Exam 1 (KIN223)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Gross anatomy refers to the study of
A) structures not visible to the unaided eye.
B) structures visible to the unaided eye.
C) structures formed by cells.
D) nasal secretions.
E) cells.
B
Which system is responsible for providing protection, regulating body temperature, and being the site of cutaneous receptors?
A) Muscular
B) Respiratory
C) Integumentary
D) Nervous
E) Urinary
C
Which of the following choices places the components of a homeostatic control system in proper order?
A) Receptor, effector, control center, stimulus
B) Effector, control center, stimulus, receptor
C) Receptor, control center, stimulus, effector
D) Stimulus, control center, effector, receptor
E) Stimulus, receptor, control center, effector
E
The word "anatomy" comes from
A) German and means "body."
B) Latin and means "to be born."
C) Greek and means "to cut apart."
D) Hebrew and means "shape."
E) Italian and means "form."
C
The axillary region is ______ to the pectoral region.
A) medial
B) proximal
C) inferior
D) distal
E) lateral
E
The directional term that means "closest to the point of attachment to the trunk" is
A) dorsal.
B) cephalic.
C) proximal.
D) distal.
E) medial.
C
The directional term that means "in back of" or "toward the back surface" is
A) proximal.
B) anterior.
C) caudal.
D) posterior.
E) cephalic.
D
Lateral to the umbilical abdominopelvic region are the _____ regions.
A) iliac
B) lumbar
C) hypochondriac
D) epigastric
E) hypogastric
B
The term that refers to the ability of organisms to react to changes in the environment is
A) development.
B) reproduction.
C) metabolism.
D) responsiveness.
E) organization.
D
What is the anatomic term for the hip region?
A) Sternal
B) Sural
C) Crural
D) Dorsal
E) Coxal
E
With a specimen in the anatomic position, you can best see the mediastinum with a _____ view.
A) inferior
B) superior
C) midsagittal
D) frontal
E) posterior
D
The correct anatomic directional term for "at the back side of the human body" is
A) dorsal.
B) ventral.
C) distal.
E) caudal.
A
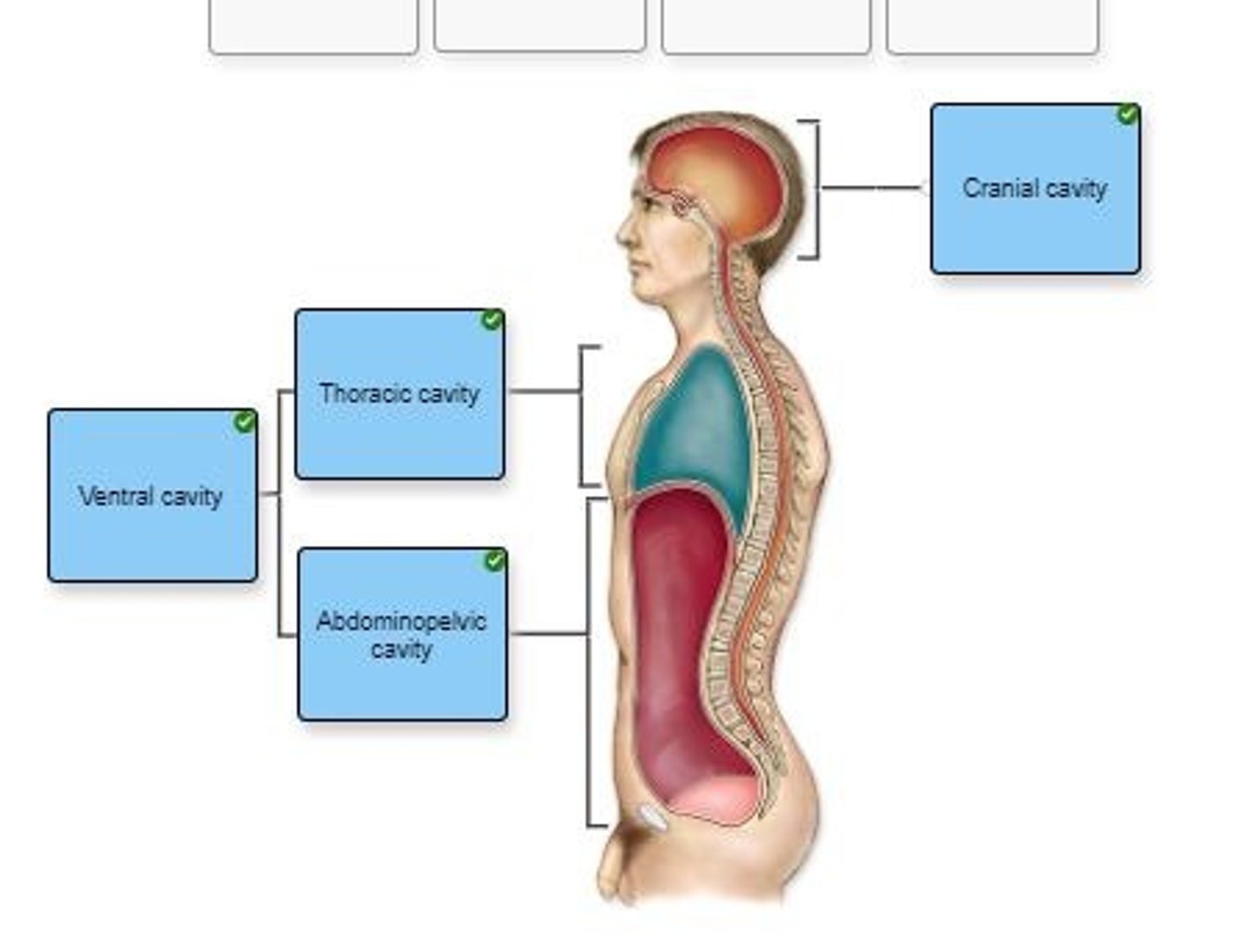
Label the body cavities in the figure.
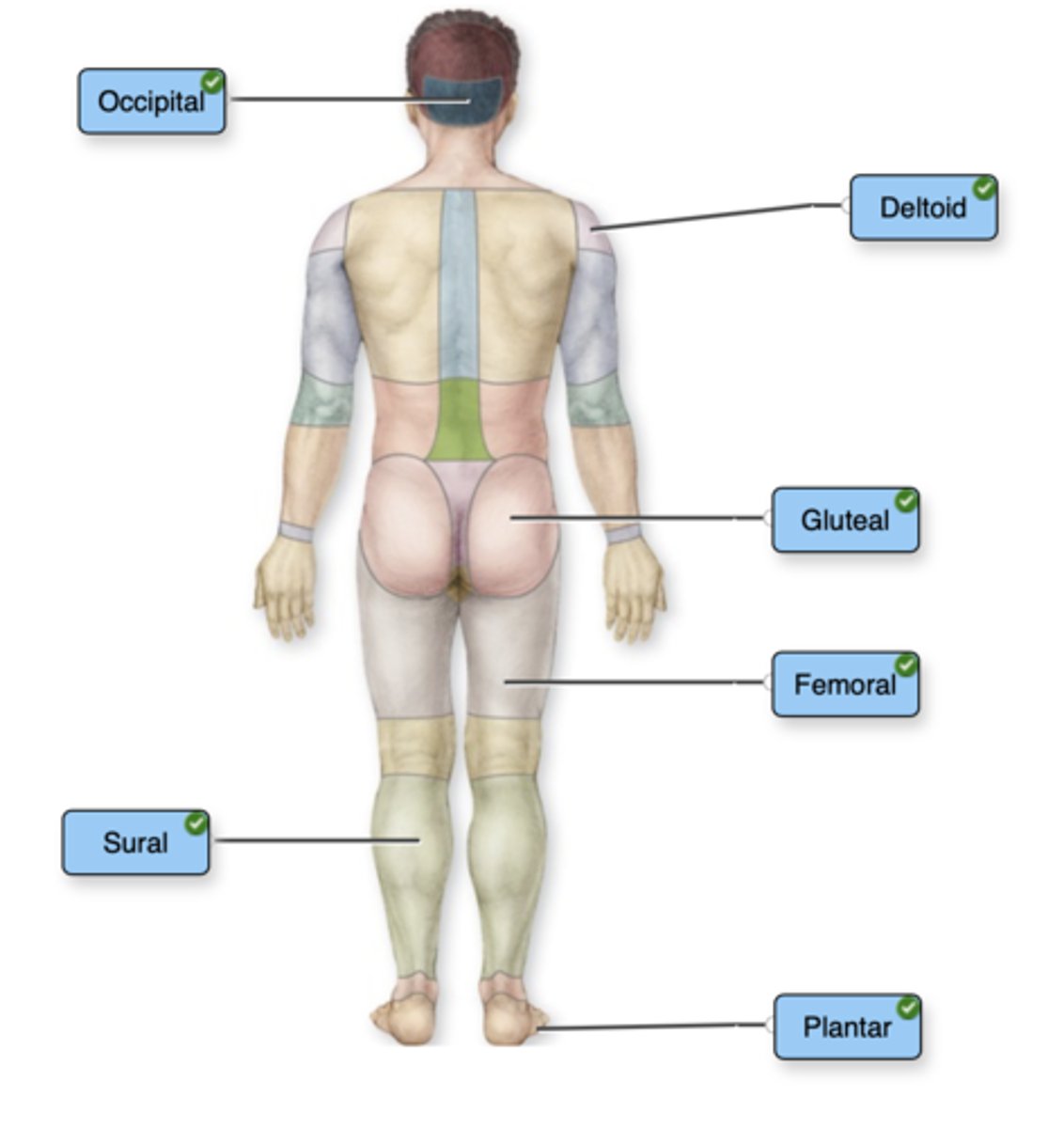
Label the body parts with the proper regional terms. Not all labels will be used.
