Physiology: Unit 5
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Sensory Input
Gathered information from the nervous system’s millions of sensory receptors
Integration
The processing and interpretation of sensory input, in which the nervous system decides what should be done at each moment of input
Motor Output
The activation of effector organs— the muscles and glands— as an effect to integration
Central Nervous System (CNS)
The processing and control center of the nervous system that creates output based on information given from the nerves
Central Nervous System (CNS)
This part of the nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The receiving and relaying section of the nervous system that receives signals through its nerves to send to the brain
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
This part of the nervous system is made up of the nerves of the body like pairs of cranial nerves and spinal nerves
Sensory (Afferent) Division
The part of the PNS that works towards the PNS to pick up information about its surroundings to then send it from itself
Motor (Efferent) Divison
The part of the PNS that works away from the PNS to send information given to itself to muscles, glands and organs on what to do
Somatic Nervous System
The part of the Motor (Efferent) Division that conducts action to skeletal muscles, or parts of the body that require active feedback (Manual Movement)
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
The part of the Motor (Efferent) Division that conducts action to organs, glands, and other types of muscles and parts of the body that don’t require active feedback (Automatic Processes)
Sympathetic Division
The part of the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) that simulates and triggers automatic proccess in the body to account for the stress of an active situation and into simulation (Fight or Flight)
