Class 20- Overweight & obesity
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
what % of Canadians are overweight or obese ? has it stabilized? what are obese ppl at higher risk for?
60% of Canadians
Overweight and obesity in children 12–17 yrs has stabilized since 2015
• Developing countries also experiencing increases in obesity
• Persons living with obesity are at higher risk for health conditions (Type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, arthritis,
sleep apnea…)
what BMI (kg/m²) values categorize OW, then the three obesity classes?
OW=25-29.9
OB 1= 30-34.9
OB 2= 35-39.9
OB 3= 40+
1/5 fact about obesity
OBESITY IS A CHRONIC DISEASE
- not a personal failure or a lack of willpower-obesity is a chronic disease. Recognizing it as a chronic disease helps remove stigma and shifts the focus to compassionate, evidence-informed healthcare.
Chronic diseases are conditions that last a lifetime, require ongoing care, and stem from complex interactions between biological, genetic, and environmental factors. Obesity fits this definition because it involves disruptions in the body's regulation of energy, appetite, and fat storage.
By properly defining obesity and recognizing its complexity, we can move away from oversimplified narratives that blame individuals. Instead, we can focus on evidence-based solutions that address the root causes of obesity and improve the lives of those living with this disease.
2/5 fact about obesity
OBESITY IS DRIVEN BY BIOLOGY, NOT CHOICE
70% of risk determined by genetics. In people living with obesity, the brain's systems for controlling hunger and energy are disrupted, creating biological barriers to weight loss that many people struggle to overcome.
Obesity is characterized by abnormal or excessive body fat (also called adiposity) that impairs health. Obesity isn't defined by a single body type-people of all shapes and sizes, including smaller bodies, can live with obesity.
Focusing on measures of health rather than appearance helps provide care that respects each individual's unique journey. Blaming individuals for their weight overlooks the powerful biological and social forces at play. A better understanding of obesity opens the door to better care and lasting solutions.
3/5 fact about obesity
OBESITY CAN IMPACT HEALTH EARLY
-often beginning in childhood. As young bodies grow, carrying excess weight can put added strain on their physical health, increasing risks for conditions like type 2 diabetes and high blood pressure later in life.
Beyond the physical, the mental and emotional toll of living with obesity-such as stigma and low self-esteem-can leave lasting impacts.
Early prevention and management are critical to reducing these risks and fostering healthy futures.
4/5 fact about obesity
OBESITY IS TREATABLE
Effective obesity care is individualized and adaptable, addressing each person's unique body, biology, and life circumstances. A one-size-fits-all approach doesn't work.
Science and treatments for obesity are rapidly evolving, offering new and more effective ways to manage this complex condition, but success is not just measured by weight loss. Improving overall health and quality of life defines effective treatment.
Evidence-based options like behavioral therapy, lifestyle adjustments, prescription medications, and surgery can all play a role in a comprehensive, personalized approach to care.
5/5 fact about obesity
WEIGHT BIAS, STIGMA, AND DISCRIMINATION HARM EVERYONE
Weight bias isn't just personal-it creates structural barriers to care that worsen health outcomes and mental well-being, contributing to depression, anxiety, and social isolation.
Studies show that fear of judgment causes many people living with obesity to avoid seeking medical help, delaying diagnosis and treatment. The societal cost is steep, contributing to higher healthcare costs and lost productivity.
Respecting people of all sizes is the first step to eliminating bias. When we eliminate weight bias and create supportive environments, we can improve health outcomes and reduce the societal impact of stigma.
what is weight bias vs weight stigma?
BIAS=assumptions are made about a person based only on their weight. For those on the receiving end, it can cause feelings of shame, anxiety, and low self-esteem, leaving emotional and mental health struggles in its wake.
STIGMA= rooted in harmful social stereotypes about people living with obesity. These misconceptions wrongly support beliefs that people living with obesity are lazy, undisciplined, or unintelligent, fueling bias and judgment that can deeply hurt.

what are Perceptions and Prejudices about obesity? what are some non-health consequences OB
• Assumption that everyone can lose weight
• Requires willpower and hard work
• Social consequences
• Discrimination
• Judgments on appearance, laziness, lack of self-control
• Psychological problems
• Embarrassment, rejection, shame, or depression
how does genetics and lifestyle choices influence obesity?
