Honors Biology Unit 3.5: Cell Division and Mitosis
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Cell Division
process by which a single cell divides to produce two identical offspring cells
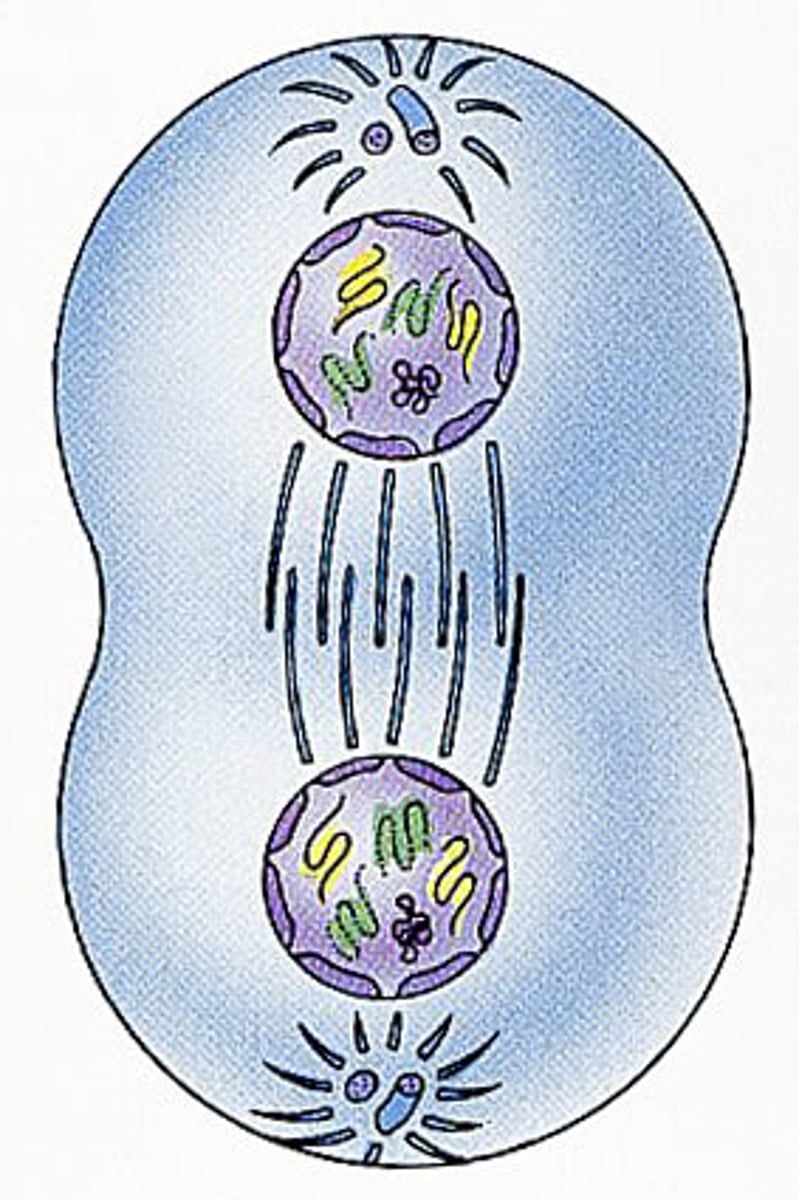
Mitosis
division of the nucleus and genetic material
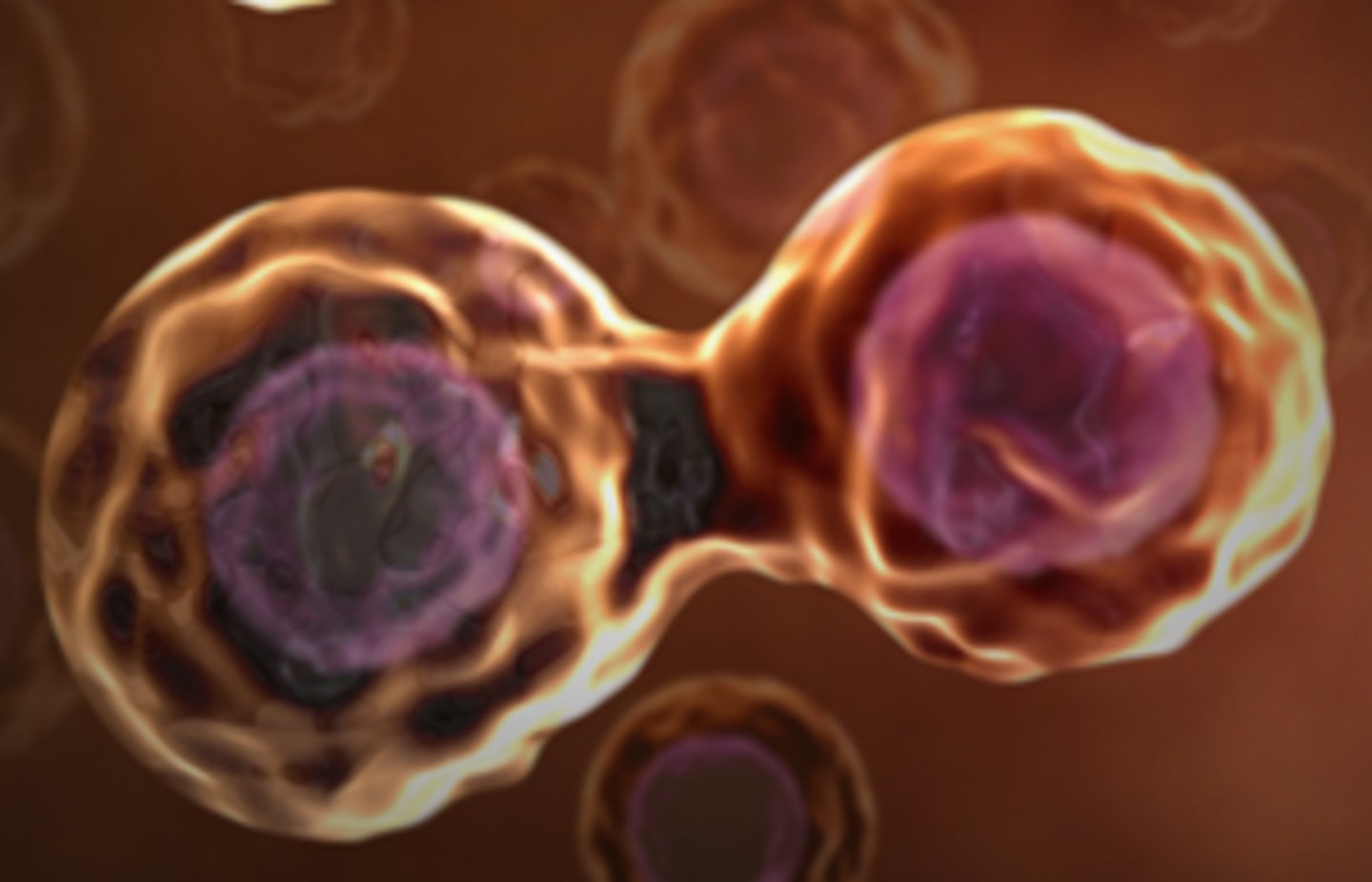
Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm
