Lesson 2 Anatomy of Cerebrum
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CSD 380
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
The central nervous system is covered with a _____ serving important protective and nutritive functions.
Triple-layer meningeal lining
Outermost meningeal lining
Dura Mater
Middle meningeal lining
Arachnoid Mater
Inner meningeal lining
Pia Mater
What are the functions of the meningeal linings?
Protect the brain, hold structures in place for movement and provides support for structures by holding brain in fluid suspension.
Space between the arachnoid and pia mater that contains cerebrospinal fluid
Subarachnoid space
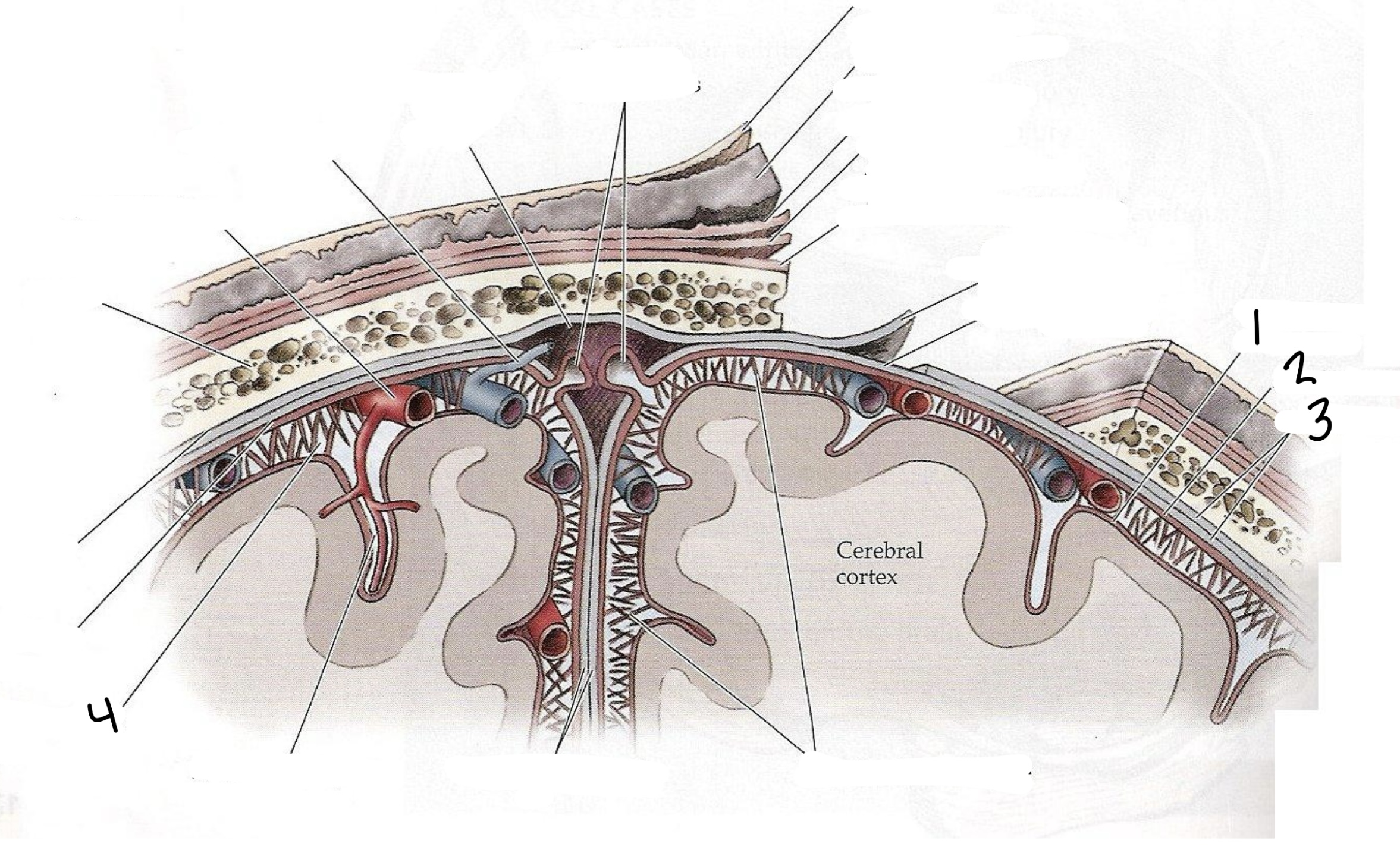
1
Pia Mater
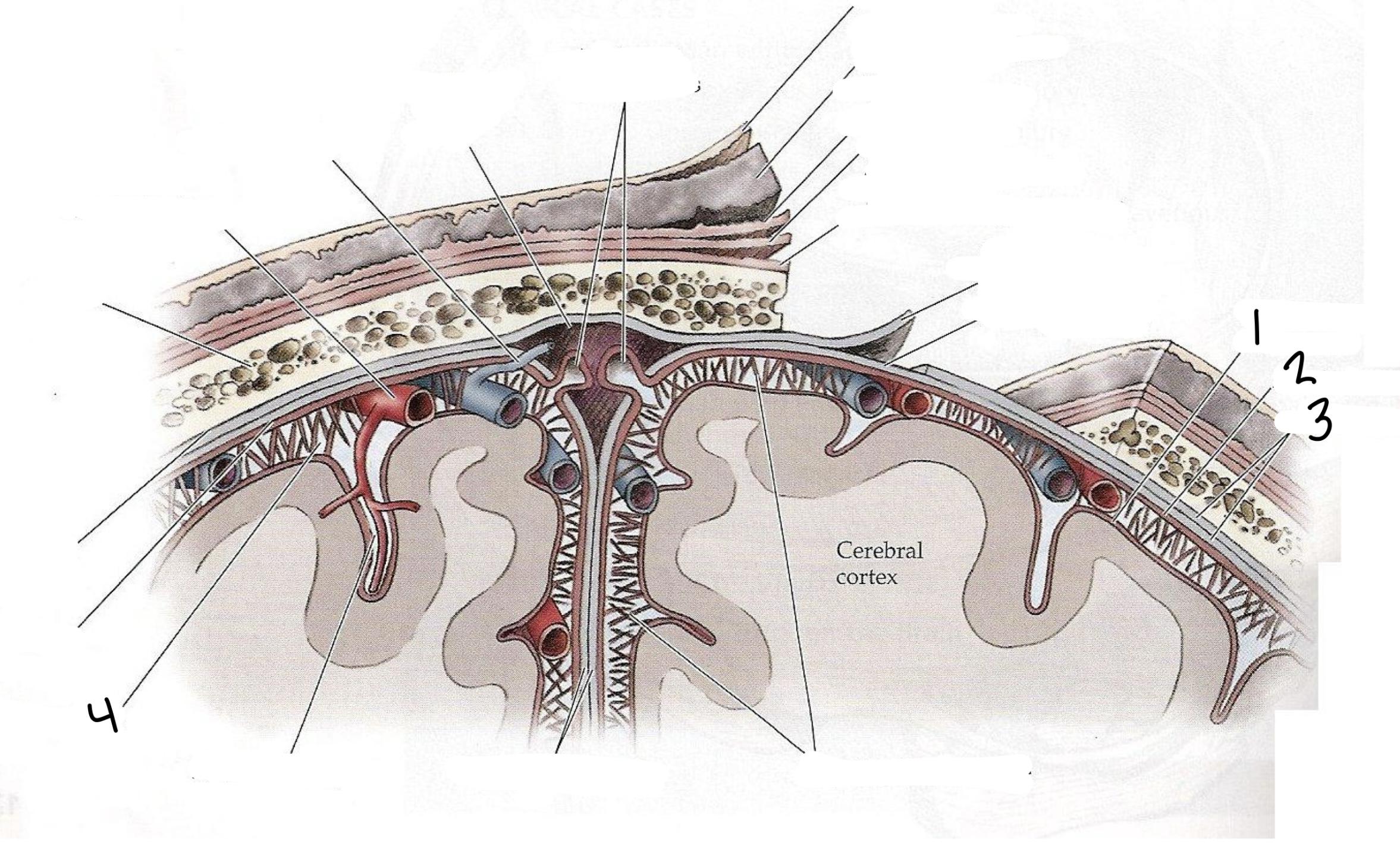