Genetic inheritance strongly influences a person’s tendency to become obese
Lifestyle choices that influence the
tendency for obesity include:
– Smoking
– Eating behaviours
– Nutrient intakes
– Physical activity
how do fat cells develop? by how much can they increase size vs #
Fat cells are capable of increasing their size
by 20-fold, and their number by several
thousandfold.

how does energy in/out affect fat cell development ?
Energy excess: energy in > energy out
• Stored in fat cells of adipose tissue
• Body fat reflected in the number and size of fat cells
• In growing years, fat cells grow most rapidly
• Obese individuals have larger and more fat cells
Energy out > energy in
• Fat cell size decreases; no change in number of fat cells
what does LPL enzyme do?
Lipoprotein lipase (LPL)
– Hydrolyzes triglycerides passing in the bloodstream
– Directs their parts into cell to be stored
– Influenced by gender
• Women have higher LPL in breasts, hips, and thighs
• Men have higher LPL in abdomen
what is the set-point theory?
= Body strives to achieve homeostasis
• Hypothalamus makes adjustments to return to the person’s “set point” or “normal” level of body fat
• This theory suggests weight loss is difficult because the body fights to regain lost weight and can make it harder to lose future weight by lowering metabolic rate and increasing hunger.
info on liposuction, can you gain fat after?
• “If the patient gains a small amount of weight after their procedure, say 5 pounds, fat cells throughout the body will get a little bigger. ”
• “Finally, in cases of considerable weight gain (i.e. 10% of their body weight); new fat cells can develop in all areas of the body, including
treated areas.”
why is the biggest looser unsustainable?
Not representative of the type of diet/exercise that most people can do. More extreme.
• Very restrictive food intake
• Very elevated amounts of daily exercise
• Rapid weight loss with doing a lot of exercise to preserve muscle mass
• Small sample size
• By the final weigh-in, contestants' leptin levels had decreased.
– Low levels of leptin tell your brain that your fat stores are low.
• Their thyroid function—which governs metabolism and many other bodily functions—had also slowed.
• Illustrates the “set point” theory, that the body tries to adapt during times of food restriction, and that adaptation can persist years later
what is big picture conclusion from biggest looser follow up study?
• Metabolic adaptation persists over time
“long term weight loss requires vigilant combat
against persistent metabolic adaptation that acts to proportionally counter ongoing efforts to reduce body weight.”
Adipose tissue not only influences the central regulation of yyy, but leads to development of xxx..
Adipose tissue not only influences the central regulation of energy homeostasis, but excessive adiposity can also become dysfunctional and predispose the individual to the development of many medical complications, such as:
• Type 2 diabetes:
Gallbladder disease
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Gout®
what are Excess and ectopic body fat sources of?
Excess and ectopic body fat are important sources of adipocytokines and inflammatory mediators that can alter glucose and fat metabolism—> leading to increased cardiometabolic and cancer risks, and thereby reducing disease-free duration and life expectancy by 6 to 14 years.,
-It is estimated that 20% of all cancers can be attributed to obesity, independent of diet.Obesity increases the risk of the following cancers:!°
Colon (both sexes)
Kidney (both sexes)Esophagus (both sexes)
Endometrium (women)
Postmenopausal breast (women)
what are key points from Obesity canada guidelines
Obesity is a prevalent, complex, progressive and relapsing chronic disease, characterized by abnormal or excessive body fat (adiposity), that impairs health.
People living with obesity face substantial bias and stigma, which contribute to increased morbidity and mortality independent of weight or body mass index.
guideline update reflects substantial advances in the epidemiology, determinants, pathophysiology, assessment, prevention and treatment of obesity, and shifts the focus of obesity management toward improving patient-centred health outcomes, rather than weight loss alone.
Obesity care should be based on evidence-based principles of chronic disease management, must validate patients' lived experiences, move beyond simplistic approaches of "eat less, move more," and address the root drivers of obesity.