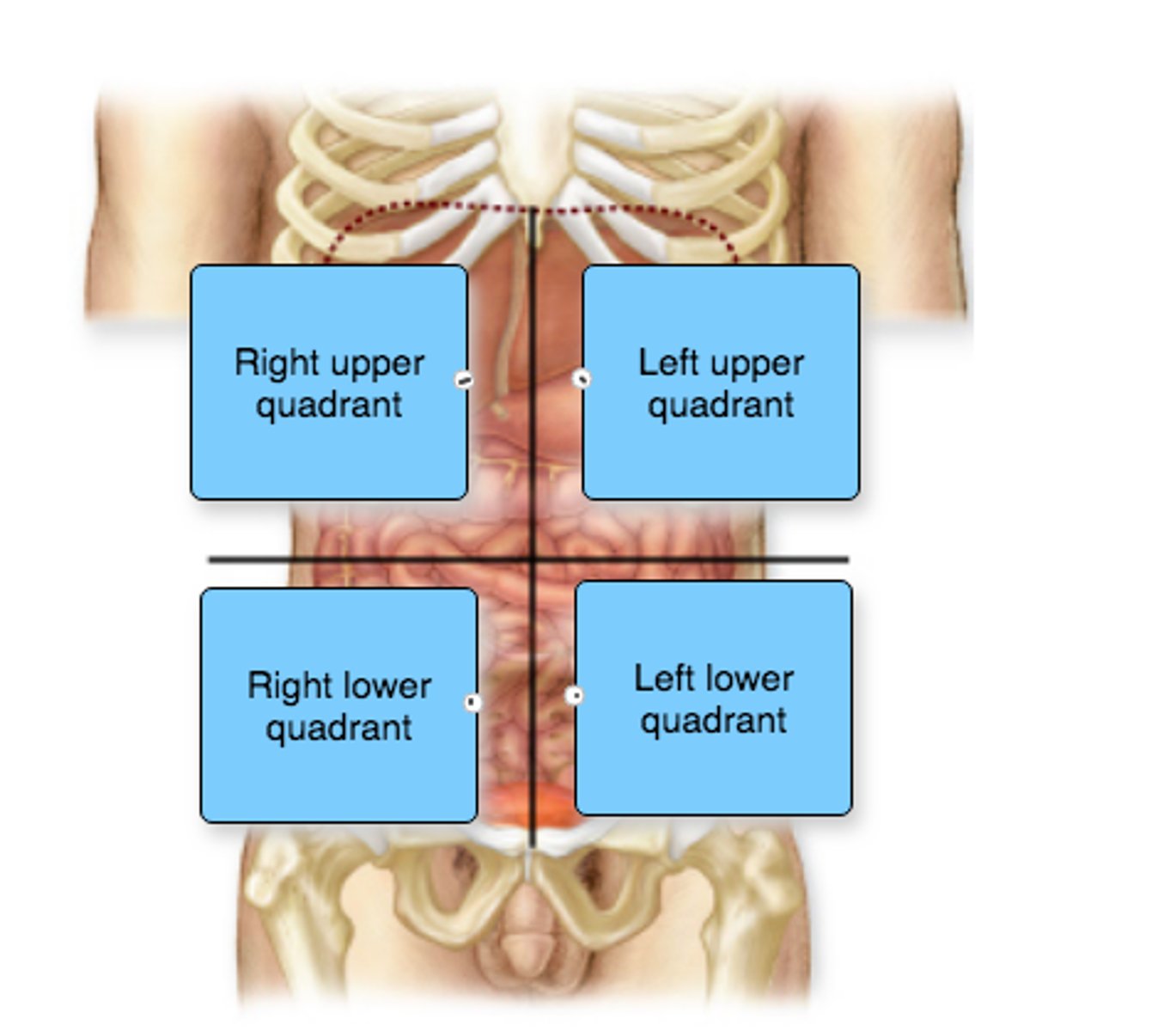
Label the abdominopelvic quadrants.
