Market Structures
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What defines the competitiveness of a market?
The number of firms within it
What are 3 important aspects of market structures?
Competitiveness
The extent to which goods or services produced are identical or different
The ways in which the barriers to entering the market affects its operation.
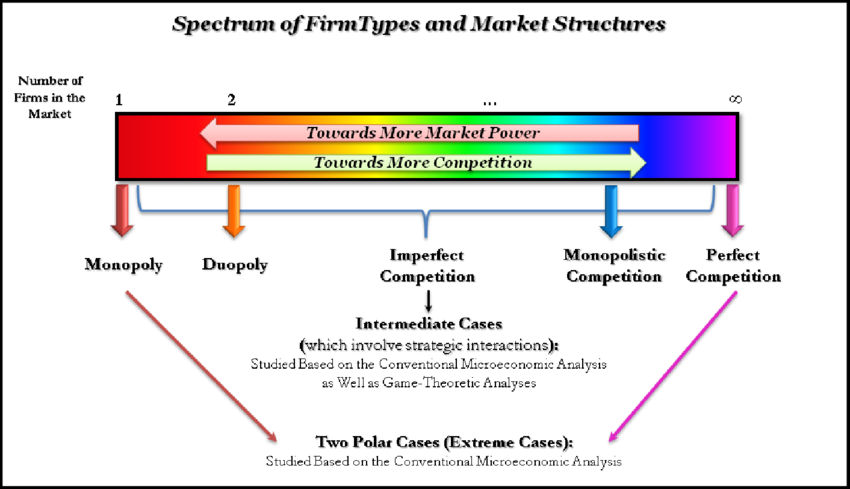
What are the range of market structures?
Price taker vs makers
Taker - lacks the market power to influence ruling market price by its own action
Maker - actively sets the price in the market.
Concentrated market - definition
A market containing very few firms which have considerable market power.
Pure monopoly - definition
A single firm produces the whole of the output of a market or industry; there are no other firms to compete against
Comparing perfect & imperfect competition and pure monopolies in these categories:
No of buyers'/ sellers
Entry and exit of market
Price
Information
Products
Perfect competition | Imperfect competition | Pure monopoly | |
No. of buyers and sellers | Many | Fewer than perfect | 1 firm |
Entry and exit | Low barriers | Medium barriers | High barriers |
Price | Takers | Makers - if they have better good | Makers |
Information | Perfect | Asymetric | Imperfect |
Products | Homogenous | Differrentiated | No substitutes |
Are pure monopolies likely?
No, in reality dominant firms are more likely.
Dominant firms - definition
Market dominated by a small number of firms, who can raise prices by restricting output.
What market share must a company have to be a monopoly or a dominant monopoly in the UK?
Must have a market share of 25% to be a monopoly, and 40% to be a dominant monopoly.
Monopoly power - definition
The power to act as a price maker rather than taker, allowing firms to set prices without worrying about competition from other firms.
Market power - definition
The ability of a business to set prices above a level that would exist in a highly competitive market.
How does market power allow firms to maintain high profits?
By using barriers to entry to prevent the profitable entry of new firms. Therefore making supernormal profits.
Supernormal profit - definition
The excess profit a firm makes above the minimum return necessary to keep a firm in business.
What’s the concentration ratio?
No. of biggest firms in the market : % of market share they hold.
7 characteristics of perfect competition
Homogenous products
Freedom of entry and exit
Prices reflect compete mobility of resources
No one buyer or seller has advantage over another
Sellers must act independently (no price collusion)
Profit maximisation is assumed as the default objective
Full access to information by all participants.
Key points on perfect competition
Each firm is a passive price taker
AR = MR
Profit/loss depends on market prices vs organisation costs
Number of firms
Number of firms in the long run will adjust to profits made.
Why does AR = MR in perfect competition?
Each participant is a price taker, with prices determined by market forces, therefore revenue received for selling one more unit is exactly the same as the current unit.
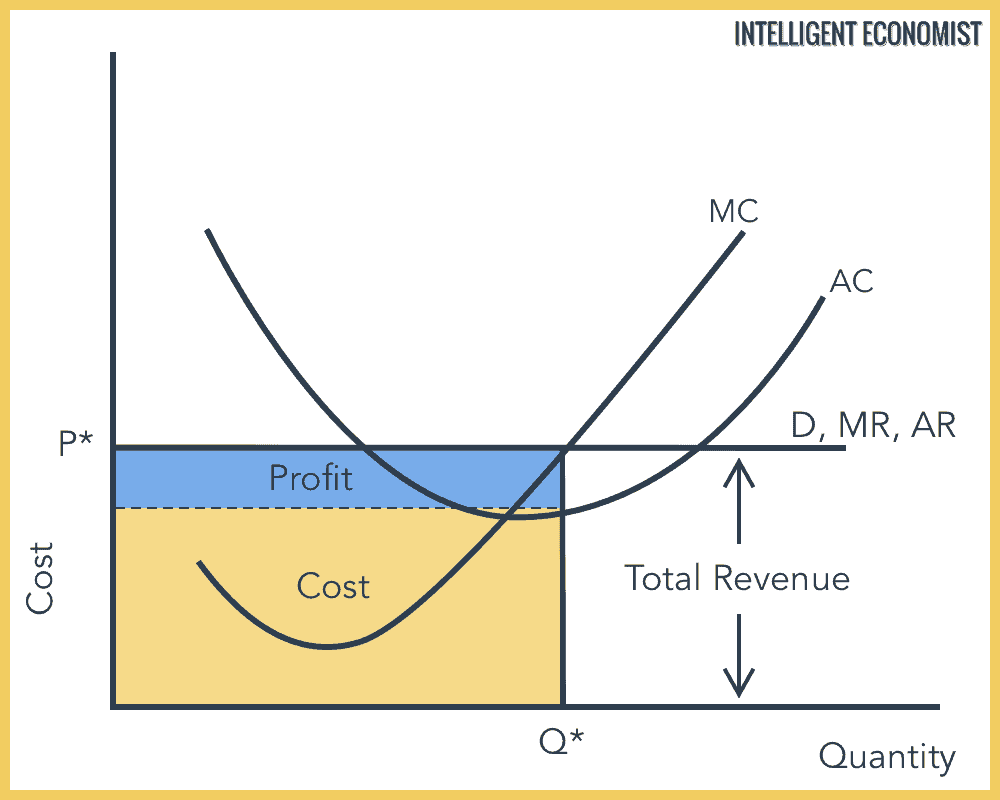
What does the revenue/cost graph look like in perfect competition?
Profit is where MC=MR, Cost is where quantity meets AC
Average revenue = the price level at the point of equilibrium between supply and demand curve.
Can instinctively tell in this scenario that supernormal profit is made, as AC falls below AR