Parasympathetic Division
The part of the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) that inhibates and relaxes automatic process in the body to resolve itself from stress and into inhibitation (Feed and Breed)
Neurons
Nerve cells, which are excitable/responding to stimuli and transmit eletrical signals
Neuroglia
Supporting nerve cells, which wrap themselves around or are near neurons. There are four main variations of them
Astrocytes
A CNS neuroglia that clings to neurons and support them both physically with bracing and nutritionally with supply lines. Has a PNS counterpart
Microglia
A CNS neuroglia that protects and aids neurons by clearing it of debris and pathogens
Ependymocytes (Ependymal Cells)
A CNS neuroglia that fills the space inside the brain and spinal cord, producing a spinal fluild to cushion and protect those parts and itself
Oligodendrocytes
A CNS neuroglia that forms myelin sheaths around smaller nerve fibers in the CNS, which allows for faster transmission of signals. Has a PNS counterpart
Satellite Cells
A PNS neuroglia that clings to neurons and support them both physically with bracing and nutritionally with supply lines. Has a CNS counterpart
Schwann Cells
A PNS neuroglia that forms myelin sheaths around thicker nerve fibers in the PNS, which allows for faster transmission of signals. They are also capable of repairing those same fibers. Has a CNS counterpart and is found lined along the axon
Myelin
An electrical insulation that protects and helps fibers transfer signals faster
Dendrites
Listening part of the neuron that receives neighboring information from other cells
Axon
Conducting part of the neuron that sends information to other neighboring cells
Soma
