Module 2 (Week 3) - Chapter 5: The Measurement of National Income
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Define double counting (or multiple counting).
The error that occurs when estimating a nation’s output by adding all sales of all firms
If we added up the values of all sales, the same output would be counted every time that it was sold by one firm to another
Provide an example of double counting.
The local baker uses flour that is the output of the flour milling company; the flour milling company uses wheat that is the farmer’s output
If we added the total value of output, we would be counting the value of wheat three times, the value of flour twice, and the value of bread once
Define intermediate goods.
Outputs of firms that are used as inputs by other firms
Define final goods.
Products that are not used as inputs by other firms
True or False: In general, it is extremely difficult to distinguish between final goods and intermediate goods.
True
Define value added.
The amount of value that firms and workers add to their products, over and above the costs of purchased intermediate goods
What is the formula for calculating value added?
Value Added = Sales Revenue — Cost of Intermediate Goods
True or False: Payments to factors of production (such as workers’ wages or profits paid to owners) are not purchases from other firms (intermediate goods), and therefore, are not subtracted from the firm’s sales revenue when calculating value added.
True
True or False: Value added is equal to the sum of national income/factor payments (payments owed to the firm’s factors of production).
True
Value added is calculated as the difference between sales revenue (output) and cost of intermediate goods (input)
The remaining value (value added) is then distributed among the factors of production (labour income and profits)
The sum of all values added in the economy is a measure of the economy’s total ______.
The sum of all values added in the economy is a measure of the economy’s total output.
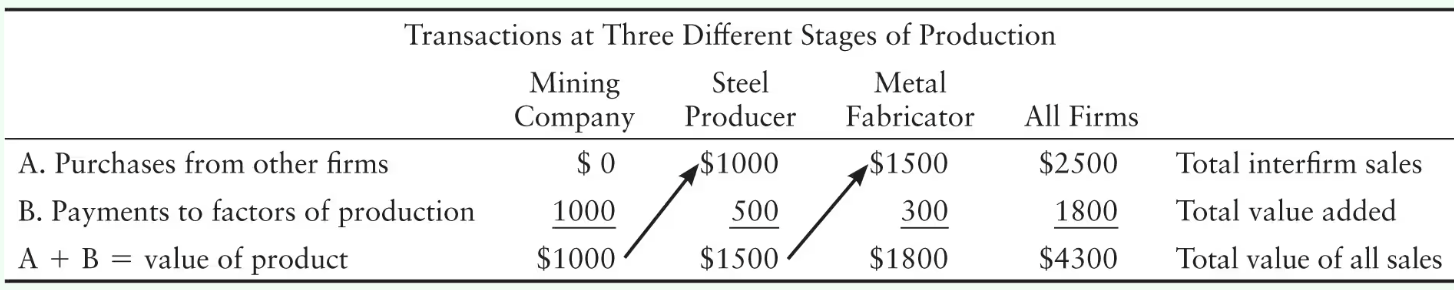
The mining company produces iron ore valued at $1,000. This firm’s value added is ______. The mining company sells iron ore to the steel producer who produces steel valued at $1,500. This firm’s value added is ______ because the value of goods has increased by _____ as a result of the firm’s activities. The steel producer sells steel to the metal fabricator who produces folding chairs valued at $1,800. This firm’s value added is ______.
The mining company produces iron ore valued at $1,000. This firm’s value added is $1,000. The mining company sells iron ore to the steel producer who produces steel valued at $1,500. This firm’s value added is $500 because the value of goods has increased by $500 as a result of the firm’s activities. The steel producer sells steel to the metal fabricator who produces folding chairs valued at $1,800. This firm’s value added is $300.
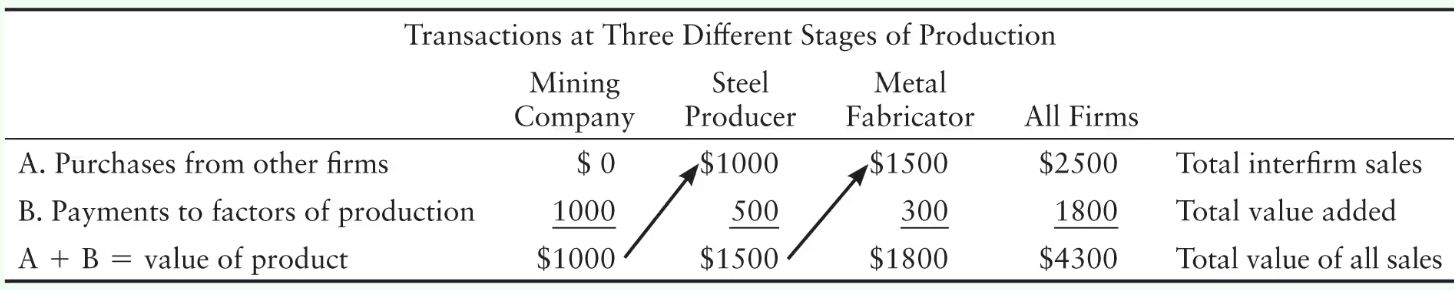
The mining company produces iron ore valued at $1,000. The mining company sells iron ore to the steel producer who produces steel valued at $1,500. The steel producer sells steel to the metal fabricator who produces folding chairs valued at $1,800. What is the value of the final goods?
