Fundamentals of Speech and Hearing Science
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
what is speech science
the basis for understanding human communication
- helps us to find normative which helps to find disordered
- helps build knowledge of A&P
what is speech production
the way in which our thought and language are converted into speech
phonotactics definition
the planning aspect of production
what is speech perception
how the brain processes speech and language
how is speech represented in the brain
comprehension
a deficit in hearing stage is an ___________ disorder
audiological
speech is a ______ act
motor
- it can take place with no meaning
what does language do?
conveys an idea
- it stays an idea until you are able to vocalize it
what is thought
ideas shared using speech and language speech
is speech tangible
YES
what is language
complex rule governed communication system
what are the components of language
semantics, syntax, morphology, phonology, pragmatics
what is semantics
word meaning
what is syntax
sentence structure
what is morphology
prefixes, suffixes, affixes, plurals, possessives (things you add on to words)
what is phonology
system of sounds
- rule based sound system
what is pragmatics
social use of language
what is the learning theory
selective reinforcement provided to the child as she or he uses language to operate on the environment
- B.F. Skinner and Mowrer
what is the innateness theory
the ability of human s to manage certain aspects of linguistic structure is innate.
- Noam Chompsky
what theory states that language drives thought
Sapir-Whorf Hypothesis
- linguistic determinism
how are speech sounds generated
they are planned
speech sounds are represented as ______
a complex of abstract phonetic features
- once you say it, it becomes concrete
- they can be changed into different patterns to make new words
the _______ allows us to analyze complex behavior into its components & better understand how those components are related
the research process
acoustic analysis
how sound is studied (both normal and disordered)
perceptual testing
can they make sense of what they hear
loosely called "experiments"
test a hypothesis; collect data to test a theory
what are the three major types of studies
normal, disordered, treatment
What is descriptive research?
observing and recording events to try to find relationships between them
- also called qualitative
what is experimental research?
observes and records behavior under controlled conditions in which the experimental variables are systematically changed by the investigator
- also called quantitative
what is the independent and dependent variable
DV: outcome
IV: what is being manipulated
research on a given topic usually starts with
descriptive research; this leads to creation of theories, which are then tested using experimental research
what is the symbolic aspect of language
linguistic organization; conceptual in nature
what is the physical aspect of language
air pressure, sound, electric signals
what is a spectrogram
a visual way of representing the signal strength (intensity) or "loudness" of a signal over time at various frequencies present in a particular waveform
explain the y and x axis of a spectrogram
time runs horizontally (x axis); frequency runs vertically (y axis)
- darker areas = more intensity
explain the source filter model
the vocal folds are the source and the filter is the articulators
physics
science that deals with matter, energy, motion, and force
acoustics
a BRANCH of physics that deals with the production, control, transmission, reception, and effects of sound
bioacoustics
combination of biology and acoustics in the study of sound production and perception in animals and humans
- human speech falls into this category
inertia
the resistance of any physical object to a change in its state of motion or rest
- AKA Newtons first law of motion
elasticity
the property of a material that returns it to its original shape after it has been changed by some external force - it allows you to change pitch
stiffness
the resistance of an elastic body to change by an applied force. The greater the stiffness of an object, the greater the force needed to displace it
intensity
the power per unit area; measured in watts/cm2 - decibels
pressure
force acting a specific surface area. can also be measured with water
sound has no ________
physical substance
- we could see a biproduct of sound
What is a longitudinal wave?
the wave motion of sound is longitudinal
- the individual molecules move parallel to the direction that the wave is traveling
- air molecules move left to right
what is a transverse wave?