The cell body that holds typical cell content, such as a nucleus, DNA, and filling
Multipolar Neuron
A type of neuron that consists of all parts of a neuron (body, axon, and some dendrites)
Bipolar Neuron
A type of neuron that consists of only an axon and a single large dendrite. Found only in places such as the retina of the eye
Unipolar Neuron
A type of neuron that has a cell body that branches between a large single axon
Frontal Lobe
Quarter of the brain that controls higher-level cognitive functions such as reasoning, decision-making, language, and motor control
Parietal Lobe
Quarter of the brain that controls sensory information processing such as touch, temperature, and pain
Temporal Lobe
Quarter of the brain that controls auditory information processing, language understanding, and memory
Occipital Lobe
Quarter of the brain that controls visual information processing
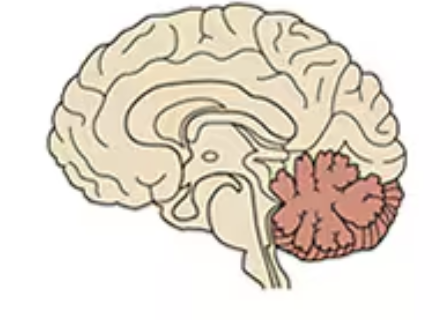
Cerebellum
Fifth section of the brain outside of the four quarters that controls voluntary movements, posture, balance, muscle tone, and motor learning
Thalamus
Name this part of the brain:
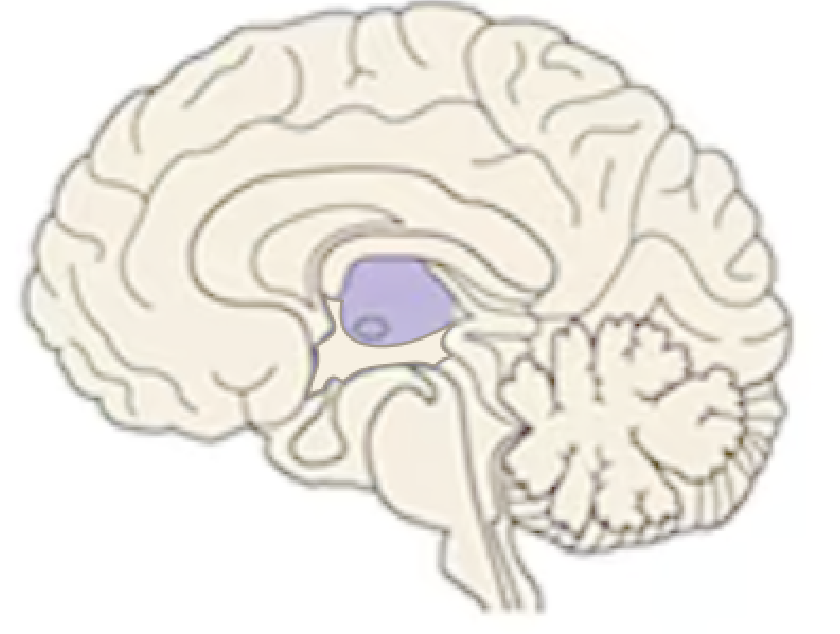
Hypothalamus
Name this part of the brain:
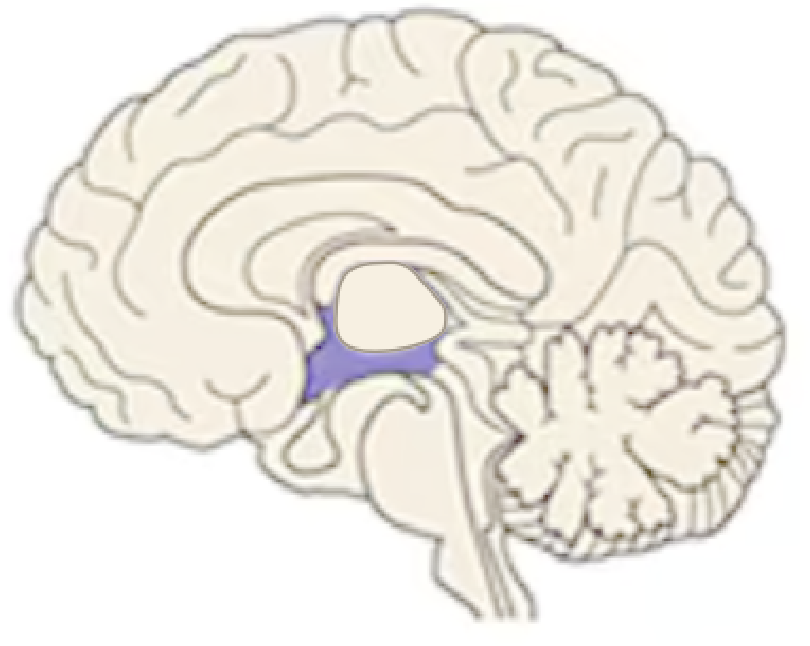
Limbic System
Name this part of the brain:
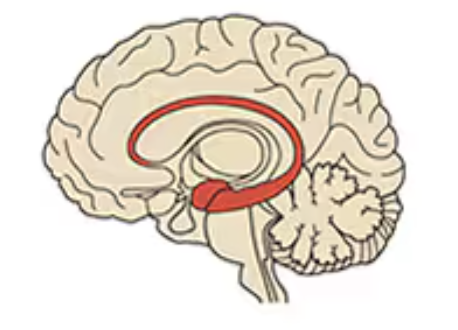
Midbrain
Name this part of the brain:
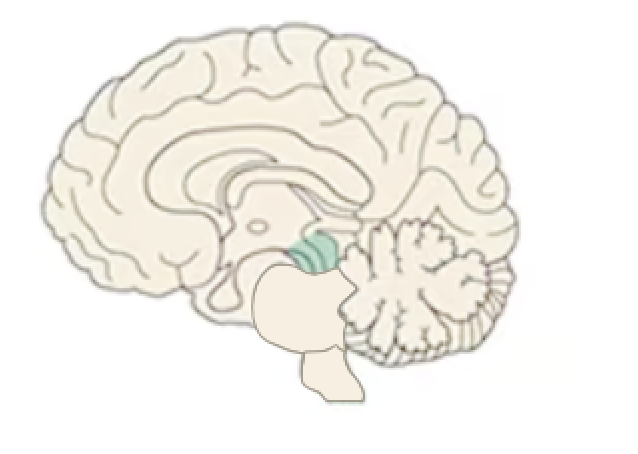
Pons
Name this part of the brain:
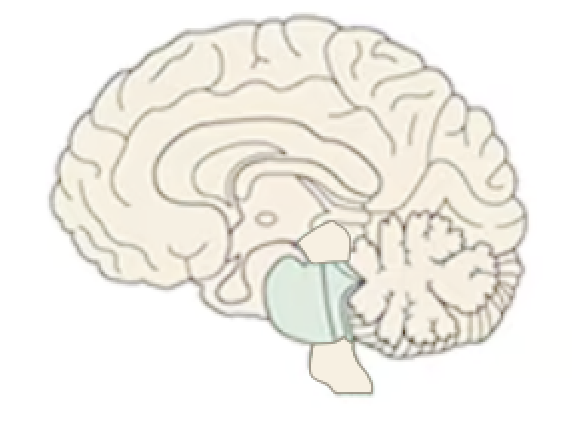
Medulla Oblongata
Name this part of the brain:
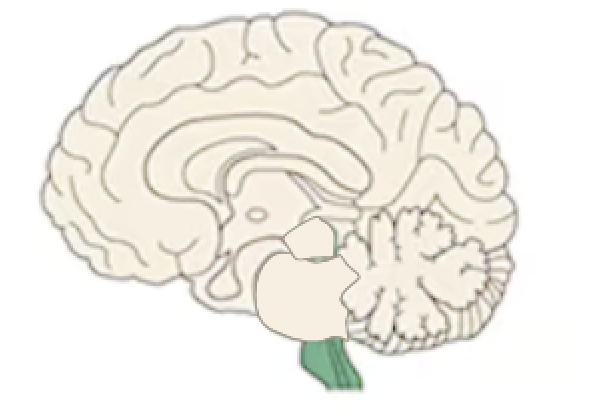
Reticular Formation
Name this part of the brain:
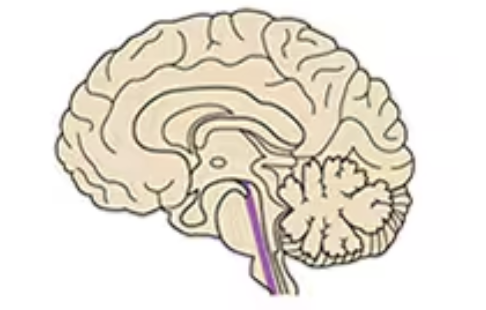
Cerebellum
Name this part of the brain:
Synaptic Cleft
The spacing between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron, which is where chemicals are produced to truely relay information between cells