$1,800
Find the value of the final goods either by counting only the sales of the last firm or by taking the sum of the values added by each firm
The value of domestic output is ______ the value of expenditure on that output. It is also ______ the total income generated by producing that output.
The value of domestic output is equal to the value of expenditure on that output. It is also equal to the total income generated by producing that output.
National income is ______ national product.
National income is equal to national product.
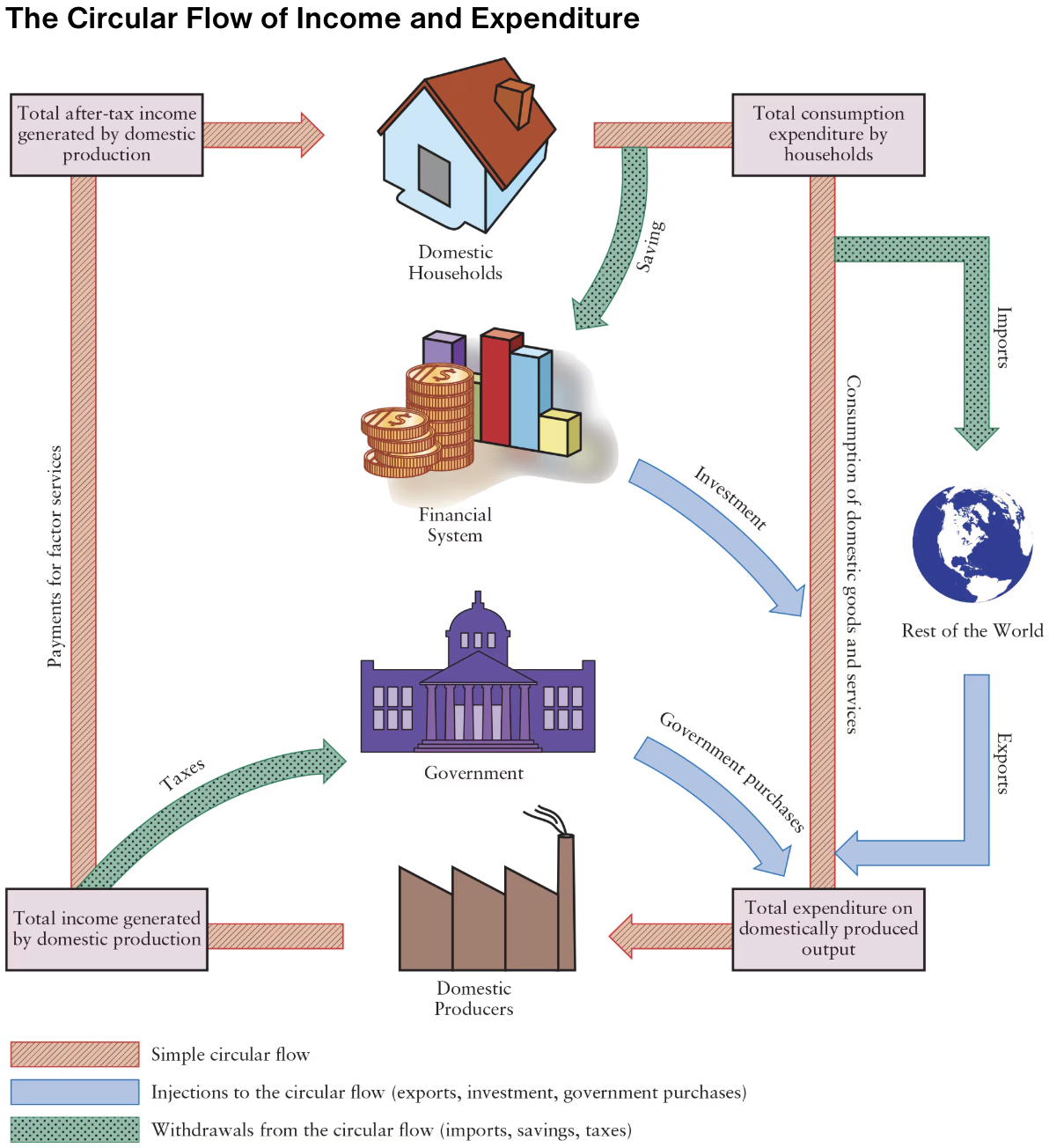
What are injections to the circular flow of income and expenditure?
