Science Topic Test - Genetics
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
15/03/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
which of the following organelles contains coding instructions for the production of enzymes that control the activities of cells?
-cell wall
-cytoplasm
-nucleus
-vacuoles
correct answer is the nucleus, all ‘coding’ instructions for protein synthesis are found in the nucleus, where DNA is stored.
in eukaryotes, DNA is mostly located in the:
-cell membrane
-endoplasmic reticulum
-nucleus
-cytoplasm
trick question! DNA is ALWAYS in the nucleus.
which of the following triplets could NOT be found in a DNA molecule?
-TCG
-CAG
-CCG
-CUC
CUC is the answer, as ‘U’ is not in DNA-it is a uracil, which is found in RNA instead.
the process of cell division that produces the gametes in the sex organs is?
meiosis is a specialized type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, resulting in the formation of four haploid gametes.
in pea plants, tall stems (T) are dominant over short stems (t). the phenotype for a pea with the gene combination Tt is?
-tall stems
-middle-sized stems
-short stems
-TT
-Tt
-tt
the answer is tall stems, as the presence of at least one dominant allele (T) results in the dominant phenotype.
in humans, black hair (B) is dominant over red hair (b), the genotype of a person with red hair is what?
The genotype of a person with red hair must have two recessive alleles, represented as 'bb'.
red hair is recessive to black hair, which of the following is possible if two parents with black hair produce a child with red hair?
-the mother has a homozygous dominant genotype
-the father has a homozygous dominant genotype
-both parents have the heterozygous genotype
the answer is “both parents have the heterozygous genotype”, as each parent must contribute a recessive allele (b) for the child to express the recessive phenotype.
when a pure-bred black (FB FB) domestic fowl is crossed with a pure-bred white (FW FW) domestic fowl, the hybrid (FB FW) offspring is speckles, or splashed white due to the co-dominance of these traits. when a pure-bred black domestic fowl is crossed with a speckled domestic fowl, the chance of that offspring being speckled is?
-0%
-25%
-50%
-75%
-100%
The chance of the offspring being speckled is 50%, as the black fowl (FB FB) can produce only FB alleles, while the speckled fowl (FB FW) can produce both FB and FW alleles, resulting in a 1:1 ratio of black to speckled offspring.
the human body cells normally contain 46 chromosomes, the number of chromosomes in the fertilized egg that forms a new zygote is?
46 chromosomes, as the fertilized egg receives 23 chromosomes from each parent, restoring the diploid number.
the alternative forms of each gene are called?
alleles are the alternative forms of each gene that can exist at a specific locus on a chromosome.
are all mutations harmful?
Not all mutations are harmful; some can be neutral or even beneficial, contributing to genetic diversity and evolution.
name two sex-linked traits that affect humans
Hemophilia and color blindness.
Both are recessive genes located on the x chromosome; males are more likely to inherit these traits due to having only one X chromosome.
Females would need to inherit TWO copies of the recessive allele to possess
in humans, 22 of the matched pairs of chromosomes are called autosomes, what is an autosome?
an autosome is any chromosome that is NOT a sex chromosome, being 22 pair of the 46 that humans have.
what type of chromosomes makes up the 23rd pair?
sex chromosomes
being (x,y) for males, and (x,x) for females.
which sex chromosome is smaller?
the ‘Y’ chromosome.
which sex chromosome carries more genes?
the 'X' chromosome.
how can mutation be useful to a species?
Mutations can introduce new traits that may provide a survival advantage, allowing species to adapt to changing environments or resist diseases.
what two of three parts of a DNA molecule are the same in each nucleotide?
-sugar
-phosphate
-nitrogenous base
The sugar and phosphate groups are consistent across all nucleotides, while the nitrogenous base varies.