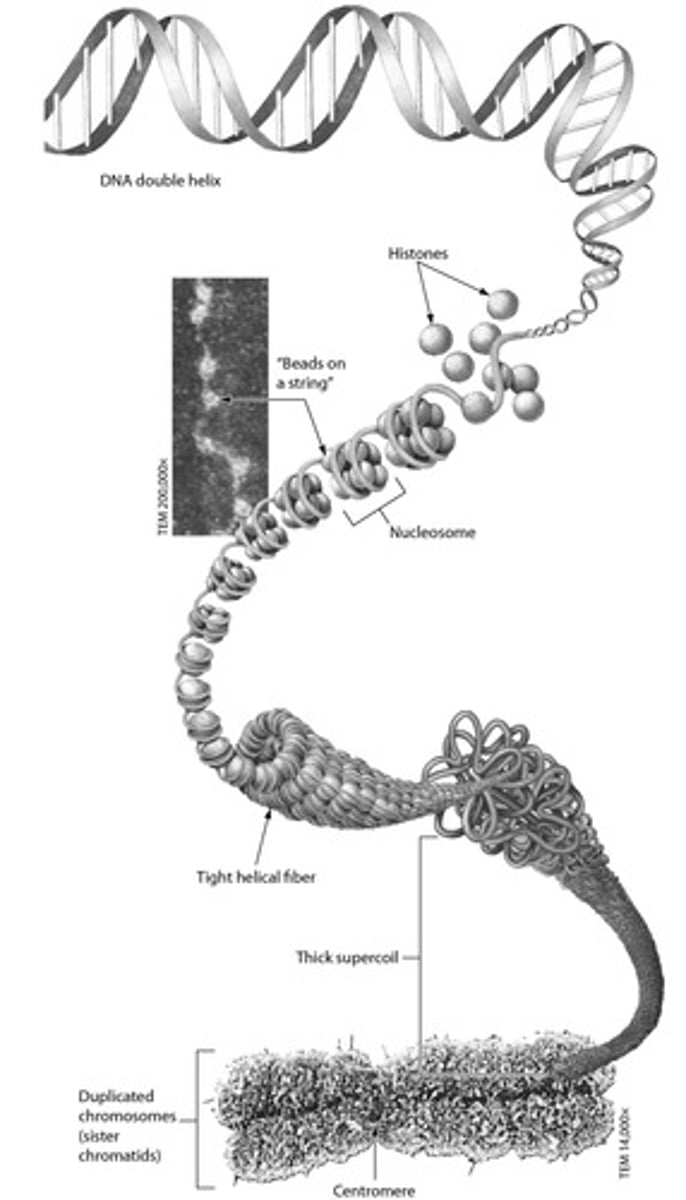
Chromosomes
condensed structures in the nucleus that carry genetic material in the form of DNA
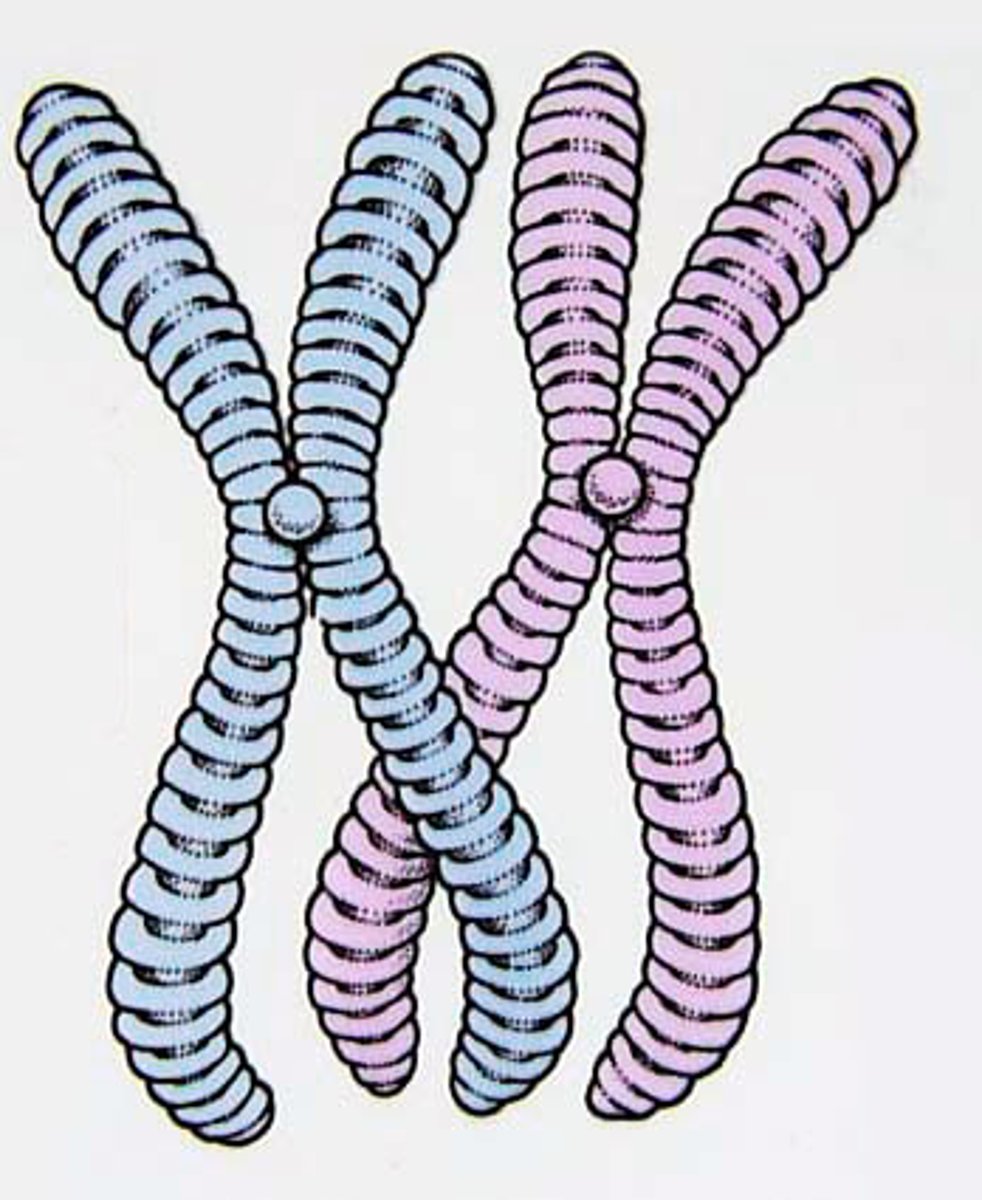
Sister Chromatids
the paired structures that make up an X-shaped, replicated chromosome
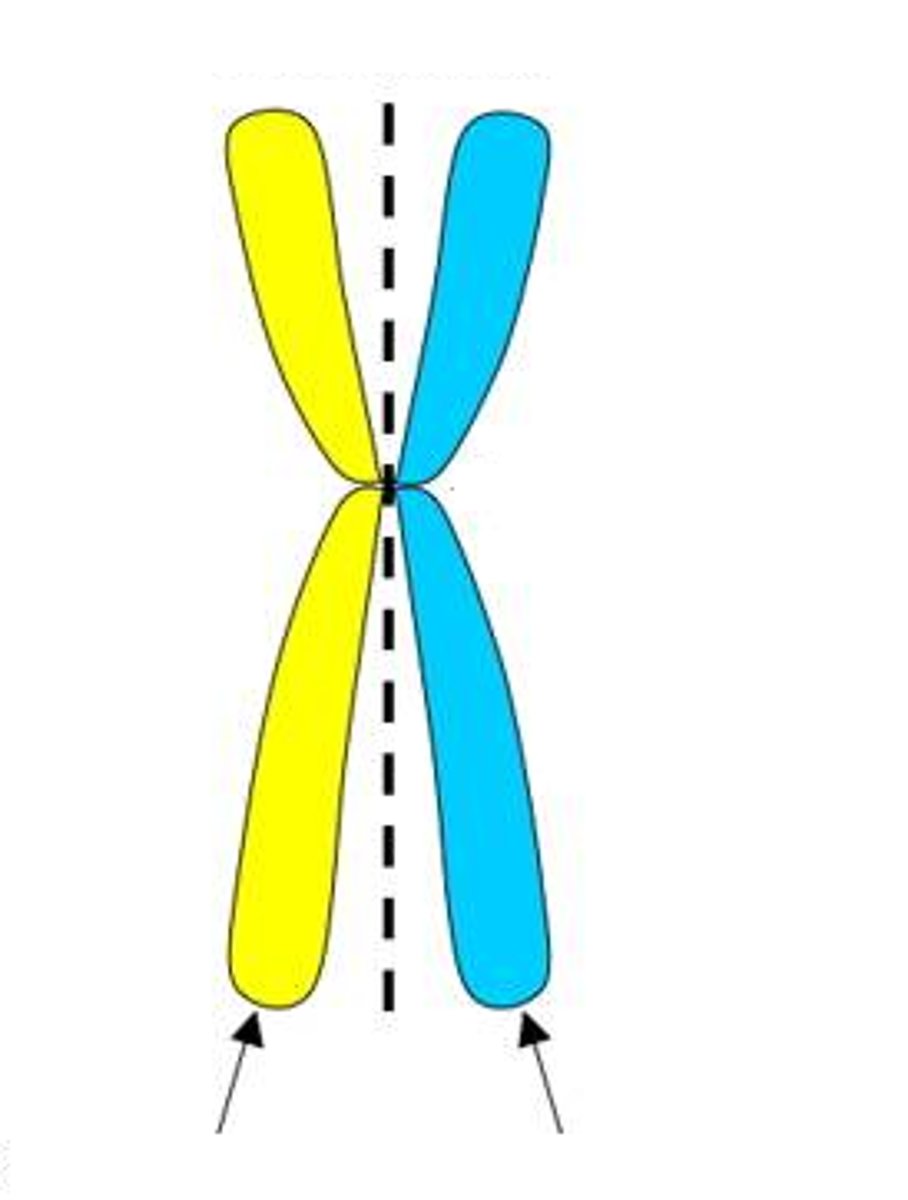
Centromere