People living with obesity should have access to evidence-informed interventions, including medical nutrition therapy, physical activity, psychological interventions, pharmacotherapy and surgery.
what is involved with appetite regulation — what there controls in the body? what controls the executive control on food choices and the decision to eat.
complex + involves the integration of the central neural circuits including the hypothalamus (homeostatic control), the mesolimbic system (hedonic control) and the frontal lobe (executive control).
The crosstalk between homeostatic and hedonic eating is influenced by mediators from adipose tissue, the pancreas, gut and other organs.
Cognitive functions in the prefrontal cortex exert executive control on food choices and the decision to eat. The interconnectivity of these neural networks drives eating behaviour and has been shown to be altered in obesity.
what are realistic weight loss goals?
mproved health measures versus just number on scale.
• Make healthy changes that can be maintained.
• Modest weight loss can help resolved co-morbidities like blood glucose control in Type 2 Diabetes, high blood pressure, blood lipids and improve physical fitness.
• 5 to 10 % weight loss is typically considered realistic
• 1 to 2 lbs per week weight loss is considered realistic
Moderate Weight Loss versus
Rapid Weight Loss, which one is preferred and why?
Gradual, moderate weight loss is preferred
– helps preserve lean body mass
– Less metabolic adaptation than “starvation” or extreme restriction
– More likely to be maintained longer
• Emphasize changing body composition not just what the scale says, build more muscle
• Aim to reduce percent body fat or to lose inches around waistline
• More likely to maintain weight loss if have gradually adopted new healthy habits that are enjoyed
what constitutes a reasonable energy-restricted plan for weight loss
=achieved by reduction in intake and increase in expenditure
• Balance between food groups, lots of fruit/vegetables
• Carb to spare protein as an energy source. High fibre for satiety and healthy gut microbiome.
• Protein for satiety & to spare protein being used as an energy source
• Healthy fats
• proper Breakfast!
• Eat small meals slowly with water for satiety
• Decrease sugar, hidden fats, alcohol, processed foods
• Be physically active regularly
why is extra protein important with weight loss
bc Satiation/Satiety!
• Amino acids will be used for energy if energy
intake if inadequate
• Protects against lean tissue and muscle loss
• At least 1.2 to 1.6 gram per kilogram body weight or 35 % of energy
• Note also physical activity is VERY IMPORTANT
what are some behaviour and attitude changes for achieving healthy BW, what are some behaviour modifications?
• Become aware of behaviours
• Change behaviours
• SMART goals
• Cognitive skills
• Personal attitude
• Support groups
Behaviour Modification
1. Identify problematic eating behaviours
2. Find strategies that are enjoyed to develop new habits. Small
achievable goals.
3. Takes time to develop new habits, at least 8 weeks, Repeat desired behaviours. Give yourself positive feedback.
what are some Benefits of Exercise-Induced Weight Loss
• Direct increase in energy expenditure
• Short term increase in BMR in hours after exercise
• Long term increase in BMR due to increased LeanBodyMass
• Target fat loss while actually increasing muscle
• Appetite control
• Control of eating due to stress and boredom
• Psychological and self-esteem benefits
• Key to maintenance of weight loss
what is the issue with Fad Diets
• Promises magic or miracle cure
• Often designed with low daily energy intake (1200 kcalories or less)
• “On diet” or “Off diet” mentality. All or nothing.
• Will lose weight, but keeping it off….? Not usually…
• Not evidence based for long-term.
• Lack support for long term changes
• Many selling fad diets also peddle dietary supplements
• Is the person promoting the fad diet making money?
what are GLP-1 drugs for diabetic ppl,
for diabetics T2: GLP-1 agonists stimulate pancreas to release insulin and suppress release of glucagon—→ hormones that help control blood sugar lvls.
their body cells are resistant to effects of insulin, does not produce enough or both
-also act in the brain to reduce hunger and act on the stomach to delay emptying, so you feel full for a longer time. These effects can lead to weight loss, which can be an important part of managing diabetes. GLP-1 agonists have been used to treat type 2 diabetes for about two decades.
FDA has approved several GLP-1 agonists for weight loss in people with obesity who do not have diabetes. When used for overweight or obesity, the drugs are typically prescribed in higher doses than when prescribed for diabetes.
