Henningsen CH 7: Renal Mass
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Two types of simple renal cysts?
Cortical and parapelvic
What are simple renal cysts?
Fluid-filled pockets that form on the kidneys
TRUE/FALSE:
Cortical renal cysts are common and benign.
TRUE
Etiology for cortical renal cysts are:
A) unknown
B) known
A) unknown
Cortical renal cysts are usually asymptomatic but if it's a large cyst it can cause possible pain or ___________.
Hematuria
The sonographic appearance of cortical renal cysts can be ___________ or multiple, ____________ or bilateral, edge shadowing, ___________ doppler flow, and the __________ sign.
Single, unilateral, absent, "claw"
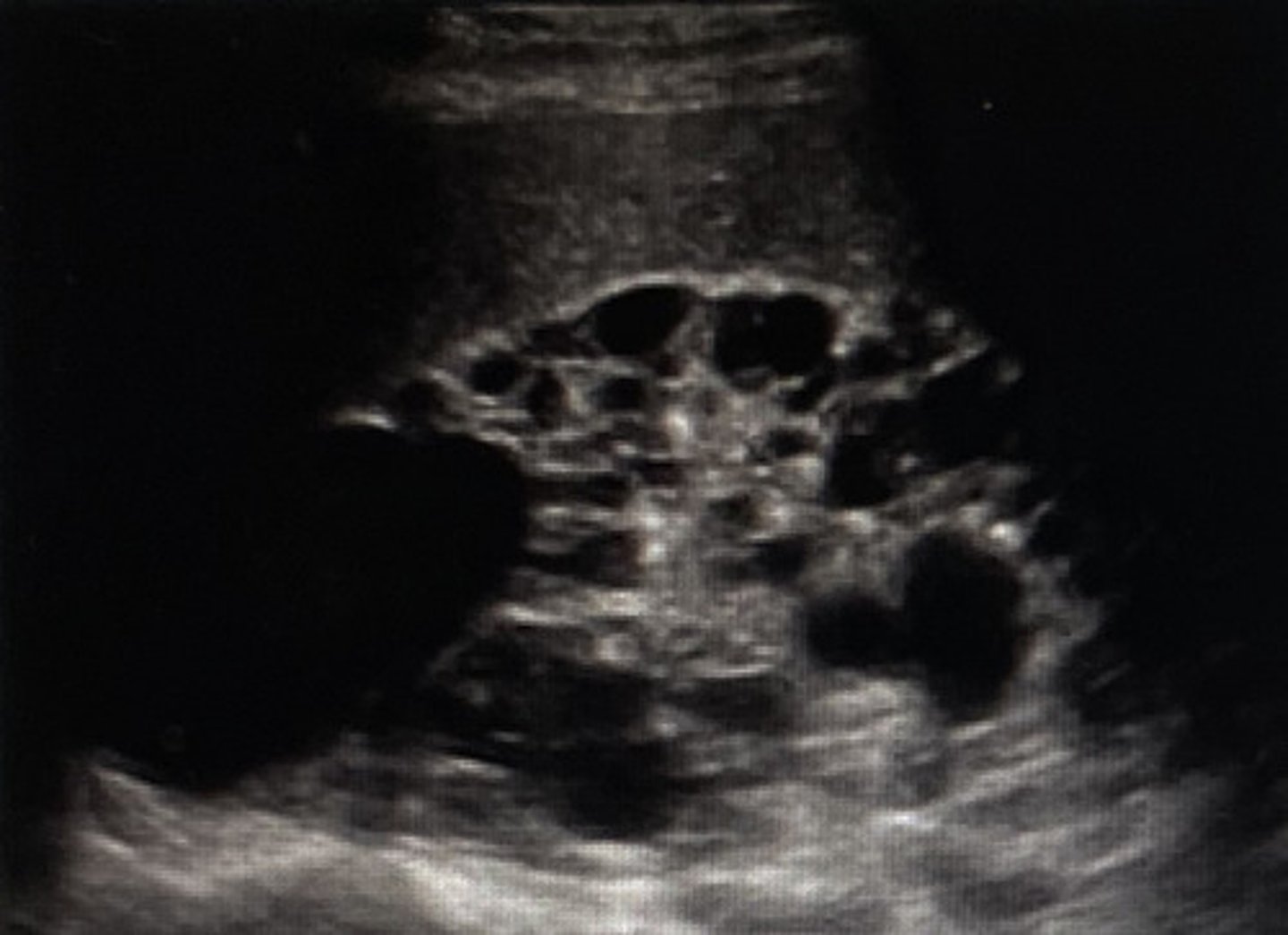
What is the location of Parapelvic renal cyst?
Renal sinus
Parapelvic renal cyst origin?