near the center of a chromosome, spot where the sister chromatids are attached
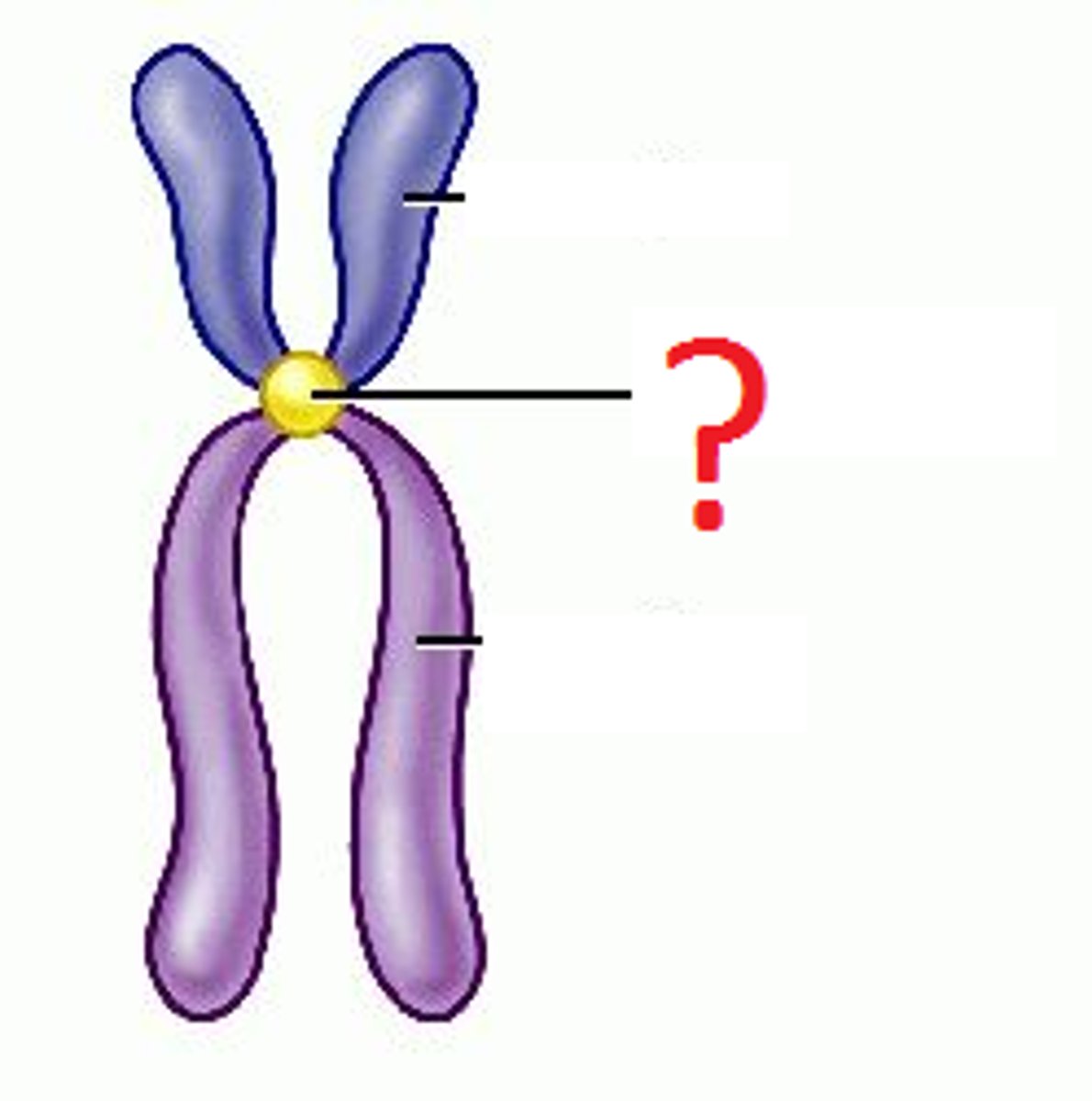
Chromatin
long, uncondensed strands of DNA wrapped around proteins called histones
Histone Proteins
DNA coils around these proteins in chromatin
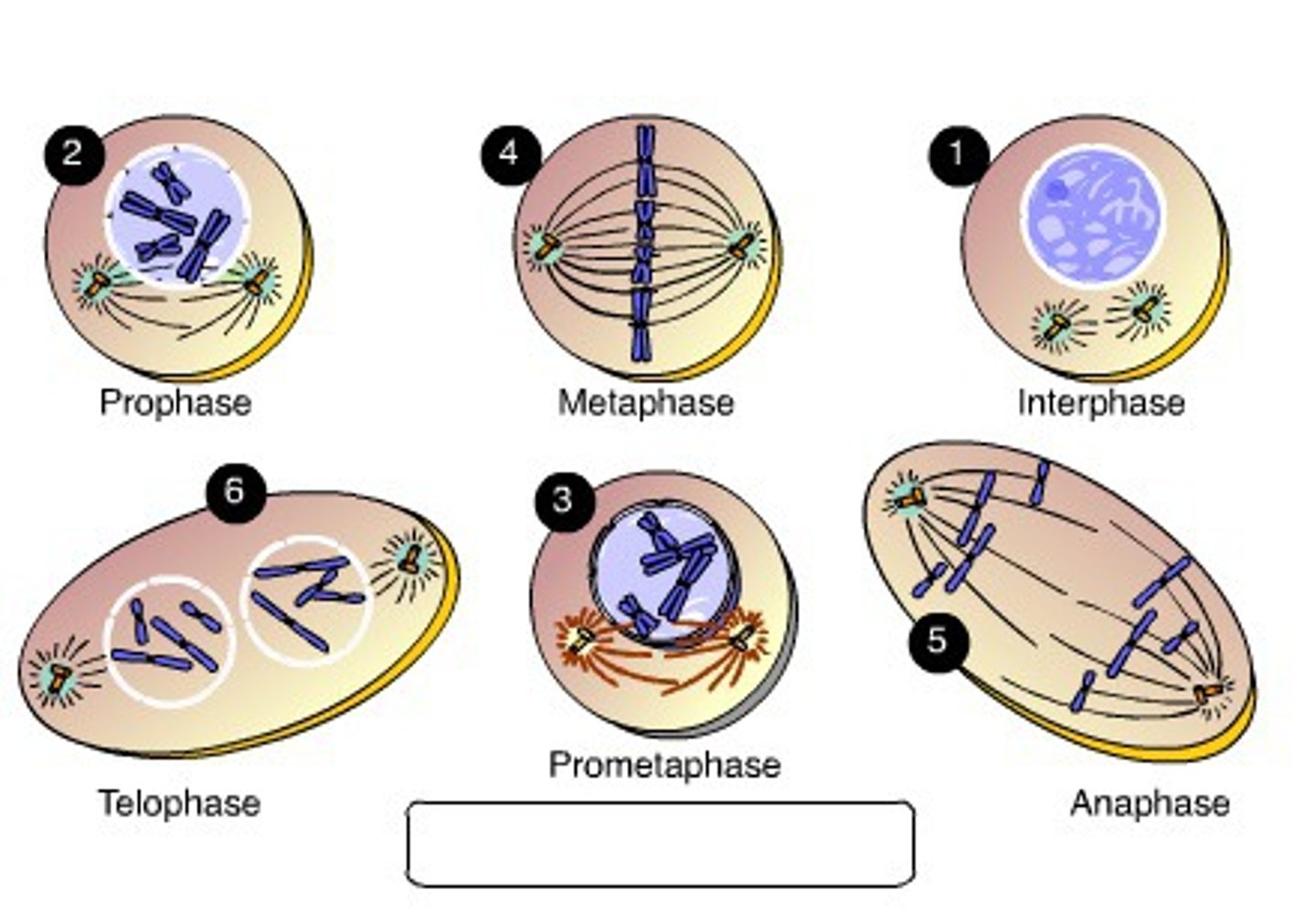
Interphase
longest phase of a cell's life cycle; when it carries out its regular activities; growth and DNA replication occur
