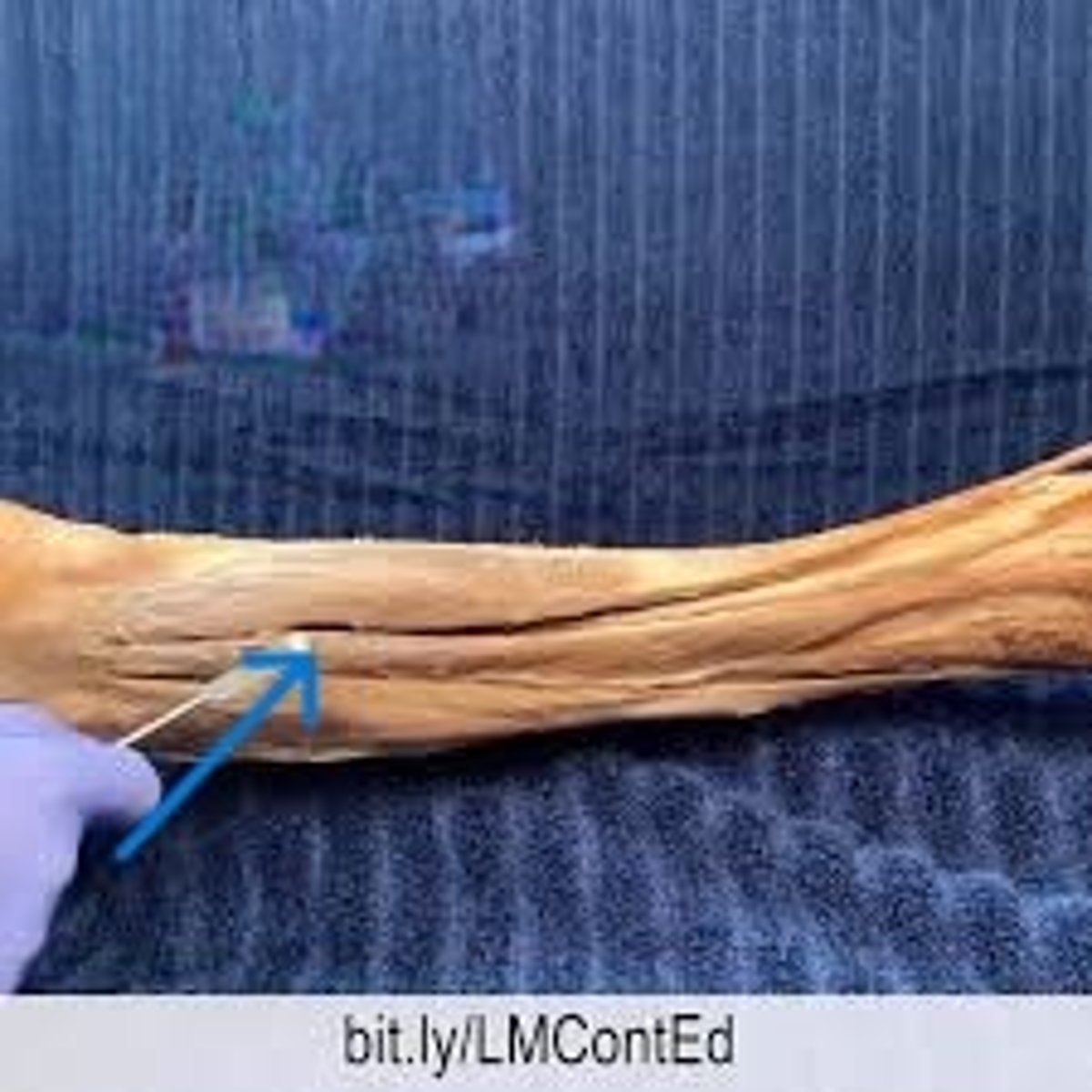
extensor hallucis longus
"The Happy Dog"
muscle body is deep to the other two muscles in the anterior compartment. If you follow the tendon inferiorly, you'll see it travels to digit 1. "Hallucis" is the anatomical name for the "big toe" or digit 1
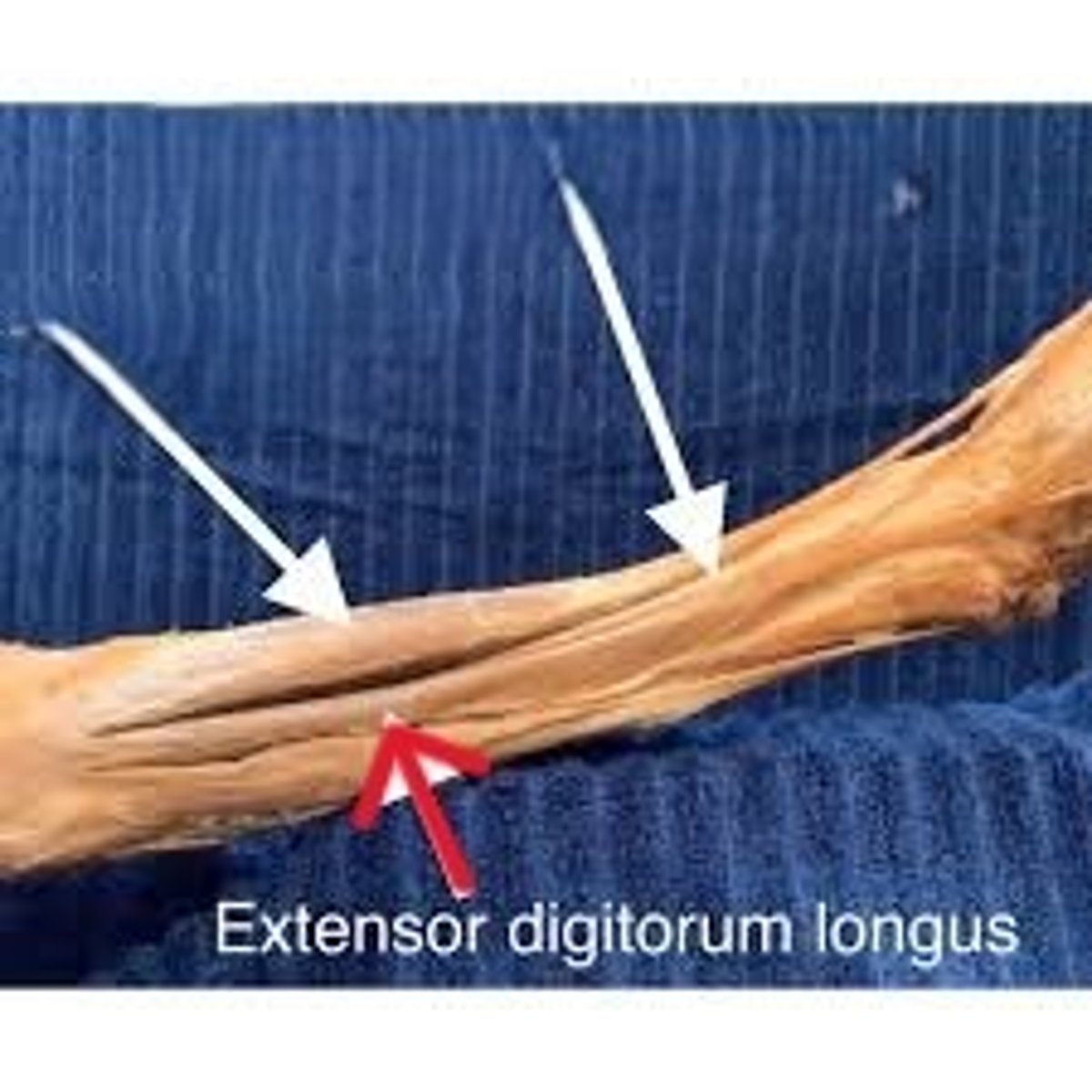
extensor digitorum longus
"The Happy Dog"
lateral to extensor hallucis longus. Follow it inferiorly and you'll find 4 tendons that travel to digits 2-5
anterior tibial a. and v.