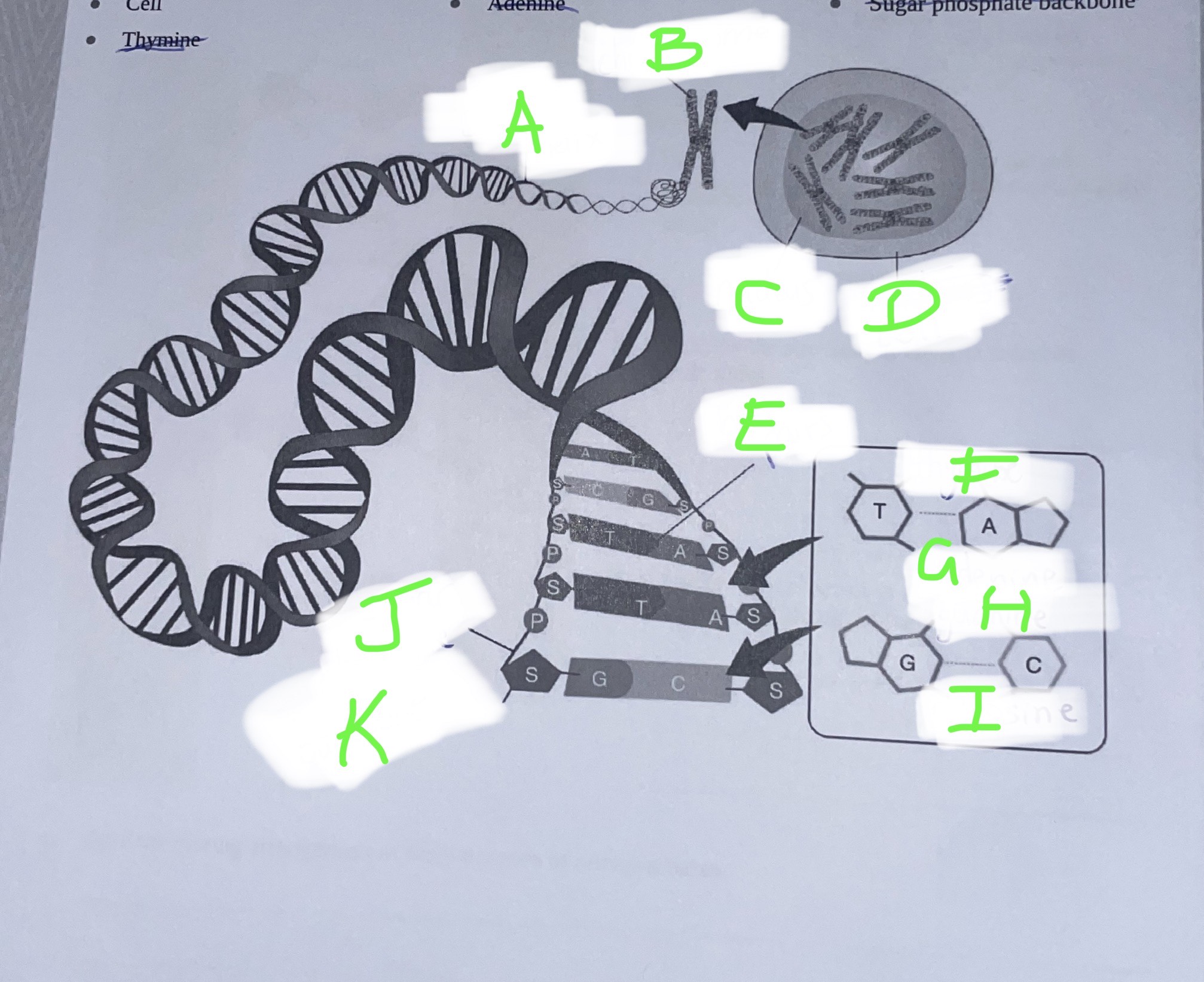
Label this DNA diagram, answers:
-chromosome
-base pairs
-cytosine
-DNA helix
-Guanine
-Nucleus
-Cell
-Adenine
-Sugar phosphate backbone
-Thymine
A- DNA helix
B- chromosome
C- nucleus
D- cell
E- base pairs
F- thymine
G- adenine
H- guanine
I- cytosine
J- sugar phosphate
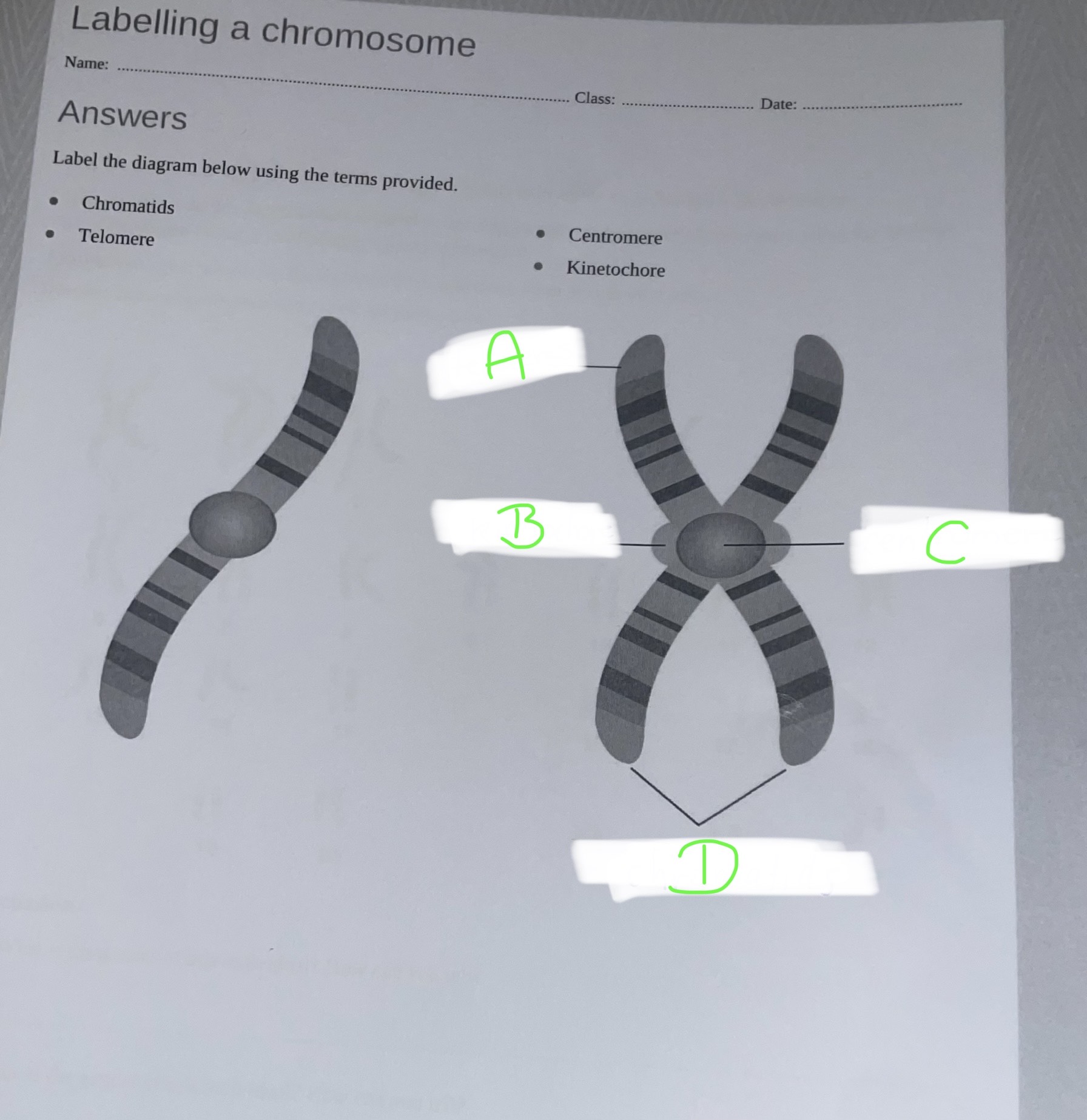
Label the chromosome, answers: chromatids, telomere, centromere, kinetochore
A- telomeres
B- kinetochore
C- centromere
D- chromatids

Complete the table comparing meiosis and mitosis
1-2
2-4
3-diploid
4-haploid
5-no
6-yes
7-identical
8-non-identical
9-growth/repair
10-reproduction
11-interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
12-prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I, prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, telophase II
explain the link between meiosis and gender
meiosis is the process that produces gametes, which carry the sex chromosomes that determine gender.
what is a pedigree diagram?
-a pedigree diagram shows the genetic relationships and inheritance patterns within a family over several generations
-males represented as squares
-females represented as circles
-lines connect parents to offspring
-shaded symbols indicate individuals expressing a trait/disorder being observed
What is DNA made of?
DNA is made of repeating nucleotides
What is a nucleotide made of?
a nucleotide is made of three components,
-nitrogenous base
-deoxyribose sugar
-phosphate group
what are the four nitrogenous bases, which go together?
-adenine (A)
-guanine (G)
-cytosine (C)
-thymine (T)
A+T
G+C
what is protein synthesis?
protein synthesis is a vital biological process that converts genetic information into functional proteins through transcription and translation.
identify the roles of each of the following in protein synthesis:
-ribosome
-tRNA
-RNA polymerase
-amino acids
-ribosome is the site of protein synthesis
-tRNA carries specific amino acids to ribosome
-RNA polymerase transcribes DNA to RNA
-amino acids are the building blocks of protein