G1 phase
sub-stage of interphase in which the cell increases in size, organelles increase in number
S phase
sub-stage of interphase in which cell makes a copy of the DNA in its nucleus; centrioles replicate
G2 phase
sub-stage of interphase in which additional cell growth occurs; cell is preparing to enter mitosis
Prophase
First phase of mitosis in which duplicated chromosomes condense and mitotic spindle fibers begin to form; nuclear membrane disappears
Spindle Fibers
Special microtubules made by centrioles which connect to centromeres and pull apart chromosomes.
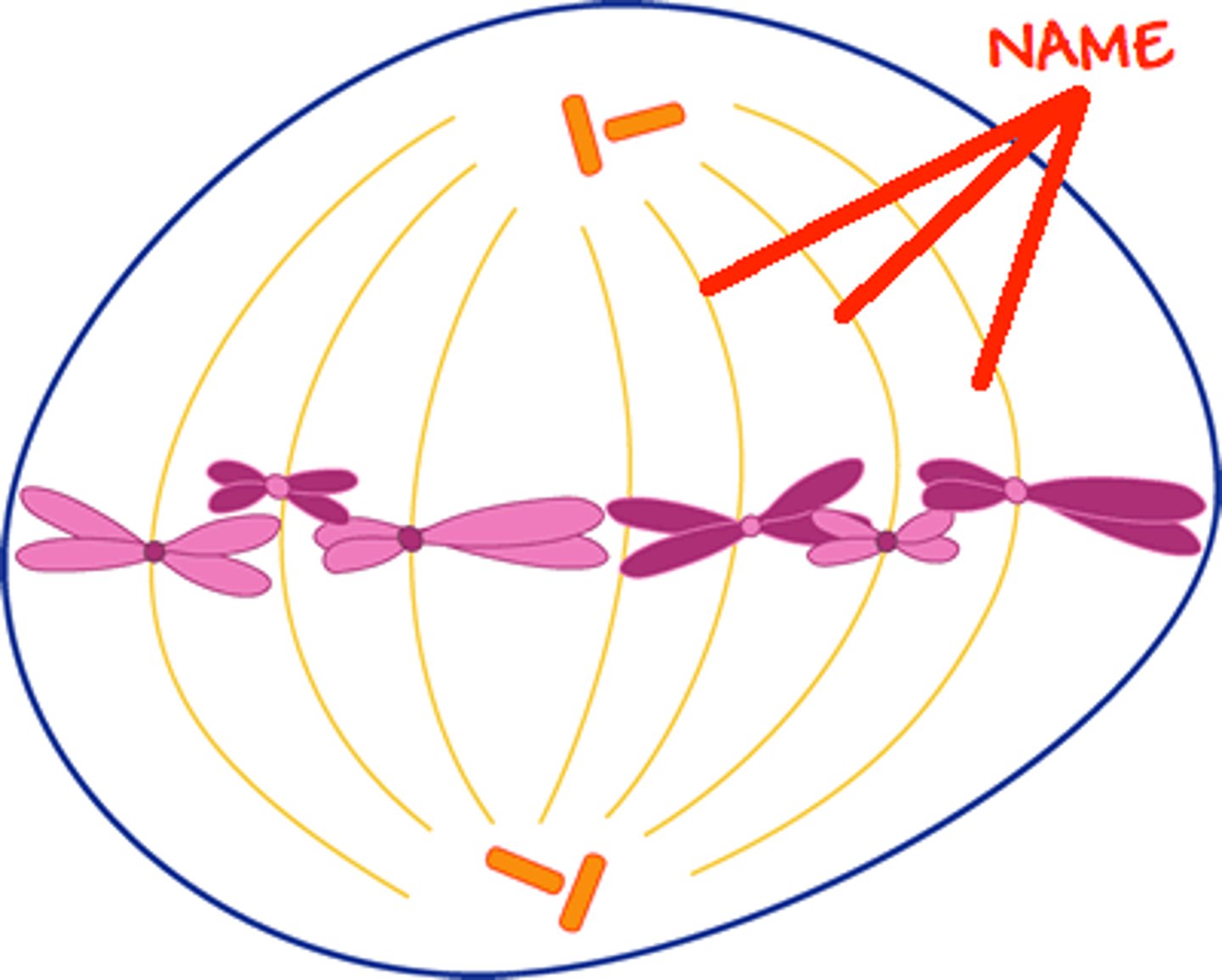
Asters
Microtubules and fibers that radiate out from the centrioles and anchor them in mitosis