Lymphatic
TRUE/FALSE:
Parapelvic renal cysts are asymptomatic
TRUE
Parapelvic renal cysts can be mistaken for what?
Hydronephrosis
Complex renal cysts __________ meet simple cyst criteria.
A) do not
B) do
A) do not
Some types of complex renal cysts are hemorrhagic, infected, ____________, calcification, milk of ___________, and cystic ____________.
Multilocular, calcium, malignancy
Signs and symptoms of hemorrhagic cyst are __________ pain, and __________.
Flank, hematuria
The sonographic appearance of a hemorrhagic cyst is variable depending upon __________ but can be ___________, low-level ___________, complex, and may demonstrate acoustic enhancement.
Age, anechoic, echoes
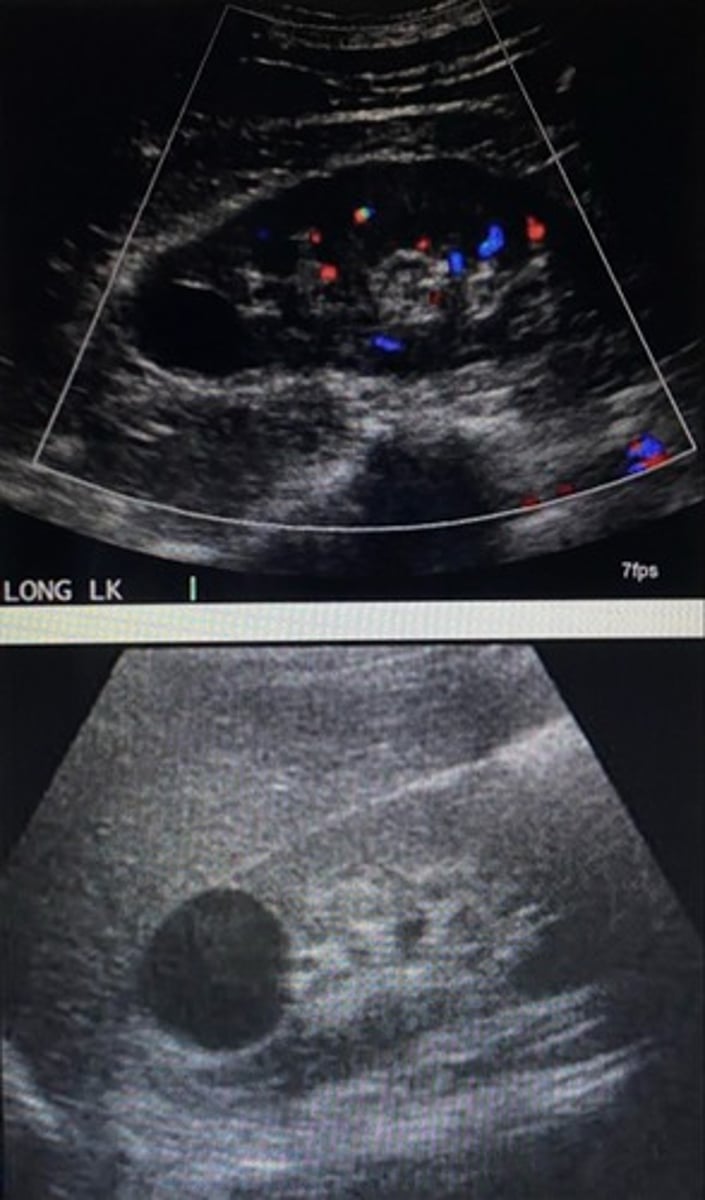
TRUE/FALSE:
Hemorrhagic cysts have Doppler flow
FALSE. Doppler flow is absent
Signs and symptoms of an infected cyst are flank pain, ___________, hematuria, and ___________ in urine.
Fever, white blood cells
Sonographic appearance of an infected cyst is _________, low-level echoes indicate __________, __________ effect, and a thickened cyst wall.
