AP Micro Unit 1 review
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Scarcity
Limited availability of resources
All scarce items
land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship. They are finite and we need them to produce goods and services. Our wants are unlimited
Fundamental problem in economics
scarcity
Land
all of the resources found in nature. Payment for use of land is called rent
Labor
human effort. Payment for the use of labor is called wages
Capital
machinery, tools, equipment. Payment for the use of capital is called interest
Entrepreneurship
innovation, ideas, Payment for entrepreneurship is called profit
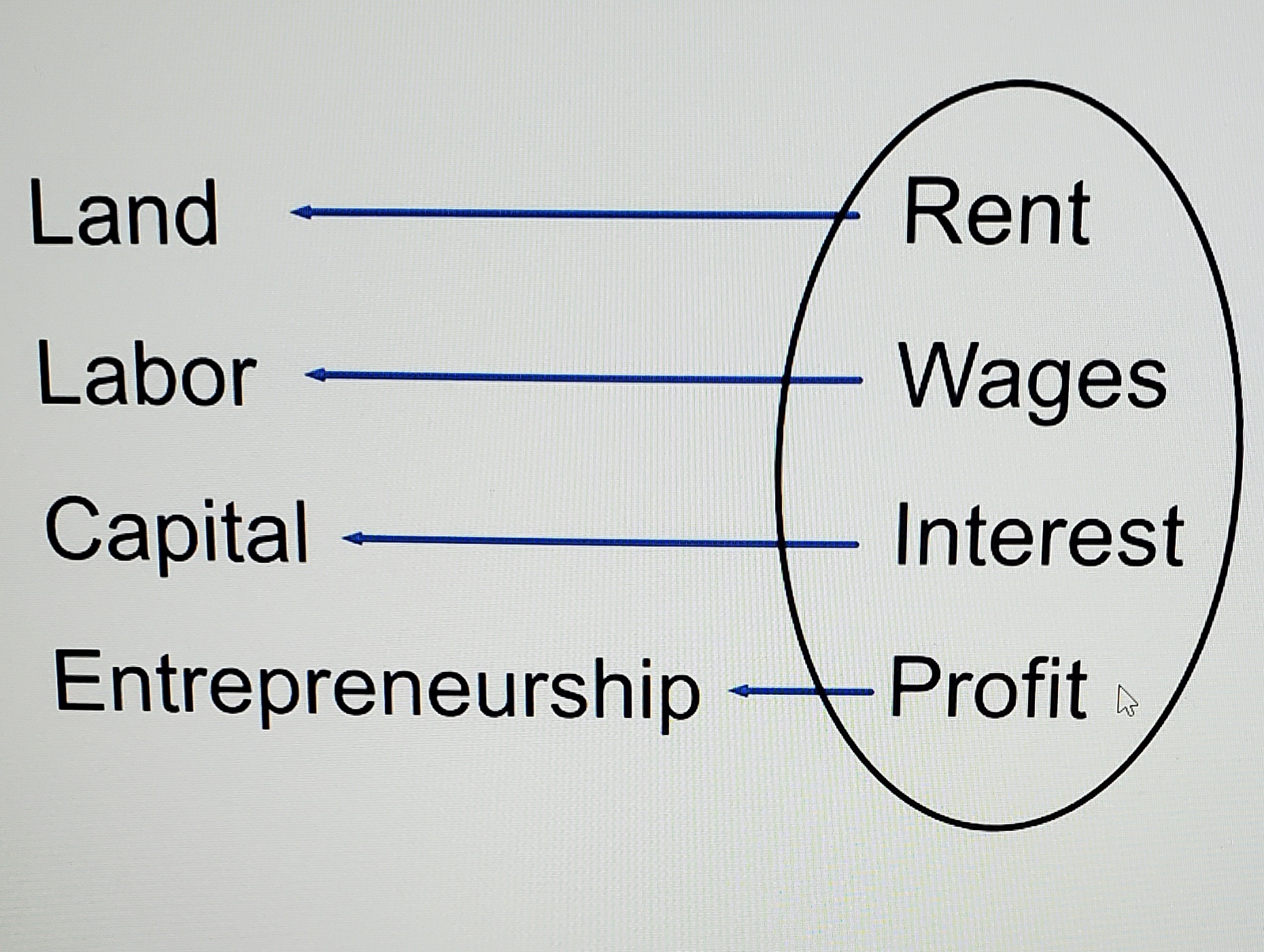
All types of income
Rent, wages, interest, profit
NOT an economic resource
Consumer goods, waste, money, stocks and bonds
The fact of scarcity means that every economy faces critical decisions about…
What to produce
How to produce
How to allocate the goods and services
Command economy
economic system where government plans and controls the production and distribution of goods and services
Market economy
Economic system in which production and prices are determined by the interactions of citizens and businesses in the marketplace.
mixed economy
private enterprises operate in a market environment, while the government plays a role in regulating certain sectors and providing public goods and services
Characteristics that define market economies
private ownership of resources
Market prices direct resource use
income depends on individual resources and is an incentive. Unemployment and inequality are tolerated.