pass in between the tibia and fibula. You will find then tucked between tibialis anterior and extensor hallucis longus
deep fibular nerve
The deep fibular nerve travels from the popliteal fossa anteriorly to innervate this anterior compartment. You will find it next to the anterior tibial artery
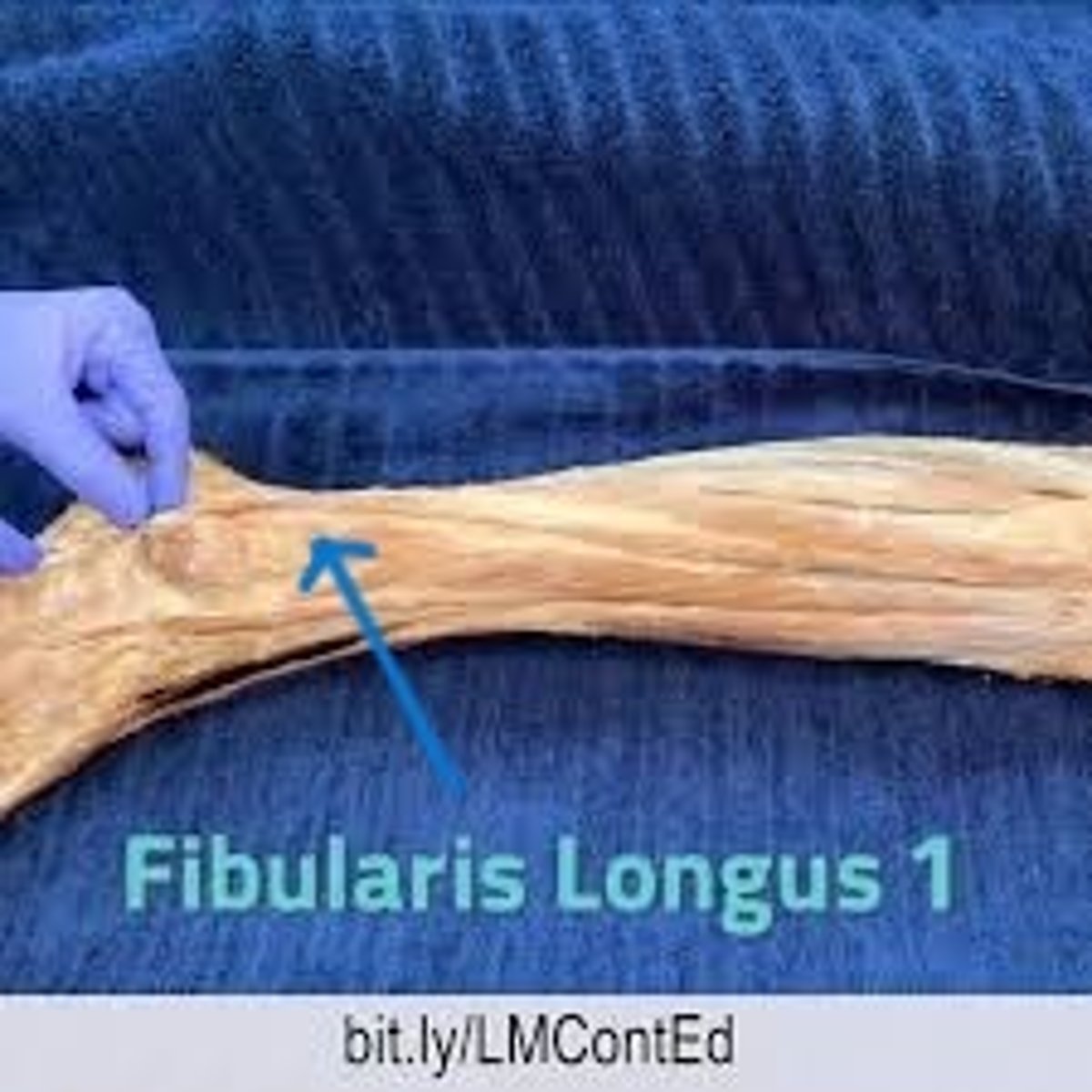
fibularis longus
A long muscles that attaches to the lateral aspect of the fibula. This muscle is so close to the anterior and posterior compartment muscles
