Avian Comparative Anatomy 🟢
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
Galliformes
_____ - chickens, pheasants, & turkeys
Anseriformes
______ - ducks, geese, & swans
Psittiformes
_____ - cockatoo, conure, macaw, & parrots
Falconiformes & Strigiformes
_____ - eagle, falcon, hawk, & owls
Passeriformes
_____ - canary, finch, crow, raven, warblers, etc
1. symmetrical vs asymmetrical vanes
2. flight
3. thermoregulation
4. sexual dimorphism
5. portection
What are the feather types?
1. barb
2. barbules
3. hooklets
What are parts of the microanatomy of the feather?
preening
Grooming or combing the feather components
primary
The _____ feather is attached to the manus
antebrachium & brachium
The secondary feather is attached to the _____
bones of digit # 1
What is the alula composed of?
prevents stalling in flight
What is the function of the alula?
fused
The skull has multiple _____ sites
notarium
Fused thoracic vertebrae
synsacrum
Fused os coxae & sacral vertebrae
manus
Reduced # of digits & fused bony components
carpometacarpus
Fused carpal bones & metacarpal bones
tarsometatarsus
Fused tarsal bones & metatarsal bones
pygostyle
Fused caudal vertebrae
1. fusion of skull bony sutures
2. single occipital condyle
What are the unique features of the avian skull?
rhinotheca
Dorsal beak - _____
gnathotheca
Ventral beak - _____
1. dorsal beak - rhinotheca
2. ventral beak - gnathotheca
3. quadrate bone
4. palatine bone
What are the parts of the beak?
stapes
Single middle ear ossicle= _____ in birds
1. coracoid
2. furcula
3. scapula
What are the 3 bones involved in the triosseal canal?
urcula
_____ - fused clavicles in avian species
supracoracoideus
Tendon of _____ muscle passes through this triosseal canal
"upstroke muscle" of wing
What is the function of the tendon of supracoracoideus muscle?
proximal humerus to lateral & central region of keel of sternum
Attachment of supracoracoideus muscle
contraction of muscle results in "upstroke" of wing
Action of supracoracoideus muscle
proximal humerus to lateral perimeter of keel of sternum
Attachment of pectoralis muscle
contraction of muscle results in "downstroke" of wing
Action of pectoralis muscle
alula
Carpal "Claws" associated with _____
1. 3
2. 4
3. 6
During embryogenesis, aortic arches #_____, #_____, & #_____ form
4
In Avian species, aortic arch #_____ becomes neonatal aorta, which arches towards the right side of the body
4
The avian heart has _____ chambers
right
The aortic arch passes to the [right/left] side in avian species
300 to 600 bpm
Avian species have high heart rates of _____ (asserine species)
> = 800 bpm
Hummingbirds have high heart rates of _____
pelvic limbs or caudal muscle masses
Medications are excreted by kidneys when these drugs are injections in the _____
pelvic
Avoid medications @ [pelvic/thoracic] limbs which are intended to not be excreted
ischiatic
_____ nerve (#17) passing dorsal to kidney tissue within ventral recess of synsacrum
kidney disease
Ischiatic nerve subject to trauma & impact when _____ is present
1. jugular vein: right > larger > left
2. brachial vein; right or left
3. medial metatarsal vein, right or left
4. dorsal vertebral vein, located midline & proximal to pygostyle
5. digital vein, via toe claw clipping
What are the avian venipuncture sites?
digital vein
Which venipuncture site is not humane, painful, and high risk of infection & contaminated blood samples?