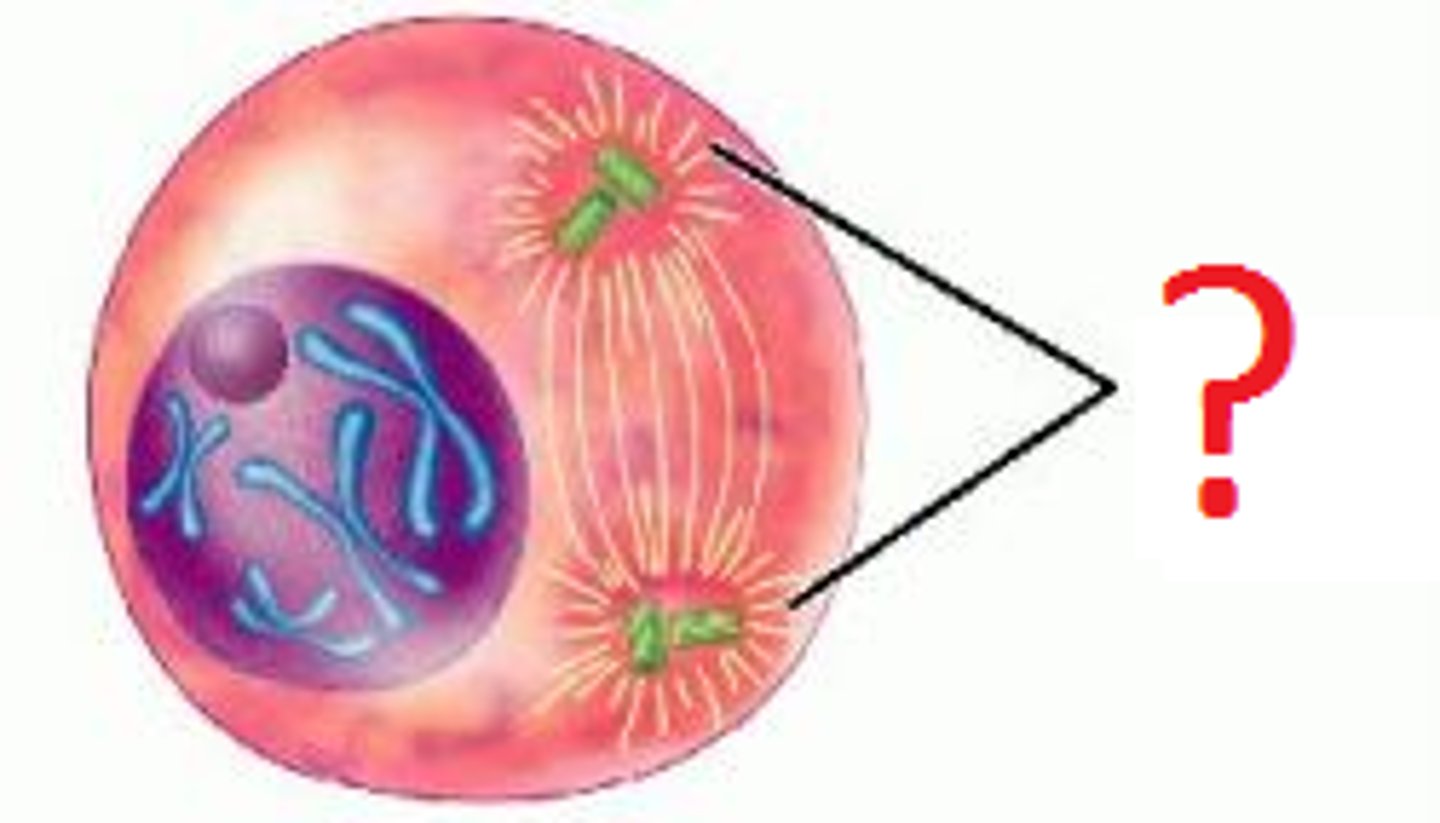
Cleavage Furrow
The area of the cell membrane that pinches in and eventually separates the dividing cell
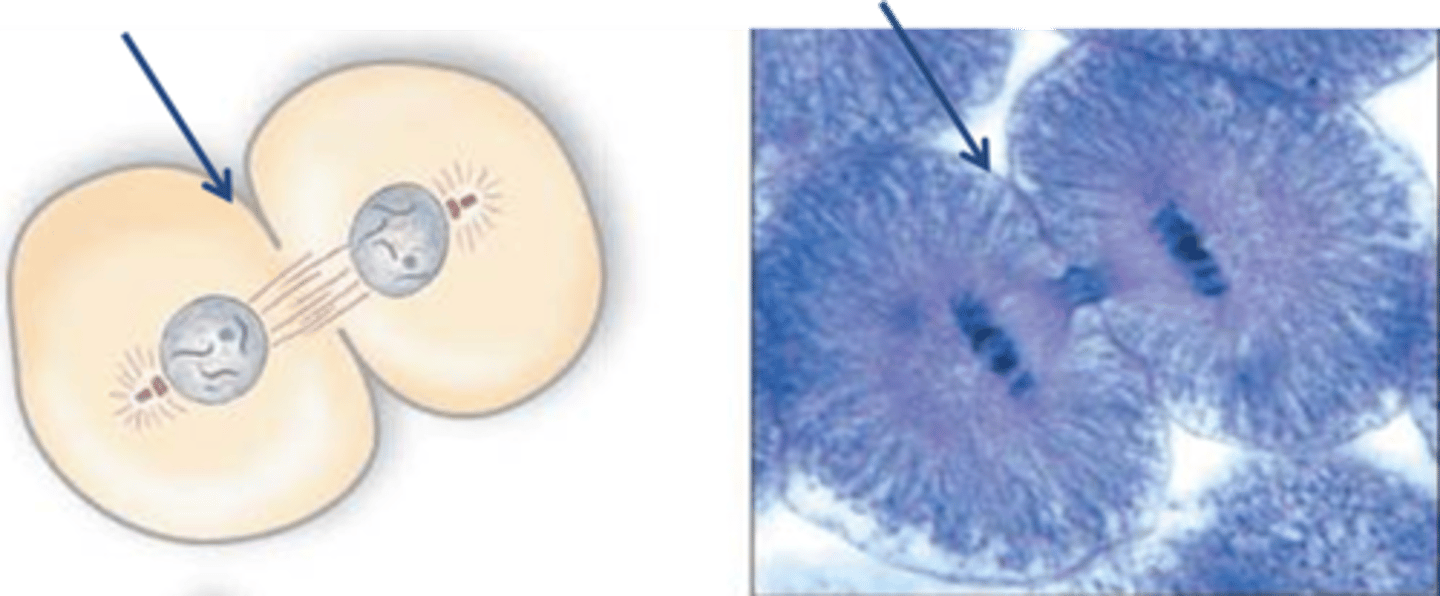
Cell Plate
Structure that forms across the midline of a dividing plant cell; location where the new cell wall forms during cytokinesis.