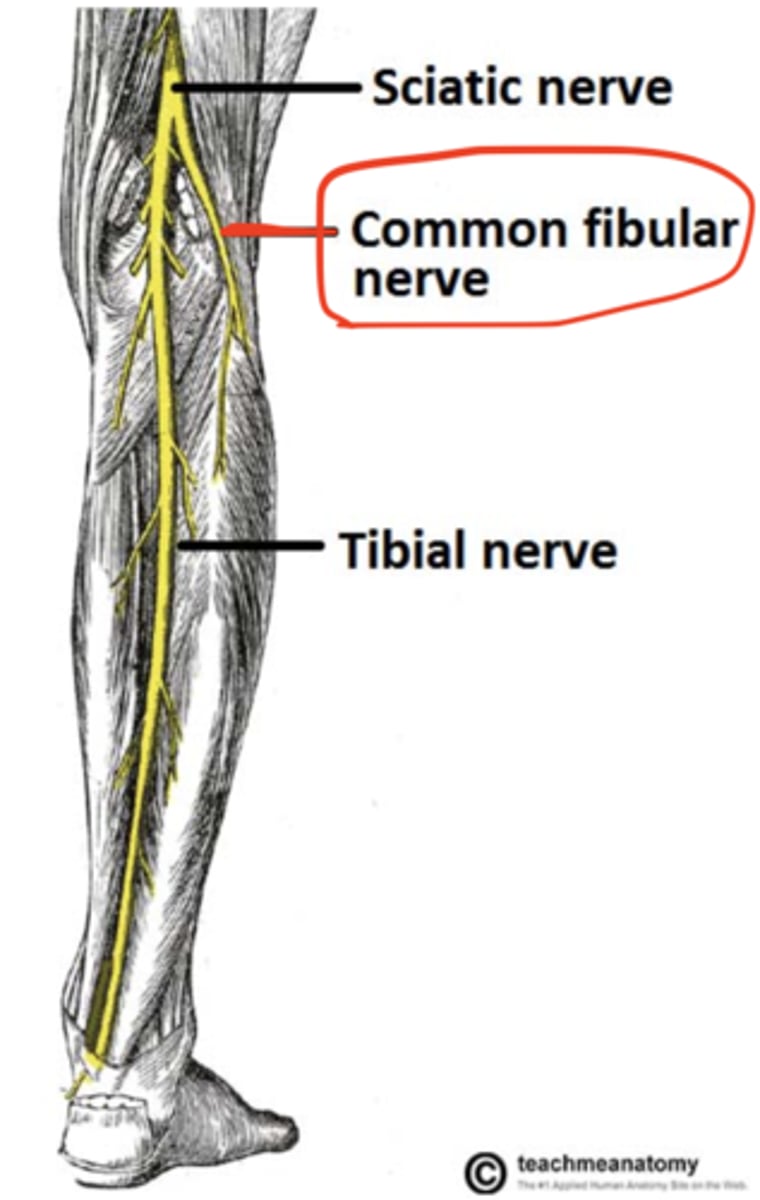
common fibular nerve
branch of the sciatic nerve and can be found in or near the popliteal fossa
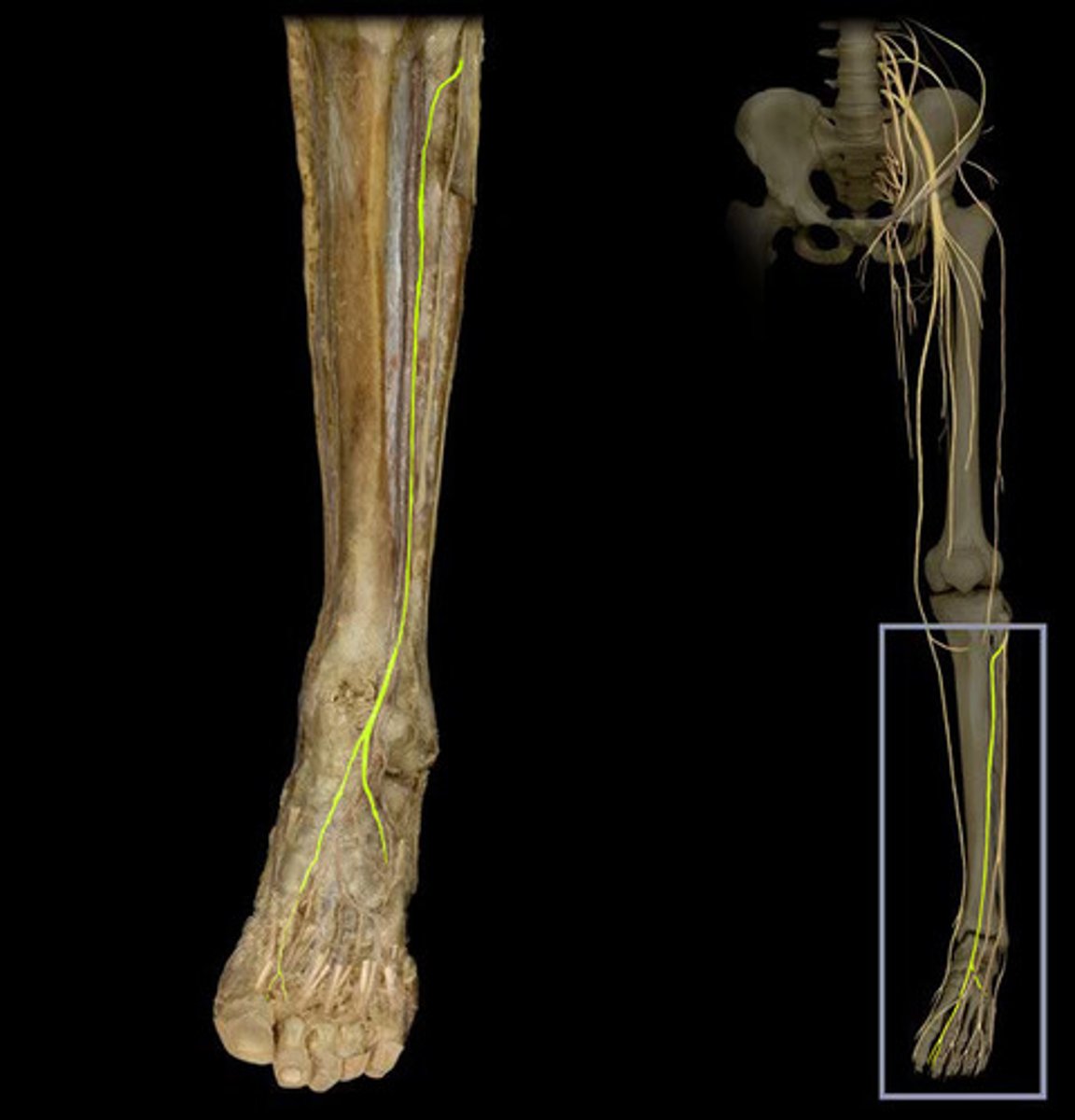
superficial fibular nerve
branch of the common fibular nerve. What was the other branch called? You will find it superficial to fibularis longus. It will likely be easiest to identify on the lateral aspect of the ankle
gastrocnemius
