3.2 metal alloys and metal framework fabrication part 2
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
which investment consists of:
80% refractory fillers (silica in form of cristobalite or quartz)
binder (magnesium oxide and phosphate)
carbon is added to produce clean castings and facilitate easy removal of castings
phosphate bonded
which investment advantages:
high strength
easily withstand temp that reach 1650℉
used w high-fusing ceramometal alloys
phosphate bonded
which is the preferred investment material for rpd?
ethyl silicate
which investment consists of:
the binder is silica gel which reverts to silica
can be heated from 2000-2150℉
ethyl silicate bonded
which investment advantages:
ability to cast high temp alloys (base metal alloys)
good finish
low distortion
high thermal expansion
ethyl silicate bonded
what lab manipulation affects the microstructure and mechanical properties of Cr-Co alloys?
casting temp
what lab manipulation is used to adjust the alloy due to hardness and strength?
high speed lab equipment
cast clasps can break in service even in short period of time, due to ?
fatigue
it is (easy/difficult) to adjust hardness, strength and low elongation
difficult
T or F: high hardness can cause excessive wear of restorations or natural teeth that contact the cast framework
true
which metal:
most allergic metal known w 10-20% incidence
most common in women/chronic exposure through jewelry
can be quite severe
nickel
T or F: all nickel allergic indivs will react to intra oral nickel
false, immunological tolerance, possible genetic component
T or F: nickel ions (Ni2+) are mutagens but not carcinogens
true
various Ni compounds may contribute to development of which cancers
nasal and lung
which material:
increase risk of lung CA and tumors