Exports
Investment
Government purchases
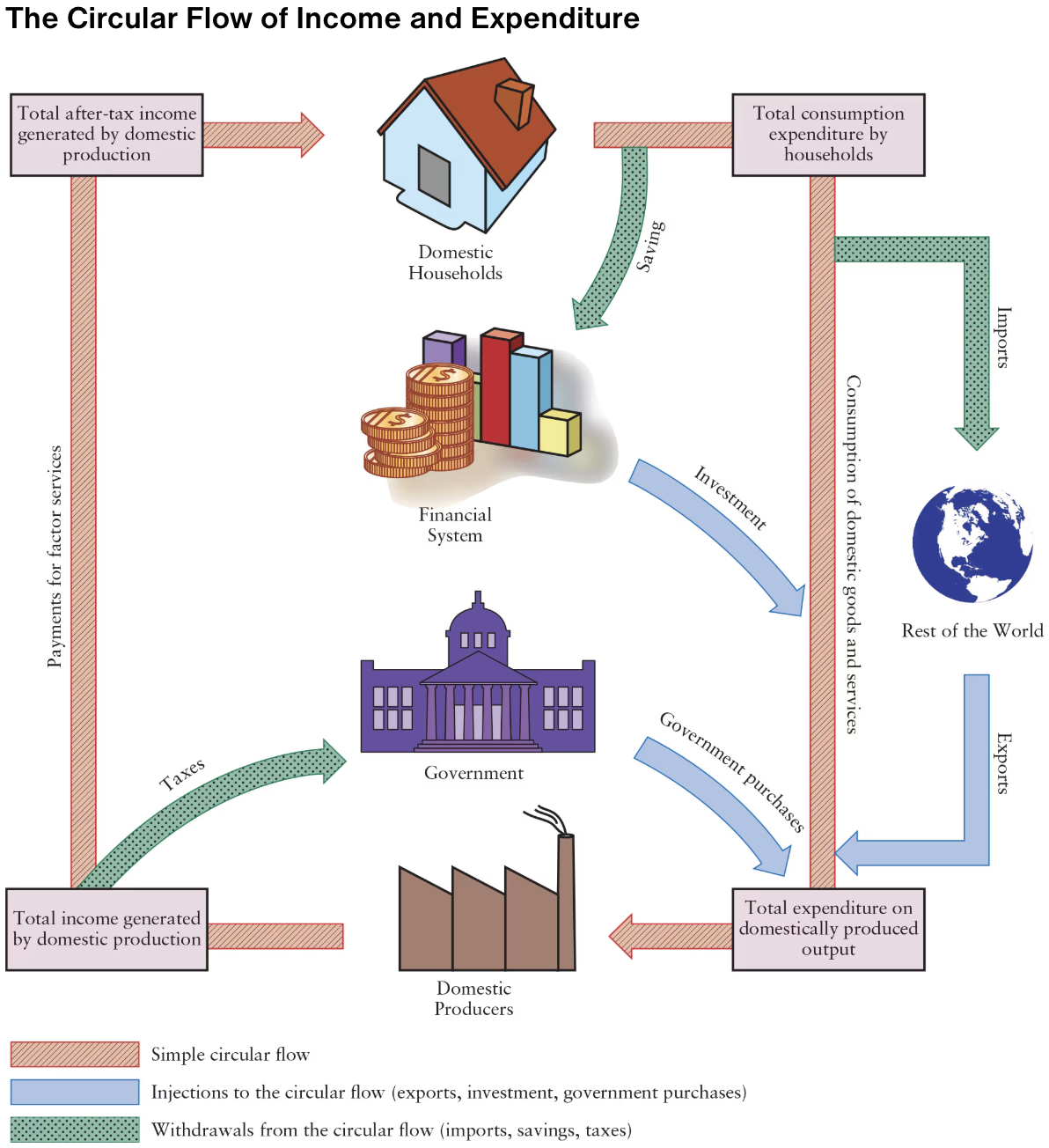
What are withdrawals from the circular flow of income and expenditure?