translates to "stomach of the leg," a name given due to its round and bulky appearance. It's the prominent and superficial muscle that you might think of as the "calf" muscle, and has two "heads" that attach to either side of the knee joint
soleus
shape of this fish - flat and broad. It also has shiny connective tissue over it, making it look like fish scales. It is found deep to the gastrocnemius
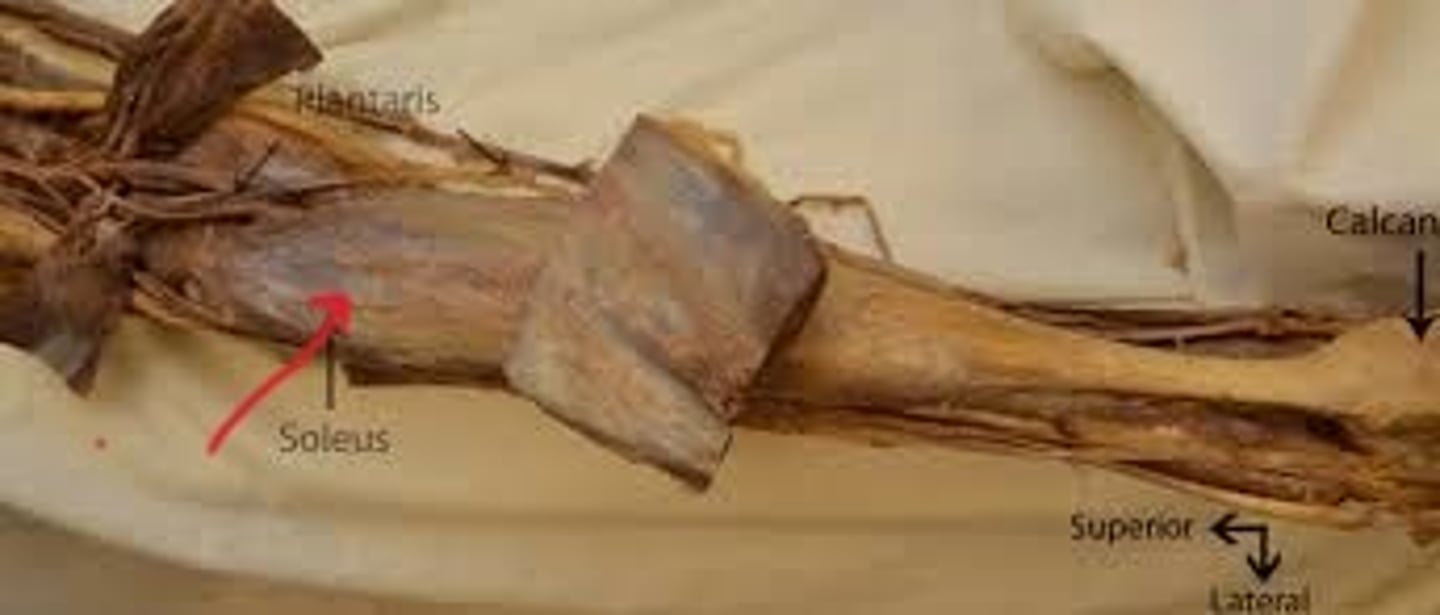

Plantaris
should plantar flex the ankle. However, it has such a small muscle body and such a long tendon that it's pretty useless compared to gastrocnemius