paired with Ni reveal high leakage
acidic environment enhances its release from Ni-Cr alloys
beryllium
what is berylliosis?
chronic allergy-type lung response and chronic lung disease caused by exposure to Be and its compounds
occupational lung disease occur only in indiv
w hypersensitivity to beryllium
T or F: berylliosis is curable
false incurable, symptoms can be treated tho
six initial steps of fabrication of metal framework
survey by retripoding master cast and outline the partial design on the cast
beading (score for better adaptation) 0,5mm deep and wide
block out and relief (four types)
duplication w reversible hydrocolloid
refractory cast trimmed and treated w model spray or beeswax
waxing
what are the four types of block out and reliefs?
parallel block out
shaped
arbitrary
relief
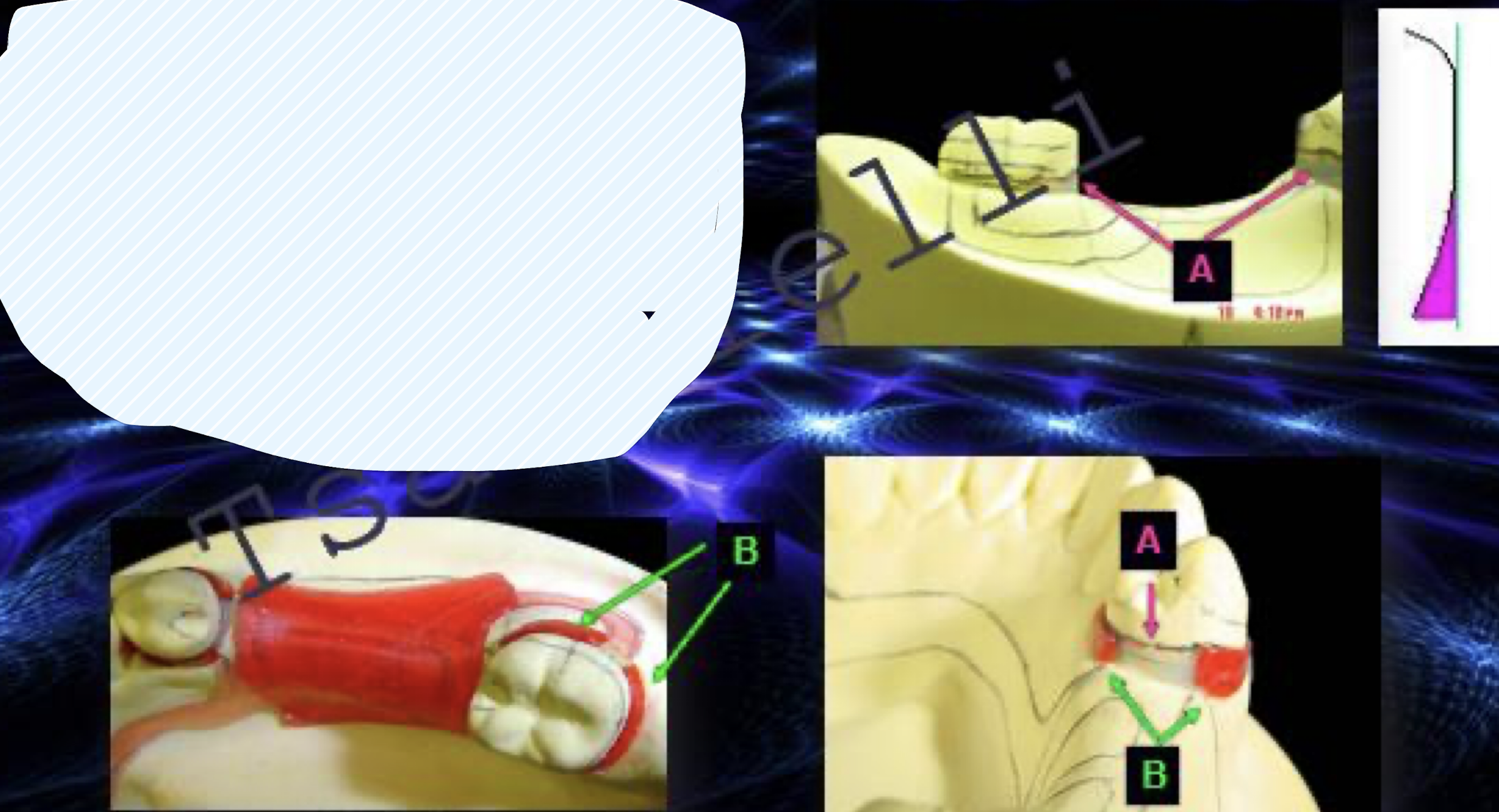
A: parallel block out
B: shaped block out
C: arbitrary aka soft tissue block out
D: relief, tissue stopper
what is a refractory cast?
refractory cast is a heat-resistant material, often a dry mixture of refractory aggregates, powders, and binders, that becomes a pourable, cement-like mass when mixed with water
why would you duplicate during fabrication of metal framework?
To create a precise, high-heat resistant model on which the framework can be waxed and cast without damaging the original master model. The duplication process produces a special model called a refractory cast.
agar storage unit, duplicating flask
what is then added to metal framework?
major connector and denture base minor connectors
clasps
spruing
investing
what is a spruing?
the process of attaching wax patterns of sprues to a wax-up of the RPD framework. These sprues form channels that will allow molten metal to flow into the mold to cast the final metal framework after the wax is removed. Proper spruing is critical to prevent casting defects and ensure the RPD framework fits correctly