the wave motion of water is transverse
- the molecules move up and down
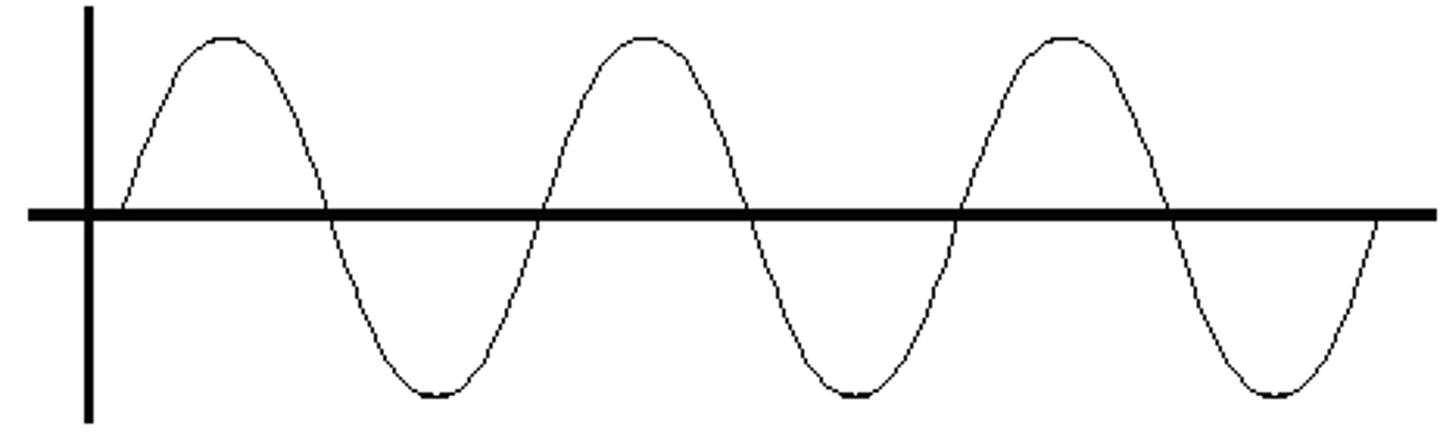
transverse wave EX
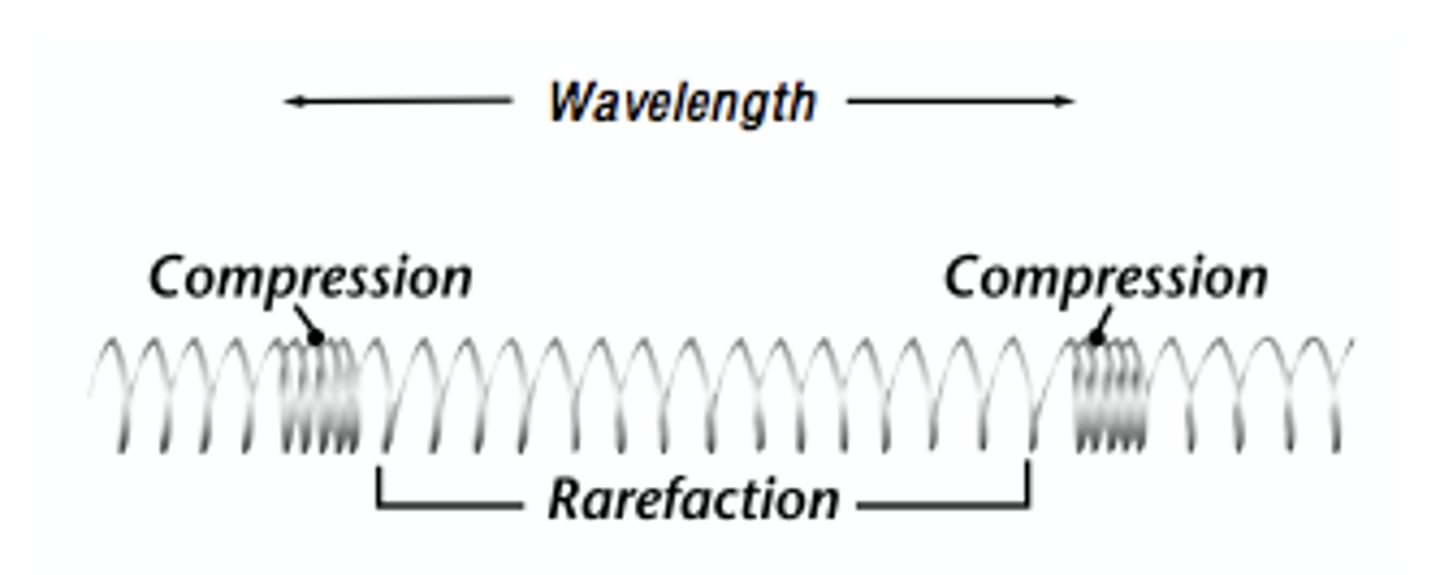
longitudinal wave EX
brownian motion
the constant state of movement that air molecules are in
what is a wavelength
the distance from any point on a wave to an identical point on the next wave
- one cycle
what is compression on a wave
as the source vibrates, it creates a chain reaction in the air molecules of adjacent areas
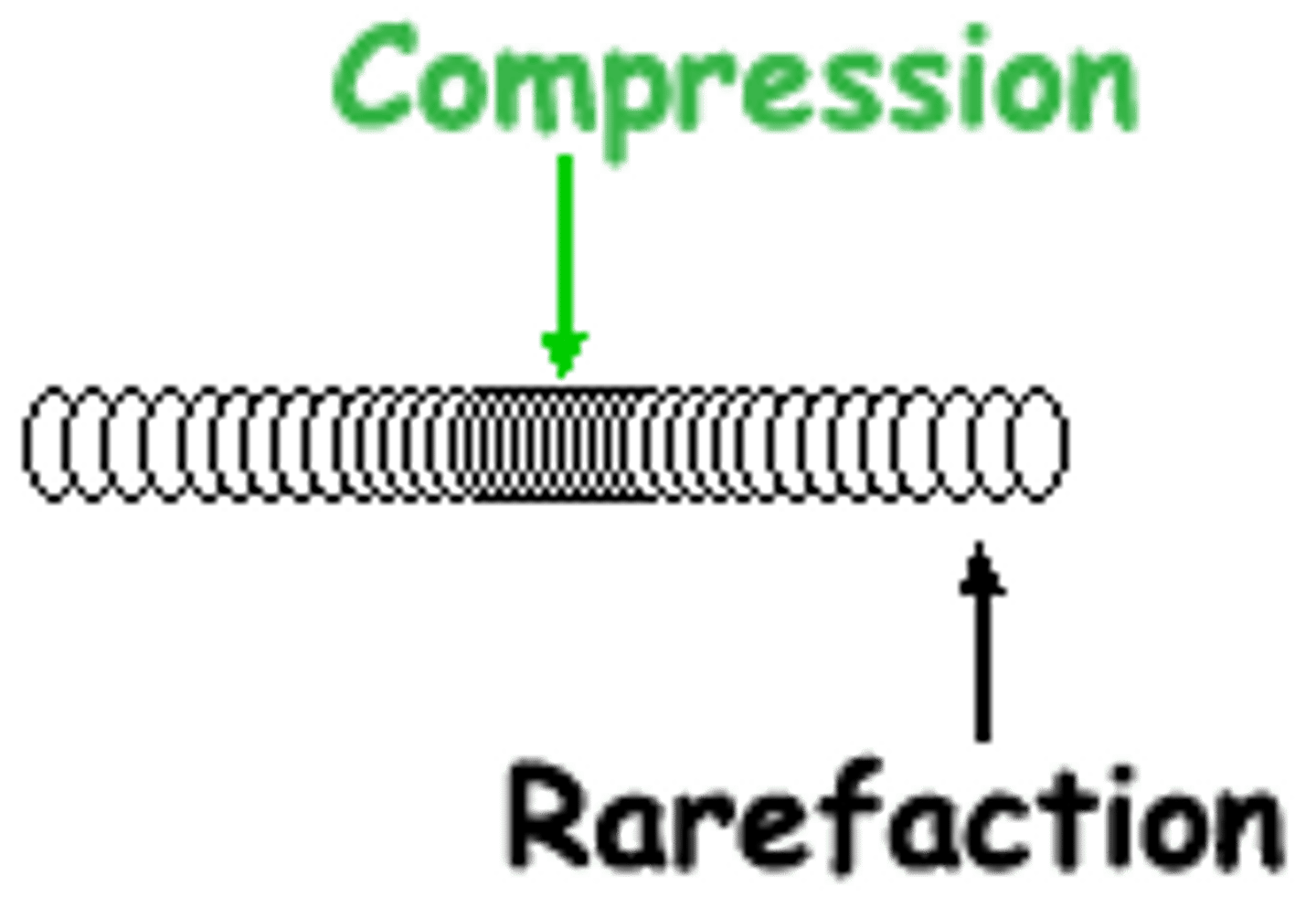
what is rarefaction on a sound wave
an increased distance between the groups of molecules involved
- aka expansion
what is ambient pressure
the pressure caused as air molecules "bump" into each other and whatever is in their path
- the collisions cause pressure
what are the essential constituents of sound
1. a souce of energy to start vibration- pressure must go from high to low
2. a force to keep the molecules moving
3. a medium of transmission (gas, solid, liquid)
what is simple harmonic motion
the period of compression or expansion
Sound disturbances are characterized as
waves
what is a simple wave
one frequency only, a pure tone
what is a complex wave
multiple frequencies; includes all other sounds, including speech