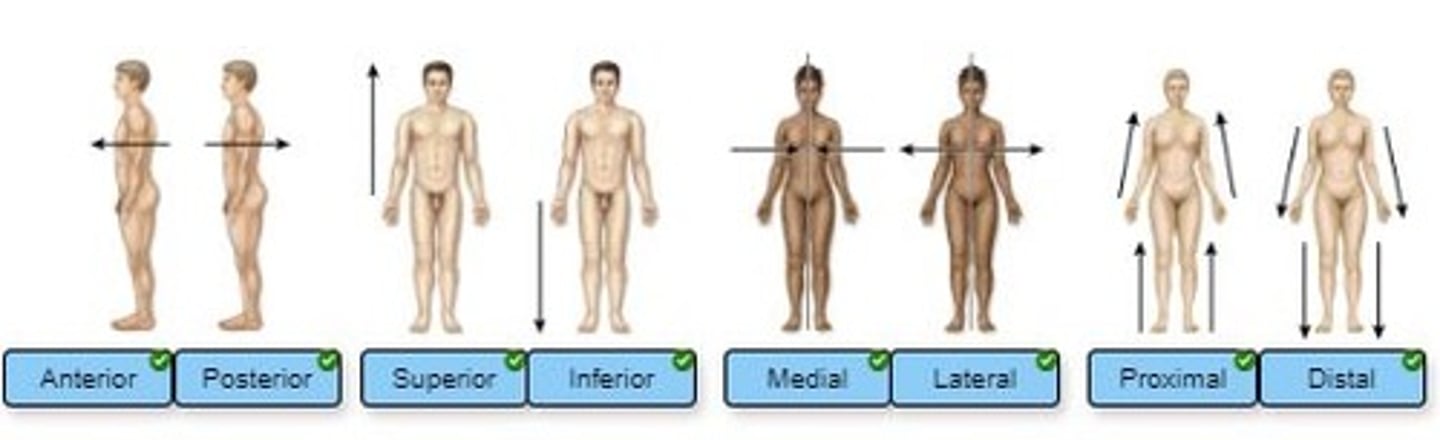
Label the image using the correct directional terms.
Water contains two hydrogen atoms bound to one oxygen atom; "H2O" is therefore water's
A) ionic compound.
B) isotope ratio.
C) molecular formula.
D) stochastic isomer.
C
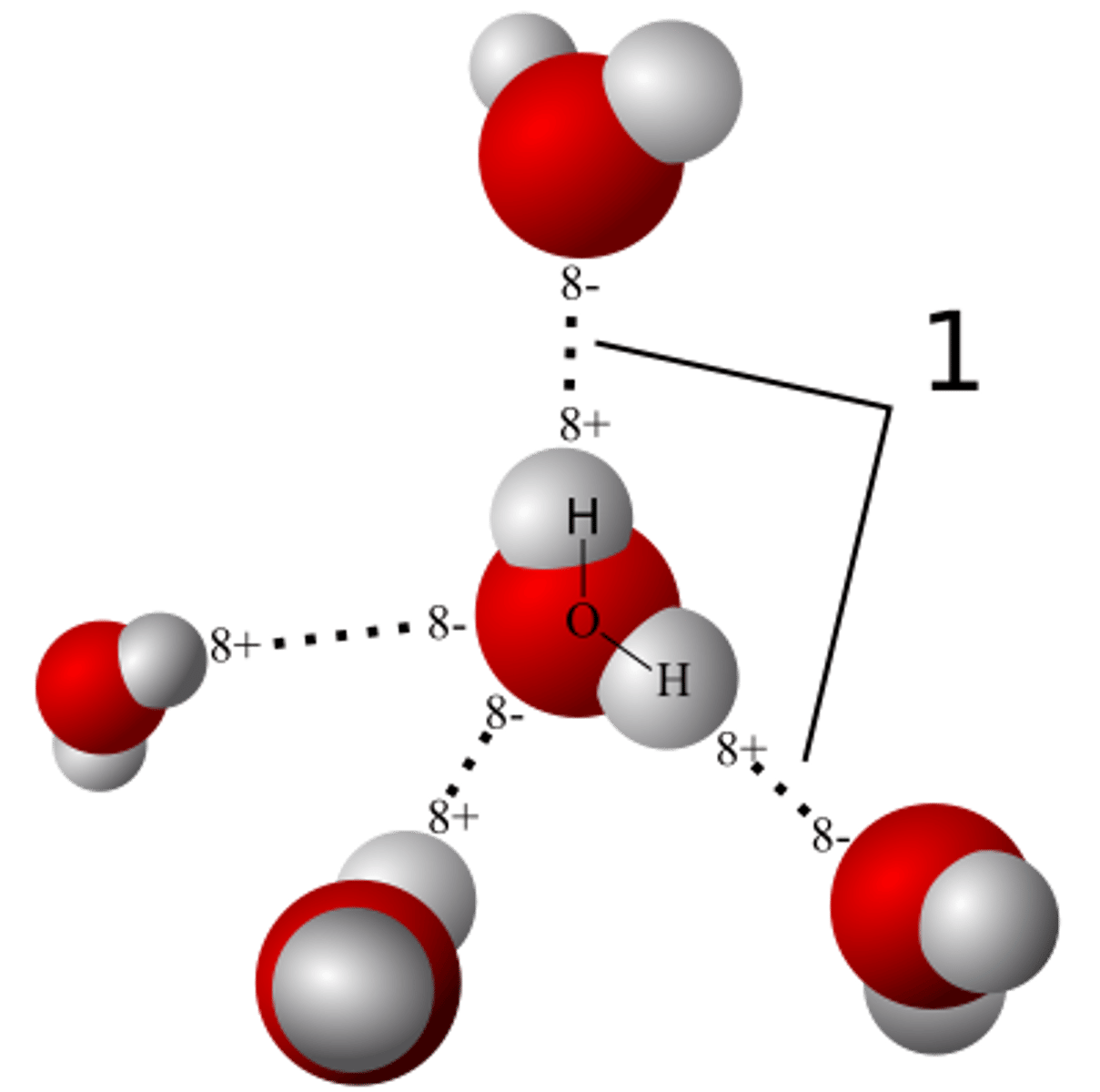
In a water molecule, each oxygen can form up to _____ hydrogen bonds with other water molecules.
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
A
Hemoglobin in blood, collagen in tendons, and enzymes in the digestive system are all examples of
A) amino acids.
B) lipids.
C) catalysts.
D) proteins.
E) carbohydrates.
D
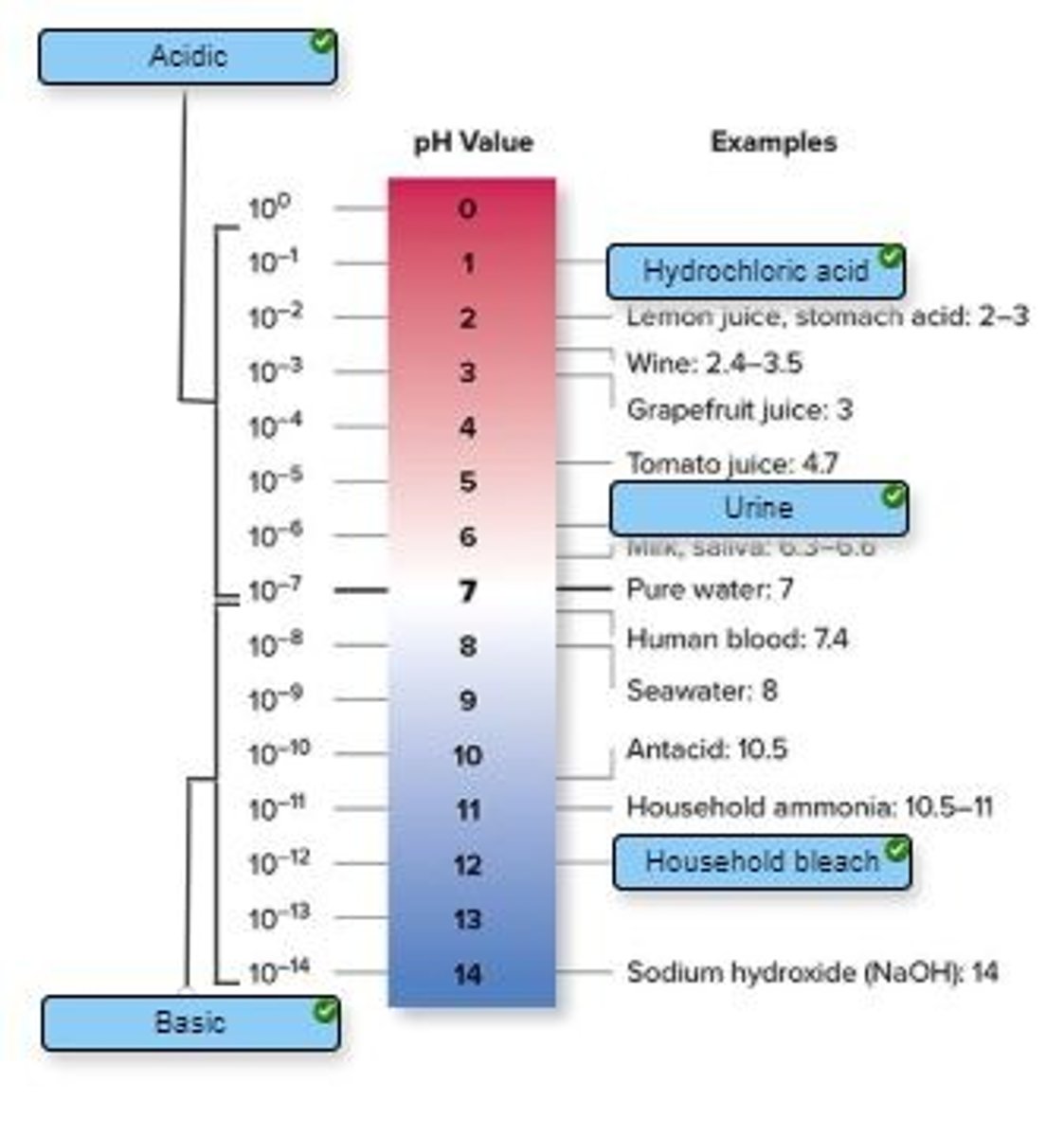
The stomach acid that enters the small intestine must be neutralized for digestion to continue properly. What will accomplish this and how will the pH change?
A) An acid; pH will increase
B) A base; pH will increase
C) A base; pH will decrease
D) An acid; pH will decrease
B
Ionic bonds involve
A) the attraction between water and salts.