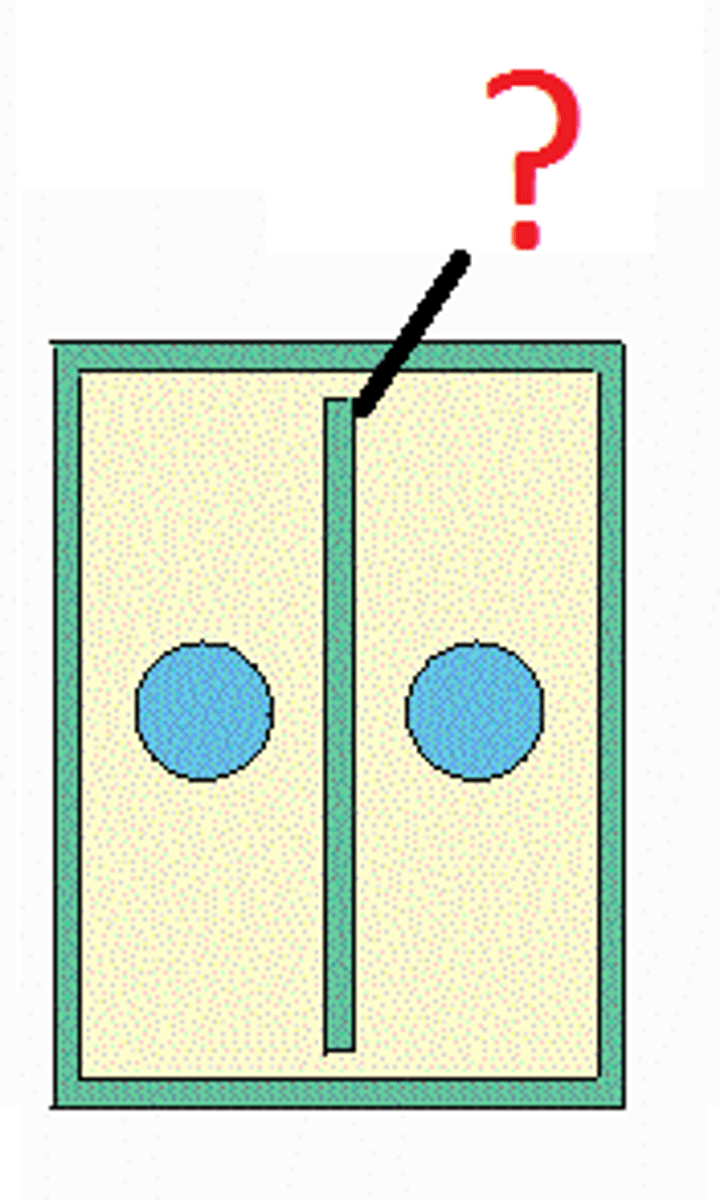
Metaphase
Phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes line up across the center/equator of the cell
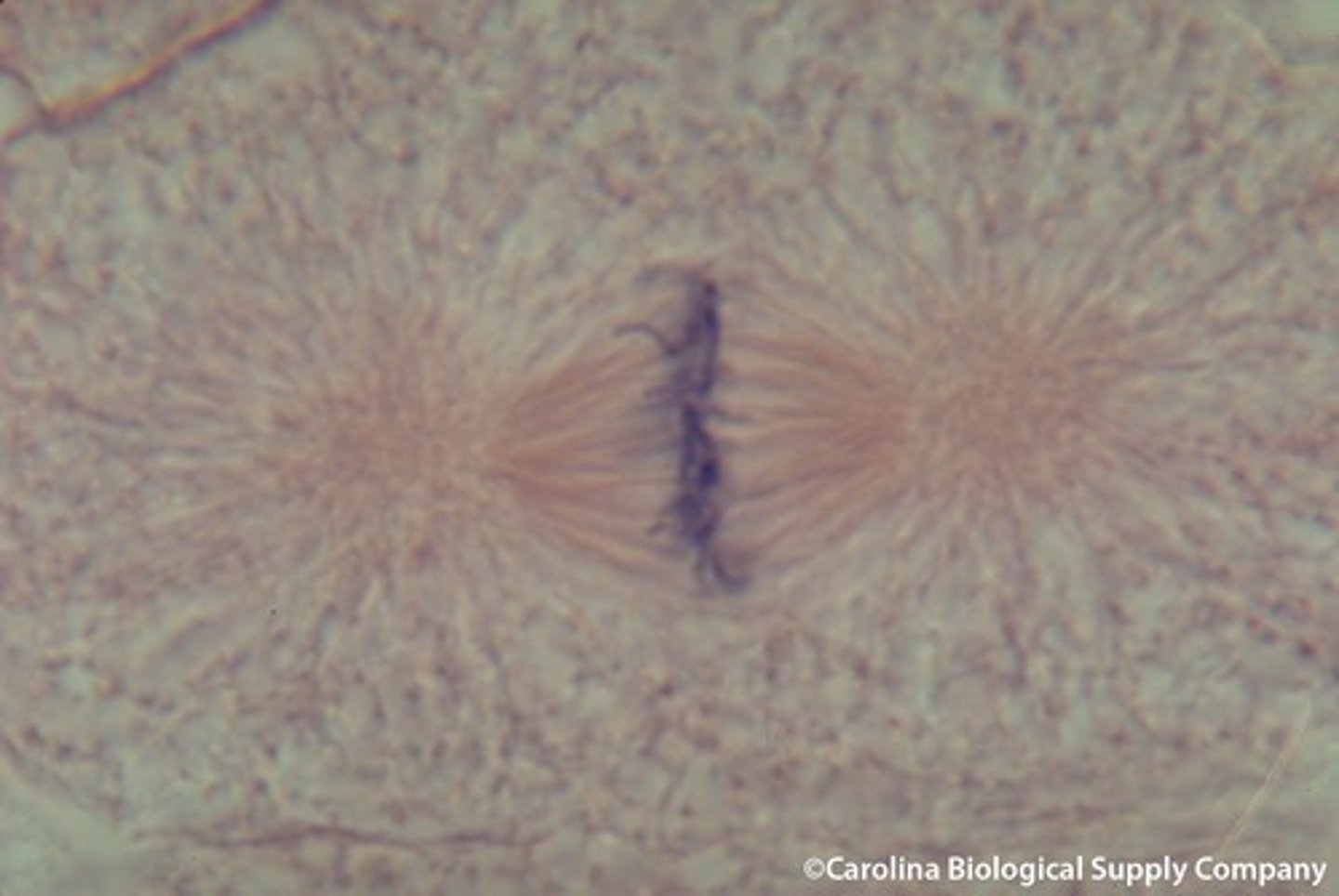
Anaphase
Phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and