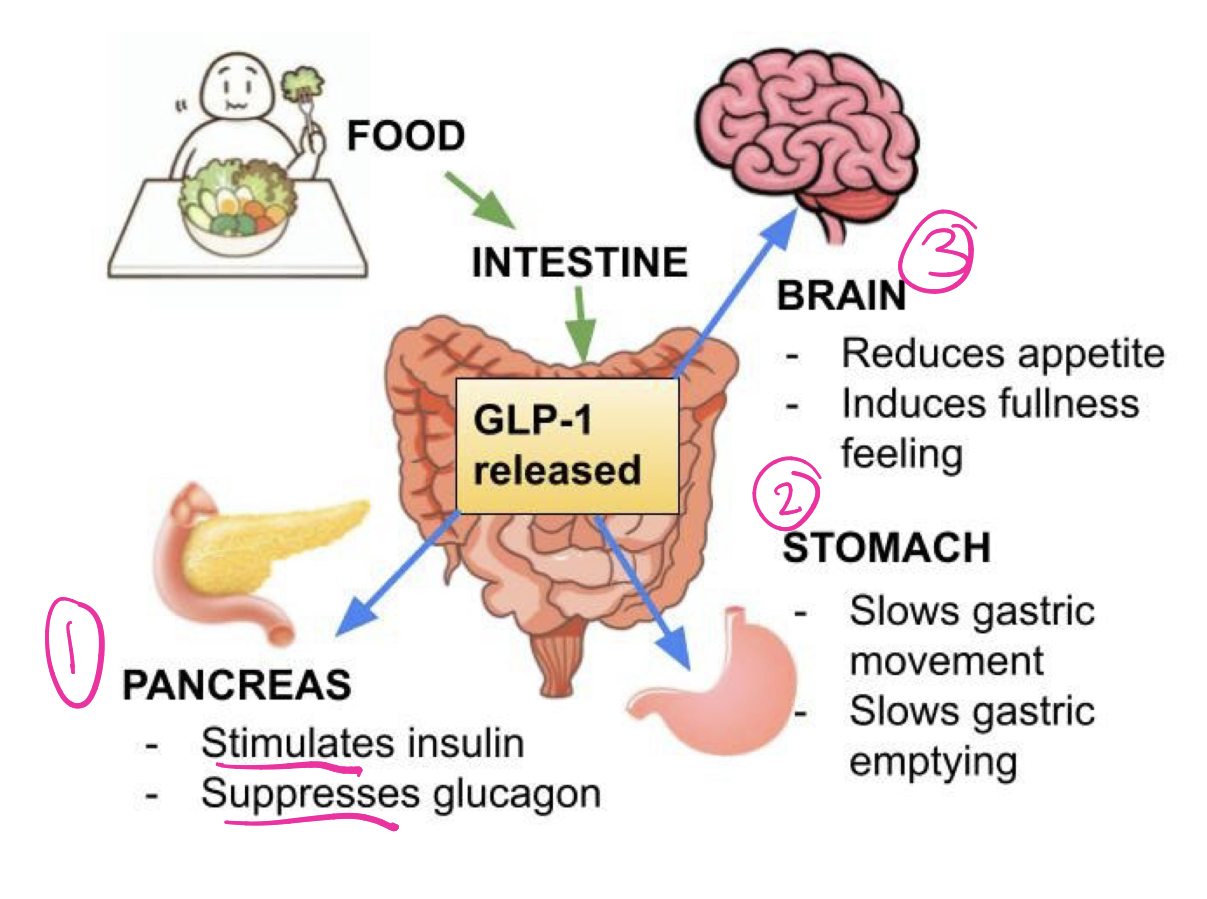
how many Americans vs Canadians are using GLP1s?
