CH12: Neural Tissue
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/134
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:31 PM on 11/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
1
New cards
Nervous system
The master controlling and communicating system of the body
2
New cards
Sensory input
Monitoring stimuli- receptors
3
New cards
Integration
Interpretation of sensory input- CNS
4
New cards
Motor output
Response to stimuli- effectors (skeletal, smooth, cardiac muscles, and all glands)
5
New cards
Central nervous system
Brain and spinal cord
Integration and command center
Integration and command center
6
New cards
Peripheral nervous system
All nervous structures outside of the brain and spinal cord
Carries messages to and from the spinal cord and brain
2 divisions: sensory (afferent) and motor (efferent) division
Carries messages to and from the spinal cord and brain
2 divisions: sensory (afferent) and motor (efferent) division
7
New cards
Sensory division
Afferent division
Transmits sensory input from receptors to CNS
Contains: somatic afferent fibers, visceral afferent fibers, and special sensory fibers
Transmits sensory input from receptors to CNS
Contains: somatic afferent fibers, visceral afferent fibers, and special sensory fibers
8
New cards
Somatic afferent fibers
Carry sensory input from skin, skeletal muscles, and joints to the CNS
9
New cards
Visceral afferent fibers
Transmit sensory input from visceral organs to the CNS
10
New cards
Special sensory fibers
transmit sensory input for vision, smell, tastes, balance and hearing to CNS
11
New cards
Motor division
Efferent division
Transmits motor output from the CNS to effector organs
2 parts: somatic nervous system and autonomic nervous system
Transmits motor output from the CNS to effector organs
2 parts: somatic nervous system and autonomic nervous system
12
New cards
Somatic nervous system
Conscious control of skeletal muscles
13
New cards
Autonomic nervous system
Subconscious control of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle and glands
Divisions- sympathetic and parasympathetic
Divisions- sympathetic and parasympathetic
14
New cards
Enteric nervous system
100 million neurons in walls of digestive tract
-as many or more than a spinal cord
-use the same neurotransmitters as the brain
Initiates and coordinates visceral reflexes locally
-without instructions from CNS
Can be influenced by ANS
-as many or more than a spinal cord
-use the same neurotransmitters as the brain
Initiates and coordinates visceral reflexes locally
-without instructions from CNS
Can be influenced by ANS
15
New cards
Histology of nervous tissue
The 2 principal cell types of the nervous system are: neurons and neuroglia
Highly cellular; little extracellular space
-tightly packed
Highly cellular; little extracellular space
-tightly packed
16
New cards
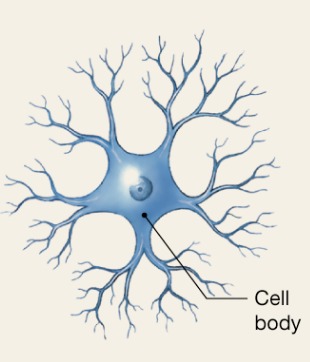
Neurons
Excitable cells that transmit electrical signals
Functional units of the nervous system
Composed of a body, axon, and dendrites
Long-lived and amitotic (no division occurs)
Plasma membrane function in ELECTRICAL SIGNALING
Functional units of the nervous system
Composed of a body, axon, and dendrites
Long-lived and amitotic (no division occurs)
Plasma membrane function in ELECTRICAL SIGNALING
17
New cards
Neuroglia