begin to move to opposite ends of the cell
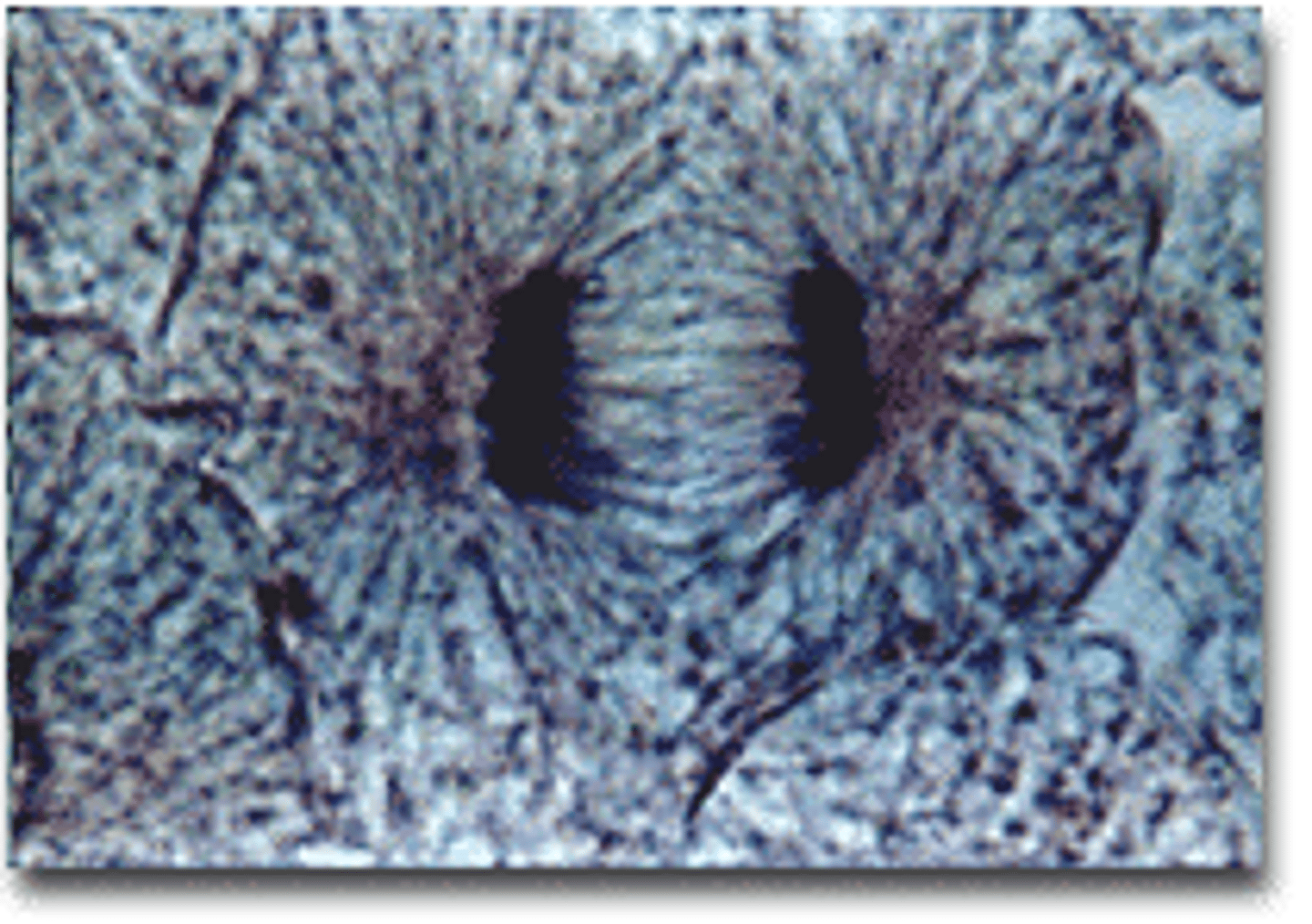
Telophase
Cell finishes dividing, chromosomes lengthen and become thinner, nuclear membrane reappears, cytoplasm gets divided up evenly