Variable, debris, layering
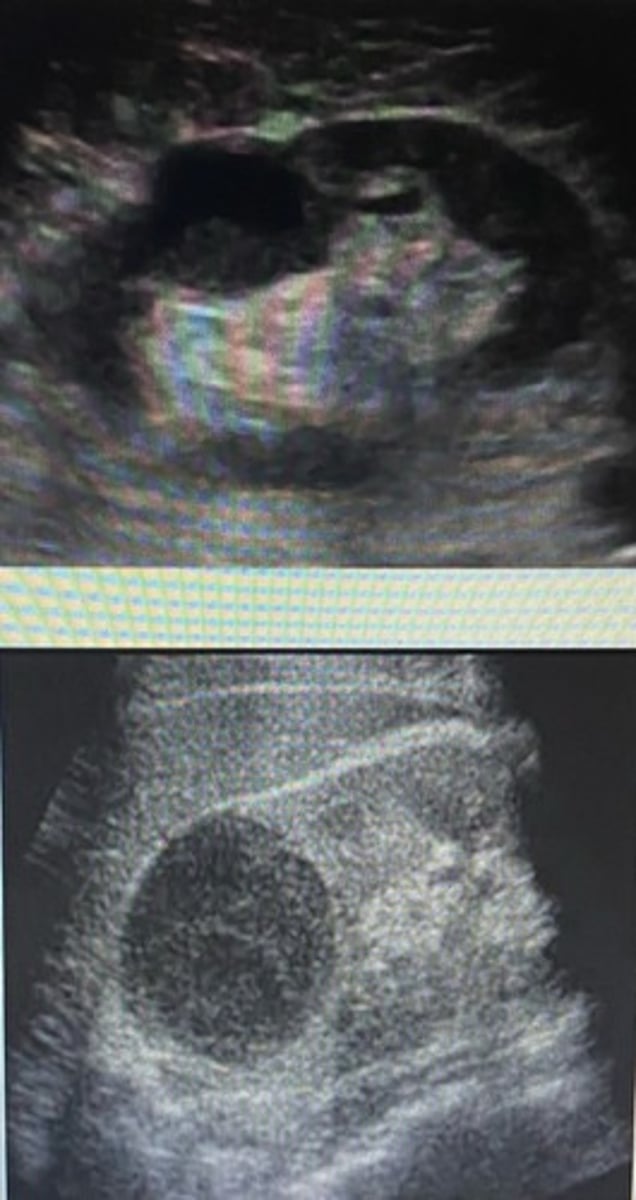
Multilocular cyst contain ___________ or ___________. Thin is clinically ___________ and thick is suspicious for __________. Papillary projection is suspicious for malignancy.
Septations, loculations, insignificant, malignancy
Calcification can result of resolved __________ or _________.
Hemorrhage or infection
A _________ calcification is clinically insignificant, and a __________ calcification is suspicious for malignancy.
A) large, small
B) small, large
B) small, large
Calcifications are ___________ with posterior shadowing.
Echogenic
Milk of calcium cyst etiology is urine stasis within __________ __________.
Calyceal diverticulum
"Milk of calcium" cyst is composed of ___________ ___________ ___________.
Calcium carbonate crystals
Milk of calcium cyst is clinically ___________.
Insignificant
Some signs and symptoms of milk of calcium cyst can be __________, hematuria, flank pain, and __________.
Asymptomatic, infection
The sonographic appearance of milk of calcium cyst is well-defined cystic ___________, ___________"milk of calcium" layered in the ____________ portion of cyst.
Lesion, echogenic, dependent
TRUE/FALSE:
Milk of calcium cyst will not shift relative to patient position.
FALSE. It will shift
Cystic malignancy are rare; cystic ___________ and cystic ___________
Nephroma, RCC
The sonographic appearance of cystic malignancy is __________ or Multilocular, possible ___________, wall irregularity, and __________.
Uni, nodules, calcifications
Large cystic malignancy masses that a heterogeneous are ___________ and ___________.
Hemorrhage, necrosis
With highly vascular cystic malignancy color Doppler _________ show blood flow within __________, nodules, walls of mass.
Will, septa
Renal Cystic Diseases are ________ ________ ________ kidney disease (ADPKD), _________ _________ kidney disease (ACKD), __________ cystic disease, and hereditary conditions.
Autosomal dominant polycystic, acquired cystic, medullary
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is ___________ and ___________.
Hereditary, progressive
ADPKD can lead to?
Renal failure
ADPKD can be discovered in patients that are __________ to __________ years of age.
30-40
ADPKD cysts are also found in the liver, ___________, and __________.
Pancreas, spleen
ADPKD cysts are prone to?
Hemorrhage and infection
Signs and symptoms of ADPKD are __________ pain and hematuria.
Flank
ADPKD sonographic appearance is bilateral, multiple cysts, ____________, and ___________.
Nephromegaly, calculi
ADPKD criteria:
<_______: 2 renal cysts (uni- or bilateral)
_______-_______: 2 cysts in each kidney
>_______: 4 cysts in each kidney
30, 30-59, 60
Acquired cystic kidney disease (ACKD) is when kidneys develop __________ __________, loose the ability to filter wastes and causes kidney failure.
Multiple cysts
ACKD complications
Hemorrhage and RCC
Sonographic appearance of ACKD is _________ or more cysts bilaterally, kidney size _________ (most common), and nephromegaly
3, decreased
TRUE/FALSE:
Medullary cystic disease is common, hereditary, and seen in all ages
FALSE. They are RARE, hereditary, and seen in all ages
Etiology for medullary cystic disease is a _________ ________ leading to cyst formation.
