Ch.3: Cells of the Nervous System
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
neuron
electrically excitable cells that processes & transmits info
sensory neuron
detect stimuli from environment (light, sound, touch) and transmit info to CNS
visual, touch, auditory neurons
motor neuron
control muscles and organs; transmits from CNS to muscles, whether to contract or relax
upper/lower motor neurons
interneuron
connect sensory neurons and motor neurons
help process info and coordinate activity of different parts of nervous system
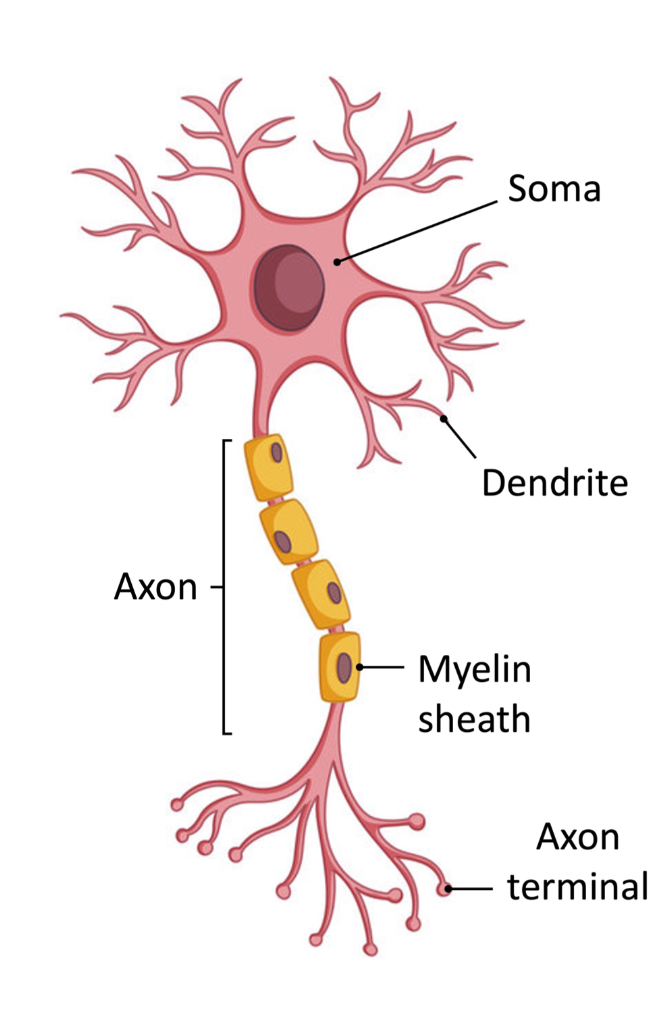
soma (cell body)
provides metabolic (energy) and synthetic (protein) support
dendrites
receives info from other neurons
dendrite spine
can rapidly change in response to environmental stimuli (neural plasticity)

axon
sends info to axon terminal
vary in length and diameter
larger diameter = faster signal
glia cells
“glue” - support neurons
non-electrical cells
Macroglia:
astrocytes
oligodendrocytes
microglia
Schwan cells
astrocytes
maintains BBB
structural & nutritional support for neurons
wraps around synapse so info. flows through and doesn’t leak
oligodendrocytes
myelinate CNS axons
multiple neurons
microglia
immune system of NS
removes dead cells and pathogens by phagocytosis
Schwann cells
myelinate neurons in PNS
one neuron
Resting Potential
-70 mV
more Na+ outside cell; more K+ inside cell → diffusion = Na goes in; K goes out
ion (leak) channels: does not use energy; passive flow
ion pump: uses energy to move ions against gradient (puts Na out and K in)
more negative inside cell = 3 Na+ = 2 K+
Action Potential
threshold = -55mV
rising phase: Na+ opens → depolarization
40mV → Na closes