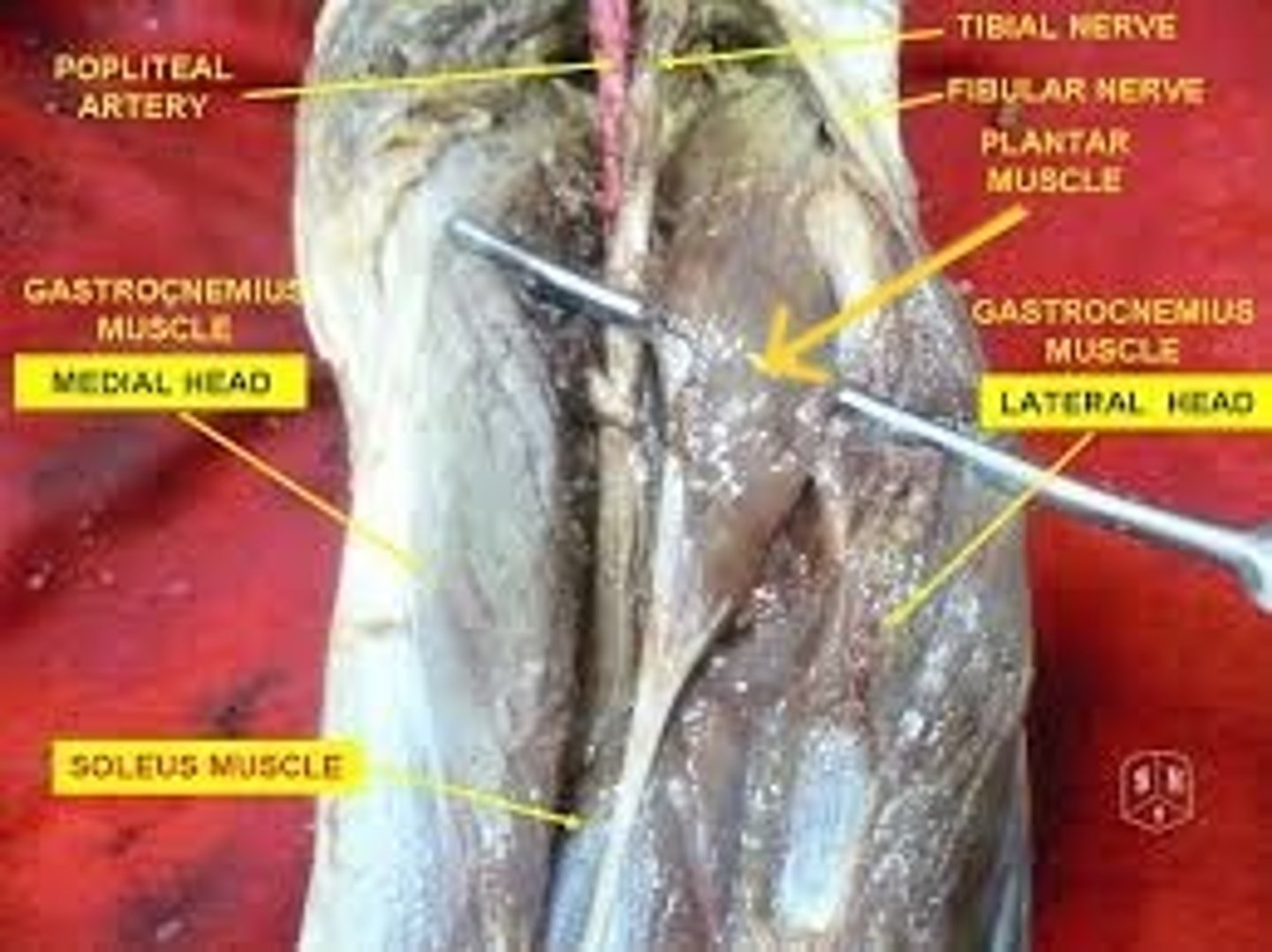
Popliteus
deep to plantaris and nestled in the popliteal fossa
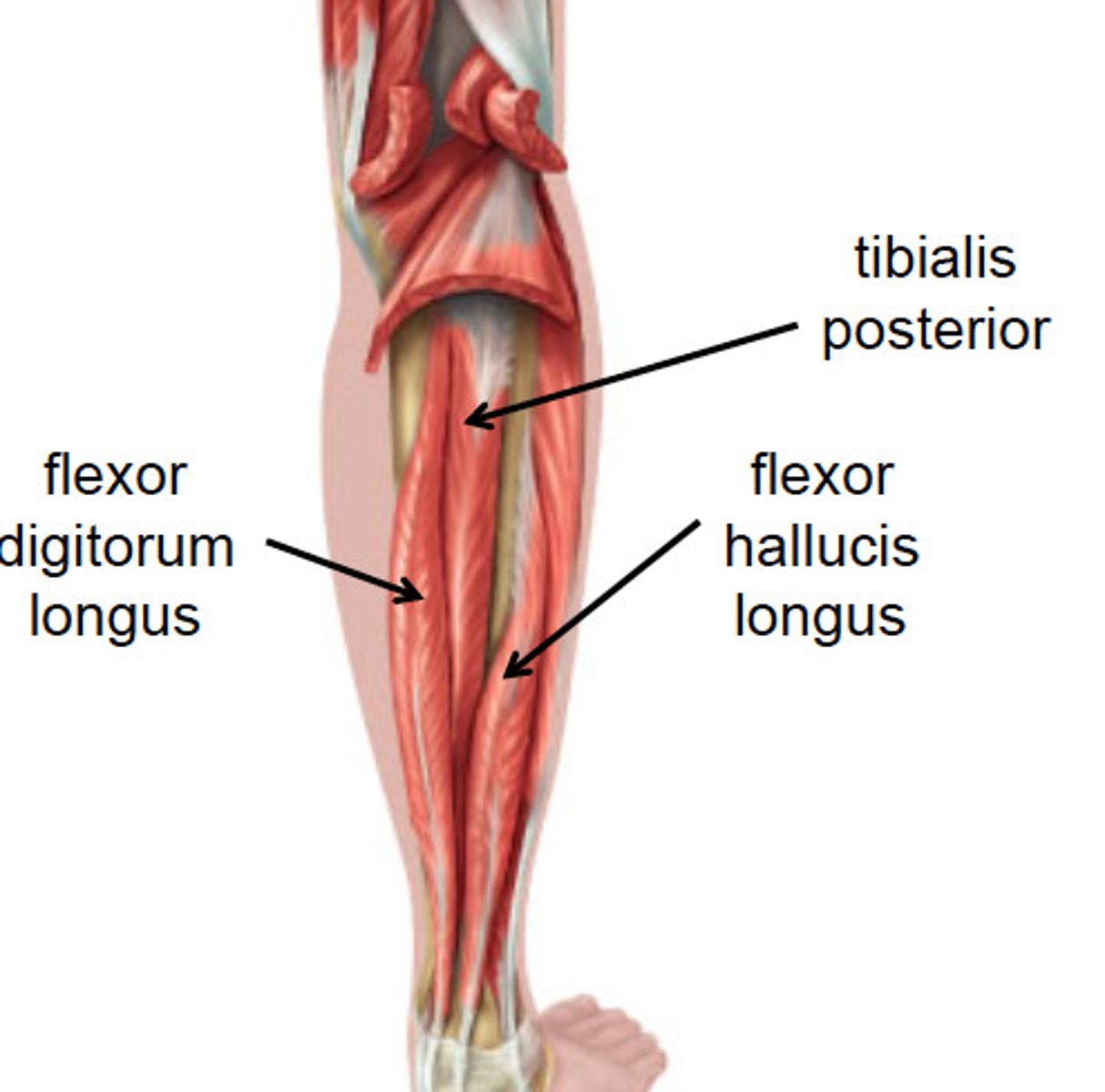
Tibialis posterior
"Down The Hatch" -medial to lateral
attached to the posterior aspect of the tibia. It is in between the flexor hallucis longus and flexor digitorum longus muscles
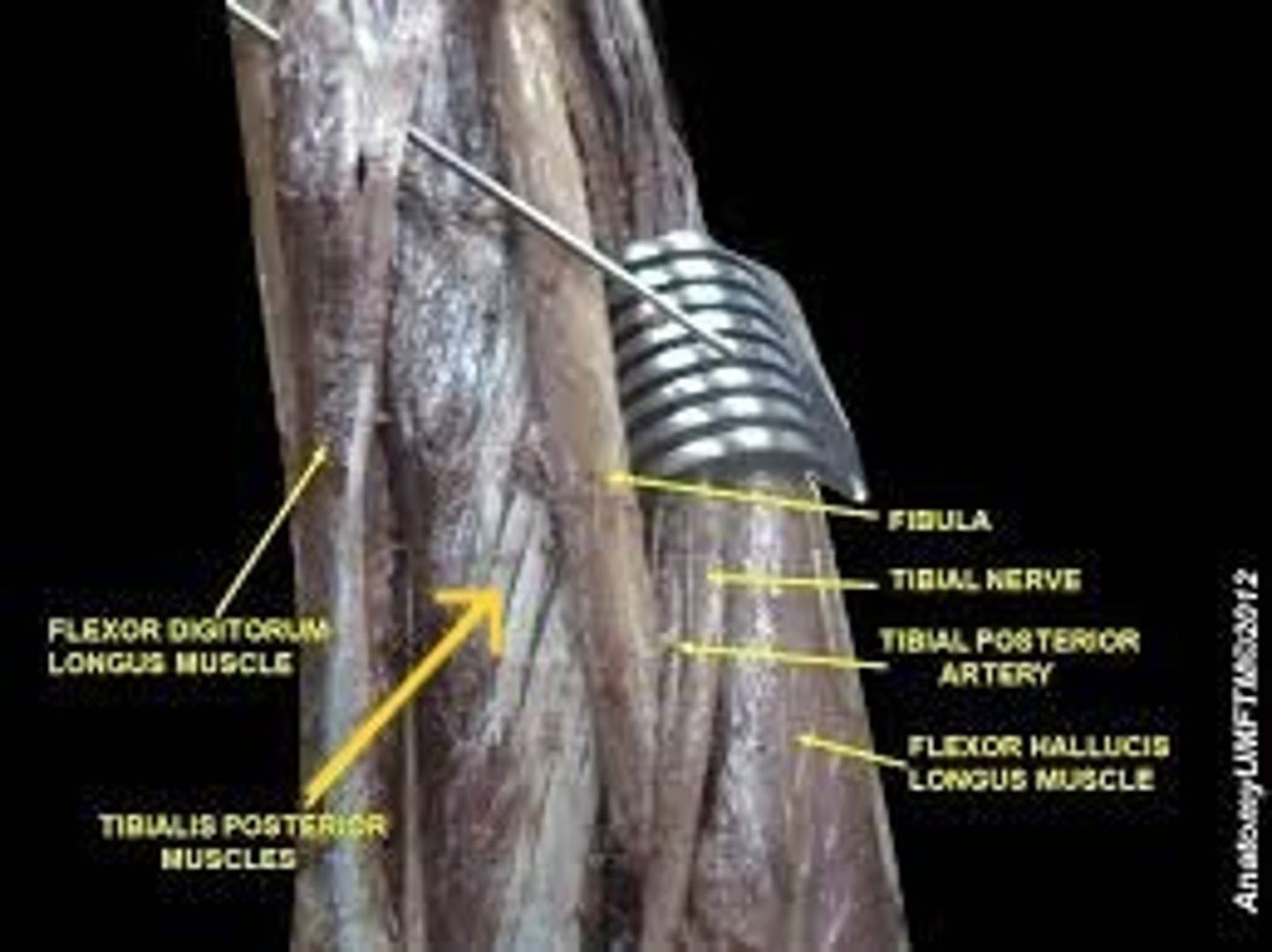
flexor hallucis longus
"Down the Hatch"