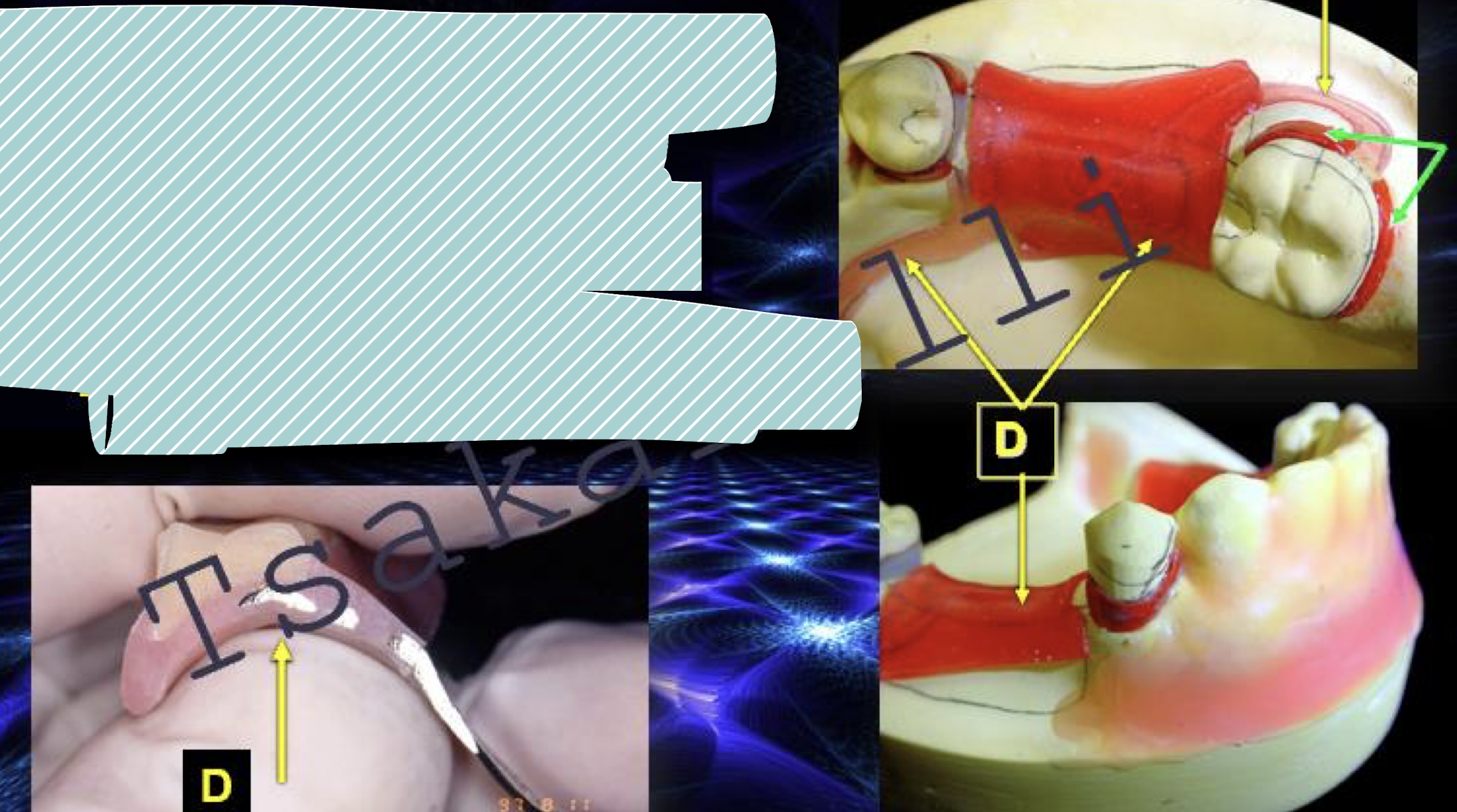
paint-on investment A first or second?

paint on investment B first or second?

what are the final steps of fabrication of metal framework?
burn out and casting
recovering the casting
finishing and polishing
what alloys are used for the retentive clasp?
cast alloy clasps or WW clasps
which alloy for retentive clasp: cast as part of framework?
cast alloy clasp
which alloy for retentive clasp: should be soldered to the framework?
WW clasp
why should excessive heating of the ww clasp be avoided during casting or soldering?
bc it will cause recrystallization compromising the wire’s mechanical properties
ww have (reduced/increased) flexibility when overheated
reduced
ww clasps should be soldered (near/at a distance from) retentive terminal reducing the likelihood of overheating during soldering procedure
at a distance
what gauge thickness are ww clasps available in?
18-20
advantages of which retentive clasp?
flexible in any direction
greater undercut 0.02”
more esthetic
minimum tooth contact
less fatigue failure
ww
disadvantages of which retentive clasp?
extra step in fabrication
distorted by pt careless handling
distortion with function
ww
what to look for w extraoral exam?
presence of defects (positive bubbles or nodules, voids or porosities)
continuity (reproduction of anatomy)
thickness of components
finish lines (staggered and less than 90°)
polish tissue surface of major connector not too much tho for good adaptation
fit
any occlusal contacts on metal components?
retention
interference
relief and block outs correct?
esthetics
damage on master cast?