2
Arachnoid Mater
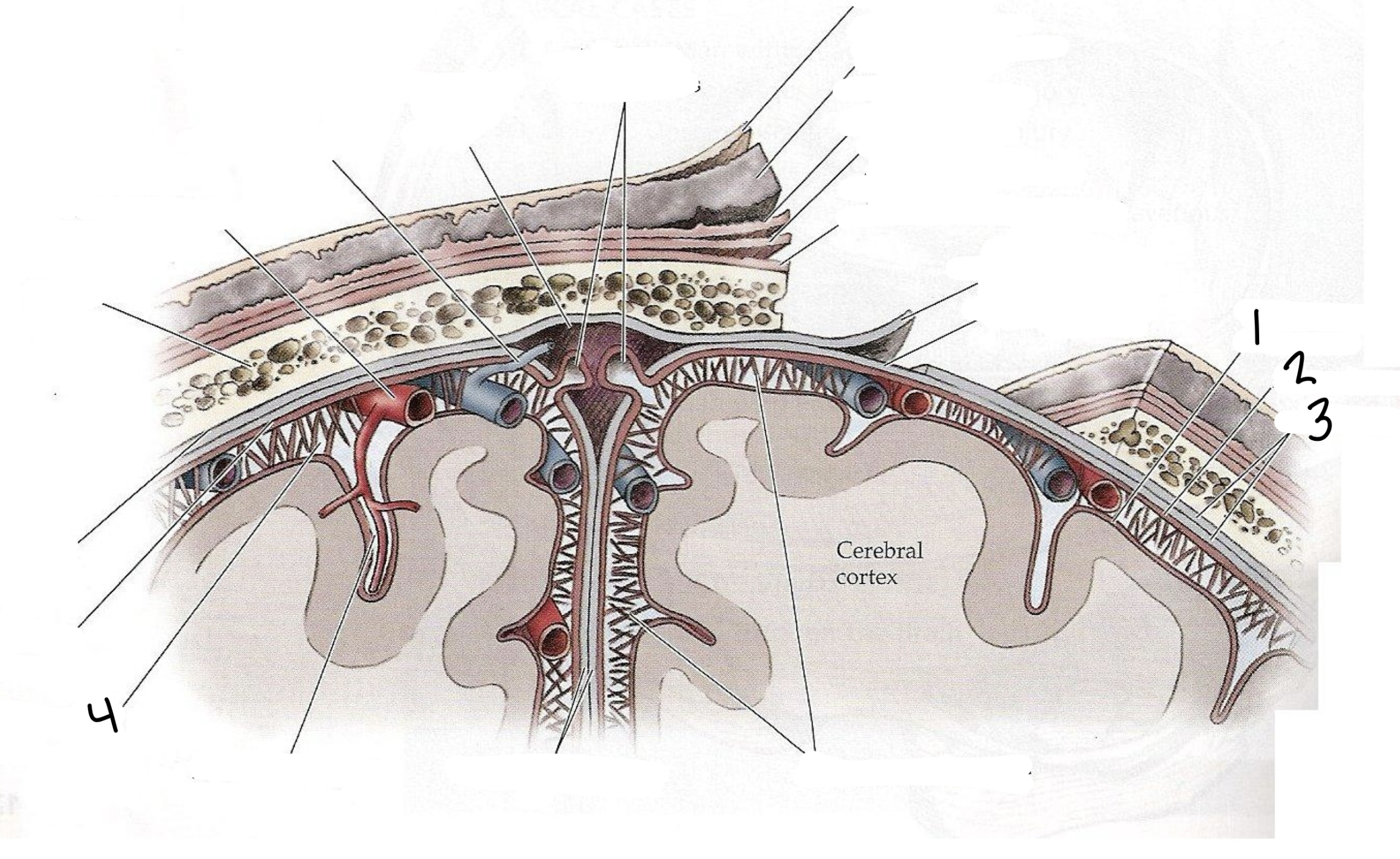
3
Dura Mater
Provides a cushion for delicate and dense neural tissue, allows for nutrient delivery, and assists with waste removal
Cerebrospinal Fluid
The ___ of the brain are spaces within the brain through which cerebrospinal fluid flows.
Ventricles
How many cavities are within the system of ventricles?