pure tones can only be described by 2 numbers:
frequency: rate of air pressure modulation (related to pitch)
amplitude: sound pressure level (related to loudness)
friction
resistance of one surface moving over another
what is restoring forces
elasticity
- it is strongest when inertia is weak
- inertia is strongest when RF is weak (at rest position)
what is a sine wave
the simplest wave form created by a vibrating body in the air
what are the number of cycles completed in one second called
the frequency of vibration
sound waves consist of a series of ________ that can be understood in terms of air molecules being pushed closer together (compression) or farther apart (rarefaction)
pressure disturbances
sound travels through the form of a
pressure wave
pure tones are ______
periodic
label a wave
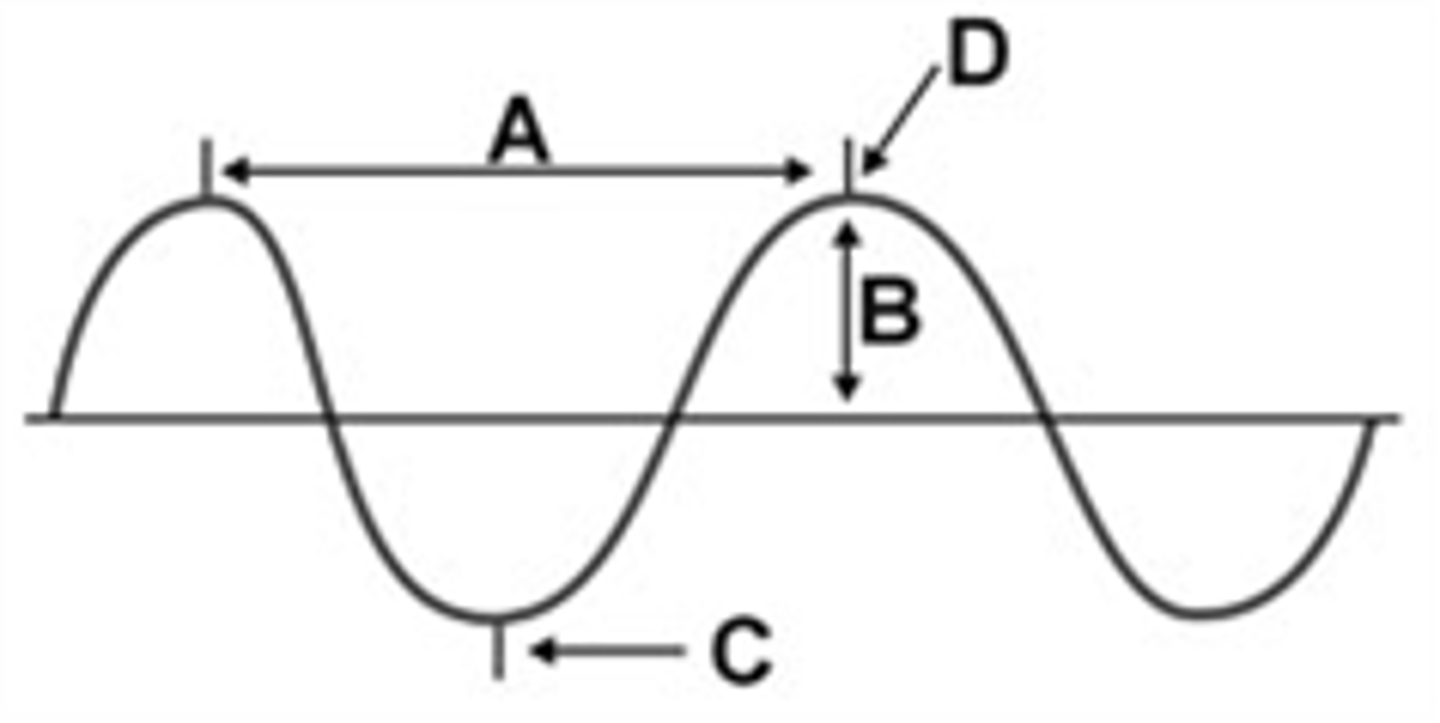
amplitude
magnitude of displacement of an object
- is directly related to the acoustic energy or intensity of a sound
what does a decibel measure
loudness (intensity)
what is the inverse law square
sound intensity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the sound source
what is an impedence
obstacle "blocked"
what are the 4 things that can happen when sound hits a barrier