(Supporting cells)
Cells that surround and wrap neurons
Provide a supportive scaffolding for neurons
Segregate and insulate neurons
Guide young neurons to the proper connections
Promote health and growth
Cells that surround and wrap neurons
Provide a supportive scaffolding for neurons
Segregate and insulate neurons
Guide young neurons to the proper connections
Promote health and growth
18
New cards
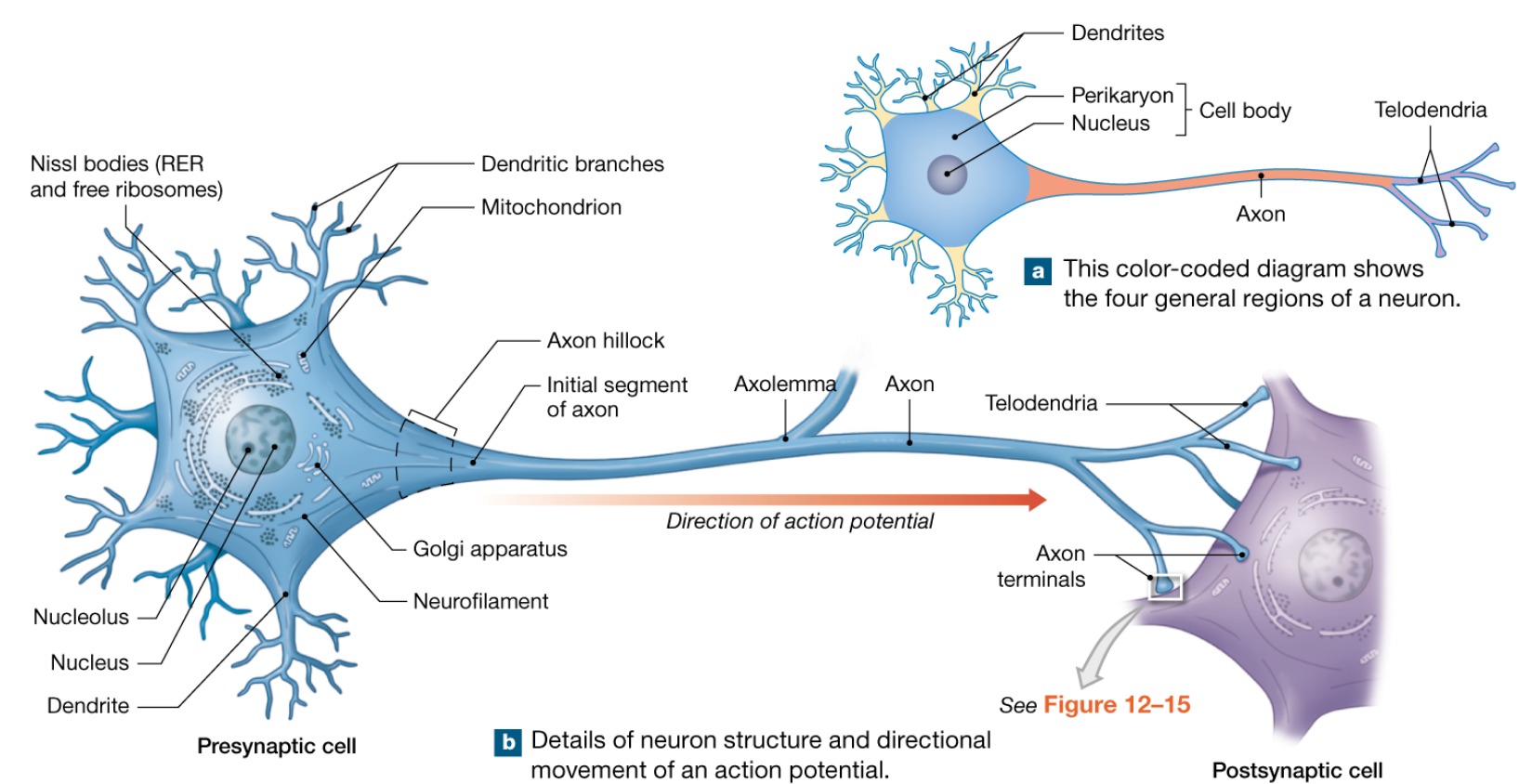
Soma
Nerve cell body
contains the nucleus with a nucleolus and many organelles
Has no centrioles
Has well-developed Nissl bodies (rough ER)
Contains an axon hillock- cone shaped area from which axons arise
Nuclei and ganglia
contains the nucleus with a nucleolus and many organelles
Has no centrioles
Has well-developed Nissl bodies (rough ER)
Contains an axon hillock- cone shaped area from which axons arise
Nuclei and ganglia
19
New cards
Nuclei
clusters of neuron cell bodies in CNS
20
New cards
Ganglia
clusters of neuron cell bodies in PNS
21
New cards
Neuron processes
Armlike processes that extend from cell body
2 types: dendrites and axon
CNS contains both neuron cell bodies and their processes
PNS contains chiefly neuron axon
Tracts and nerves
2 types: dendrites and axon
CNS contains both neuron cell bodies and their processes
PNS contains chiefly neuron axon
Tracts and nerves
22
New cards
Tracts
Bundles of neuron axons in CNS
23
New cards
Nerves
Bundles of neuron axons in PNS
24
New cards
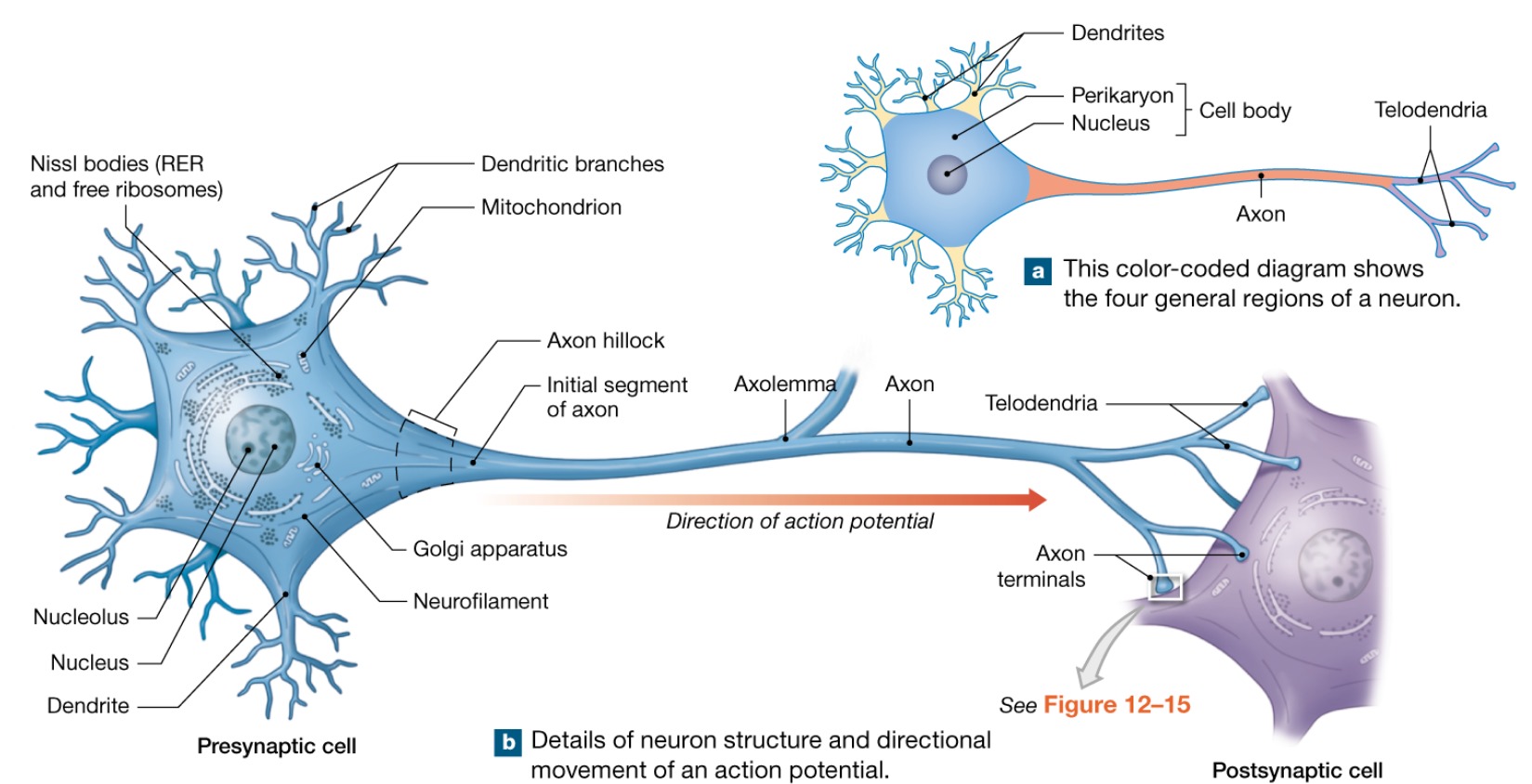
Dendrites
Short, tapering, and diffusely branched processes
They are the receptive regions of the neuron
Electrical signals are conveyed as graded potentials (not action potentials)
They are the receptive regions of the neuron
Electrical signals are conveyed as graded potentials (not action potentials)
25
New cards
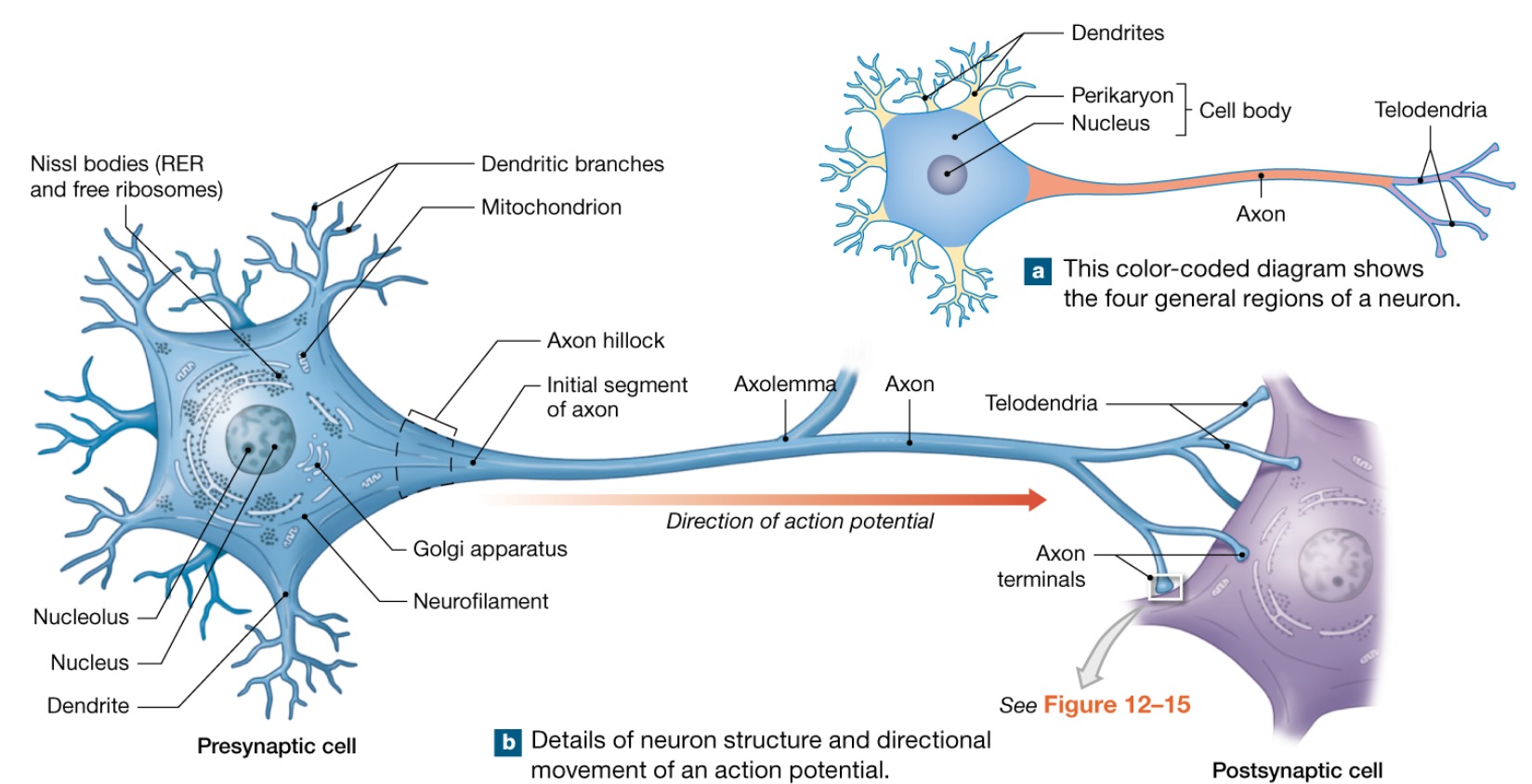
Axons structure
AKA nerve fibers
Slender processes of uniform diameter arising from the axon hillock
Usually there is only one unbranched axon per neuron
Occasional branches are called AXON COLLATERALS
Slender processes of uniform diameter arising from the axon hillock
Usually there is only one unbranched axon per neuron
Occasional branches are called AXON COLLATERALS
26
New cards
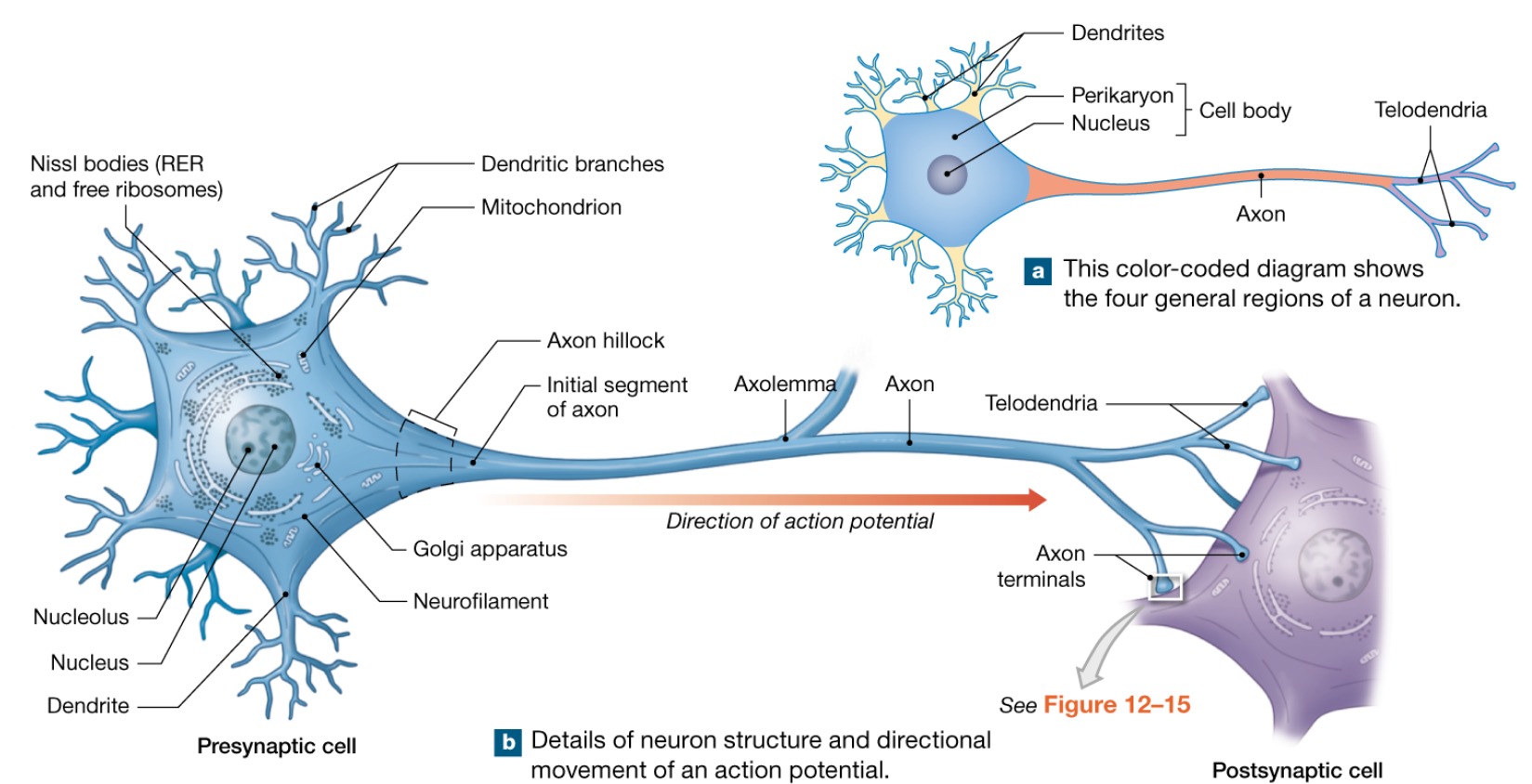
Telodendria
Small branches arising from axon extensions end
27
New cards
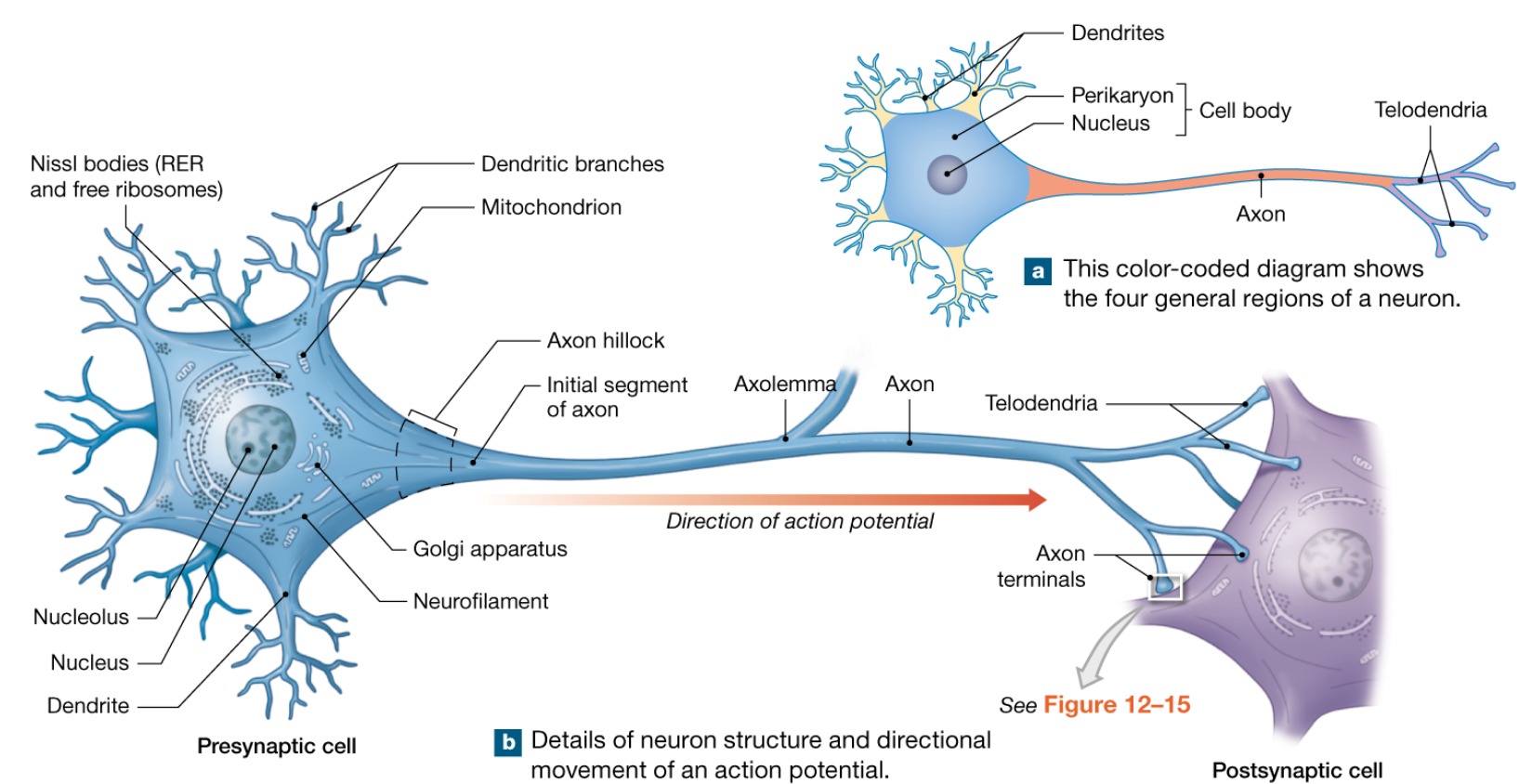
Axon terminals
AKA end synaptic bulbs
Arise from telodendria components that communicate with target cell
Arise from telodendria components that communicate with target cell
28
New cards
Axolemma
Plasma membrane of axon
29
New cards
Axons function
Generate and transmit action potentials
Secrete neurotransmitters from the axonal terminals
Sends signal away toward target cell
Secrete neurotransmitters from the axonal terminals
Sends signal away toward target cell
30
New cards
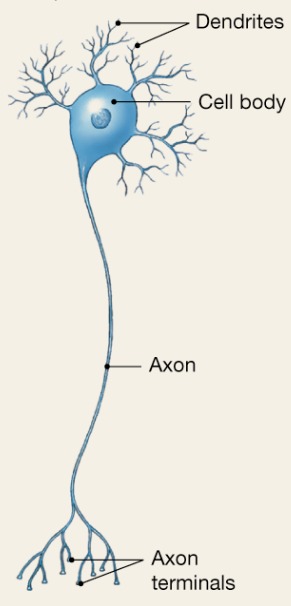
Multipolar
3 or more processes
Motor and interneurons
MOST COMMON
Motor and interneurons
MOST COMMON
31
New cards
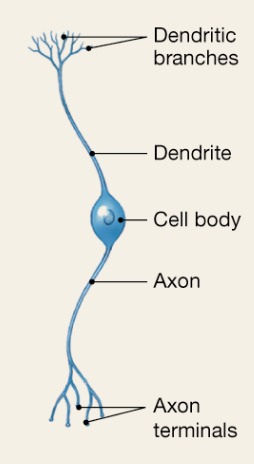
Bipolar
2 processes (axon and dendrite)
Special sensory
Special sensory
32
New cards
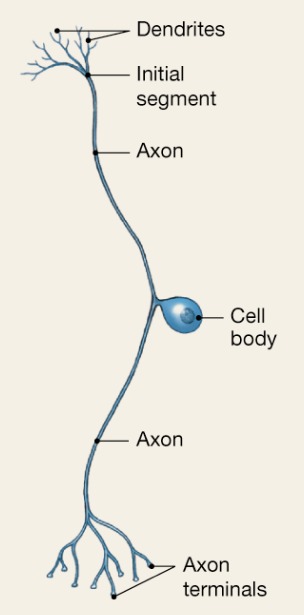
Unipolar
One T-like process (2 axons)
Sensory information from skin, muscles, etc
Sensory information from skin, muscles, etc
33
New cards
