MP3 -> Relationship Marketing
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Relationship Marketing
identifying, developing, maintaining, and terminating relational exchanges to improve performance and build relationship equity
In which types of markets does relational exchange happen
Both B2B and B2C, the more intangible the product, the more important relationship
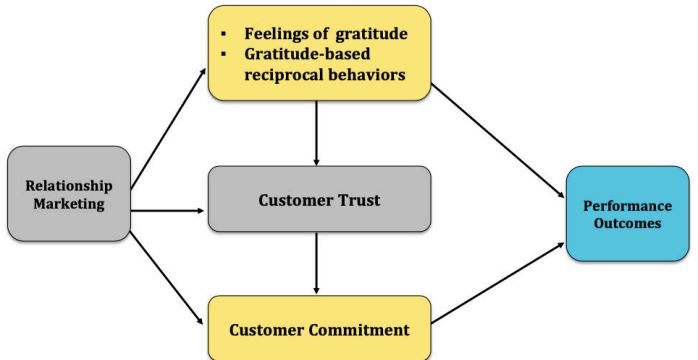
CRM
A managerially relevant, firm-wide, IT-enabled, customer-focused application of RM used to achieve performance objectives.
Social Exchange Theory
relationships are maintained based on the perceived balance of rewards and costs.
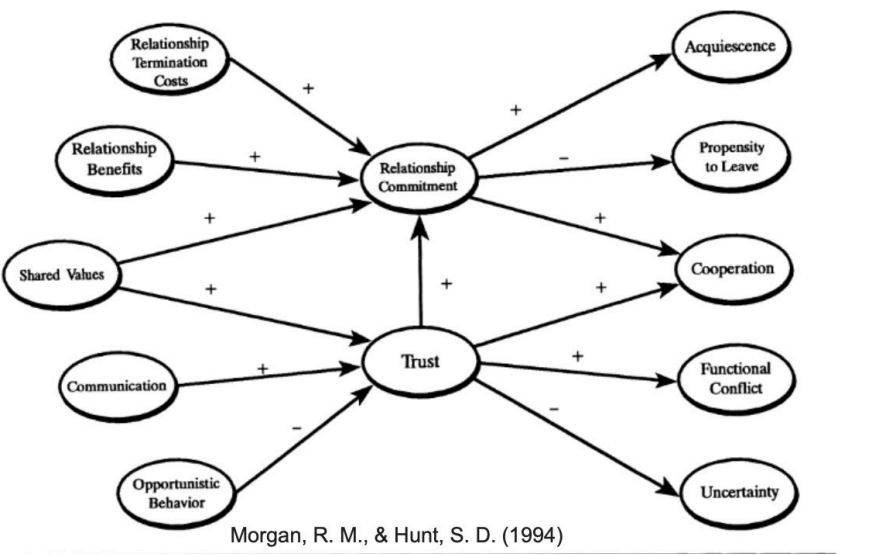
Breadth’ mean in RM?
The number of relational ties/contacts with a partner. More ties = more info & less risk when a contact is lost.
Quality in RM
The trust, commitment, and gratitude between contacts. Higher quality = higher value
What does ‘Composition’ refer to in network theory?
The diversity of ties. Higher diversity = more broad and meaningful impact.
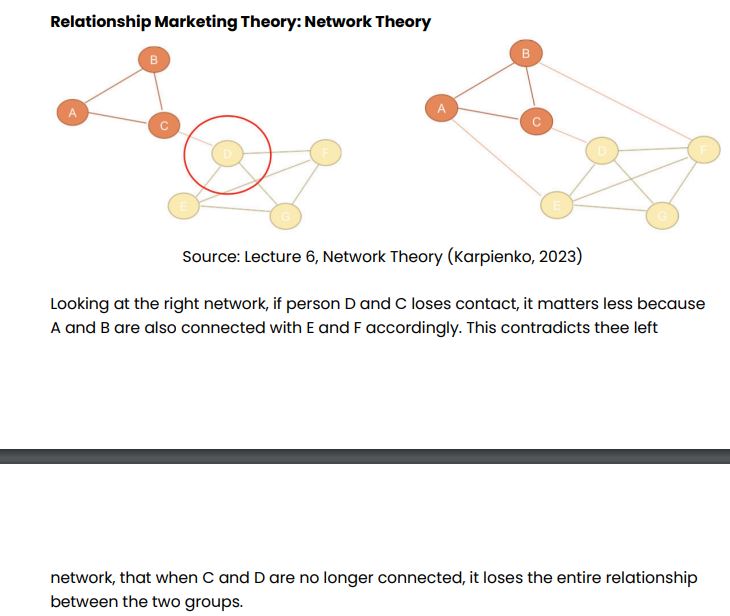
Network Theory
value comes from how interconnected and redundant network ties are
Name the four mechanisms through which RM leads to sustainable advantage
Relational Loyalty
Referrals/Word of Mouth (WOM)
Empathetic Behaviours
Cooperative Behaviours
How does RM influence Relational Loyalty
Customers trust the seller more, when perceive less risk dealing with trusted partners, feel belonging, and minimize costs by buying from valued sellers.
o Loyalty = determinant of firm success in competitive marketplaces
What drives Referrals and WOM?
Trust, gratitude, and relational bonds. Only loyal customers risk their reputation to advocate.
Empathetic Behaviours
Customers understand seller’s difficulties, may forgive service failures, and don’t pressure for price cuts.