International specialization promotes competition and holds costs/prices down
Prices fluctuate with supply and demand in markets
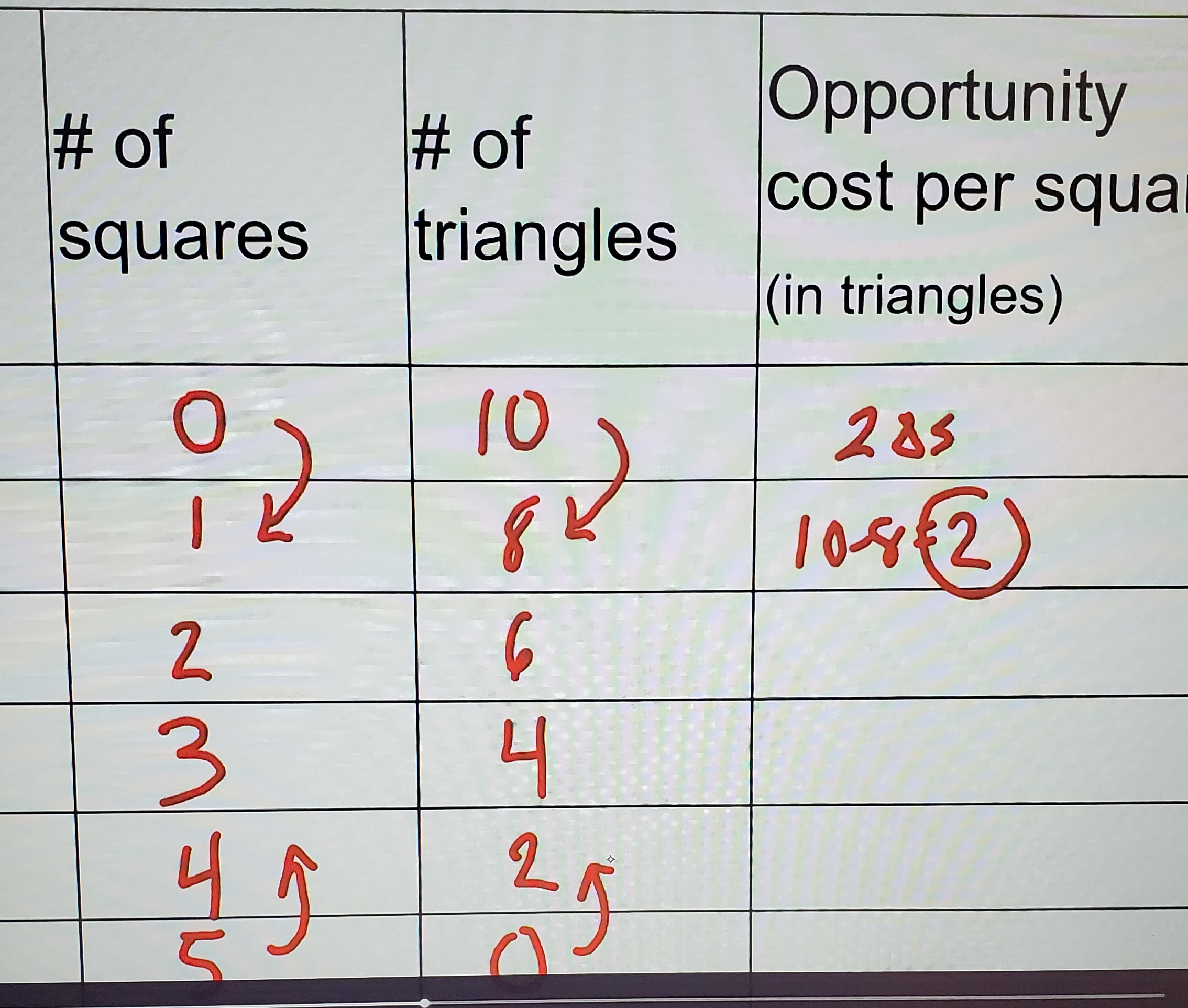
Opportunity cost
The value of the foregone (next best) option
Absolute Advantage
The ability to produce more of a good/service than someone else, in the same amount of time
Comparative advantage
the ability to produce something at a lower opportunity cost than someone else, given the same resource