hallucis (digit 1) is medial on the foot, flexor hallucis longus is lateral to tibialis posterior in the posterior compartment of the leg
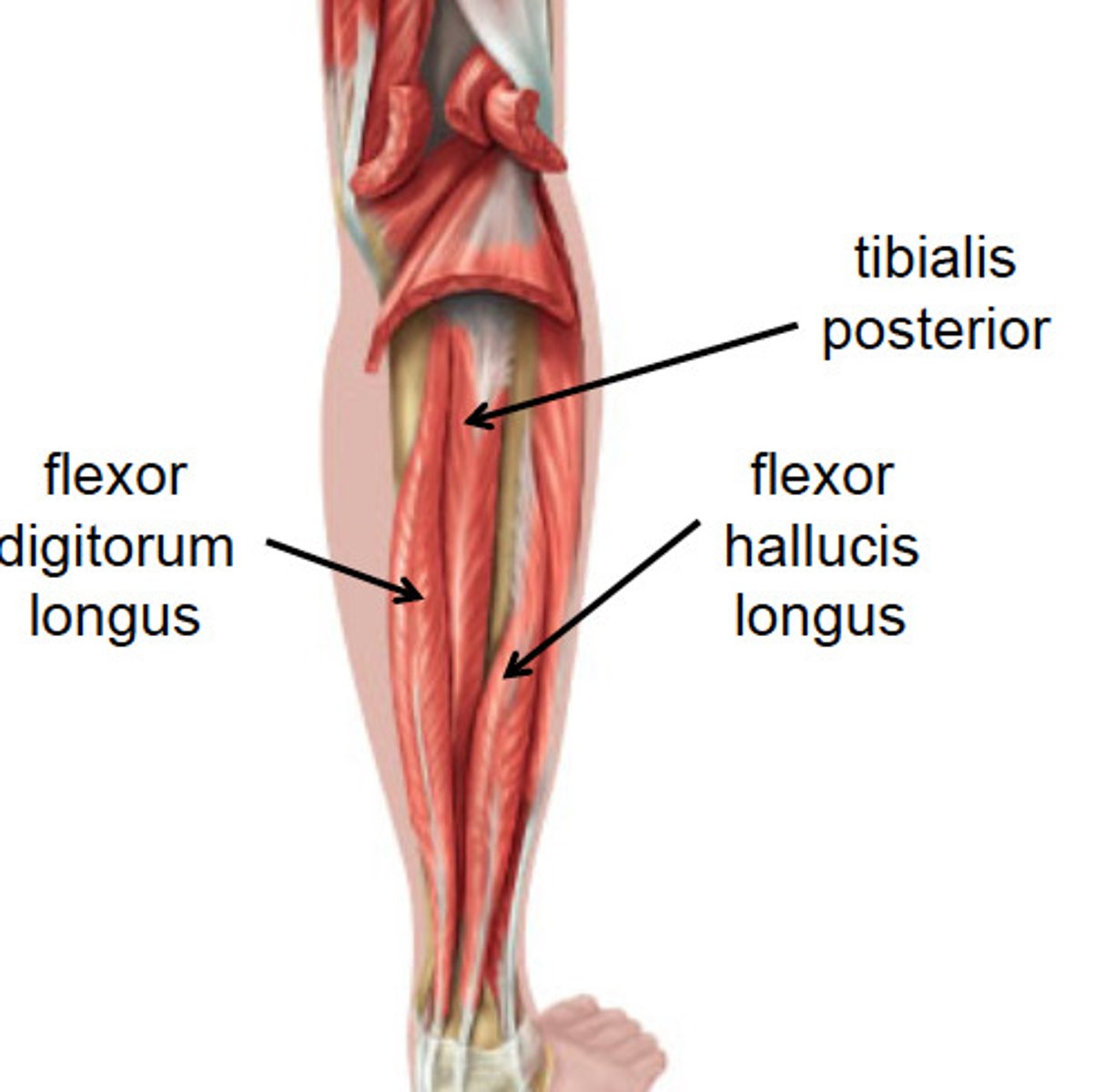
flexor digitorum longus
Although digits 2-5 are lateral on the foot, flexor digitorum longus is medial to tibialis posterior in the posterior compartment of the leg. The reason is that its tendon crosses medially around the ankle and superficial to the tendon of flexor hallucis longus