Axoaxonic
All cell processes look alike
34
New cards
Sensory
Afferent
Transmit impulses TOWARD the CNS
Transmit impulses TOWARD the CNS
35
New cards
Motor
Efferent
Carry impulses AWAY from the CNS
Carry impulses AWAY from the CNS
36
New cards
Interneurons
Association neurons
shuttle signals through CNS pathways
99% of neurons
shuttle signals through CNS pathways
99% of neurons
37
New cards
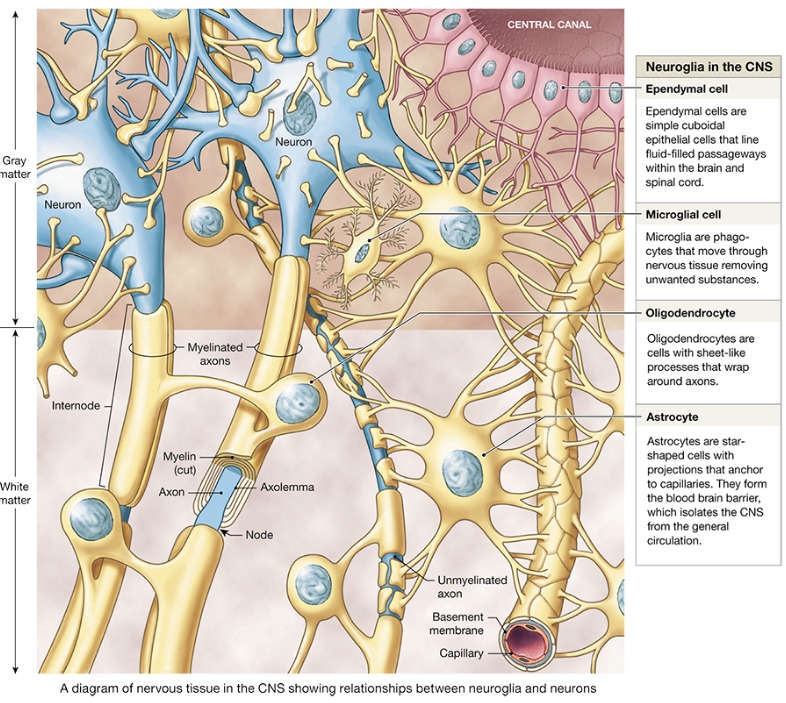
Astrocytes
ONLY in CNS
Most abundant, versatile, and highly branched neuroglial cells
They cling to neurons and cover capillaries
Most abundant, versatile, and highly branched neuroglial cells
They cling to neurons and cover capillaries
38
New cards
Astrocytes function
Support and brace neurons
Anchor neurons to their nutrient supplies
Guide migration of young neurons
Help control the chemical environment as part of blood brain barrier
Anchor neurons to their nutrient supplies
Guide migration of young neurons
Help control the chemical environment as part of blood brain barrier
39
New cards
Microglia
ONLY in CNS
Small, oval cells with spiny processes
-phagocytes (immune cells to protect)
Small, oval cells with spiny processes
-phagocytes (immune cells to protect)

40
New cards
Ependymal cells
ONLY in CNS
Range in shape from squamous to columnar
-they line the ventricles of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord
-assist in producing, circulating, and monitoring cerebrospinal fluid
Range in shape from squamous to columnar
-they line the ventricles of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord
-assist in producing, circulating, and monitoring cerebrospinal fluid
41
New cards
Oligodendrocytes
ONLY in CNS
Branched cells that wrap CNS nerve fibers and form myelin sheath
Branched cells that wrap CNS nerve fibers and form myelin sheath
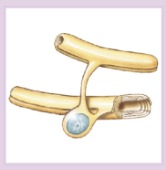
42
New cards
Schwann cells
ONLY in PNS
Surround fibers of the PNS and form myelin sheath
"Electrical wire is to electrical tape as peripheral neurons is to ____ ____"
Surround fibers of the PNS and form myelin sheath
"Electrical wire is to electrical tape as peripheral neurons is to ____ ____"

43
New cards
Satellite cells
ONLY in PNS
Surround neuron cell bodies
Regulate O2, CO2, nutrient, and neurotransmitter levels around neurons
Surround neuron cell bodies
Regulate O2, CO2, nutrient, and neurotransmitter levels around neurons
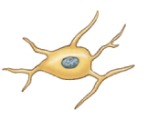
44
New cards
Myelin sheath
Whitish, fatty (protein lipid), segmented sheath around most long axons
Protection of axon
Electrically insulates fibers from one another
Increase the speed of the nerve impulse transmission
NOT ALL AXONS HAVE A ____ ____
Protection of axon
Electrically insulates fibers from one another
Increase the speed of the nerve impulse transmission
NOT ALL AXONS HAVE A ____ ____
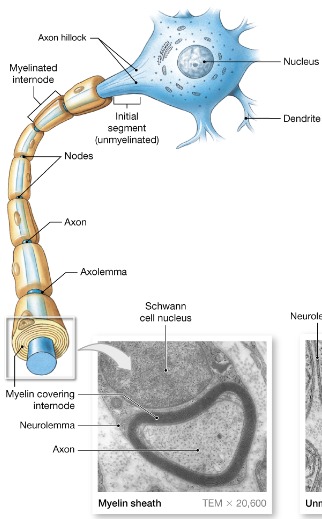
45
New cards
Formation
_____ of myelin sheath and neurolemma
formed by Schwann cell:
-envelopes an axon in a trough
-encloses the axon with its plasma membrnae
-lays concentric layers of membrane that make up the myelin sheath
formed by Schwann cell:
-envelopes an axon in a trough
-encloses the axon with its plasma membrnae
-lays concentric layers of membrane that make up the myelin sheath
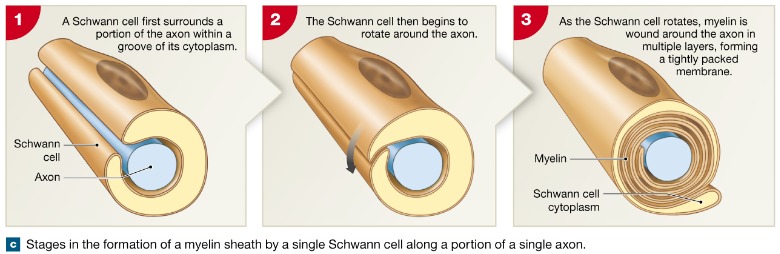
46
New cards
Neurolemma