falling phase: K+ gate opens
hyperpolarization: past resting potential → K gate closes

absolute refractory period
no stimulus can produce another AP during a specific time of an AP
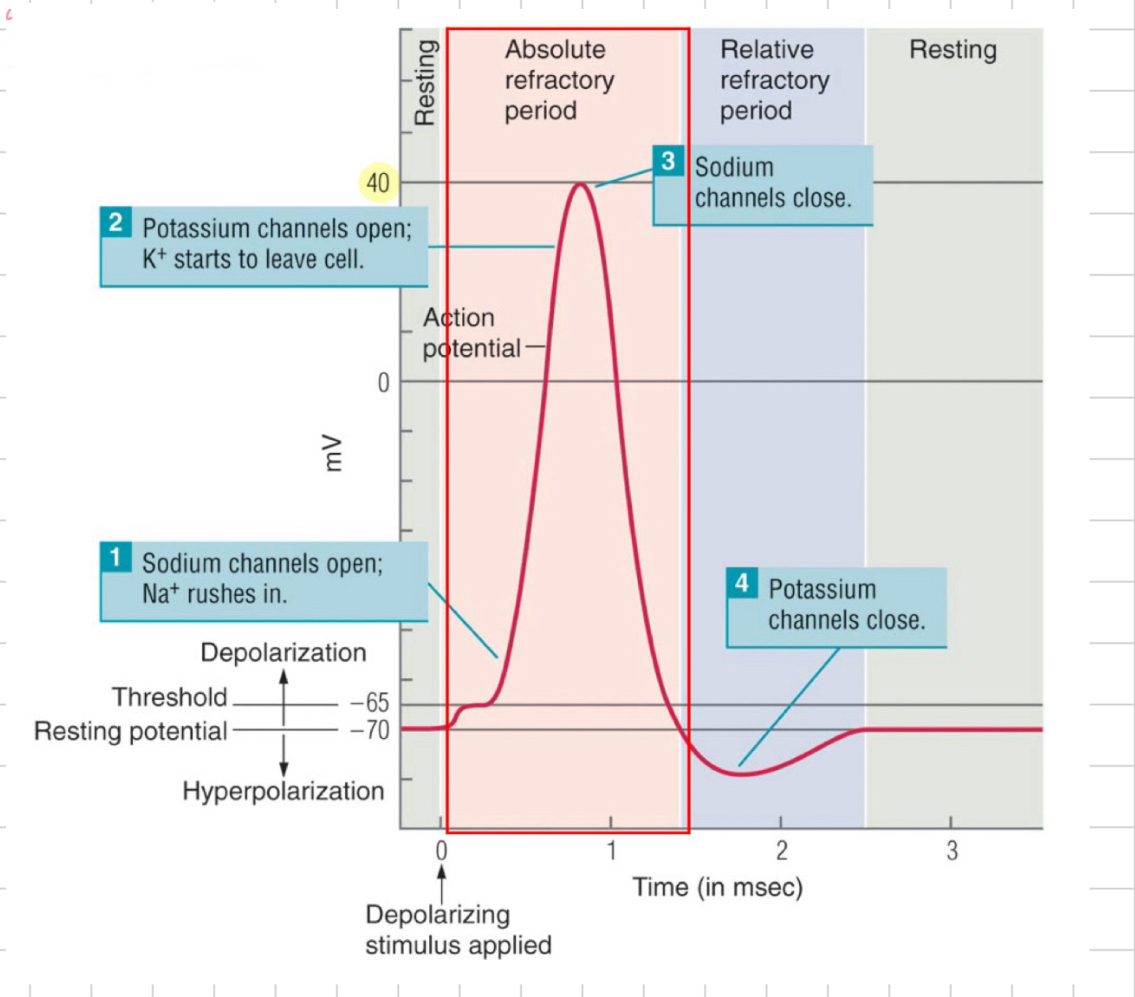
relative refractory period
cell can produce another action potential with a stronger stimulus
all-or-none
either you have an AP that reaches +40mV or you don’t (higher frequency, NOT amplitude)
Propagation of AP
myelinated = faster, jumps from node to node
unmyelinated = slower
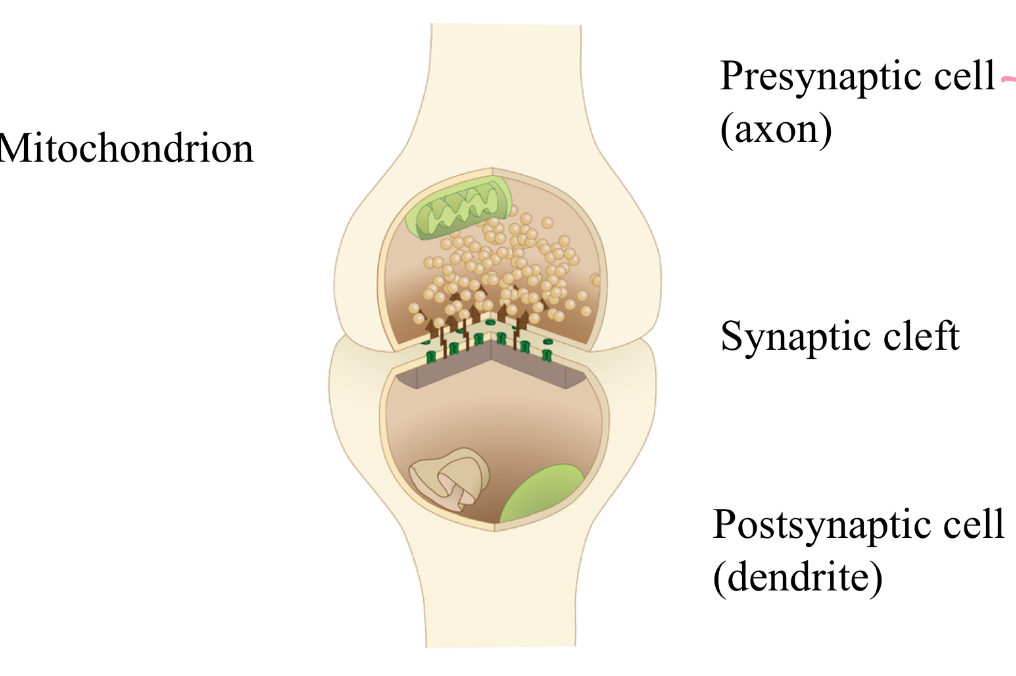
synapse
electrical synapse
small synaptic cleft
very fast
transmission by direct movement of ions
chemical synapse
large synaptic cleft
transmission takes up to many milisec.
transmission by release of neurotransmitters
neurotransmitter must bind to receptor to let ions flow
neurotransmitter in vesicles while AP reaches pre-synaptic terminal
AP opens voltage-gated Ca2+ channels, neurotransmitters released to synaptic cleft by exocytosis
transmitter binds to post-synaptic receptor (ligand-gated ion channels), ions flow
Post-synaptic response: EPSP, IPSP, neuromodulation
EPSP (excitatory post-synaptic potential)
brief electrical change to excite neuron (depolarization)
AP more likely
IPSP (inhibitory post-synaptic potential)
brief electrical change to inhibit neuron (hyperpolarization)
AP less likely
neuromodulation
changes in intracellular signaling that modulates neuronal function more long-term
post-synaptic potentials
spatial summation: inputs from multiple neuron trigger an AP
temporal summation: when large amounts of presynaptic APs trigger postsynaptic APs
Deactivation of neurotransmitters
diffusion
degradation
reuptake