Imports
Saving
Taxes
What are the 3 ways of measuring national income?
Adding up the value of all domestic output (goods and services produced in the economy)
This requires the concept of value added
Adding up the total flow of expenditure on domestic output
Adding up the total flow of income generated by domestic production
Define GDP on the expenditure side.
When GDP is calculated by adding up total expenditure on components of output
Define GDP on the income side.
When GDP is calculated by adding up all the income generated by the act of production
True or False: GDP calculated from the income and expenditure sides are conceptually identical, differing only because of errors in measurement.
True
What are the 4 categories of expenditure?
Consumption (C)
Investment (I)
Government purchases (G)
Net exports (NX)
Define consumption expenditure.
Expenditure on all goods and services sold to their final users (households or businesses) during the year
Actual measured consumption expenditure is denoted by the symbol Ga
Ex: haircuts, clothing, cars
Define investment expenditure.
Expenditure on goods not for present consumption
Ex: inventories of goods produced but not yet sold; inventories of inputs purchased but not yet used in production; new plant and equipment; and residential housing (investment goods)
Define inventories.
Stocks of inputs and outputs
The accumulation of inventories counts as ______ investment because it represents goods produced but not used for current consumption.
The accumulation of inventories counts as positive investment because it represents goods produced but not used for current consumption.
The decumulation of inventories counts as ______ investment, or ______, because it represents a reduction in the stock of goods available to be sold.
The decumulation of inventories counts as negative investment, or disinvestment, because it represents a reduction in the stock of goods available to be sold.
Define capital stock.
The economy’s total quantity of capital goods accumulated through past production
Often called “plant and equipment,” referring to any manufactured aid to production used by firms
Define fixed investment (business fixed investment).
The act of investment by adding to the existing stock of capital goods (such as new plant and equipment)
Housing construction is counted as ______ expenditure rather than ______ expenditure.
Housing construction is counted as investment expenditure rather than consumption expenditure.
What are the 3 types of expenditures included in total investment?
The sum of changes in inventories (inventory accumulation)
New plant and equipment
New residential construction
______ total investment expenditure is denoted by the symbol Ia.
Actual total investment expenditure is denoted by the symbol Ia.
The ______ of capital occurs through the wear and tear of machines used in production. Thus, ______ is included in the calculation of GDP.
The depreciation of capital occurs through the wear and tear of machines used in production. Thus, depreciation is included in the calculation of GDP.
Define government purchases.
Goods and services included as part of national expenditure
Actual government purchases of goods and services are denoted by the symbol Ga
Ex: street cleaning, firefighting, paying public servants to design and implement social programs
True or False: Government output is typically valued at cost (rather than at market value).
True
Define transfer payments.
Government expenditures that are not made in exchange for goods or services
Transfer payments are not included in GDP (not included in a nation’s total output)
Ex: employment insurance, welfare, pension plans
Only government ______ of goods and services are included in GDP (not government ______).
Only government purchases of goods and services are included in GDP (not government expenditures).
Define imports.
Domestic expenditure on foreign-produced goods and services
The value of actual imports is denoted by the symbol IMa
Define exports.
Foreign expenditure on domestically produced goods and services
The value of actual exports is denoted by the symbol Xa
To calculate the total value of expenditure on Canadian output, it is necessary to include the value of Canadian ______ of goods and services.
To calculate the total value of expenditure on Canadian output, it is necessary to include the value of Canadian exports of goods and services.
Define net exports.
The value of total exports minus the value of total imports (Xa — IMa)
Net exports are denoted by the symbol NXa
When the value of exports exceeds the value of imports, net exports are ______.
When the value of Canadian exports exceeds the value of Canadian imports. net exports are positive.
When the value of imports exceeds the value of exports, net exports are ______.
When the value of imports exceeds the value of exports, net exports are negative.
What is the equation for calculating GDP from the expenditure side?
GDP = Ca + Ia + Ga + (Xa — IMa)
True or False: GDP from the expenditure side is equal to the total expenditure on domestically produced output.
True
What are the 3 main components of factor incomes?
Wages and salaries
Interest
Business profits (including rent received by property owners)
Define wages and salaries.
Payments for services of labour
Wages and salaries include all pre-tax labour earnings (payment to workers before deductions for income taxes, employment-insurance contributions, pension-fund contributions, and other employee benefits)
What types of interest are included in factor incomes?