what is a eukartyote?
organelles in cells
what is a diploid?
two sets of chromosomes
what is a haploid?
one set of chromosomes
what is genetic mutation?
when chromosomes don’t properly split during replication, the cells that take less during this split recieve incorrect information.
what is CRISPR?
CRISPR is a cheap and precise genetic engineering tool, in the form of bacteria. This bacteria cuts and adds/removes genes from DNA, modifying DNA and passing it down through generations as usual.
what is horizontal gene transfer?
the process in which an organism transfers genetic material to another organism that is not its offspring.
there are three methods
transformation : involves uptake of free DNA from the environment, bacteria can take in DNA to incorporate it into its own genes.
transduction : involves viruses infecting bacteria, a virus can accidentally pick up DNA from one bacterium and transfer it from another when it infects a new bacterium.
conjugation : where two bacteria connect through pili and transfer DNA directly to each other, involving plasmids which are small DNA circles.
what is genetic drift?
a random change in gene variants over time, occurs due to chance rather than natural selection.
what happens in the four stages of mitosis
interphase (beginning)
prophase
metaphase
anaphase
telophase
prophase - chromosomes double
metaphase- chromosomes align at equatorial plate
anaphase-chromatids separate
telophase- nuclei reform
NOTE: for meiosis, this same process occurs, except there is no interphase between phase 1 and 2, the process repeats twice, resulting in four cells.
what is microevolution?
small-scale evolutionary changes in a population (mutation), driven by natural selection, genetic drift, and gene flow.
what is macroevolution?
large-scale evolutionary changes over long periods, leading to new species and biological diversity.
what were gregor mendels’s experiments?
he experimented with breeding yellow seeded and green seeded pea plants, discovering that yellow is the dominant seed colour and round seeds were dominant.