Remaining nucleus and cytoplasm of a Schwann cell
47
New cards
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in the myelin sheath between adjacent Schwann cells
Areas of bare axon
Areas of bare axon
48
New cards
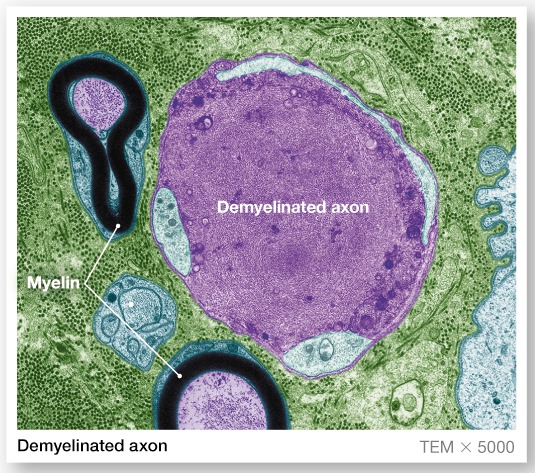
Unmyelinated axons
A Schwann cell surrounds nerve fibers, but coiling does not take place
Schwann cells partially enclose 15 or more axons
Schwann cells partially enclose 15 or more axons
49
New cards
Regeneration
_____ of nerve fibers
Damage to nerve tissue is serious because mature neurons are amitotic
In the PNS, if the cell body of a damaged nerve remains intact, damage can be repaired
CNS oligodendrocytes bear growth-inhibiting proteins that prevent CNS fiber regeneration
Slow process, depends on the length of damage and there is guarantee that it will be partially/fully repaired
Damage to nerve tissue is serious because mature neurons are amitotic
In the PNS, if the cell body of a damaged nerve remains intact, damage can be repaired
CNS oligodendrocytes bear growth-inhibiting proteins that prevent CNS fiber regeneration
Slow process, depends on the length of damage and there is guarantee that it will be partially/fully repaired
50
New cards
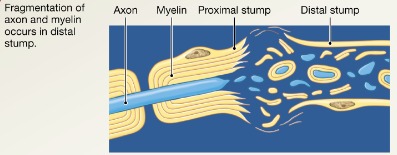
PNS regeneration step 1
Axon fragments and myelin sheaths distal to injury degenerate (Wallerian degeneration); degeneration spreads down axon
51
New cards
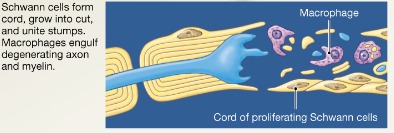
PNS regeneration step 2
Macrophages clean dead axon debris; Schwann cells are stimulated to divide and form regeneration tube
52
New cards
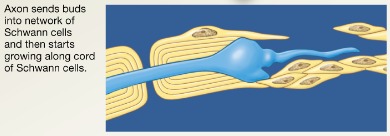
PNS regeneration step 3
Axon filaments grow through regeneration tube
53
New cards
PNS regeneration step 4
Axon regenerates, and new myelin sheath forms
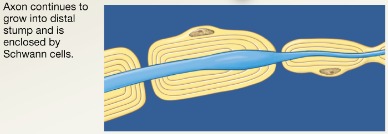
54
New cards
Axons of the CNS
Both myelinated and unmyelinated fibers are present
Myelin sheaths are formed by oligodendrocytes
Can wrap up to 60 axons at once
Nodes of Ranvier are widely spaced
There is no neurolemma
Myelin sheaths are formed by oligodendrocytes
Can wrap up to 60 axons at once
Nodes of Ranvier are widely spaced
There is no neurolemma
55
New cards
White matter
Dense collections of myelinated fibers
56
New cards
Gray matter
Mostly cell bodies and unmyelinated fibers
57
New cards
Neurophysiology
Neurons are highly excitable
Action potentials, or nerve impulses, are:
-Electrical impulses carried along the length of axons
-Always the same regardless of stimulus
-The underlying functional feature of the nervous system
Action potentials, or nerve impulses, are:
-Electrical impulses carried along the length of axons
-Always the same regardless of stimulus
-The underlying functional feature of the nervous system
58
New cards
Principles of Electricity
Opposite charges attract each other
Energy is required to separate opposite charges across a membrane
Energy is liberated when the charges move toward one another
If opposite charges are separated, the system has potential energy
Energy is required to separate opposite charges across a membrane
Energy is liberated when the charges move toward one another
If opposite charges are separated, the system has potential energy
59
New cards
Voltage
Measure of potential energy generated by separated charge (V)
60
New cards