Interest earned on bank deposits
Interest earned on loans
Miscellaneous other investment income
What types of interest are not included in factor incomes?
Interest income earned from loans to governments
Some profits are paid out as ______ to owners of firms. The rest of the profits (______) are held by firms.
Some profits are paid out as dividends to owners of firms. The rest of the profits (retained earnings) are held by firms.
Both dividends and retained earnings are included in the calculation of ______.
Both dividends and retained earnings are included in the calculation of factor incomes.
What types of profits are included in total profits?
Corporate profits
Incomes of unincorporated businesses (such as small businesses, farmers, partnerships, and professionals)
Rent paid on land and buildings
Profits of government business enterprises and Crown corporations (such as Canada Post)
______ and ______ represent the payment for the use of capital (______ for borrowed capital, and ______ for capital contributed by the owners of firms).
Interest and profits represent the payment for the use of capital (interest for borrowed capital, and profits for capital contributed by the owners of firms).
Define net domestic income at factor cost.
The sum of wages and salaries, interest, and profits
Net: meaning it excludes the value of output that is used as replacement investment
Domestic Income: meaning it is income earned by domestic factors of production
At Factor Cost: meaning it represents only part of the value of output that is paid to factors of production
What are the 2 types of non-factor payments?
Indirect taxes and subsidies
Depreciation
Define indirect tax.
A tax on the production and sale of goods and services
Ex: provincial sales taxes, excise taxes, federal Goods and Services Tax (GST)
True or False: To calculate GDP, we must include the value of output received by the government in the form of indirect taxes.
True
To calculate the market value of total output, it is necessary to ______ the value of subsidies (given to firms by the government), since subsidies allow factors incomes to ______ the market value of output.
To calculate the market value of total output, it is necessary to subtract the value of subsidies (given to firms by the government), since subsidies allow factors incomes to exceed the market value of output.
When GDP is measured from the ______ side, we add depreciation.
When GDP is measured from the income side, we add depreciation.
Define GDP from the income side.
The sum of factor incomes, plus indirect taxes (net of subsidies), plus depreciation
Define nominal GDP.
GDP valued at current prices
Define real GDP.
GDP valued at base-period prices, measured in constant dollars
______ GDP tells us about the money value of output. ______ GDP tells us about the quantity of physical output.
Nominal GDP tells us about the money value of output. Real GDP tells us about the quantity of physical output.
What is the formula for calculating the GDP deflator?
GPD Deflator = Nominal GDP (GDP at Current Prices) / Real GDP (GDP at Base-Period Prices) X 100
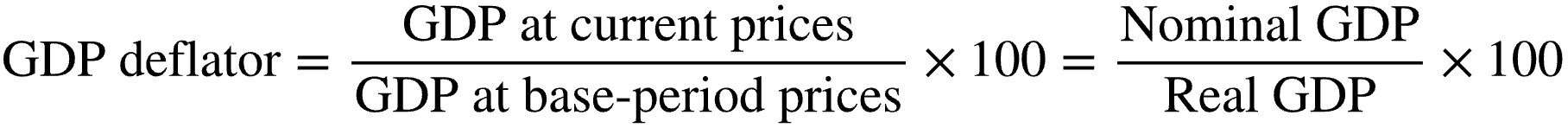
Define GDP deflator.
A price index measuring the change in prices of all goods and services produced by the economy
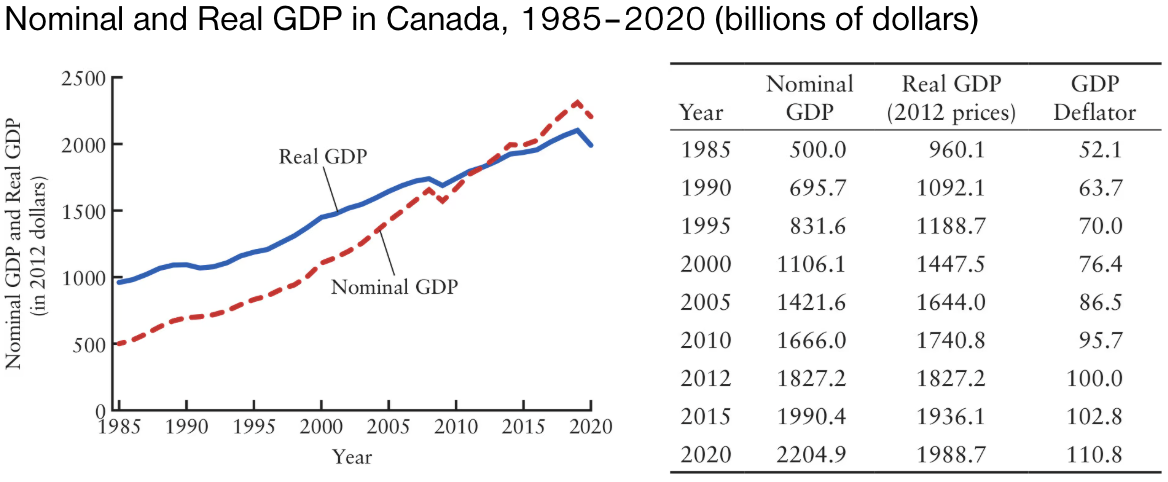
In 2020, Canadian nominal GDP was ______% higher than in 1990. This increase was due to a ______% increase in prices (as calculated by the percentage change in GDP deflator) and ______% increase in real GDP.