B) electrostatic interactions between anions and cations.
C) the release of protons by negatively charged particles.
D) the sharing of electrons between two atoms of the same element.
B
Which of the following statements accurately describes electrons?
A) They are in orbitals outside the nucleus and have a negative charge.
B) They are found inside the nucleus and have a positive charge.
C) They are found inside the nucleus and have a negative charge.
D) They are in orbitals outside the nucleus and have a positive charge.
A
An ion is an atom or group of atoms that has
A) lost or gained an electron.
B) a different number of neutrons than most atoms of that element.
C) lost or gained a proton.
D) a biological half-life due to radioactive decay.
A
Fructose and galactose are isomers of
A) sucrose.
B) glucose.
C) maltose.
D) lactose.
B
Which of the following is not one of the four most common elements in the body?
A) Carbon
B) Nitrogen
C) Calcium
D) Oxygen
E) Hydrogen
C
How many osmoles are present in a solution of 1 M MgCl2?
A) 3 osm
B) 2 osm
C) 1 osm
D) 4 osm
A
The most common lipids in the body are
A) glycoproteins, and they are used as backbones for cell membranes.
B) eicosanoids, and they are used as hormonal messengers.
C) phospholipids, and they are used as key ingredients of bile salts.
D) steroids, and they are used as signaling molecules in inflammatory responses.
E) triglycerides, and they are used for energy storage in adipose.
E
Lipids
A) are composed of amino acids linked together.
B) are a major component of the cell membrane.
C) are polymers.
D) include DNA and RNA.
B
For every atom of carbon in a carbohydrate
A) there is approximately one atom of hydrogen.
B) there are approximately four atoms of hydrogen
C) there are approximately two atoms of hydrogen.
D) there are approximately three atoms of hydrogen.
C
When two or more polypeptide chains come together to give a protein its ultimate shape, that structure is described as the _________ structure.