4
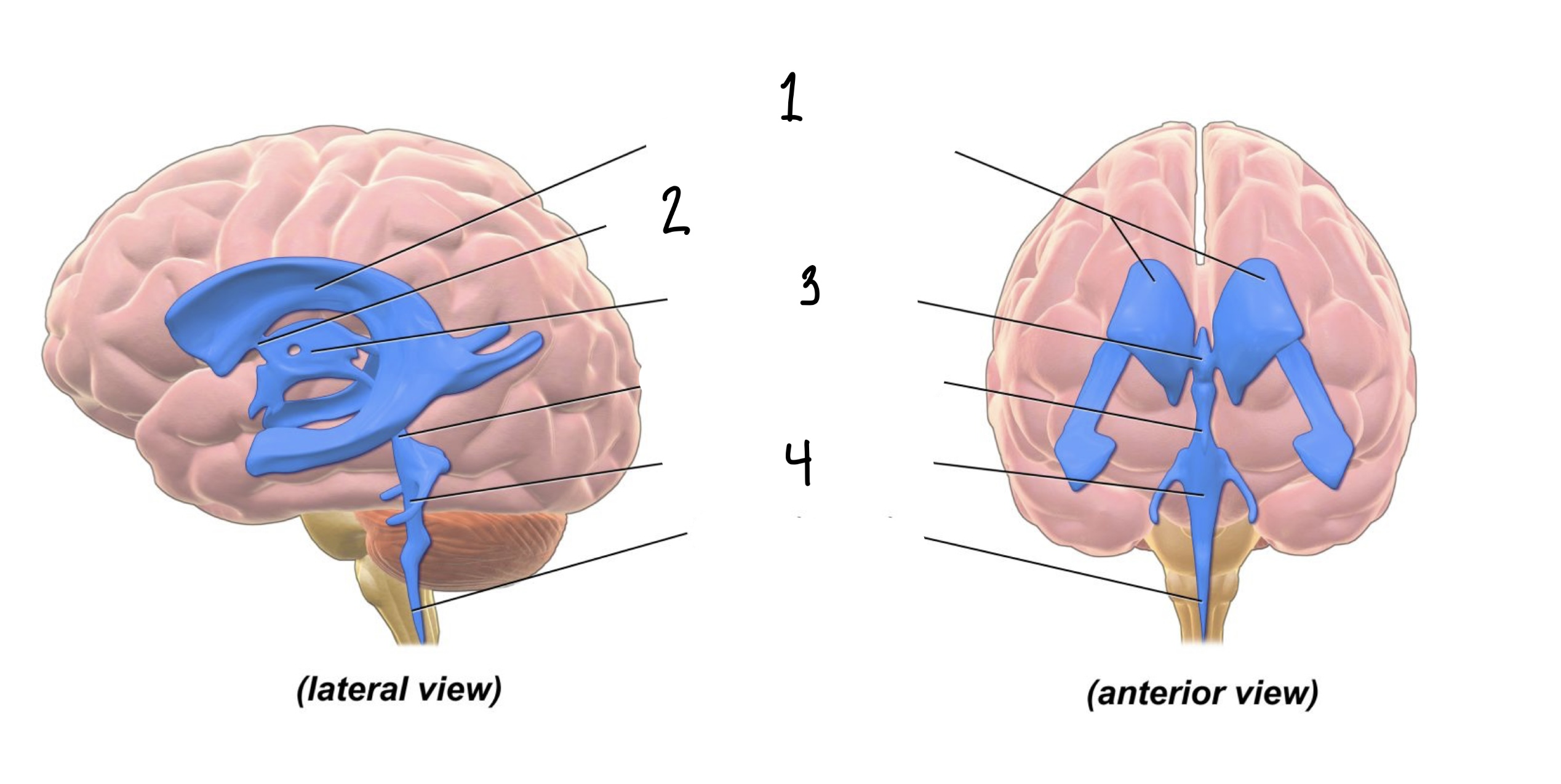
1
Lateral Ventricles
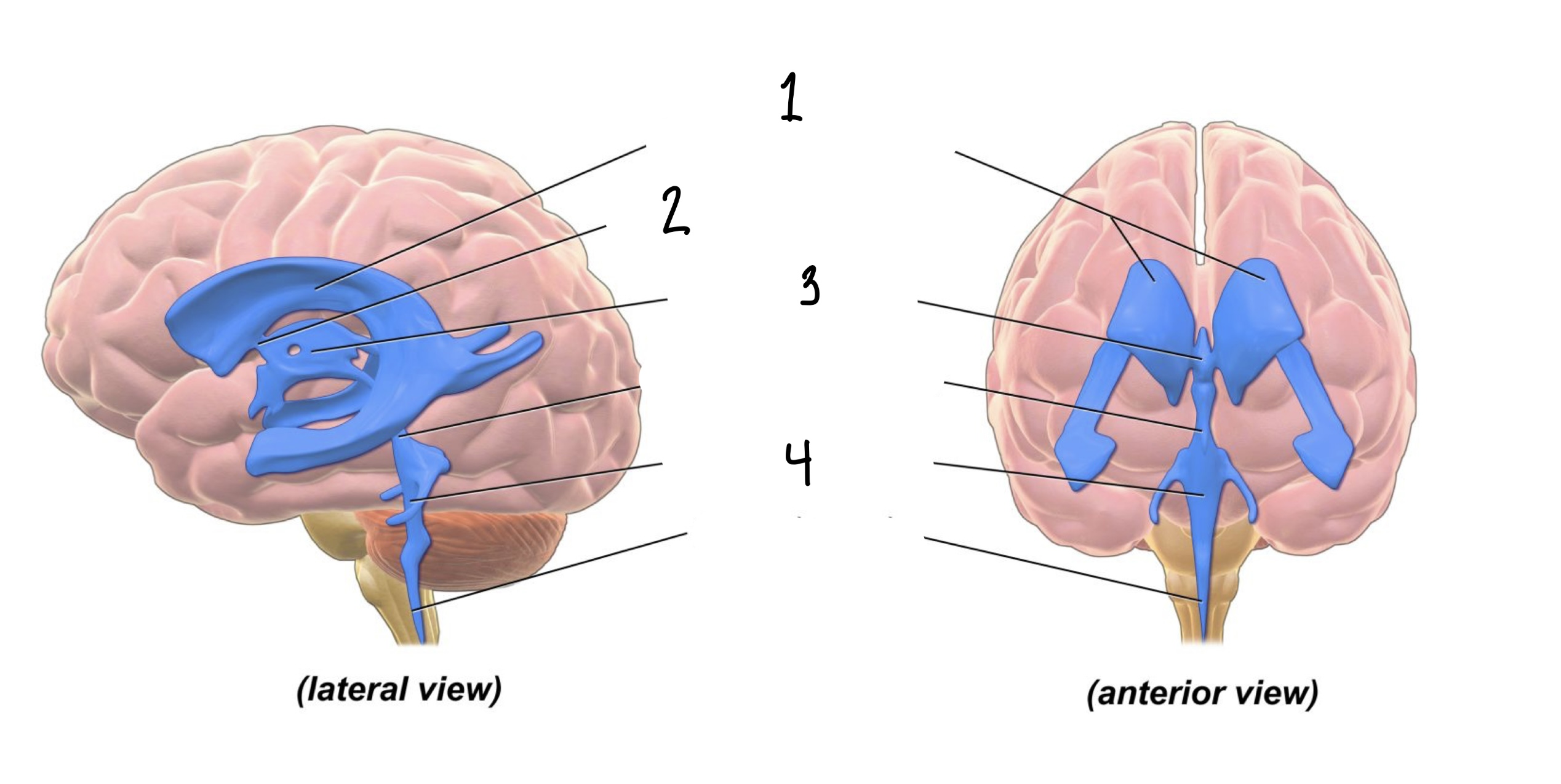
2
Interventricular Foramen
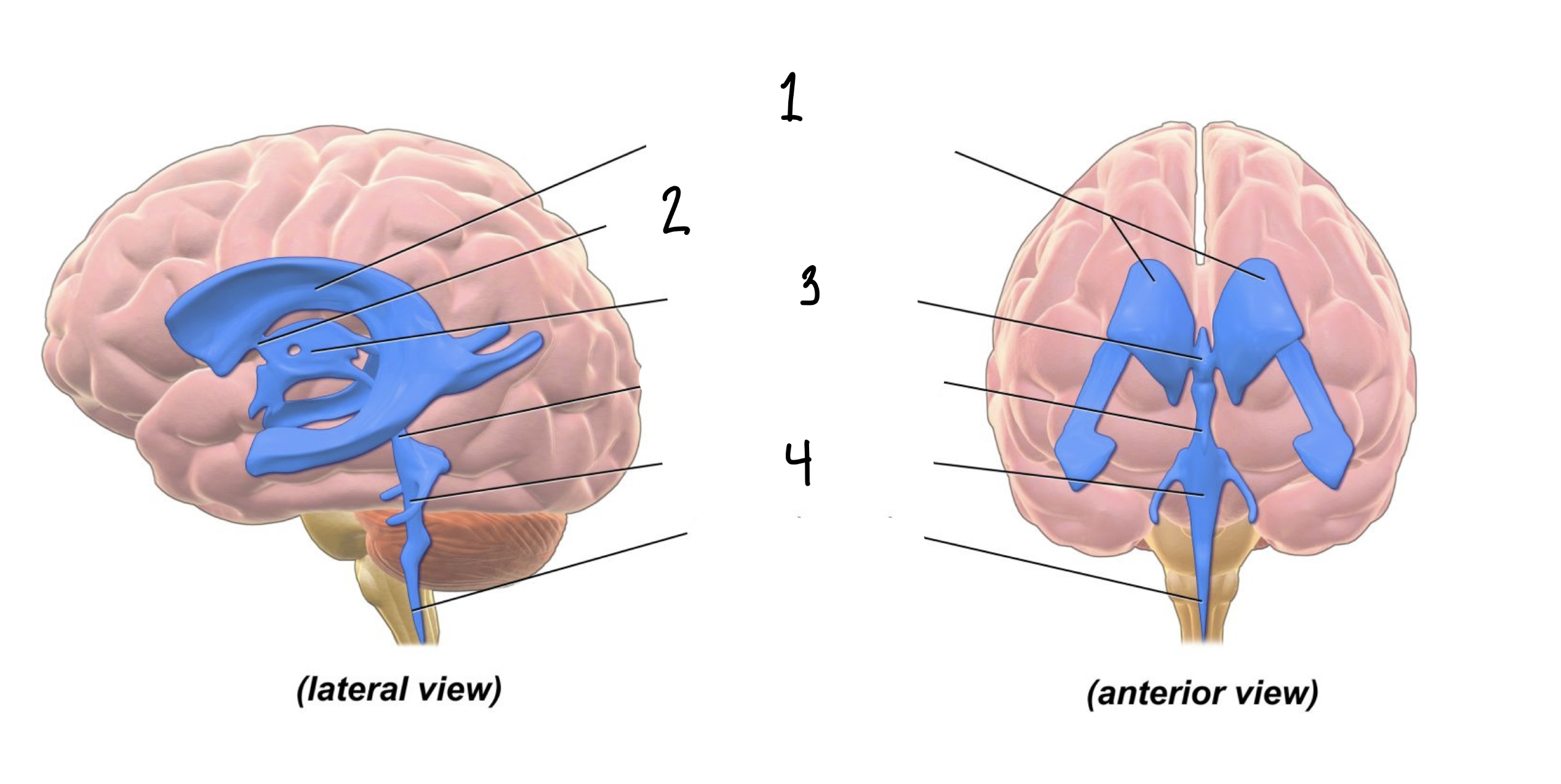
3
Third Ventricle
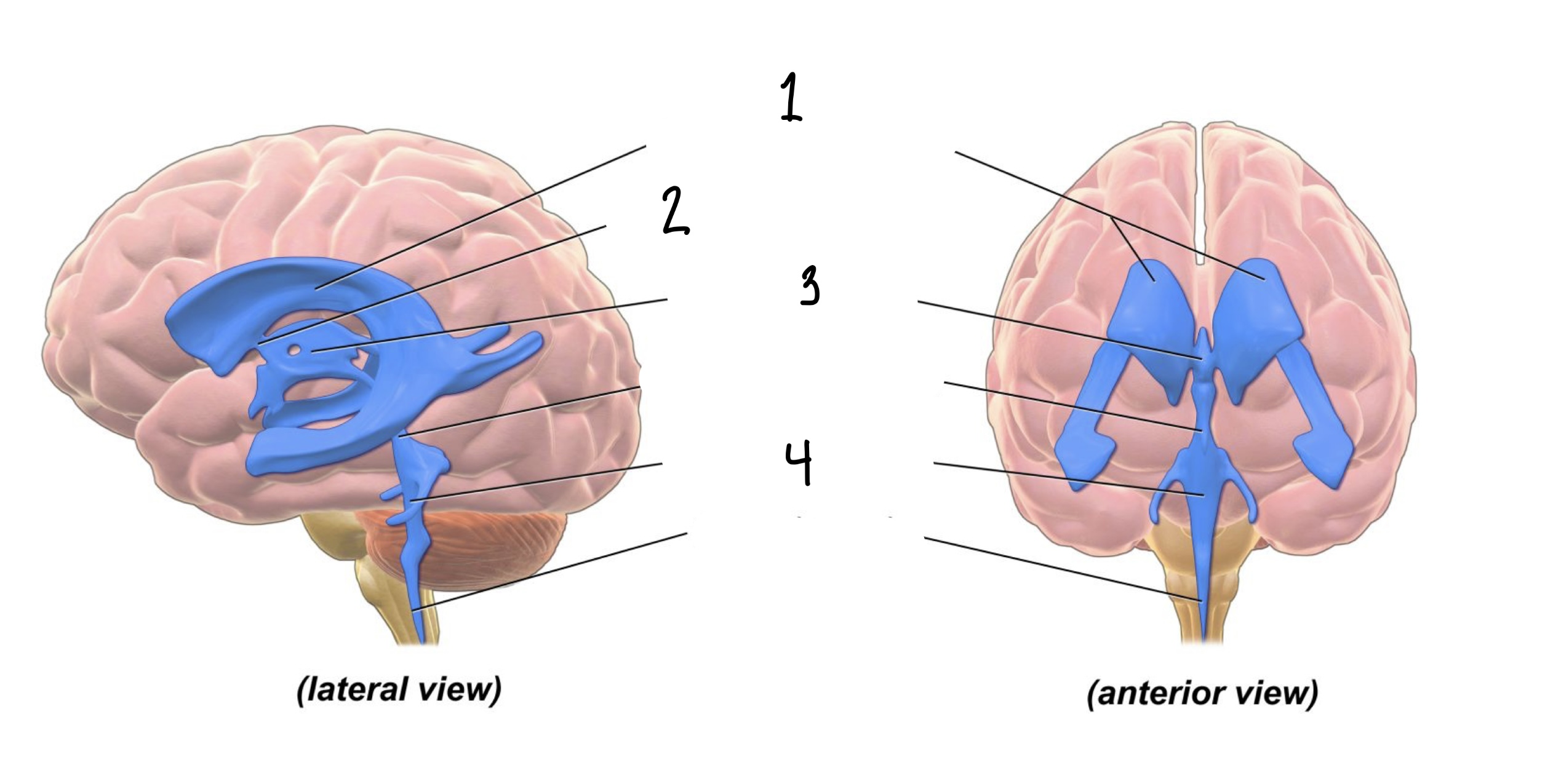
4
Fourth Ventricle
Within each ventricle is a _____, an aggregate of tissue that produce cerebrospinal fluid.
Choroid Plexus
The cerebrum is seperated into two cerebral hemispheres, what is the outermost layer of the cerebrum?
Cortex
What are the four lobes of the cerebrum?
Frontal, temporal, parietal, & occipital