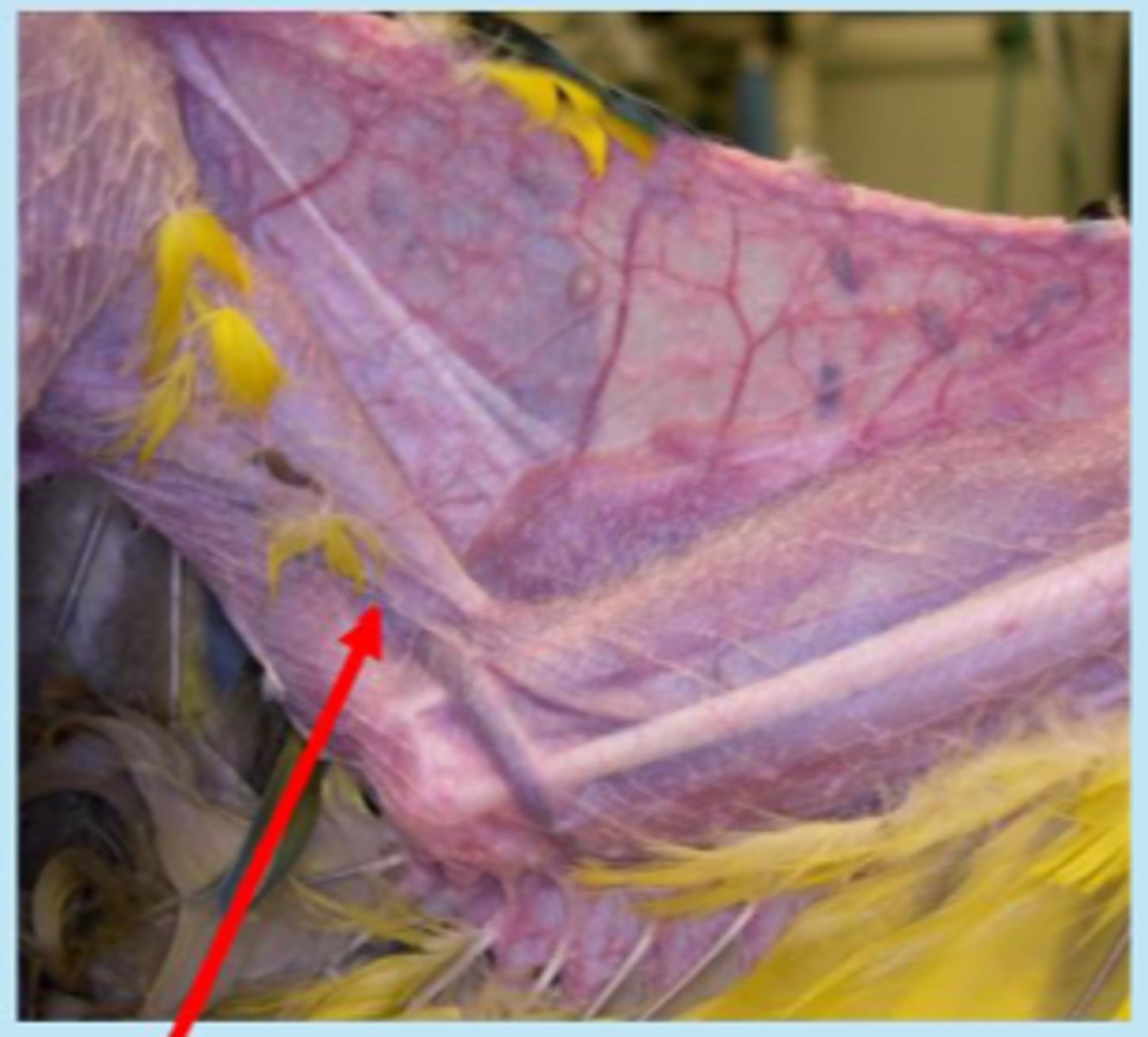
brachial vein
What is shown here?
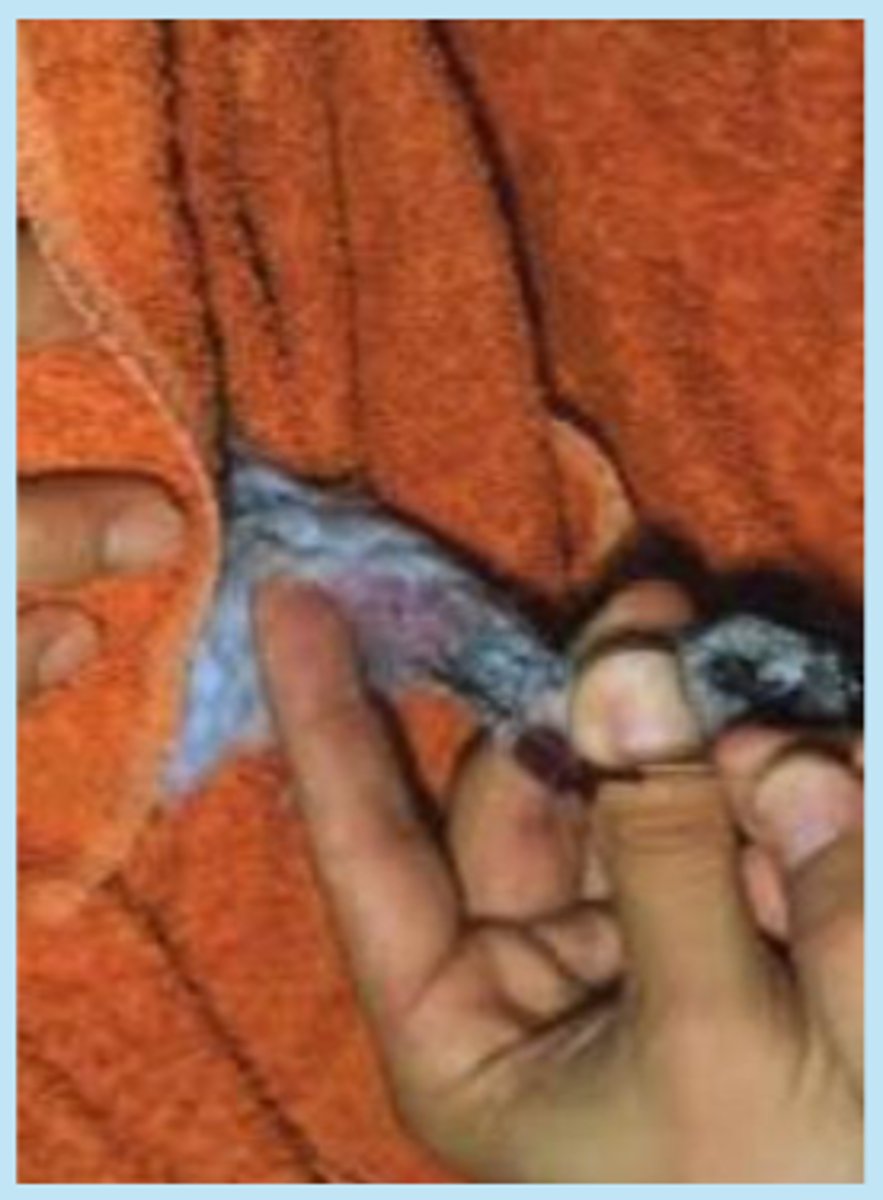
medial metatarsal vein
What is shown here?
no
Do birds have true thoracic or abdominal cavities?
coelomic cavity
Avian species have 1 body cavity known as _____
air sacs
There are multiple _____ throughout coelomic cavity
proximal humeri
Some air sacs penetrate pneumonic bones, including ______, bilaterally
no
Do birds have a true muscular diaphragm?
horizontal septum
_____ is an alternative structure to the muscular diaphragm
cranial to caudal
There are multiple air sacs, positioned _____ in coelomic cavity
kaolin
_____ lining within ventriculus (stomach)
true
T/F - Some species ingest gravel or small stones to assist in grinding ingesta during digestive process
true
T/F - Birds have a relatively simple digestive system
ceci
The Galliformes species have double _____
cecum
The Psittacine species have no _____
Meckel's diverticulum
Yok sac remnant
1. Coprodeum
2. Urodeum
3. Proctodeum
What are the cloacal regions?
Coprodeum
Receives feces from gi tract
Urodeum
Receives urates from kidneys & either eggs or sperm from reproductive tract
Proctodeum
Common cloacal region
1. dorsal concha
2. middle concha
3. ventral concha
What things constitute the nasal cavity?