Potential difference
Voltage measured between two points
61
New cards
Current
The flow of electrical charge between two points (I)
62
New cards
Resistance
Hindrance to charge flow (R)
63
New cards
Insulator
Substance with high electrical resistance (myelin sheath)
64
New cards
Conductor
Substance with low electrical resistance
65
New cards
Electrical Current and the Body
Reflects the flow of ions rather than electrons
There is a potential on either side of membranes when:
-The number of ions is different across the membrane
-The membrane provides a resistance to ion flow
There is a potential on either side of membranes when:
-The number of ions is different across the membrane
-The membrane provides a resistance to ion flow
66
New cards
Leak channels
Always open
67
New cards
Chemically gated channels
Open with binding of a specific neurotransmitter
ex: Na+
Closed when a neurotransmitter is not bound to the extracellular receptor
-Na+ cannot enter the cell
-Open when a neurotransmitter is attached to the receptor
-Na+ enters the cell
ex: Na+
Closed when a neurotransmitter is not bound to the extracellular receptor
-Na+ cannot enter the cell
-Open when a neurotransmitter is attached to the receptor
-Na+ enters the cell
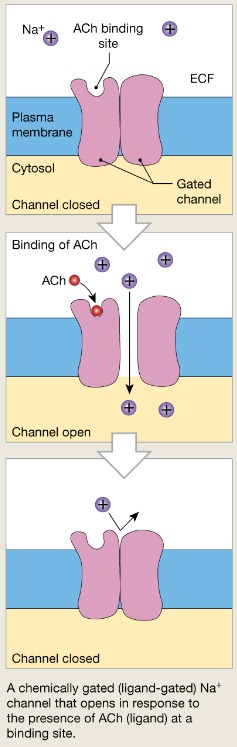
68
New cards
Voltage gated channels
Open and close in response to membrane potential
ex: Na+
1. Resting, closed but capable of opening
-Activation gate is closed, inactivation gate is open
2. Open (activated)
3. Closed, not capable of opening (inactivated)
-Inactivation gate is closed, activation gate is open
Closed when the intracellular environment is negative (Na+ cannot enter the cell)
Open when the intracellular environment is less negative (Na+ can enter the cell)
ex: Na+
1. Resting, closed but capable of opening
-Activation gate is closed, inactivation gate is open
2. Open (activated)
3. Closed, not capable of opening (inactivated)
-Inactivation gate is closed, activation gate is open
Closed when the intracellular environment is negative (Na+ cannot enter the cell)
Open when the intracellular environment is less negative (Na+ can enter the cell)
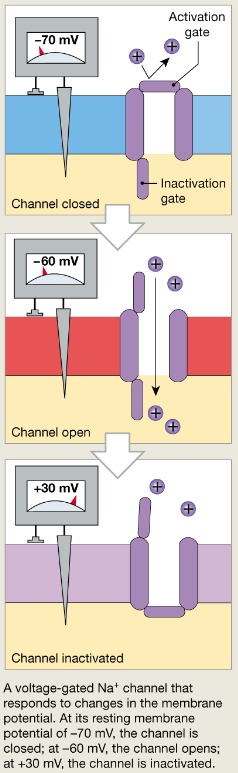
69
New cards
Mechanically gated channels
Open and close in response to physical deformation of receptors
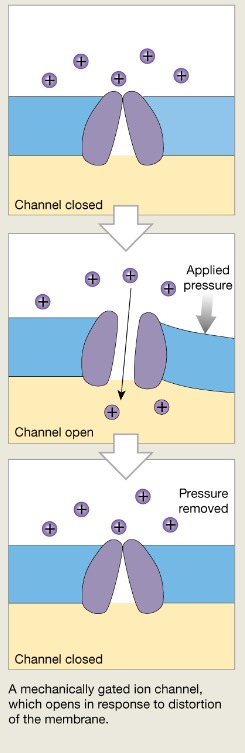
70
New cards
Gated channels
When ____ ____ are open:
Ions moved quickly across the membrane
Movement is along their electrochemical gradients
An electrical current is created
Voltage changes across the membrane
Ions moved quickly across the membrane
Movement is along their electrochemical gradients
An electrical current is created
Voltage changes across the membrane
71
New cards
Resting state
Voltage gated channels
Channels are closed; no potassium ions are able to cross plasma membrane
Channels are closed; no potassium ions are able to cross plasma membrane
72
New cards
Activated state
Voltage gated channels
Channels are open; potassium ions are able to flow out of the cell along its concentration gradient
Channels are open; potassium ions are able to flow out of the cell along its concentration gradient
73
New cards
Increases
Sodium ion centration in the cytoplasm of a neuron ___ when its voltage-gated sodium ion channels open
74
New cards
Electrochemical gradient
THE COMBINATION OF...
