POCUS -Skin, MSK, & Procedures
1/39
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What are POCUS signs of cellulitis?
anechoic fluid surrounding SQ fat and connective tissue → “cobblestone” appearance of tissue
What are POCUS signs of an abscess?
mixed echogenic spherical shaped entity w/ poorly defined borders in soft tissues; posterior enhancement
± visualized swirling of pus w/in the entity w/ compression
What are POCUS signs of necrotizing fasciitis?
dirty air shadowing
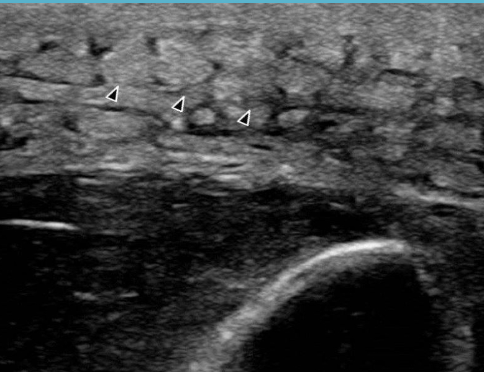
What is this?
Cellulitis
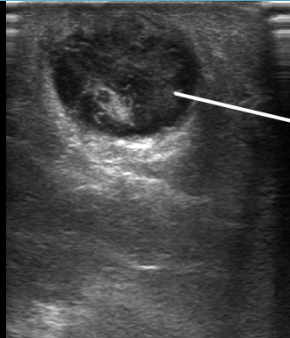
What is this?
Abscess
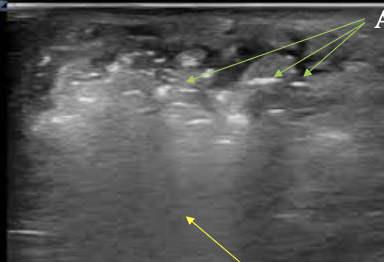
What is this?
Necrotizing fasciitis
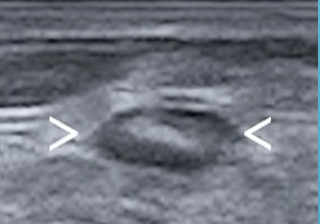
What is this?
Lymph node
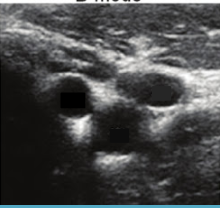
What is this?
Vessel
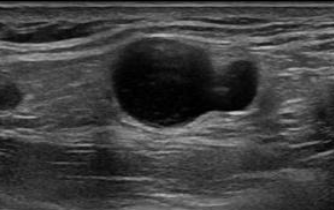
What is this?
Lymphoma
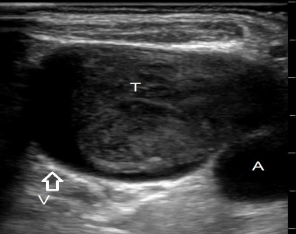
What is this?
Thrombosed Vessel
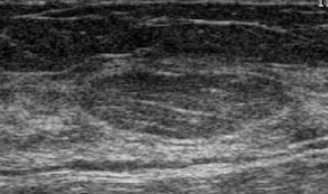
What is this?
Lipoma
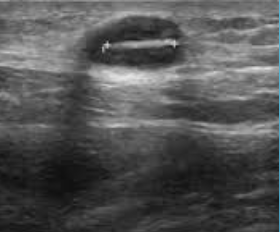
What is this?
FB
What are POCUS signs of a FB?
echogenic structure in soft tissues, hypoechoic rim surrounding the entity (if > 24hrs)
posterior shadowing ± reverberation artifact
How should pt be positioned to examine the quad tendon?
pt supine w/ knee flexed at 20-30 degrees
What is a common cause of ant. knee pain in active adults?
lat. femoral condyle friction syndrome
Tx: RICE
What will you see on POCUS of lat. femoral condyle friction syndrome?
impingement of Hoffa fat pad btwn inf patella and lat. femoral condyle; fat pat will be very echogenic
How do you have the pt positioned to assess medial knee?
*MCL, medial meniscus
20-30 knee flexion; externally rotate at the hip
What can mimic a baker’s cyst?
anisotropy
What are subacromial impingement syndromes?
rotator cuff tears, calcific tendinitis, biceps tendinopathies, subacromial bursitis
What is the MC shoulder dislocation?
anterior
What are the shoulder muscles?
SITS: supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis
What is the MC shoulder tear?
supraspinatus
How do you asses the anterior glenohumeral joint?
have pt abduct and adduct their arm
*bunching of the tend at the coracoid process= impingement
What is a Hill-Sachs lesion?
glenoid impacts the lateral humeral head → lesion
What is a Bankart lesion?
avulsion of the labrum dt ant. shoulder disolocation
Review pictures from the slide
:)
What are the 3 MC US guided procedures?
paracentesis, thoracentesis, central venous access placement
What are indications for placing central venous access?
volume resuscitation, emergency venous access, nutritional support, vasopressors, pacing wire placement, hemodialysis
What are absolute CI to placing central venous access?
abn anatomy secondary to injury or radiation
infxn at insertion site
What are potential complications for placing central venous access?
inadvertent puncture of carotid artery, damage to nearby structures, bleeding
What are indications for paracentesis?
new onset ascites, suspected spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, resp. compromise, abd pain/pressure, dec appetite/mobility
What are absolute CI to paracentesis?
surgical acute abdomen
What are potential complications of paracentesis?
leakage of ascitic fluid, local infxn, abd wall hematoma, intraperitoneal hemorrhage, intestinal perforation
What are indications for a thoracentesis?
relief of SOB, determine etiology of pleural effusion
What are CI for thoracentesis?
INR > 2, infxn or cellulitis at puncture site
What are potential complications of a thoracentesis?
pneumothorax, re-expansion pulm edema, bleeding, injury to nearby structures
When can you usually sign off and d/c rounding on pts post-procedure?
after PPD #1
Which technique utilizes a guide wire?
Seldinger technique
Review steps to placing a tube/line using Seldinger technique
:)
What size needle & cath do you use for a paracentesis & thoracentesis?
21g & 5-7fr