1. reflection: sound bounces off the barrier
2. absorption: sound is absorbed into barrier
3. transmission: sound is transmitted through the barrier
4. diffraction: sound bends around the barrier
complex sound
two or more component frequencies that are harmonically related: a fundamental frequency plus harmonics
periodic
equal points between frequency; pure tone simple waves are always periodic
aperiodic
a wave in which individual cycles do not take the same amount of time to occur
can a simple wave be periodic and aperiodic?
no; just periodic
can a complex wave be periodic and aperiodic
yes: a complex tone of two or more frequencies that are harmonically related are periodic while a two or more frequencies not harmonically related are aperiodic
continuous
a sustained output of acoustic energy
transient
a sudden and brief burst of acoustic energy
is a pure tone continuous or transient?
can be either!
is the human voice periodic or aperiodic?
quasi-periodic (partially)
what is baseline
fundamental frequency
fundamental frequency
the lowest frequency which is produced by the oscillation of the whole object
harmonic
an overtone accompanying a fundamental tone at a fixed frequency
what is Fouriers Basic Principle
all complex period waveforms can be analyzed into a "sum of harmonics"
- you can break down a wave to see the different components
psychoacoustics
study of relationship between physical properties of stimulus and our and our subjective experience of the stimulus
- physical qualities mixed with perceptual qualities
pitch
perceptual correlate of frequency; affected by intensity
- vocal folds is a physical property
loudness
perceptual correlate of intensity; affected by frequency
- the stress put on vocal folds
you cant ______ if you cant ________
perceive; hear
frequencies produced during speech correspond with _______
human auditory sensitivity
differentiate frequency/pitch from loudness/intensity
frequency: measurable characteristic of acoustic signals
pitch: a listeners perceptual response (mainly) to frequency
what is the measurement "unit" for measuring the pitch
Mel Scale
resonance
increase in vibration when a force is applied at a natural frequency of the medium
resonator
object or medium set into vibration (tuning fork, vocal tract)
natural or resonant frequency
the object vibrates most easily and with the widest amplitude
larger vocal tract and cavity--
the lower frequency to which they will resonate
smaller vocal tract and cavity--
the higher frequency to which they will resonate