A) quaternary
B) micro-
C) heme group
D) tertiary
E) secondary
A
Drag each label to the appropriate location.
Label the following diagram with the appropriate terms.
Insert the correct word or words into the sentences regarding cations and anions.
WORD BANK
right, positive, Loses, gains, negative
A) A cation is formed when an atom ____ an electron or electrons.
B) Cations have a _____ charge.
C) Anions are formed when an atom _____ an electron or electrons.
D) Anions have a _______ charge.
E) Atoms on the ______ side of the periodic table tend to become anions in order to satisfy the octet rule.
A) Loses
B) positive
C) gains
D) negative
E) right
The enzyme-substrate complex is
A) another name for the active site.
B) a pocket on the substrate that the enzyme recognizes.
C) the reactants whose chemical reaction the enzyme catalyzes.
D) the chemical structure formed when the substrate binds to the active site.
D
What is the net number of ATP molecules that can be produced from the oxidation of a glucose molecule under anaerobic conditions?
A) 4
B) 36
C) 32
D) 2
D
The electron transport chain
A) requires oxygen, and involves proteins in the cristae of mitochondria.
B) does not require oxygen, and involves proteins in the outer membrane of mitochondria.
C) requires oxygen, and involves proteins in the outer membrane of mitochondria.
D) does not require oxygen, and involves proteins in the cristae of mitochondria.
A
Reactions that release energy are called
A) exergonic reactions.
B) exothermic reactions.
C) endothermic reactions.
D) endergonic reactions.
A
The region of an enzyme into which the substrate fits is a
A) one-size-fits-all active site.
B) highly specific antibody.
C) highly specific active site.
D) one-size-fits-all antibody.
C
The coenzymes that will provide the electrons needed for the electron transport system are
A) pyruvate and NADH.
B) FAD and decarboxylase.
C) NAD and FAD+.
D) acetyl CoA and citrate.
E) NADH and FADH2.
E
The term "metabolism" refers to
A) reactions involving the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones.
B) all the chemical reactions in the body.
C) digestive system reactions that are either catabolic or exchange reactions.
D) reactions involving the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler ones.
E) reactions involving the breakdown of complex molecules or the exchange of atoms between similarly sized reactants.
B
Which of the following choices lists the order of stages of cellular respiration in proper order?
A) Glycolysis, intermediate stage, electron transport system, and the citric acid cycle
B) Citric acid cycle, glycolysis, intermediate stage, and the electron transport system
C) Glycolysis, citric acid cycle, intermediate stage, and the electron transport system
D) Citric acid cycle, electron transport chain, intermediate stage, and glycolysis
E) Glycolysis, intermediate stage, citric acid cycle, and the electron transport system
E
In a lab setting, heating a vessel full of reactants will generally
A) raise the activation energy and catalyze the reaction.
B) lower the activation energy and the kinetic energy of the reactants.
C) increase the kinetic energy of the molecules and increase the reaction rate.
D) lower the reaction rate due to the change in structure of the reactants.
E) convert products to reactants by increasing the energy requirements.
C
How many ATP are produced using the energy from each NADH?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 1
D) 4
B
Hexokinase is an enzyme involved in cellular respiration and its substrate is glucose. Considering this information, hexokinase must be located
A) in the lumen of the stomach.
B) in the lumen of the small intestine.
C) in the cytosol of cells.
D) inside the mitochondria of cells.
C
One turn of the citric acid cycle results in the formation of
A) 2 ATP, 2 NADH+, and 3 FADH.
B) 2 citrates, 4 ATP, and 3 FADH2.
C) 2 pyruvates and 2 ATP.
D) 1 ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2.
D
Building glycogen from glucose molecules is an example of
A) decomposition.
B) an exchange reaction.
C) anabolism.
D) catabolism.
C
Which of the following is a product of glycolysis?
A) Oxygen
B) Carbon dioxide
C) NAD+
D) FADH2
E) Pyruvate
E
Place the correct word into each sentence about the flow of energy in living things.
WORD BANK
potential, work, heat, motion, stored, chemical
A) Energy is the capacity to do _______. Energy comes in two forms: kinetic and potential energy.
B) Kinetic energy is the energy of _________.
C) Potential energy is ______ energy.
D) Plants convert solar energy to _______ energy (a potential energy source).
E) Chemical energy is used to do work in cells because the bonds in molecules contain _____ energy.
F) Eventually, all solar energy absorbed by plants dissipates as ________.