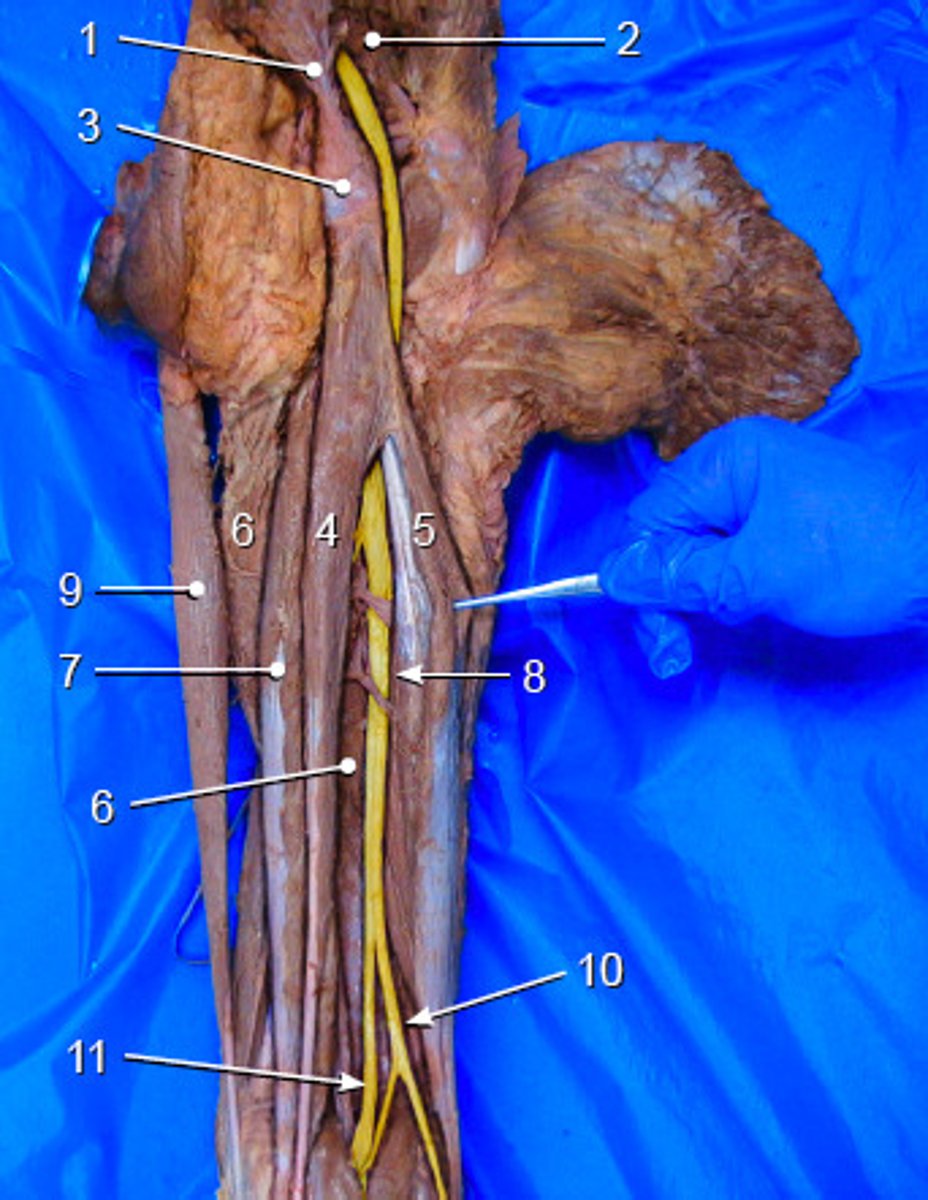
Tibial nerve
A branch of the sciatic nerve, which can be found medial to tibialis posterior and alongside the posterior tibial artery and vein
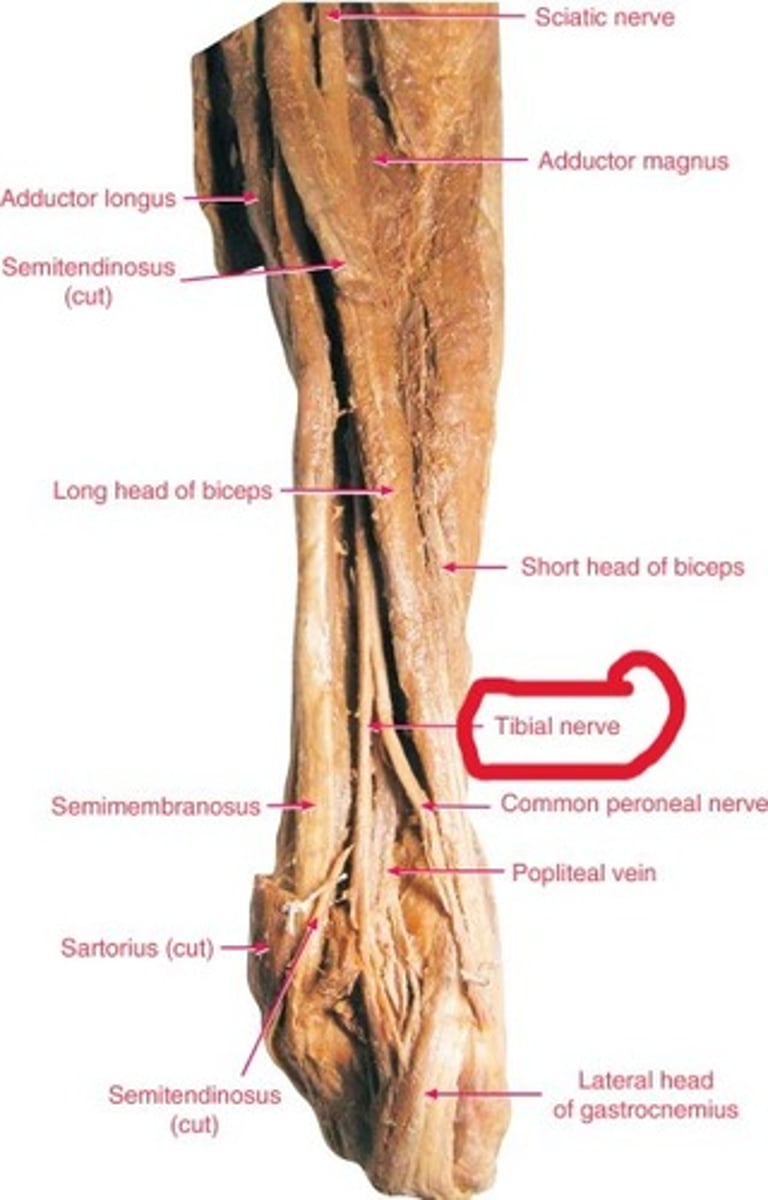
Fibular artery and vein
A branch of the posterior tibial artery and vein, which can be found lateral to tibialis posterior
Posterior tibial artery and vein
can be found lateral to the tibial nerve
sternal end of clavicle
articulates with sternum
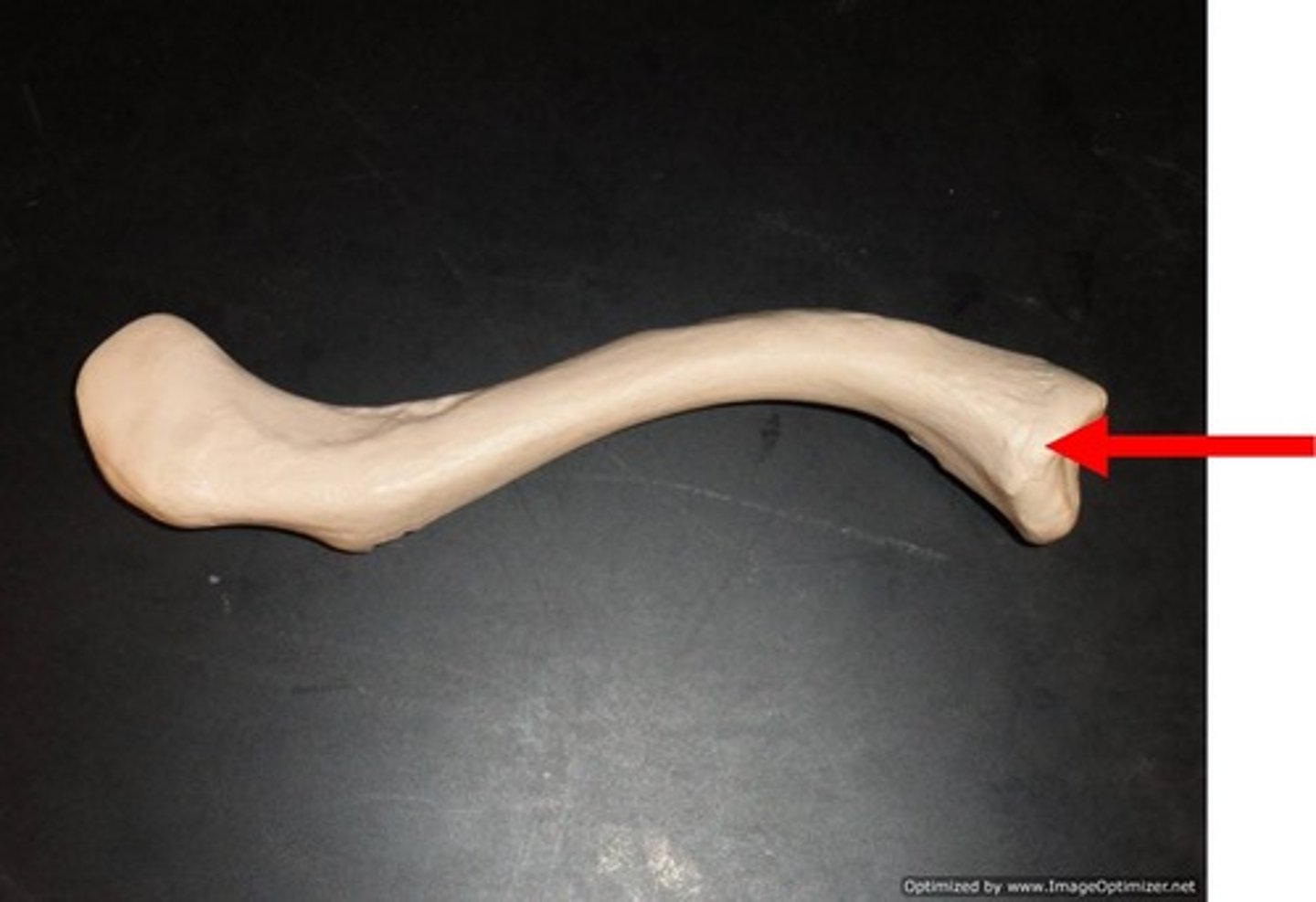