Ions flow along their ELECTRICAL GRADIENT when they move toward an area of opposite charge
Ions flow along their CHEMICAL GRADIENT when they move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
Ions flow along their ELECTRICAL GRADIENT when they move toward an area of opposite charge
Ions flow along their CHEMICAL GRADIENT when they move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
75
New cards
Resting membrane potential
The potential difference (-70mV) across the membrane of a resting neuron
Thin layer of negatively charged ions exists in cytosol on inside of cell; thin layer of positively charged ions exists on outside of cell
Lose more K+ and gain less Na+ equals charge will drop
Generated by:
Differences in ionic makeup of ICF and ECF
It is generated by different concentrations of Na+, K+, Cl-, and protein anions (A-)
Differential permeability of the plasma membrane
Thin layer of negatively charged ions exists in cytosol on inside of cell; thin layer of positively charged ions exists on outside of cell
Lose more K+ and gain less Na+ equals charge will drop
Generated by:
Differences in ionic makeup of ICF and ECF
It is generated by different concentrations of Na+, K+, Cl-, and protein anions (A-)
Differential permeability of the plasma membrane
76
New cards
Ionic makeup
ECF has higher concentration of Na+ than ICF
-balanced chiefly by chloride ions (Cl-)
ICF has higher concentration of K+ than ECF
-balanced by negatively charged proteins (A-)
K+ plays most important role in membrane potential
-balanced chiefly by chloride ions (Cl-)
ICF has higher concentration of K+ than ECF
-balanced by negatively charged proteins (A-)
K+ plays most important role in membrane potential
77
New cards
Permeability
Impermeable to A-
Slightly permeable to Na+ (through leakage channels)
25 times more permeable to K+ (more leakage channels)
Always sodium leaking into channels
Slightly permeable to Na+ (through leakage channels)
25 times more permeable to K+ (more leakage channels)
Always sodium leaking into channels
78
New cards
Sodium potassium pump
Stabilizes the resting membrane potential by maintaining the concentration gradients for Na+ and K+
Repolarization
-restores the resting electrical conditions of the neuron
-Does not restore the resting ionic conditions
Ionic redistribution back to resting conditions is restored by the ___ ___ ___
Repolarization
-restores the resting electrical conditions of the neuron
-Does not restore the resting ionic conditions
Ionic redistribution back to resting conditions is restored by the ___ ___ ___
79
New cards
Membrane potential changes
Concentrations of ions across membrane change
Membrane permeability to ions changes
Produces graded and action potentials
Used as signals to receive, integrate, and send information
Caused by depolarization, repolarization, and hyperpolarization
Membrane permeability to ions changes
Produces graded and action potentials
Used as signals to receive, integrate, and send information
Caused by depolarization, repolarization, and hyperpolarization
80
New cards
Graded potentials
Incoming signals operating over short distances
Short-lived, local changes in membrane potential
Occur on dendrites and cell bodies
Magnitude varies directly with the strength of the stimulus
Stronger stimulus -> more voltage changes; farther current flows
Sufficiently strong graded potentials can initiate action potentials
Short-lived, local changes in membrane potential
Occur on dendrites and cell bodies