Tubular atrophy
Kidney size for medullary cystic disease of sonographic appearance is __________ and __________.
Normal, decreased
Rare autosomal dominant conditions are ________ _______ ________ disease and _________ __________.
Von hippel-lindau, tuberous sclerosis
Sonographic appearance of hereditary conditions are multiple ___________ ___________ cysts.
Cortical renal
Which of the following would disqualify a cyst from being simple?
Select one:
A) internal blood flow visualized with color Doppler
B) anechoic
C) irregular walls
D) calcifications
E) round
F) posterior enhancement
G) edge shadowing
H) low-level internal echoes
I) thin septations
J) thick septations
K) all of the above
L) A, C, D, H, I, J
M) B, E, F, G,
L) A, C, D, H, I, J
Where are cortal cysts located?
A) renal sinus
B) renal medulla
C) renal cortex
D) renal pelivs
C) renal cortex
The ___________ is a concavity in the renal contour where the parenchyma appears to be the cupping the cyst or mass, indicating a renal origin.
A) claw sign
B) loculation
C) simple cyst criteria
D) septation
A) claw sign
Which of the following would most likely be considered a complex renal cyst?
A) milk of calcium cyst
B) cortical renal cyst
C) parapelvic cyst
D) B & C
A) milk of calcium cyst
Which of the following is most likely to be confused with Hydronephrosis?
A) cortical cyst
B) parapelvic cyst
C) ADPKD
D) milk of calcium cyst
B) parapelvic cyst
Which type of cyst is caused by urine stasis within calyceal diverticulum?
A) milk of calcium cyst
B) cortical renal cyst
C) parapelvic cyst
D) hemorrhagic cyst
A) milk of calcium cyst
Which of the following is untrue about Multilocular cysts?
A) papillary projections are suspicious for malignancy
B) contains septations or loculations
C) possible result of resolved hemorrhage or infection
D) thick septations are clinically insignificant
D) thick septations are clinically insignificant
Which of the following sonographic findings would be considered suspicious for malignancy?
A) thin septations
B) blood flow within septations
C) posterior enhancement
D) small calcifications within a cyst wall
B) blood flow within septations
___________ is a progressive disorder that results in chronic renal failure from a noncystic renal disorder.
A) ADPKD
B) multicystic dysplastic kidney
C) acquired cystic kidney disease
D) ARPKD
C) acquired cystic kidney disease
With ADPKD, where are cysts commonly found?
A) kidney
B) liver
C) pancreas
D) spleen
E) all of the above
F) A & C
E) all of the above
When utilizing the Bosniak Renal Cyst Classification System, which number indicates the lesion is clearly malignant?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 2F
D) 3
E) 4
E) 4
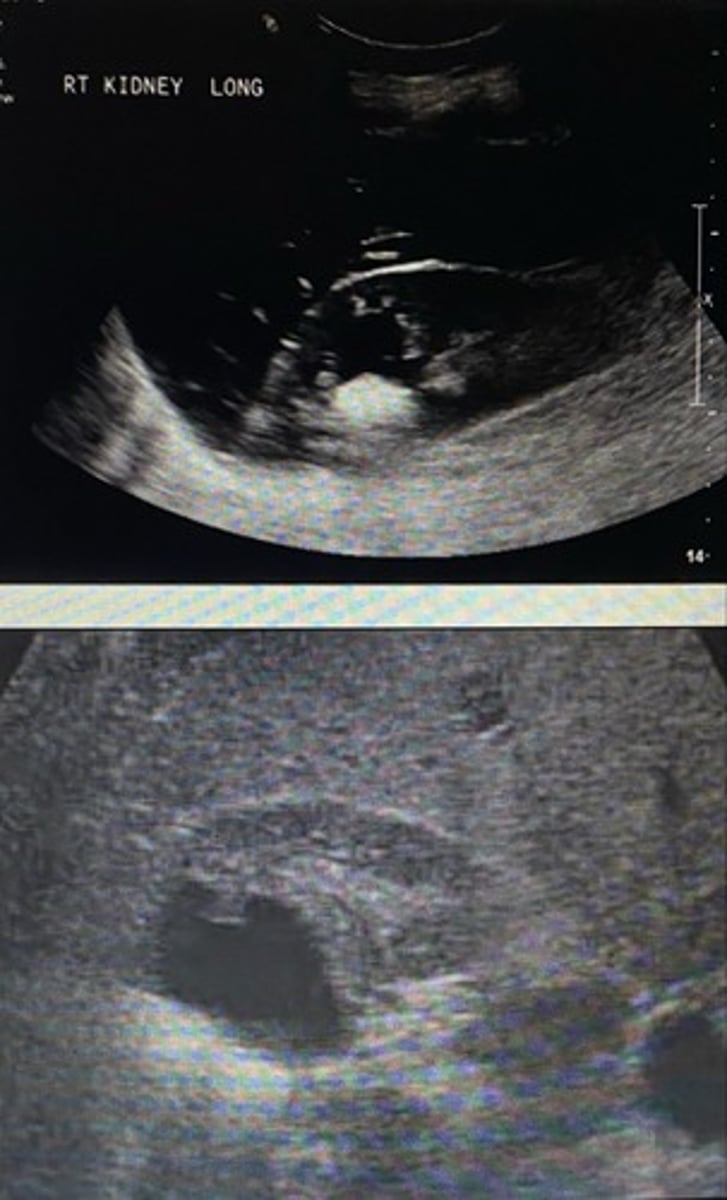
Do the following images demonstrate all of the necessary criteria to be classified as a simple renal cyst?