choanal slit
Split hard palate
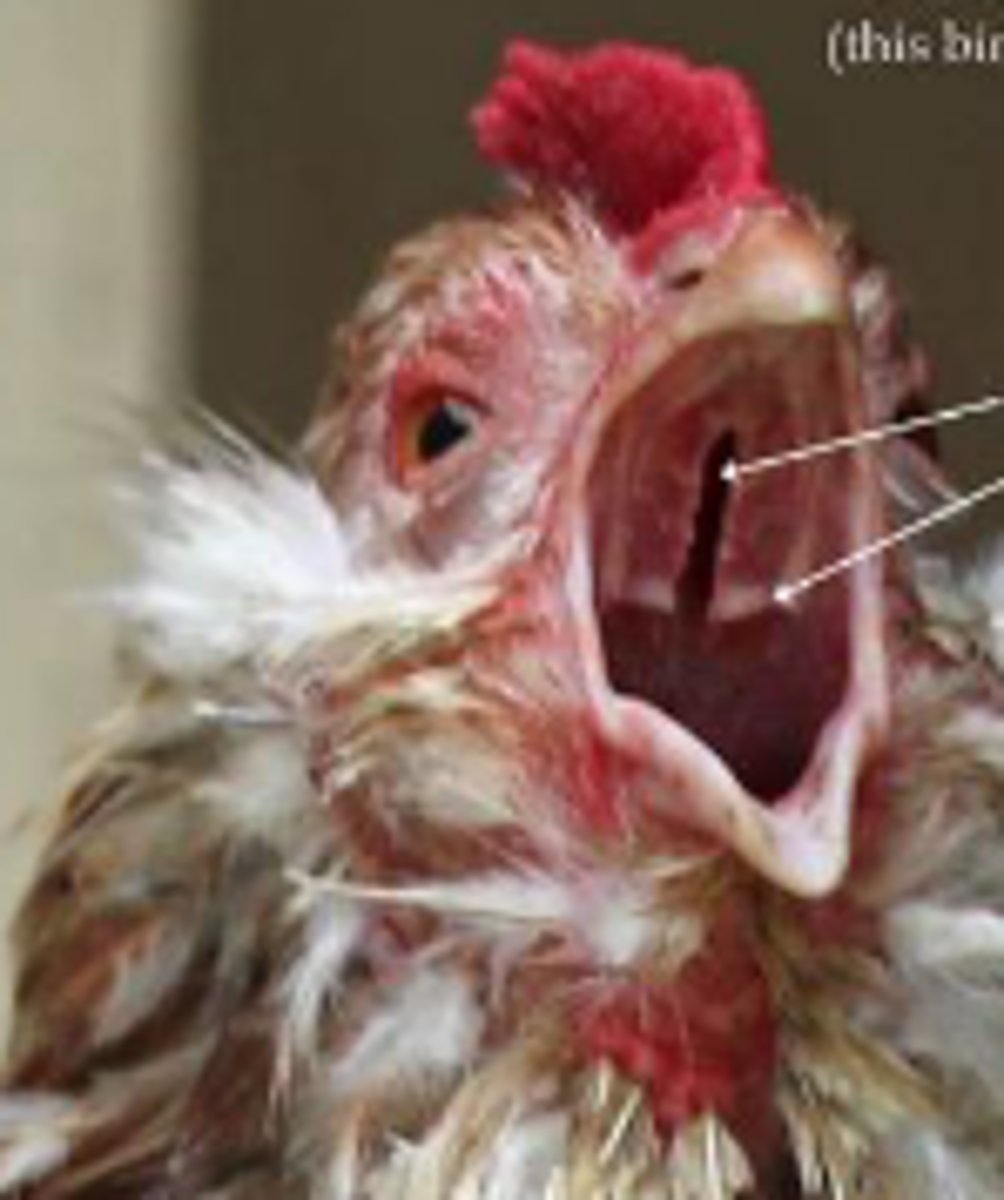

complete
Birds have [complete/incomplete] tracheal rings
ossified
Birds often possess _____ tracheal rings
syrinx
Origin of sound production
ceolom
Most of air sacs are bilaterally symmetrical, while some air sacs are single, but span across entire _____
air flows to caudal air sacs
What happens on inspiration 1?
air flows through lungs
What happens on expiration 1?
air flows to cranial air sacs
What happens on inspiration 2?
air flows out trachea
What happens on expiration 2?
1. ovaries
2. infundibulum
3. magnum
4. uterus (shell gland)
5. vagina
6. urodeum
6. cloaca
What are the parts of the "hen"/female chicken repro tract?
1. testes
2. ductus deferens
3. urodeum
4. cloaca
5. phallus
What are the parts of the "rooster"/male chicken repro tract?
displays lissencephalia (smooth external surface)
Describe the avian brain
1. olfactory lobe
2. cerebral hemispheres
3. optic lobe
4. optic chiasma
5. hypothalamus
6. infundibulum &
7. hypophysis
8. cerebellum
9. medulla oblongata
What are the major regions/structures of the avian brain?
scleral
Birds possess _____ bones in series which overlap to form circle of bony plates, forming the "orbit"
ring
In owls, the scleral ossicles form a ______
tetrachromacy
Birds have _____ - 4 types of color receptors
1. red
2. green
3. blue
4. ultraviolet
What are the 4 types of color receptors?
pecten oculi
_____ provide nutritional support to the retina
binocular
Birds have _____ vision, overlap of field of view
limited
Most avian species have _____ binocular vision!
AVIAN ANATOMY NOTES
AVIAN ANATOMY NOTES
6
There are _____ orders of avian species
anseriformes & passeriformes
Avian influenza is being spread by _____
flock medicine
When you are working with big bird populations, its known as _____
skin
What is the largest organ in the body?
rachis
What is the shaft going down the middle of the feather called?
cranial
Smaller surface area is associated with the [cranial/caudal] edge of the feather
primary
_____ feathers are attached to the manus
antebrachium & brachium
Secondary feathers are attached to the _____
asymmetrical; symmetrical
A _____ feather is for flight, while a _____ feather is found on the tail
contour
_____ feathers cover the body of the bird
1. flight
2. thermoregulation
3. sexual dimorphism
4. protection
Feathers help with.....
hooklets
_____ connect/keep the barbs and barbules together
alula
The ______ is the "thumb" and helps with readjustment when flying
atlas
The single occipital condyle articulates with the _____