The frontal lobe is made of what structures?
Prefrontal cortex, premotor cortex, primary motor strip, and broca’s area (speech production & articulation)
What are three functions of the frontal lobe?
Planning, initiation, inhibition, cognitive function, motor function, & expressive language
What structures make up the temporal lobe?
Primary auditory cortex (Heschl’s gyrus) & Wernicke’s area (language comprehension)
What are the functions of the temporal lobe?
Auditory reception & receptive language processing
What structures make up the parietal lobe?
Primary sensory cortex, supramarginal gyrus, & angular gyrus
What are the functions of the parietal lobe?
Sensory reception, visuospatial processing, & reading/writing
What structure make up the occipital lobe?
Primary visual cortex
What are the functions of the occipital lobe?
Visual perception
Gyri is described as the ___ on the surface of the cerebral cortex that elevates ridges of tissue.
Peaks
Sulci is described as the ___ on the cerebral cortex that separates gyri.
Shallow valleys
Fissure is described as the ___ on the cerebral cortex that separates larger regions of the brain.
Deep valleys
A deep groove that runs along the midline of the cortex, separating the two cerebral hemispheres.
Longitudinal fissure
Separates the frontal lobe from the parietal and the temporal lobe. Damage above the parietal and frontal lobe causes speech production deficits.
Sylvian Fissure
Separates the frontal and parietal lobes, also known to go ear to ear.
Rolandic fissure
Representation of structure to function along motor and sensory strips
Homunculus
Located deep to a region of the cerebrum, is needed for motor speech planning and perception of taste.
Insula