Yes
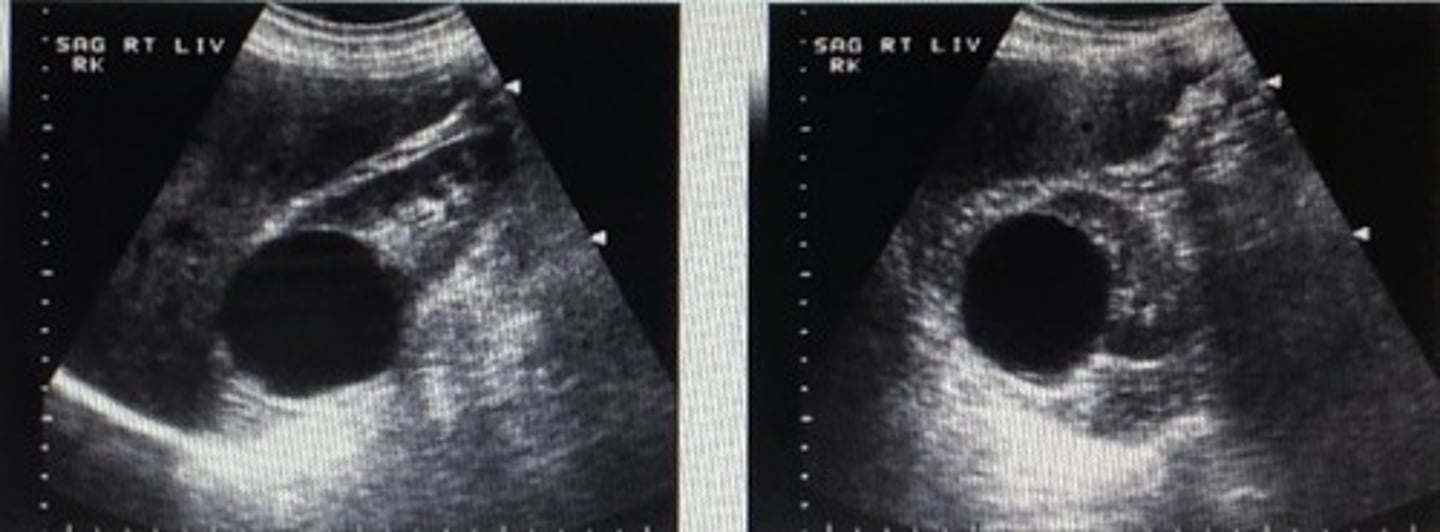
Which of the following cysts may show a layering effect that moves with a shift in patient's position?