describe thickness of major connector, rest, and clasp
major connector: rigid and strong
rest: minimum 1.5 mm at junction
clasp: uniformly tapered

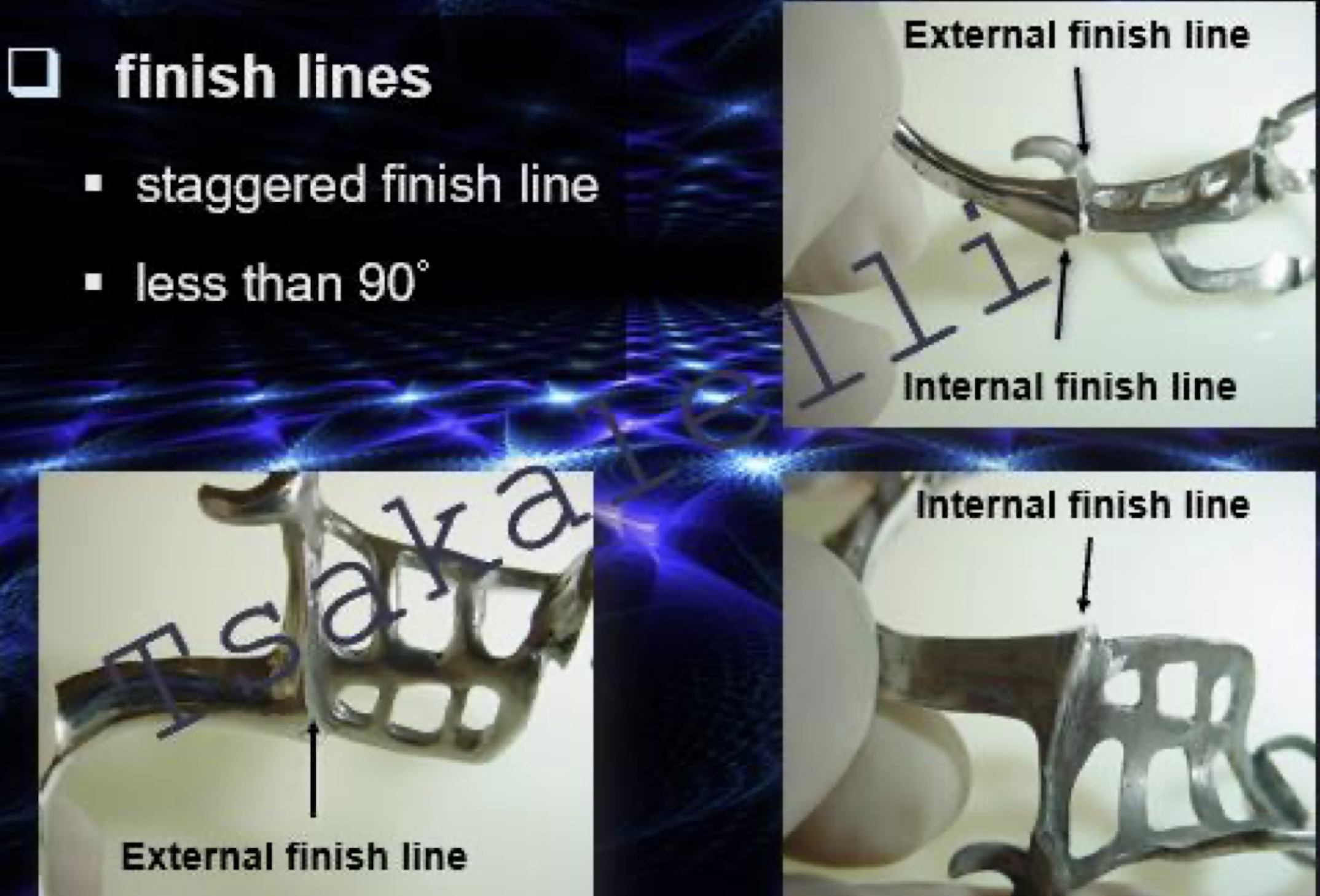
internal vs external finish lines
Internal and external finish lines are the junctions where the acrylic resin denture base meets the metal framework
The external finish line is on the visible, polished surface of the RPD, while the internal finish line is on the tissue-facing side.