In 2020, Canadian nominal GDP was 216.9% higher than in 1990. This increase was due to a 73.9% increase in prices (as calculated by the percentage change in GDP deflator) and 82.1% increase in real GDP.
Canadian Nominal GDP: 2204.9 (in 2020) — 695.7 (in 1990) = 1509.2
(1509.2 / 695.7) X 100 = 216.9% increase
Price (GDP Deflator): 110.8 — 63.7 = 47.1
(47.1 / 63.7) X 100 = 73.9% increase
Real GDP: 1988.7 — 1092.1 = 896.6
(896.6 / 1092.1) X 100 = 82.1% increase
True or False: If nominal GDP and real GDP change by different amounts over a given time period, then prices must have changed.
True
Ex: if nominal GDP increases by 6% and real GDP increases by 4%, averages prices must have increased by 2%
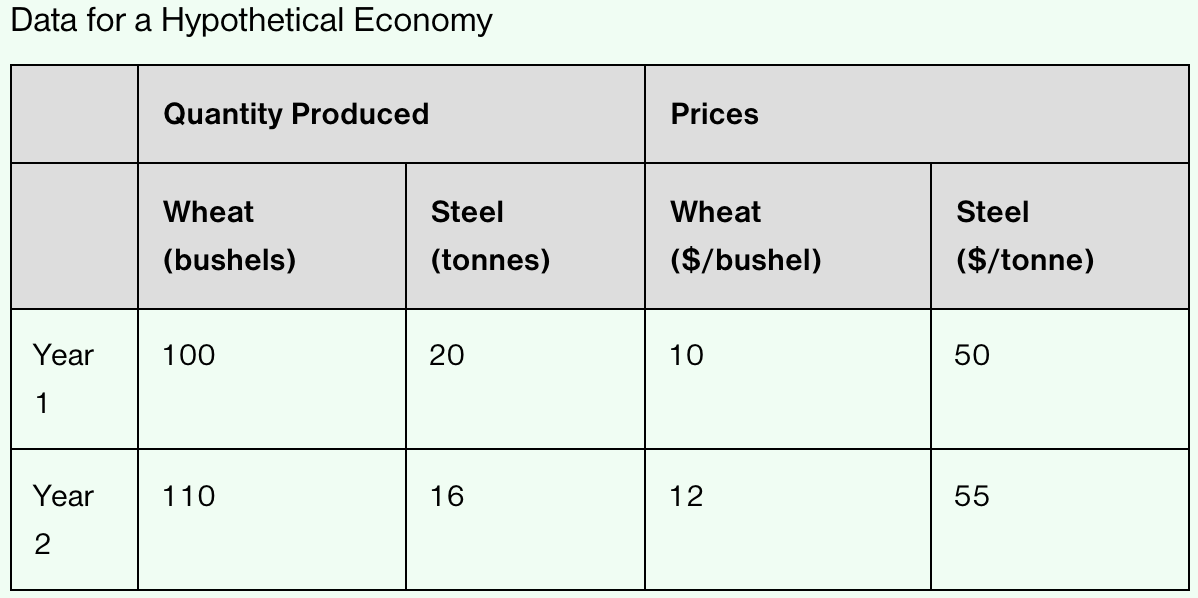
What was the nominal GDP in Year 1 and in Year 2?