A) infected cyst
B) hemorrhagic cyst
C) cysts associated with ADPKD
D) parapelvic cyst
A) infected cyst
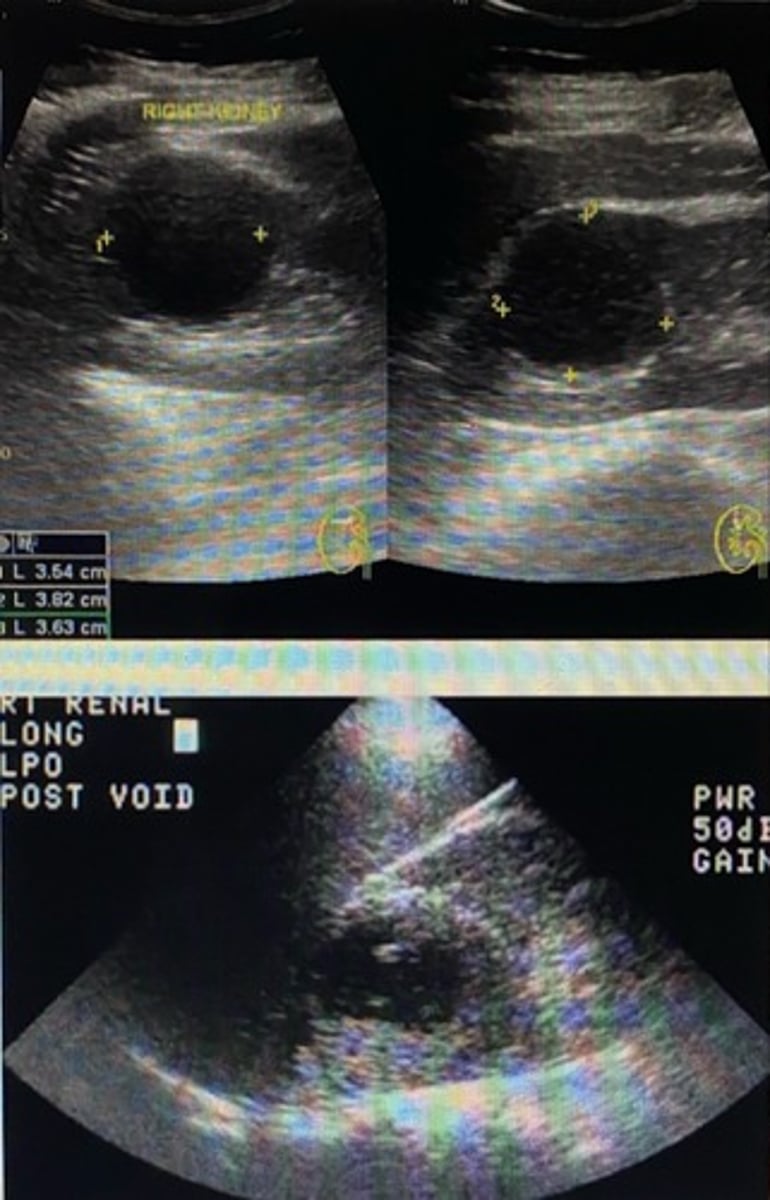
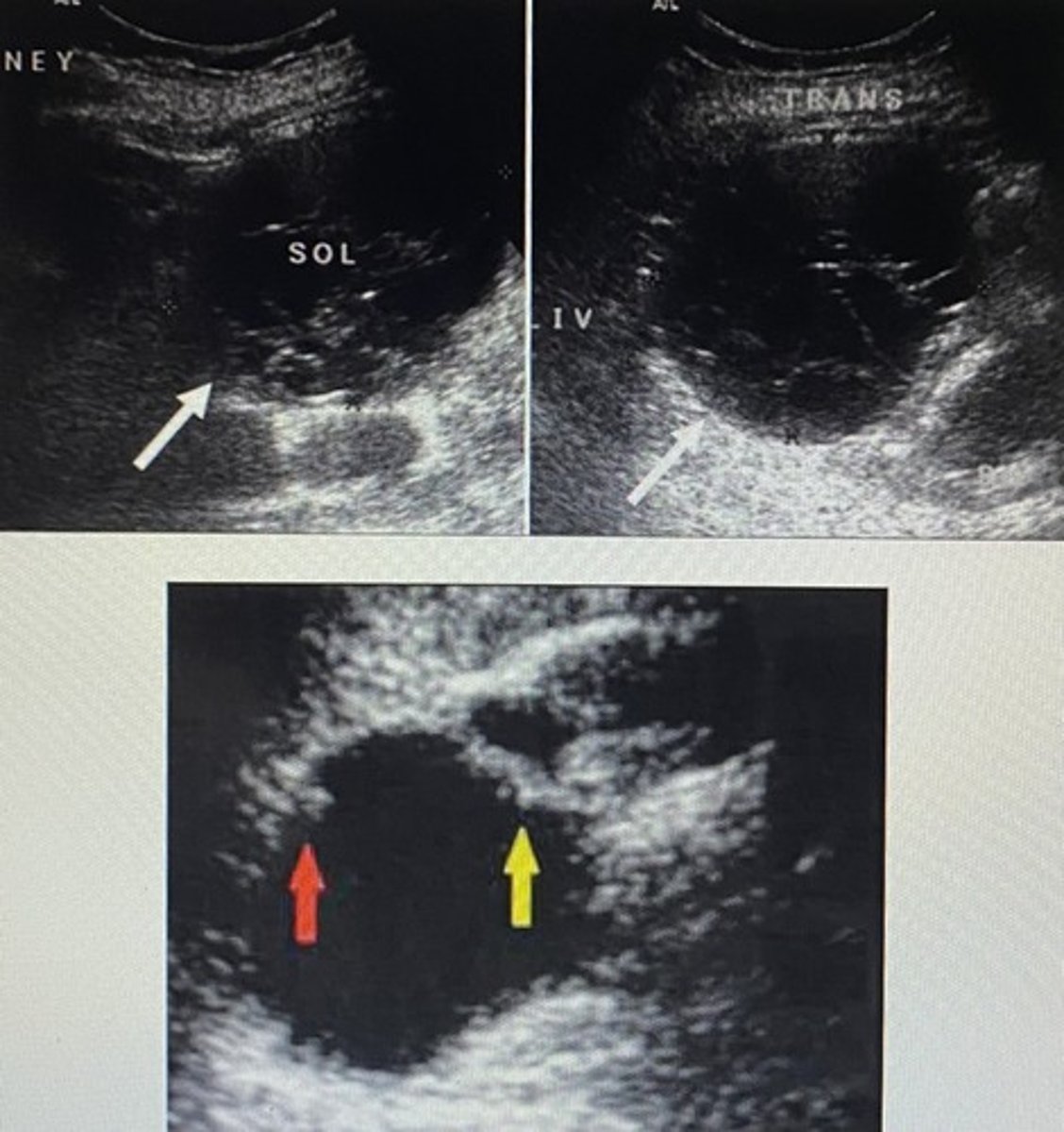
Where is the cyst in the following image located?