They are staggered, or offset, to prevent a thin, weak area at the junction, which improves the strength and durability of the denture.
which portion of major connector is highly polished?
tissue surfaces crossing the gingival margin
mandibular major connector

T or F: technician can change design w/o doctor permission
false!
what to note for extraoral examination fit?
guide plate, rest confined in rest seat & tissue stop
intimate adaptation of rests, linguoplates, clasp arms
any spaces will promote plaque accumulation, decay & tissue inflammation
rocking
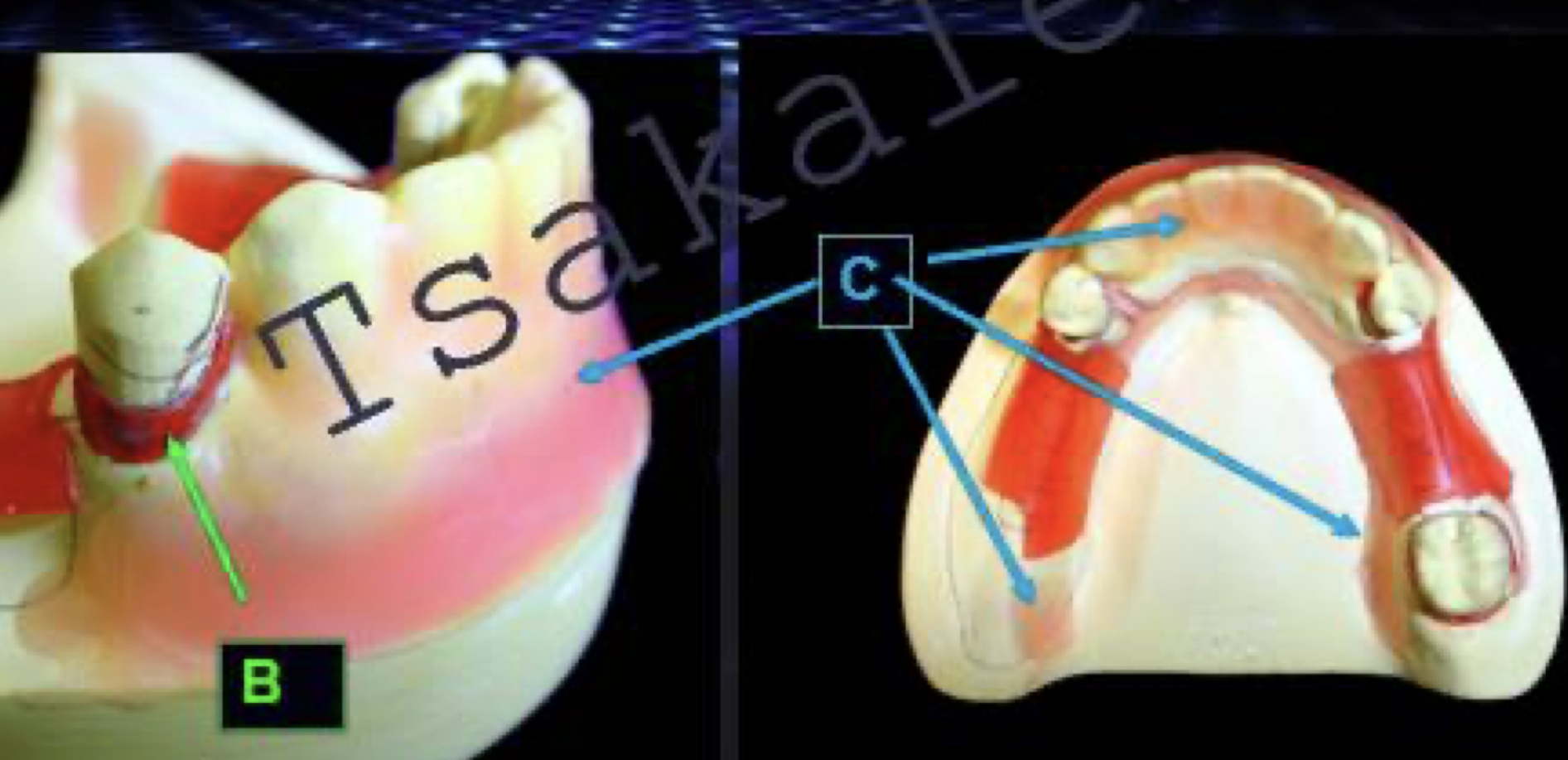
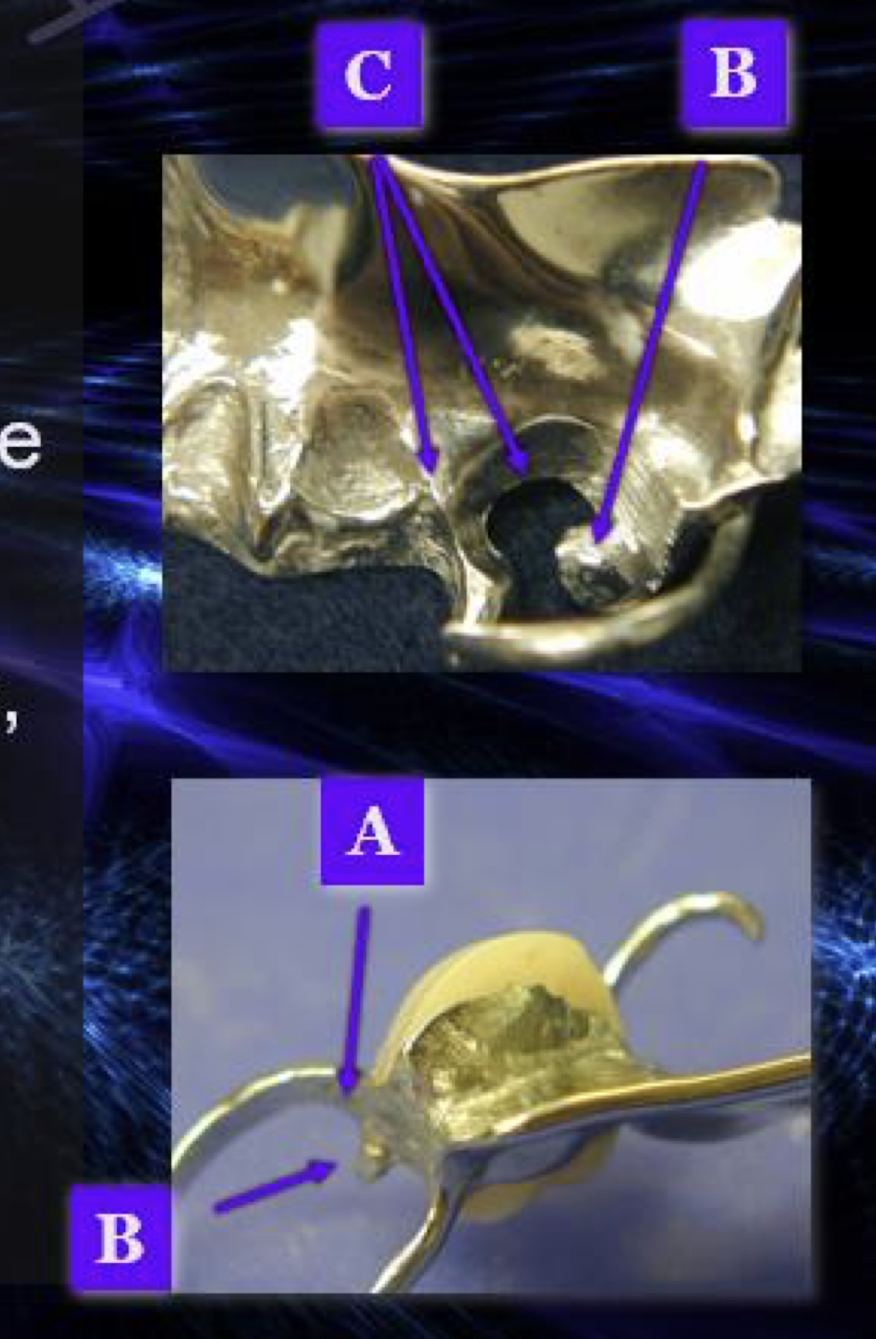
