FMI Lec4 The money markets
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Money Market
highly liquid, short-term financial assets
Why do businesses not store money in banks?
tax benefits
During 2008, money market assets ____ their liquidity
lost
3 characteristics of money markets
large denominations (>= 1million)
Low default risk
low maturity (<= 120 days)
Is a 2 year bond that matures in 100 days a money market asset?
no— it has low residual maturity
Does return matter in money markets?
not really. Lenders/Buyers just want to store surplus funds. Only liquidation
Appeal of money markets
access quickly to short term funds at low cost. great for cash flow management when inflows and outflows aren’t well synchronized
Why are money markets at a cost advantage over banks?
banks have EoS, info advantage, but they are too heavily regulated
banks cannot lend 100% of their borrowed$ but money markets can
Regulation Q (Glass-Steagall Act 1933): put an interest rate cap on deposits to limit competition btwn banks
Regulation Q (Glass-Steagall Act 1933)
limit competition between banks by putting an interest rate cap
excessive competition leads to market failure. sacrifice welfare for financial stability. repealed
THe Glass-steagall act caused money markets to ____
boom
rose 3000%
effects lasted even after repeal in 87
money market borrowers
gov
finance companies
banks and corps
money market lenders
mutual funds
insurance companies
pension funds
banks and corps
T-bill
<3 months, 1 year
zero-coupon discount
T notes
2-10 years
semiannual
T bonds
10+ years
semiannual
TIPS
5-30 yr
semiannual
inflation adjusted
Annualized discount rate
n=maturity in days
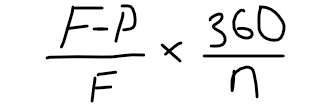
Investment rate
n=maturity in days
replace F of annualized discount rate with P
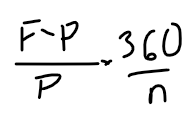
competitive bid at a T-bill auction
bids accepted in descending order of price until Q reached. then sold at lowest price.
<35% of issuance to each bidder
noncompetitive bid of t-bill auctions
bidders only provide amount not price, and they will take the price of the competitive bidders. their amount is guaranteed but they have no say over price
Federal Funds
short-term, unsecured loans between financial institutions to meet reserve requirements”
“Fed has cut interest rates”means ____
Federal Funds rate
How does federal reserve control federal fund rates?
influencing supply and demand.
rates move with T-bills.
Repos; Repurchase Agreements for Central Banks
a short-term loan where one party (usually a bank or dealer) sells securities — usually bonds — to another party (like the central bank) with a promise to buy them back later at a slightly higher price.
collateralized borrowing by CB
Negotiable certificates of deposit
deposit with specified interest rate and maturity.
term deposit: cannot withdraw before maturity
100k-10m USD
1-60 months
large market, second only to T bill
Buyers/lenders: wealthy individuals and pension funds
Commercial Paper CP
unsecured promissory notes
issued by a corporation maturity <270 days
drop in crises (like 9/11)
Asset-backed CP
secured by assets— securitized mortgages
collapsed during 2007 subprime mortgage crisis
Eurodollars
dollar denominated deposits in non-US bank
basis for LIBOR (London Interbank Offer Rate)
LIBOR scandal
LIBOR: the rate at which major global banks lend money to each other in the eurocurrency market
one side pays a fixed rate, and the other pays floating LIBOR rate betting it will decrease.
profit= $position(fixedrate - LIBOR)
banks colluded to get interest rate swaps
the Rates for different money market securities move ____
very closely
The primary differences between money market securities are in their ___ and ___ risk
credit and liquidity risk
money market securities should have
high liquidity
little price risk