Nominal GDP in Year 1: (100 X 10) + (20 X 50) = $2,000
Nominal GDP in Year 2: (110 X 12) + (16 X 55) = $2,200
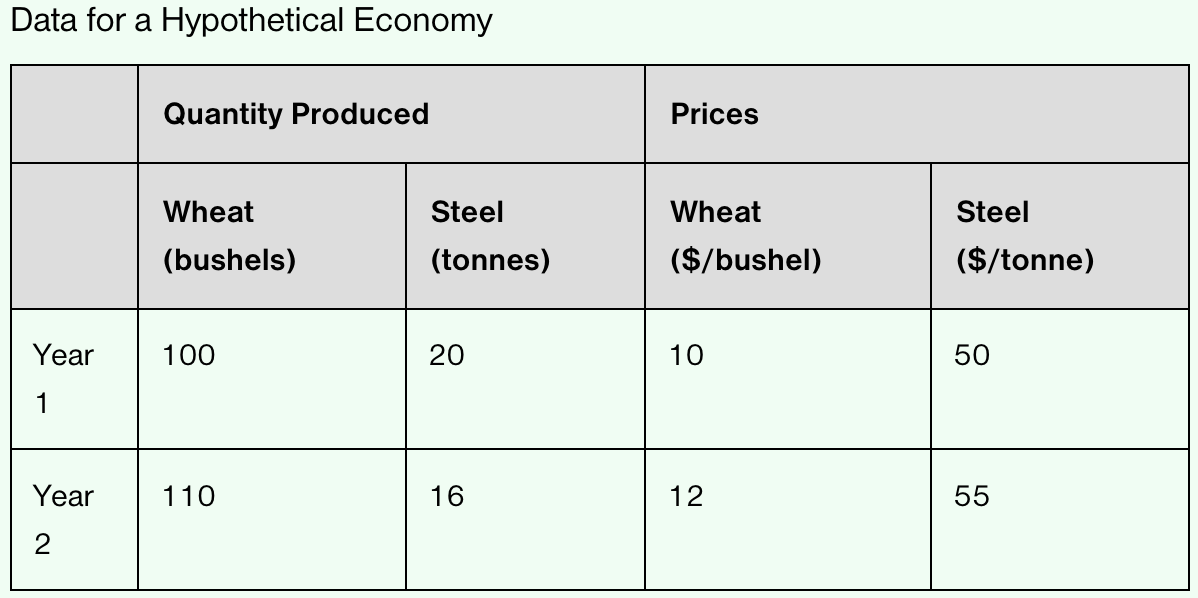
What was the real GDP in Year 1 and in Year 2 (calculated using Year 2 prices)?
Real GDP in Year 1: (100 X 12) + (20 X 55) = $2,300
Real GDP in Year 2: (110 X 12) + (16 X 55) = $2,200
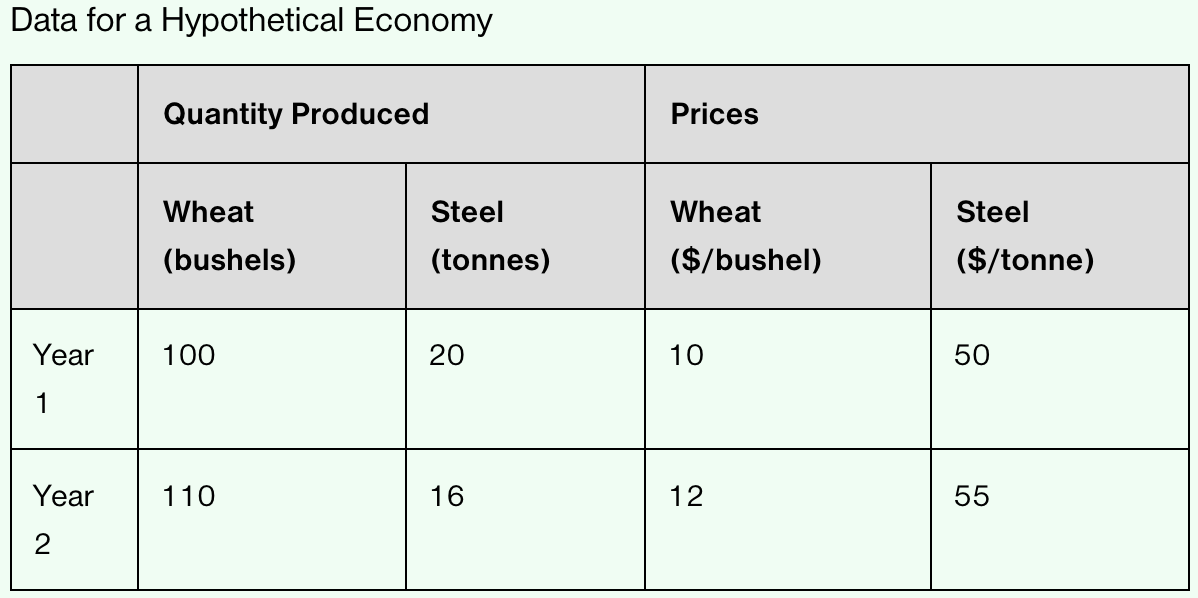
What is the GDP deflator in Year 1 and in Year 2?