Magnitude varies directly with the strength of the stimulus
Stronger stimulus -> more voltage changes; farther current flows
Sufficiently strong graded potentials can initiate action potentials
81
New cards
Action potentials
Long-distance signals of axons
A brief reversal of membrane potential
Action potentials are only generated by muscle cells and on axons of neurons
They do not decrease in strength over distance
They are the principal means of neural communication
The nerve impulse
ALL OR NONE
A brief reversal of membrane potential
Action potentials are only generated by muscle cells and on axons of neurons
They do not decrease in strength over distance
They are the principal means of neural communication
The nerve impulse
ALL OR NONE
82
New cards
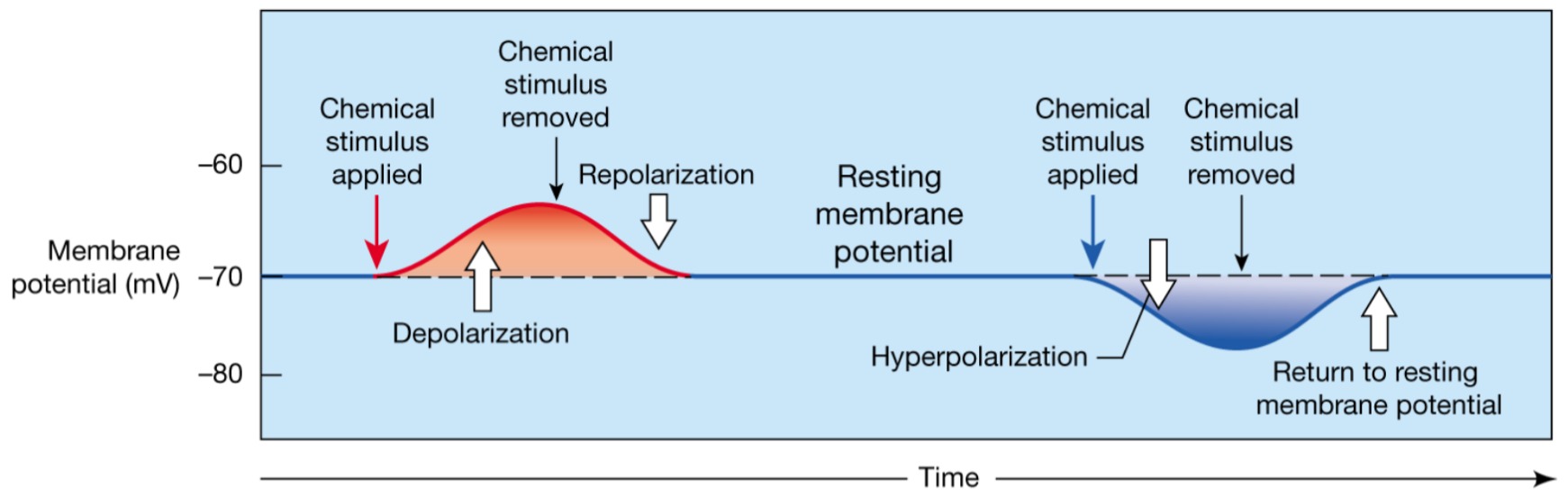
Depolarization
The inside of the membrane becomes less negative
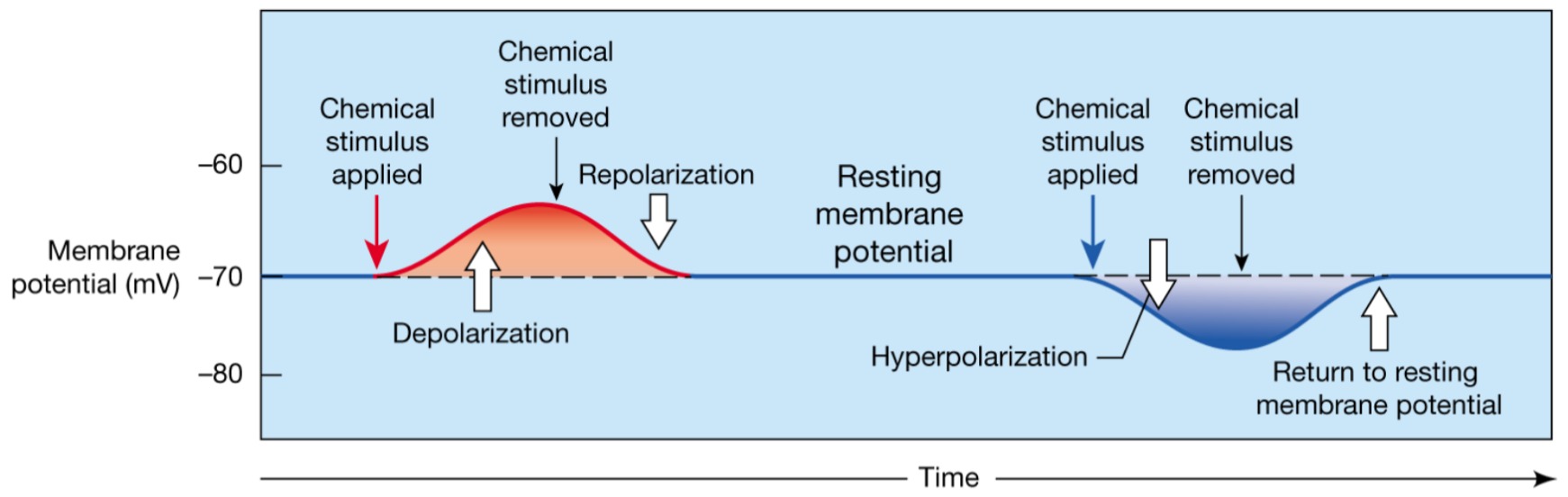
83
New cards
Repolarization
The membrane returns to its resting membrane potential
-Same for graded
-Same for graded
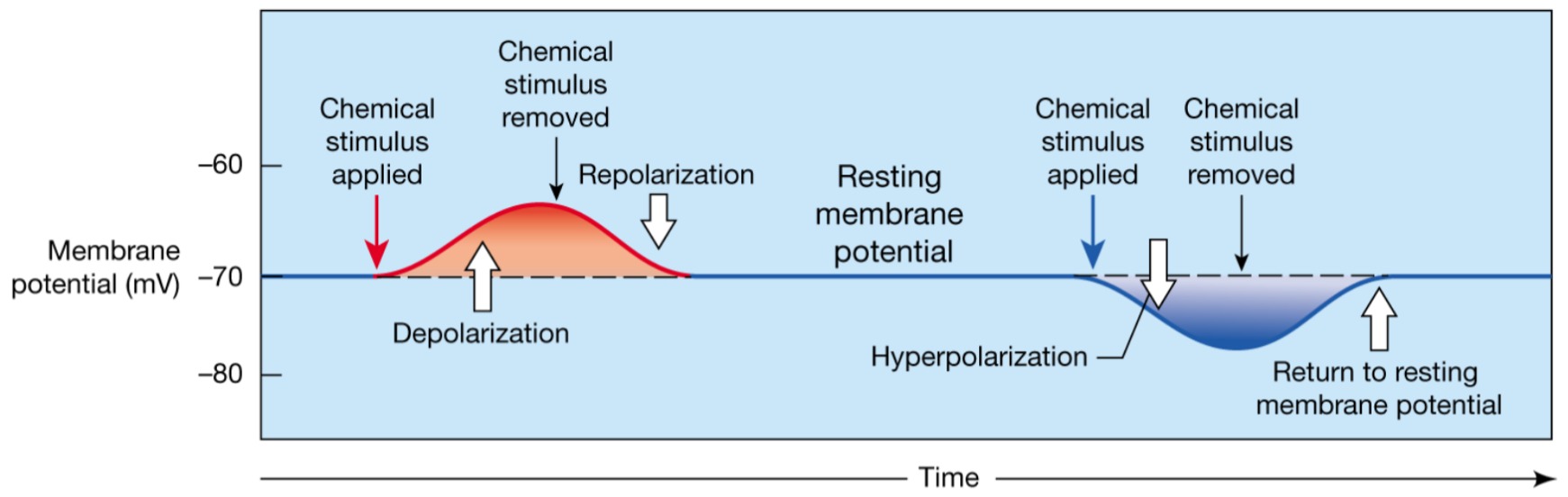
84
New cards
Hyperpolarization
The inside of the membrane becomes more negative than the resting potential
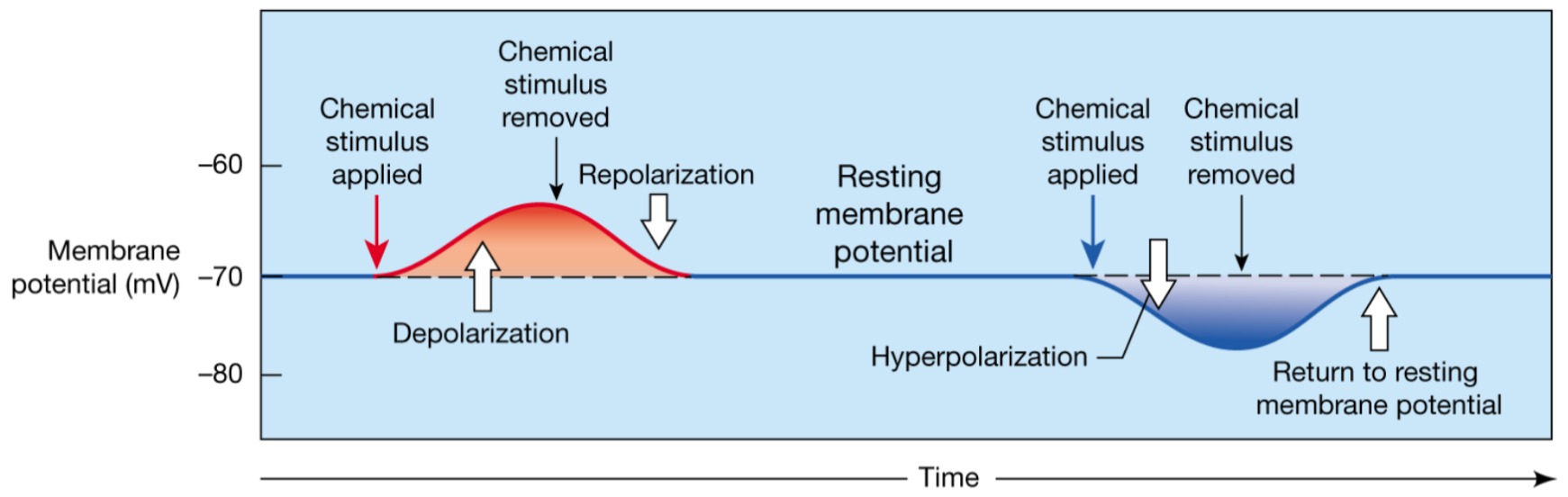
85
New cards
Graded depolarization
Can excite the neuron into generating and action potential
A shift in membrane potential toward 0mV
-movement of Na+ through channel
-produces local current
-Depolarizes nearby plasma membrane (graded potential)
-change in potential is proportional to stimulus
A shift in membrane potential toward 0mV
-movement of Na+ through channel
-produces local current
-Depolarizes nearby plasma membrane (graded potential)
-change in potential is proportional to stimulus
86
New cards
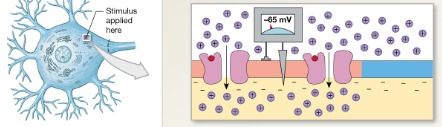
1 GD
Step ? of graded depolarization
Stimulation
Membrane exposed to chemical that opens the sodium ion channels
Stimulation
Membrane exposed to chemical that opens the sodium ion channels
87
New cards
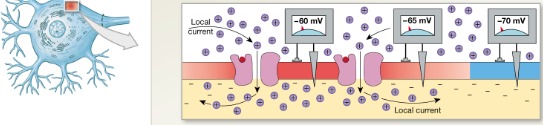
2 GD
Step ? of graded depolarization
Graded potential
Spread of sodium ions along inner surface produces a local current that depolarizes adjacent portions of the plasma membrane
Graded potential
Spread of sodium ions along inner surface produces a local current that depolarizes adjacent portions of the plasma membrane
88
New cards
Graded hyperpolarization
Increasing negativity of the resting potential
Result of opening a potassium channel
Opposite effect of opening a sodium channel
Positive ions move out, not into cell
Result of opening a potassium channel
Opposite effect of opening a sodium channel
Positive ions move out, not into cell
89
New cards
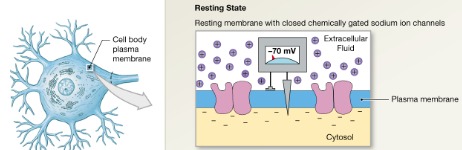
Resting state
Na+ and K+ channels are closed
Leakage accounts for small movements of Na+ and K+
Each Na+ channel has two voltage-regulated gates- activation and inactivation
Leakage accounts for small movements of Na+ and K+
Each Na+ channel has two voltage-regulated gates- activation and inactivation
90
New cards
Activation gates
Closed in the resting state
91
New cards
Inactivation gates
Open in the resting state
92
New cards
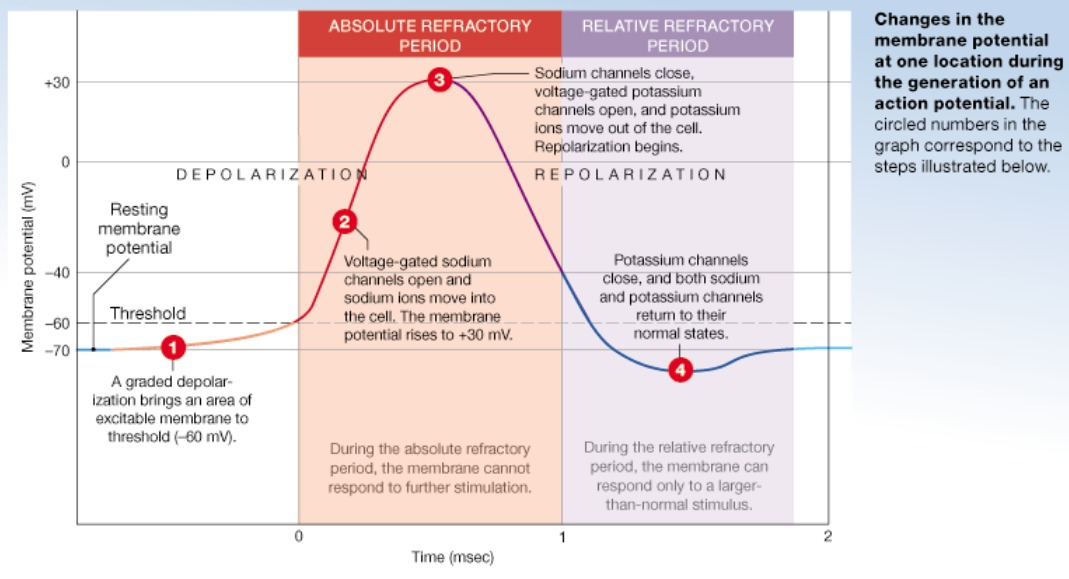
Ap depolarization
Na+ permeability increases; membrane potential reverses
Na+ gates are opened, K+ gates are closed
Graded potential must be able to depolarize axon strongly enough to reach level called threshold (-55mV)
At threshold, depolarization becomes self-generating
Membrane potential rises to +30mv
Na+ gates are opened, K+ gates are closed