USA= ~12%, most are women aged 50-64
CAN= 1Million
side effects= nausea, diarrhea
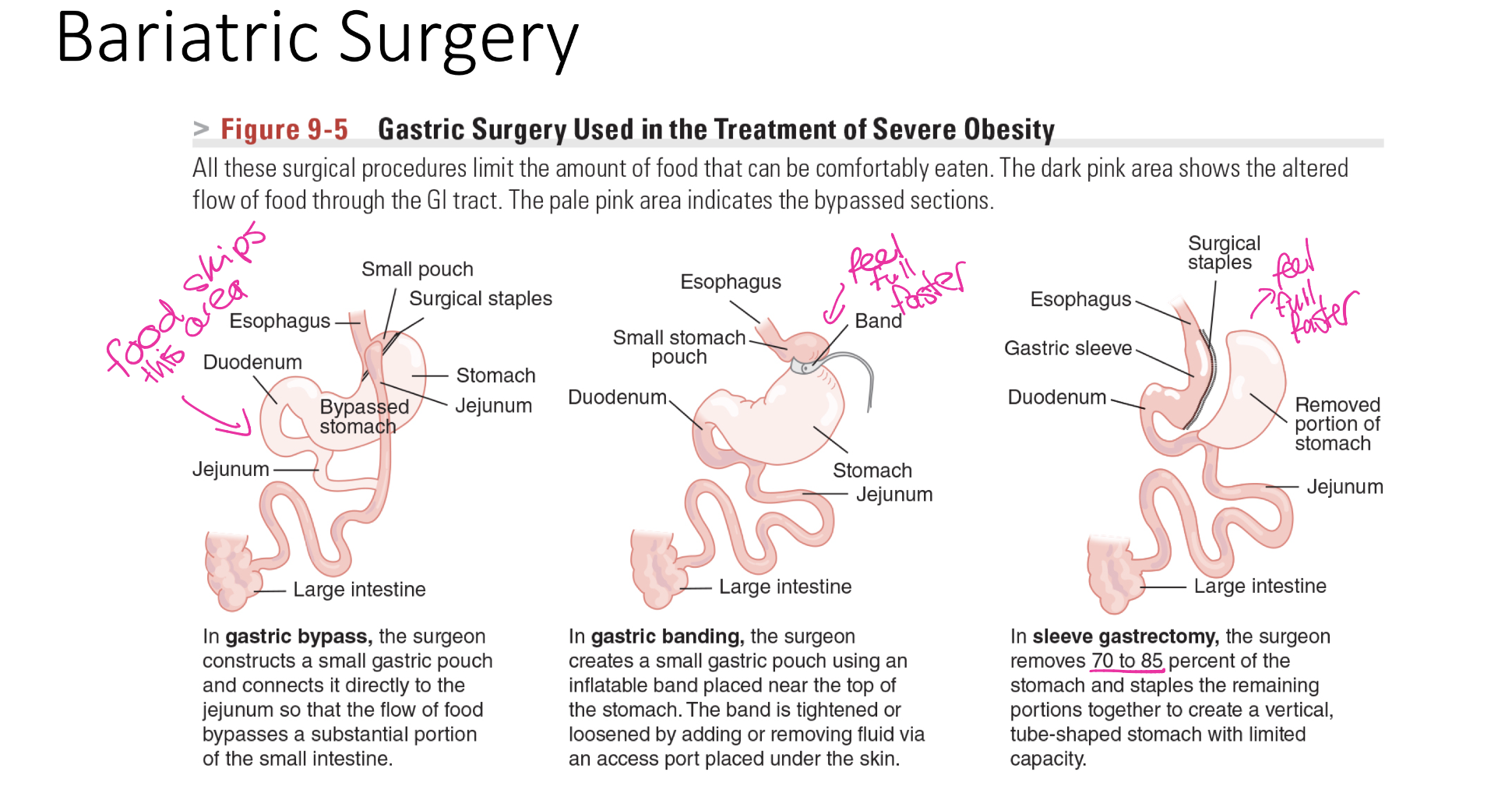
when are surgical procedures considered and option for OB, what are 3 most common metabolic and bariatric surgery procedures
gastric bypass: reduces stomach size and reroute digestion to promote WL and improve t2 diabetes
sleeve gastrectomy: removes portion of stomach, limiting food in and affecting hunger hormones
duodenal switch: extensive procedure that alters digestion to limit cal absorption

what is surgically involved with gastric bypass, gastric banding and sleeve gastrectomy