common areas to check for complete and stable seating: locating interferences: contacts btwn framework and abutment teeth
areas: above the survey line
shoulder region of circumferential clasps A
under rests B
on minor connectors and interproximal extension of lingual plates C
extraoral or intraoral exam: disclosing medium, show-through metal, carbide but or abrasive stone in high speed handpiece
intraoral
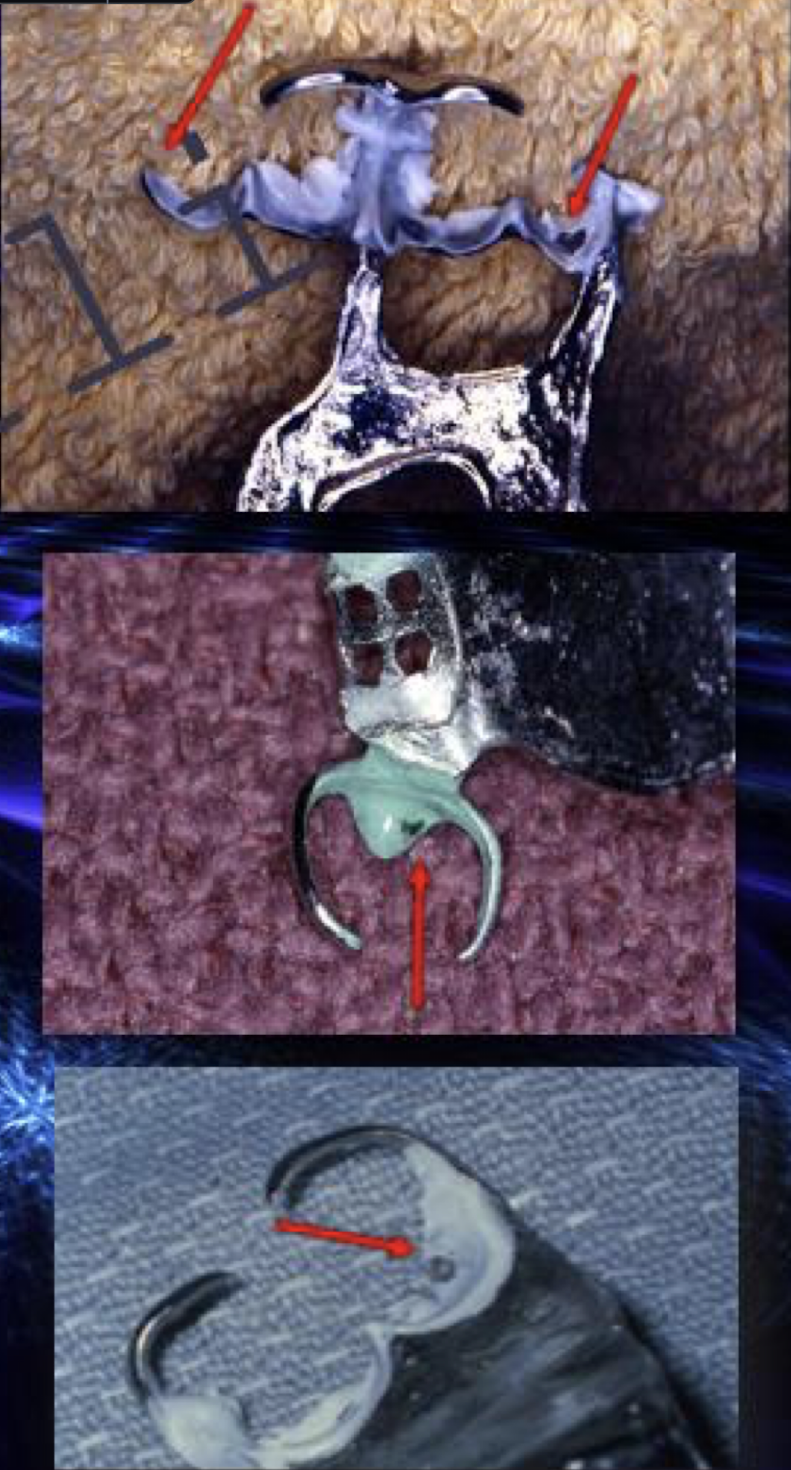

which part of intraoral exam:
confirm intimate contact w disclosing medium (no psaces)
abutment teeth and mucosal surfaces
adaptation
5 things to consider for occlusal eval (articulating paper and carbide bur in high speed handpiece)
check pt occlusion w nothing in the mouth
check centric contacts w on framework at a time
adjust contacts until original contacts established
repeat w other framework
check eccentric contacts and repeat w other framework
check occlusal contacts w both frameworks
final correction
what are some considerations for intraoral exam?
overcutting leading to mechanical failure
lost rest = lost support for denture
weakend clasp will fracture
reduction of opposing teeth
avoid if possible
adequate design and sufficient prep
what should be used for finishing and polishing?
mounted stone, rubber point