A) superior pole of the right kidney
B) inferior pole of the right kidney
C) at the renal hilum
D) in the renal sinus
A) superior pole of the right kidney
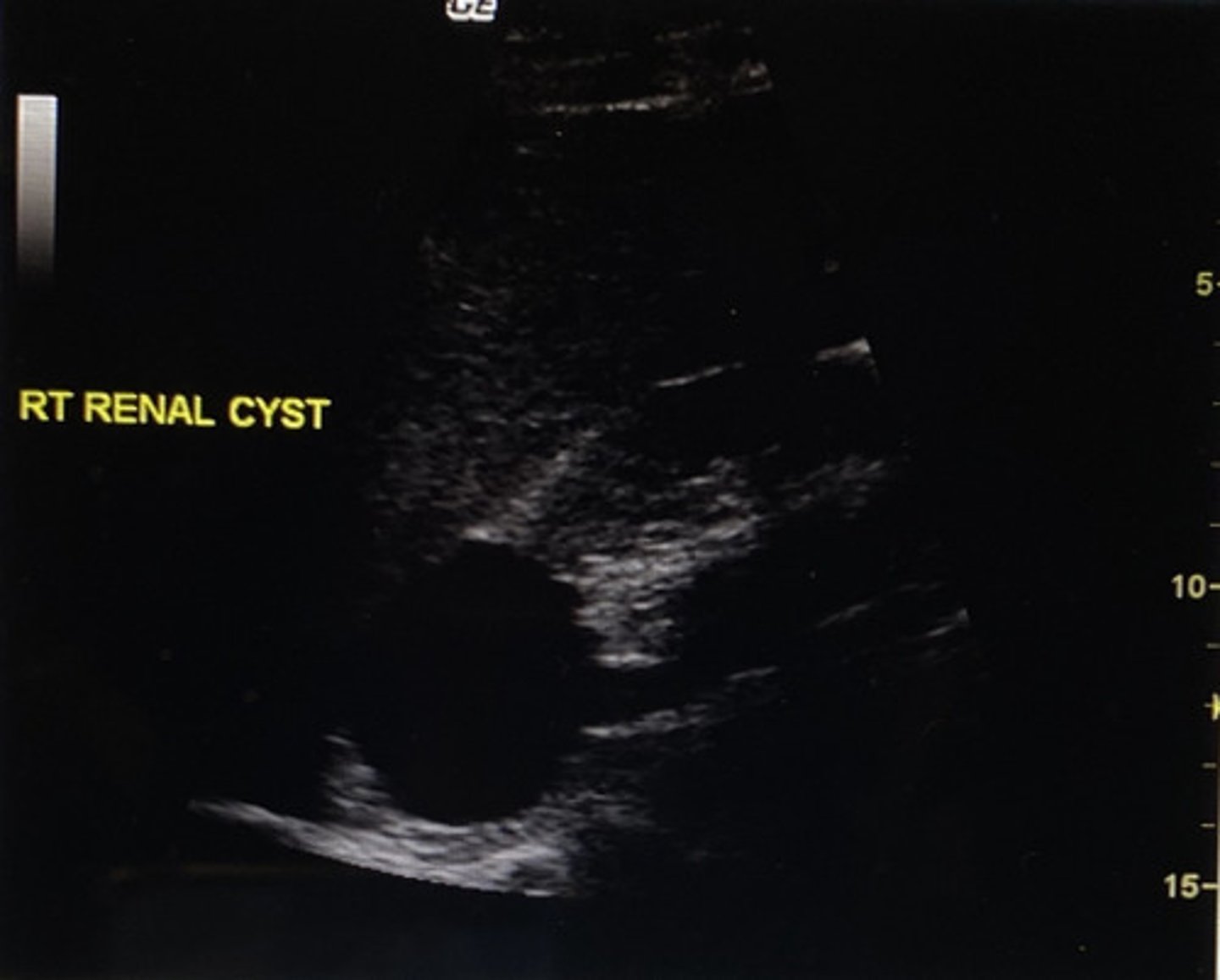