A) work
B) motion
C) stored
D) chemical
E) potential
F) heat
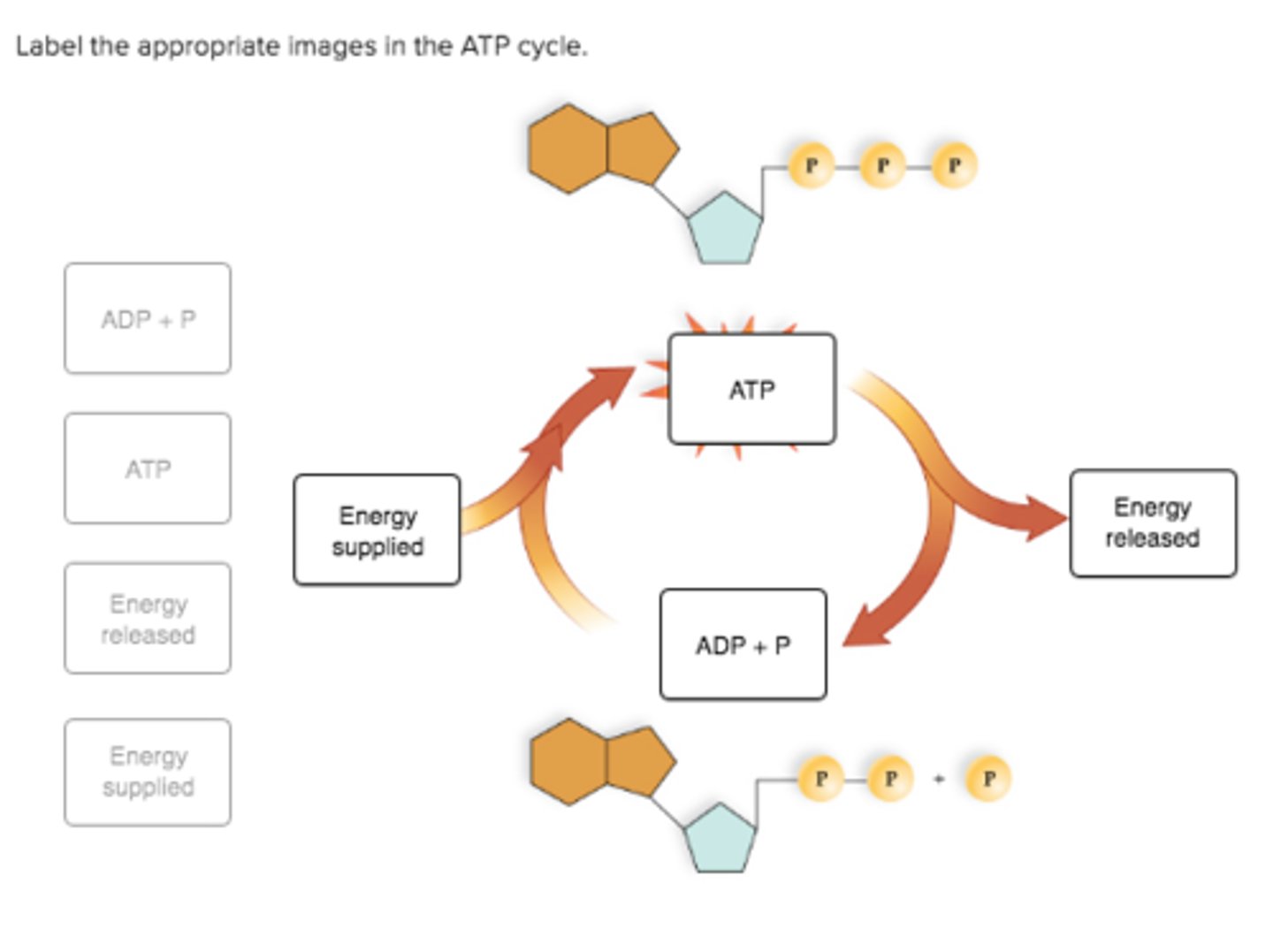
Label the appropriate images in the ATP cycle.
Place the correct word into each sentence.
WORD BANK
energy, lower, catalysts, activation
A) Enzymes act as _______, speeding up the rate of reactions.
B) Every reaction has a certain amount of _______ needed to begin.
C) This initial energy is called the energy of ________.
D) Enzymes are used to ______ the energy of activation needed to begin a reaction.
A) catalysts
B) energy
C) activation
D) lower