Cooperative Behaviours
Mutual actions to achieve goals. Encourages adaptiveness, flexibility, and reciprocity even if delayed
United Airlines cited its contractual policies when it refused to spend $1200 to repair a passenger’s guitar that its baggage handlers had carelessly broken. The passenger received word that he was ineligible for compensation because he failed to make the claim within United’s stipulated 24-hour timeframe. The passenger vented his frustration by creating a song entitled “United Breaks Guitars” and uploaded it on YouTube. As of 2019, it garnered almost 20 million views. The song has been estimated to have cost United Airlines $180 million. In this case, losses loom larger than gains as the loss of just repairing the guitar for $1200 translates to a loss of up to $180 million.
Why are companies trying to omit such situations?
Prospect Theory: losses loom larger than gains
When you exceed customer expectation, it leads to a lower increase in value compared to a bigger loss when customer expectations are not fulfilled.
Toxic Poisons
Actions that create perceptions of unfairness, especially in loyalty or reward programs
antidote to RM unfairness
Use pre-emptive approaches and make benefits invisible to bystanders.
3 elements RM strategies must balance
Reward Elements
RM Delivery
Customer Portfolio (targets vs bystanders)
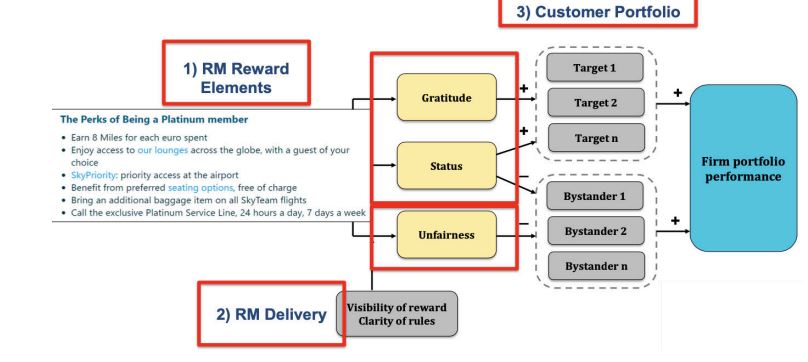
RM strategies can hurt firm performance
When bystanders feel unfairness, leading to negative perceptions and harming overall outcomes
the “highest impact” RM strategy
Preventing customer perceptions of unfairness. It's more effective than promoting positive experiences
true effectiveness multidimensional view
Reward element perspective
Reward delivery perspective
Portfolio perspective (targets and bystanders)
4 lifecycle stages of customer relationships
Exploratory/Early
Growth/Developing
Maturity/Maintaining
Decline/Recovery
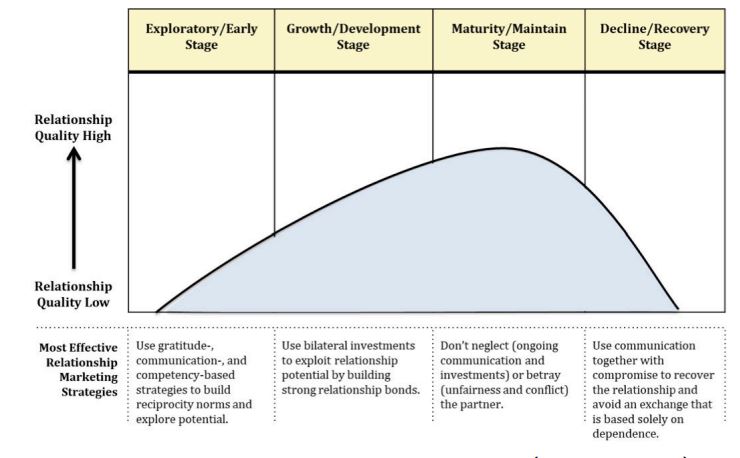
Building relationship equity
Develop a strong foundation that supports relationship building and maintenance: Invest in customer-facing employees, create effective communication, and avoid service failures from unfairness and unresolved conflict
Implement relationship marketing and loyalty programs targeted at specific customer groups
3 types of RM programs
Social RM (e.g., free tickets)
Structural RM (e.g., customized packaging)
Financial RM (e.g., discounts – but easily copied)
Multivariate Regression Analysis key purposes
To determine whether a marketing intervention has a statistically significant effect on a marketing outcome.
To understand the sign (positive/negative)
To compare the relative strength of multiple interventions
To control for confounding variables and isolate the true effect of each intervention
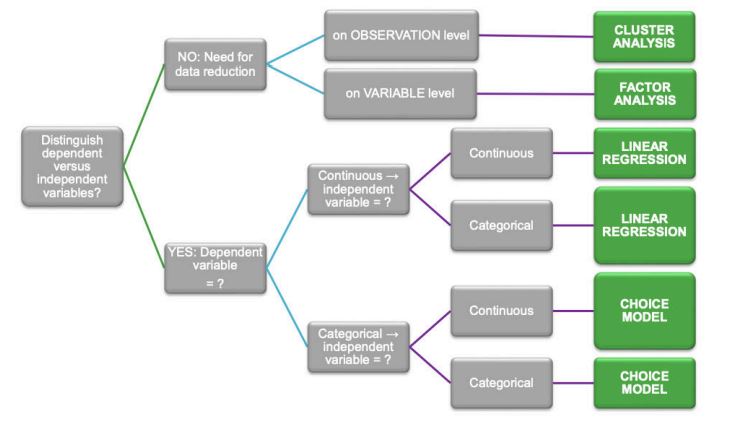
When to use which method of analysis
just read
Discrete Choice Model
Predicts if a relationship continues (1) or ends (0) based on Social, Structural, and Financial RM inputs
probability of ContinueRelationship = 1
P(ContinueRelationship=1)=e^z/(1+e^z)
Why is the effect size not immediately clear in a Discrete Choice Model
Because the model is non-linear, the coefficients (βs) affect the log-odds, not the probability directly
log-odds z
z = log of (prob continue relationship/prob not continuing)