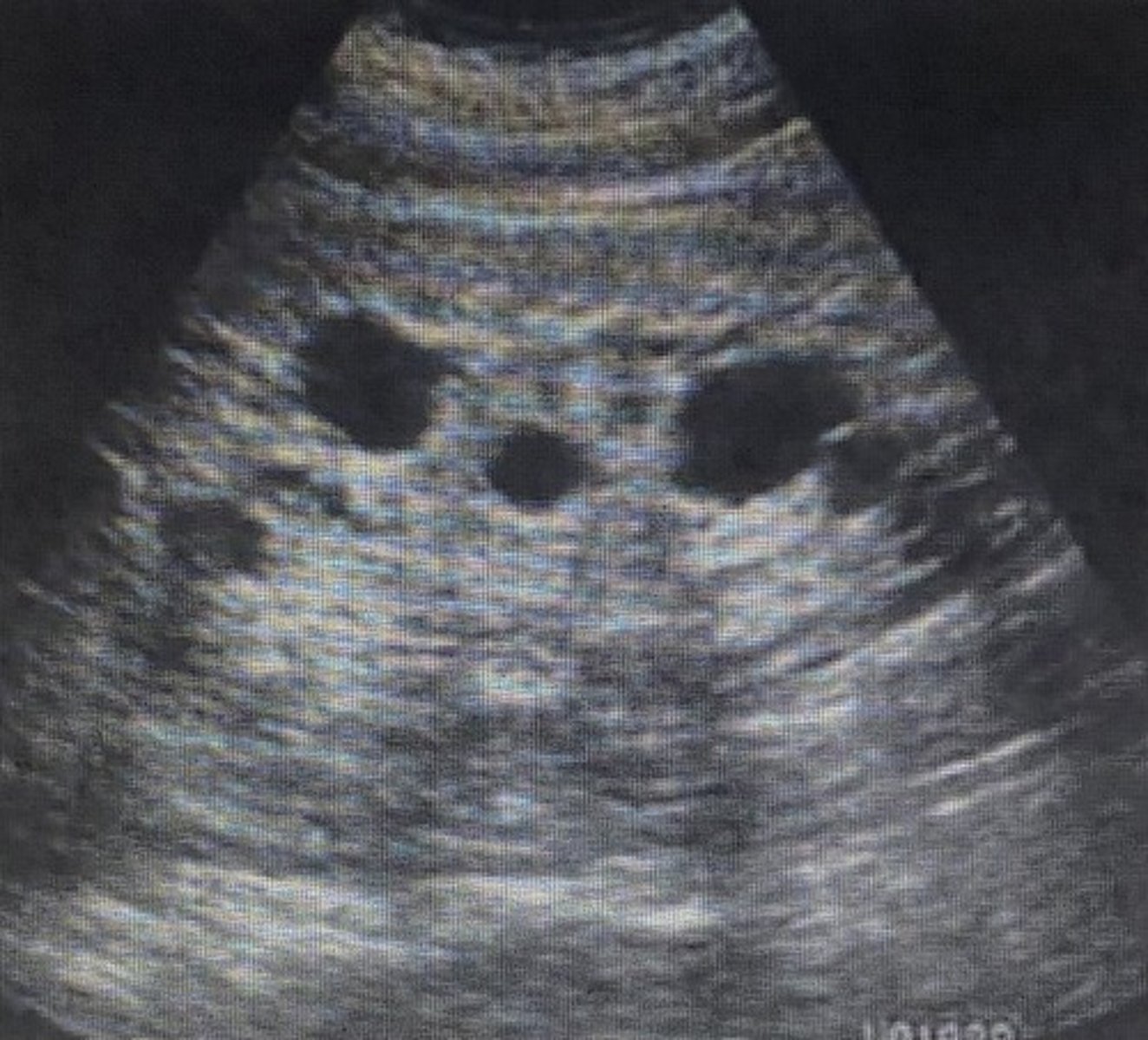
What does the following image most likely represent?
A) ADPKD
B) medullary cystic disease
C) multiple cortical cysts
D) multiple parapelvic cysts
A) ADPKD