acromial end of clavicle
articulates with the acromion of the scapula
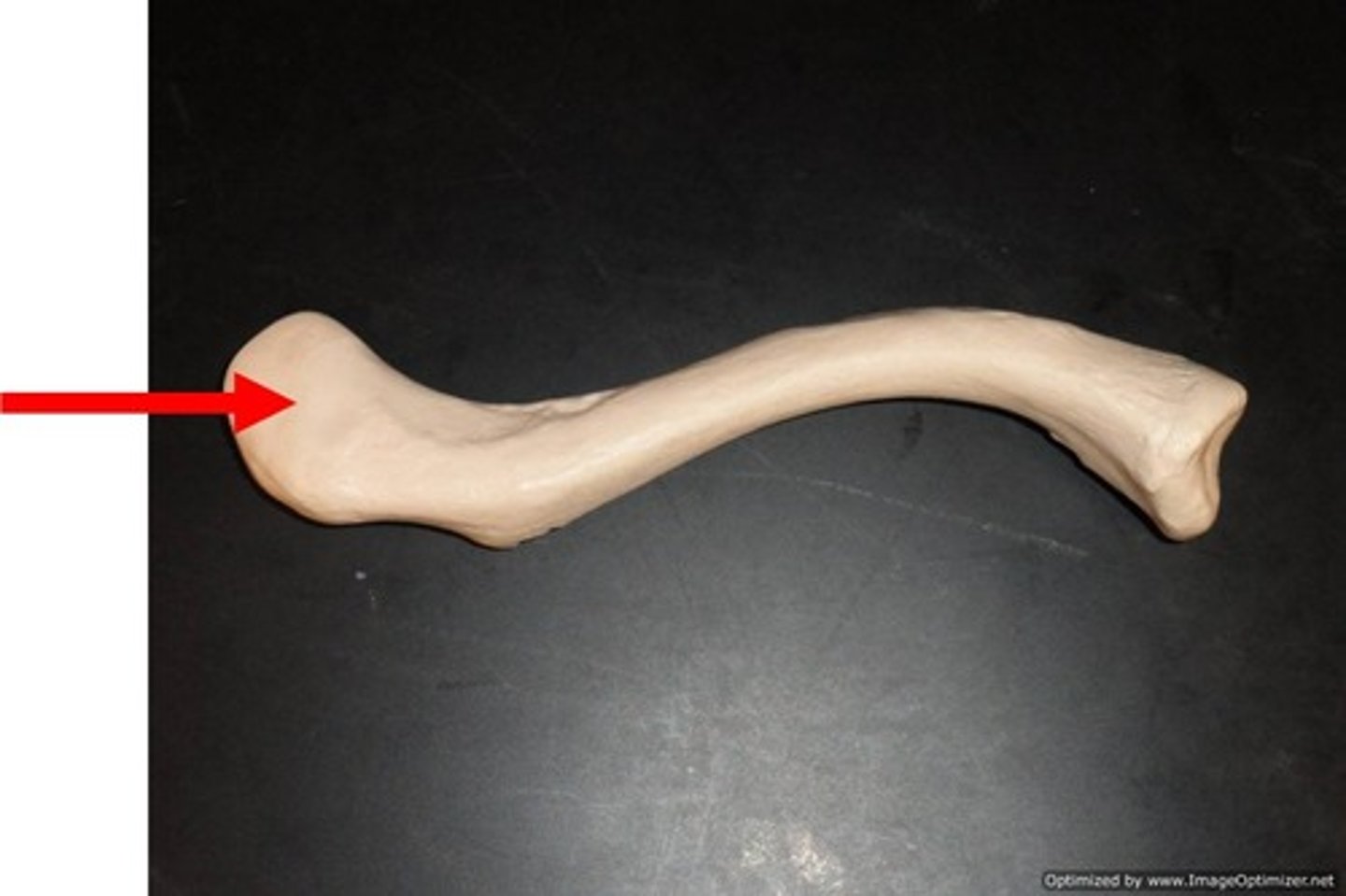
head of the humerus
rounded and smooth proximal end. This interacts with the glenoid fossa at the shoulder joint
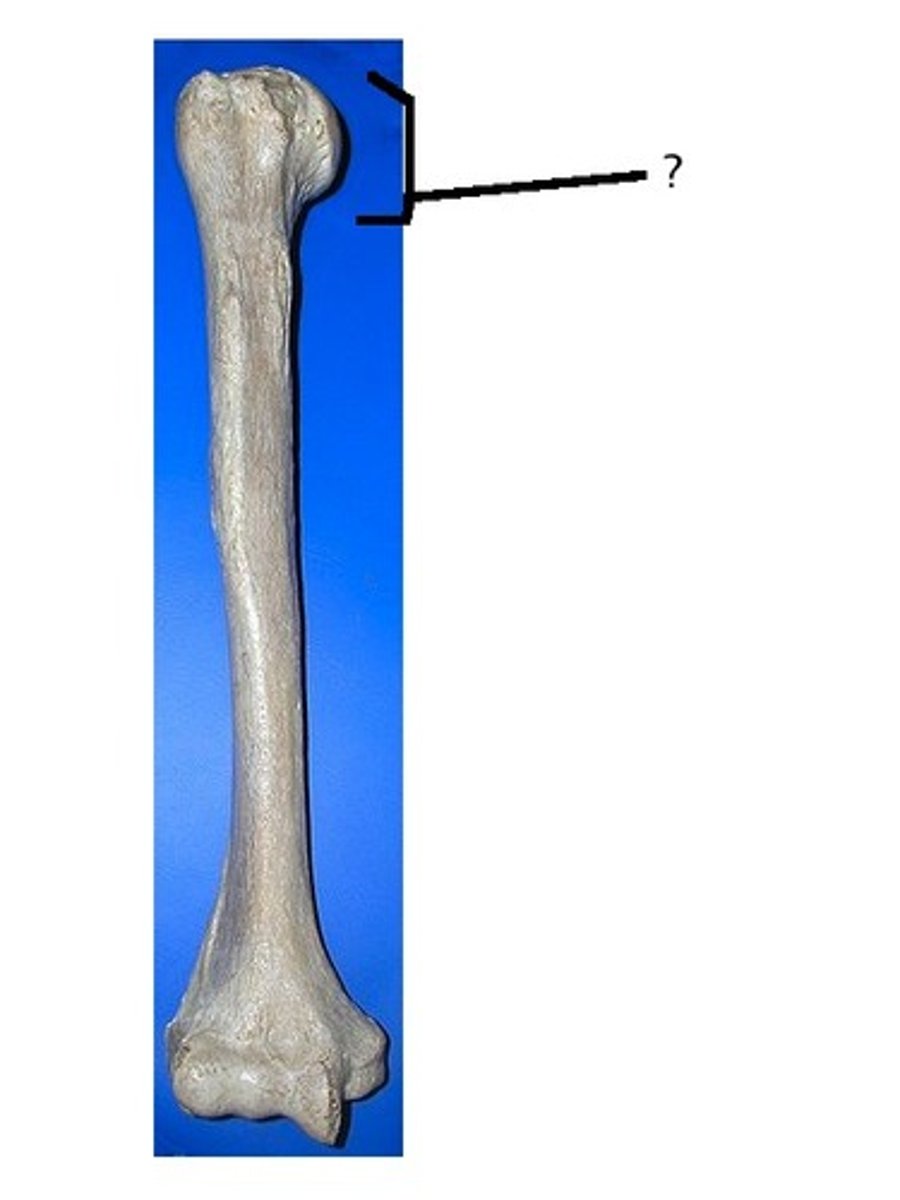
greater tuberosity of the humerus
lateral to the head
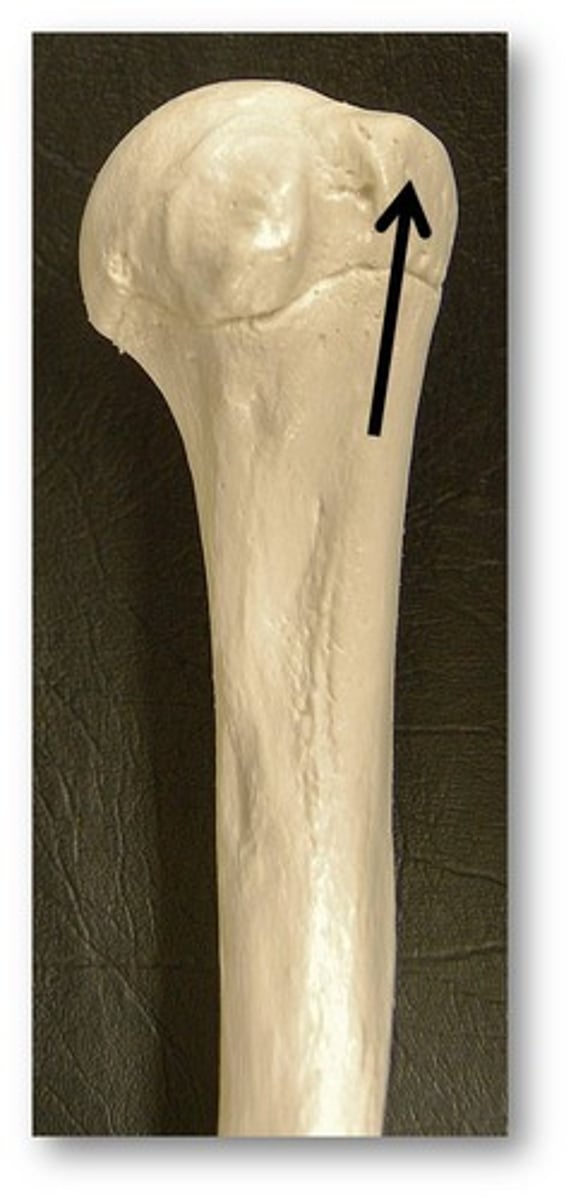
lesser tuberosity of the humerus
more medial than the greater tuberosity and slightly more inferior