Graded potential must be able to depolarize axon strongly enough to reach level called threshold (-55mV)
At threshold, depolarization becomes self-generating
Membrane potential rises to +30mv
93
New cards
Threshold
Not all depolarization events produce APs
For axon to fire, depolarization must reach ___
-voltage at which the AP is triggered
Membrane has been depolarized by ~15mV
Na+ permeability increases
Na+ influx exceeds K+ efflux
The positive feedback cycle begins
For axon to fire, depolarization must reach ___
-voltage at which the AP is triggered
Membrane has been depolarized by ~15mV
Na+ permeability increases
Na+ influx exceeds K+ efflux
The positive feedback cycle begins
94
New cards
AP repolarization
Sodium inactivation gates close
Membrane permeability to Na+ declines to resting levels
As sodium gates close, voltage-sensitive K+ gates open
K+ exits the cell and internal negativity of the resting neuron is restored
Drops back down towards -70mV
Membrane permeability to Na+ declines to resting levels
As sodium gates close, voltage-sensitive K+ gates open
K+ exits the cell and internal negativity of the resting neuron is restored
Drops back down towards -70mV
95
New cards
AP hyperpolarization
Potassium gates remain open, causing an excessive efflux of K+
This efflux causes ____ of the membrane
Drops below -70mV
Flow of ions through leak channels restores resting membrane potential
This efflux causes ____ of the membrane
Drops below -70mV
Flow of ions through leak channels restores resting membrane potential
96
New cards
Absolute refractory period
Time from beginning of depolarization into mid-repolarization
Coincides with voltage gated sodium channels being activated and inactivated
Prevents the neuron from generating another action potential
Ensures that each ___ ___ ____ is separate
Coincides with voltage gated sodium channels being activated and inactivated
Prevents the neuron from generating another action potential
Ensures that each ___ ___ ____ is separate
97
New cards
Relative refractory period
Mid-repolarization through hyperpolarization
-Voltage gated Na+ channels returned to resting state; able to open again
-K+ channels are activated
Second action potential possible with larger than normal stimulus
-Voltage gated Na+ channels returned to resting state; able to open again
-K+ channels are activated
Second action potential possible with larger than normal stimulus
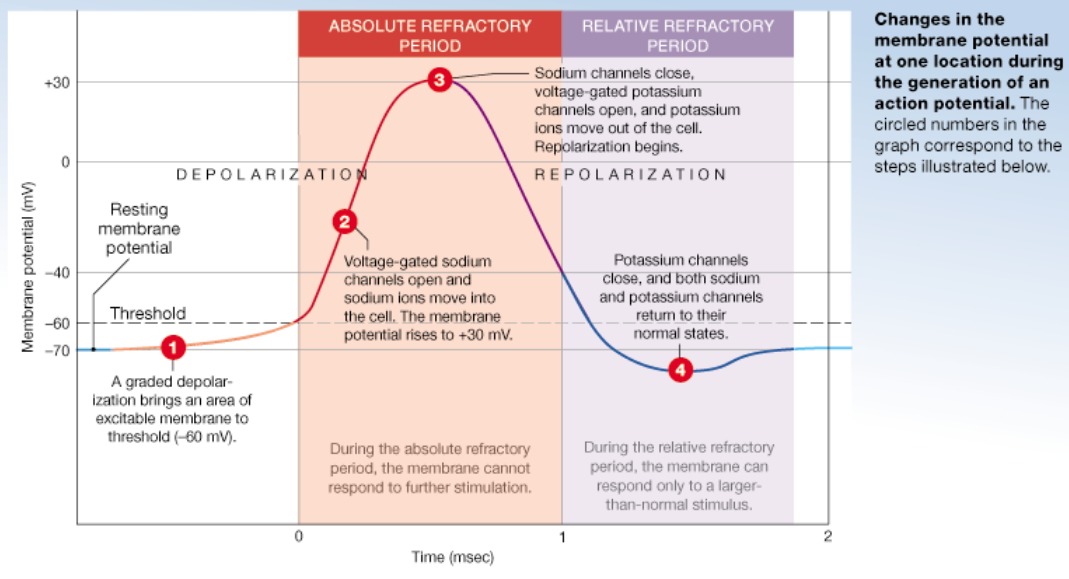
98
New cards
Propagation
Allows AP to be transmitted from initial segment down entire axon length toward axon terminals
Na+ influx through voltage gates in one membrane area cause local currents that cause opening of Na+ voltage gates in adjacent membrane areas
-Leads to depolarization of that area, which in turn causes depolarization in next area.
Na+ influx through voltage gates in one membrane area cause local currents that cause opening of Na+ voltage gates in adjacent membrane areas
-Leads to depolarization of that area, which in turn causes depolarization in next area.
99
New cards
Velocities of axons
Propagation
Velocities vary
Rate of impulse is determined by: axon diameter (the larger the faster) and presence of myelin sheath (presence increases speed)
Velocities vary
Rate of impulse is determined by: axon diameter (the larger the faster) and presence of myelin sheath (presence increases speed)
100
New cards
Continuous propagation
Unmyelinated axon
Impulse continues smoothly down the axon
Impulse continues smoothly down the axon