GPD Deflator = Nominal GDP / Real GPD X 100
GDP Deflator in Year 1:
Nominal GDP in Year 1: (100 X 10) + (20 X 50) = $2,000
Real GDP in Year 1: (100 X 12) + (20 X 55) = $2,300
GDP Deflator: (2,000 / 2,300) X 100 = 86.96
GDP Deflator in Year 2:
Nominal GDP in Year 2: (110 X 12) + (16 X 55) = $2,200
Real GDP in Year 2: (110 X 12) + (16 X 55) = $2,200
GDP Deflator: (2,200 / 2,200) X 100 = 100.00
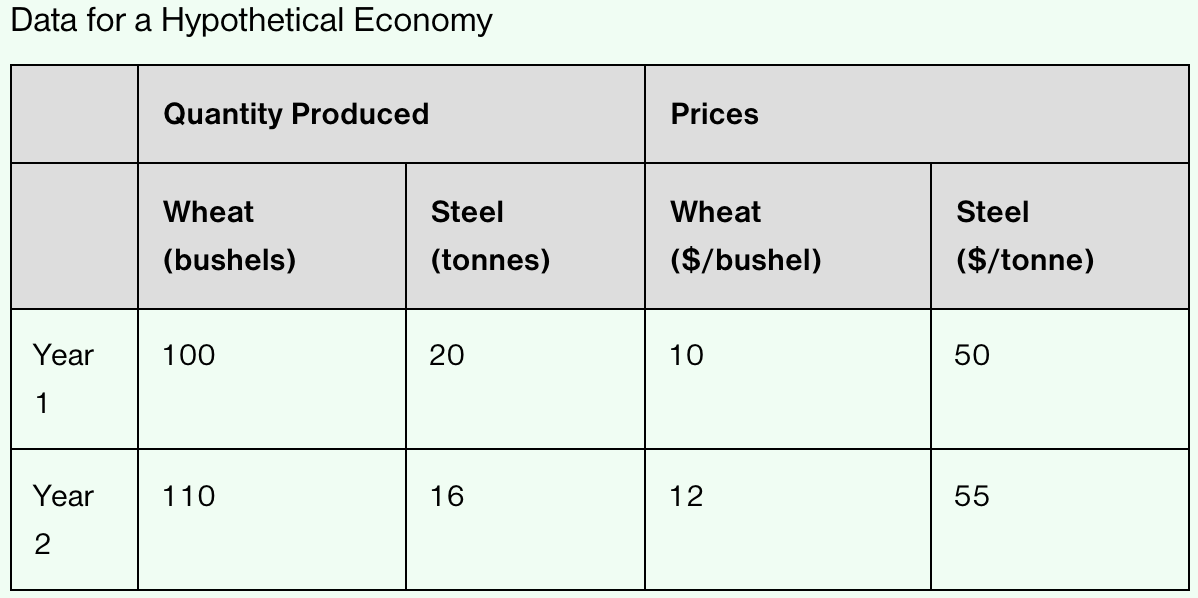
If the GDP deflator of Year 1 is 86.96 and the GDP deflator of Year 2 is 100.00, what is the percentage change in GDP deflator between Year 1 and Year 2?
% Δ GDP Deflator: (100.00 - 86.96) / 86.96 X 100 = 15%
Movements in the ______ measure the change in average price of consumer goods, whereas movements in the ______ reflect the change in average price of goods produced in the nation.
Movements in the CPI measure the change in average price of consumer goods, whereas movements in the GDP deflator reflect the change in average price of goods produced in the nation.
True or False: Changes in relative prices may cause the GDP deflator and CPI (Consumer Price Index) to move in different ways.
True
What are the 5 types of economic activities omitted from the GDP?
Illegal activities
Ex: illegal gambling, prostitution, drug trade
Underground economy (transactions not reported for tax purposes)
Home production, volunteering, and leisure (non-market activities)
Free products in the digital world
Economic “bads”
Ex: environmental damage, pollution, addiction to social media