Dinosaurs, Fossils, and Earth's Geological History
1/289
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
290 Terms
Where did dinosaurs live?
on every continent, including Antarctica.
What is the distinction between non-avian and avian dinosaurs?
Non-avian dinosaurs are true dinosaurs, while avian dinosaurs are considered birds.
Is Archaeopteryx classified as a bird or a dinosaur?
considered an early bird dinosaur, often referred to as a 'dino-bird'.
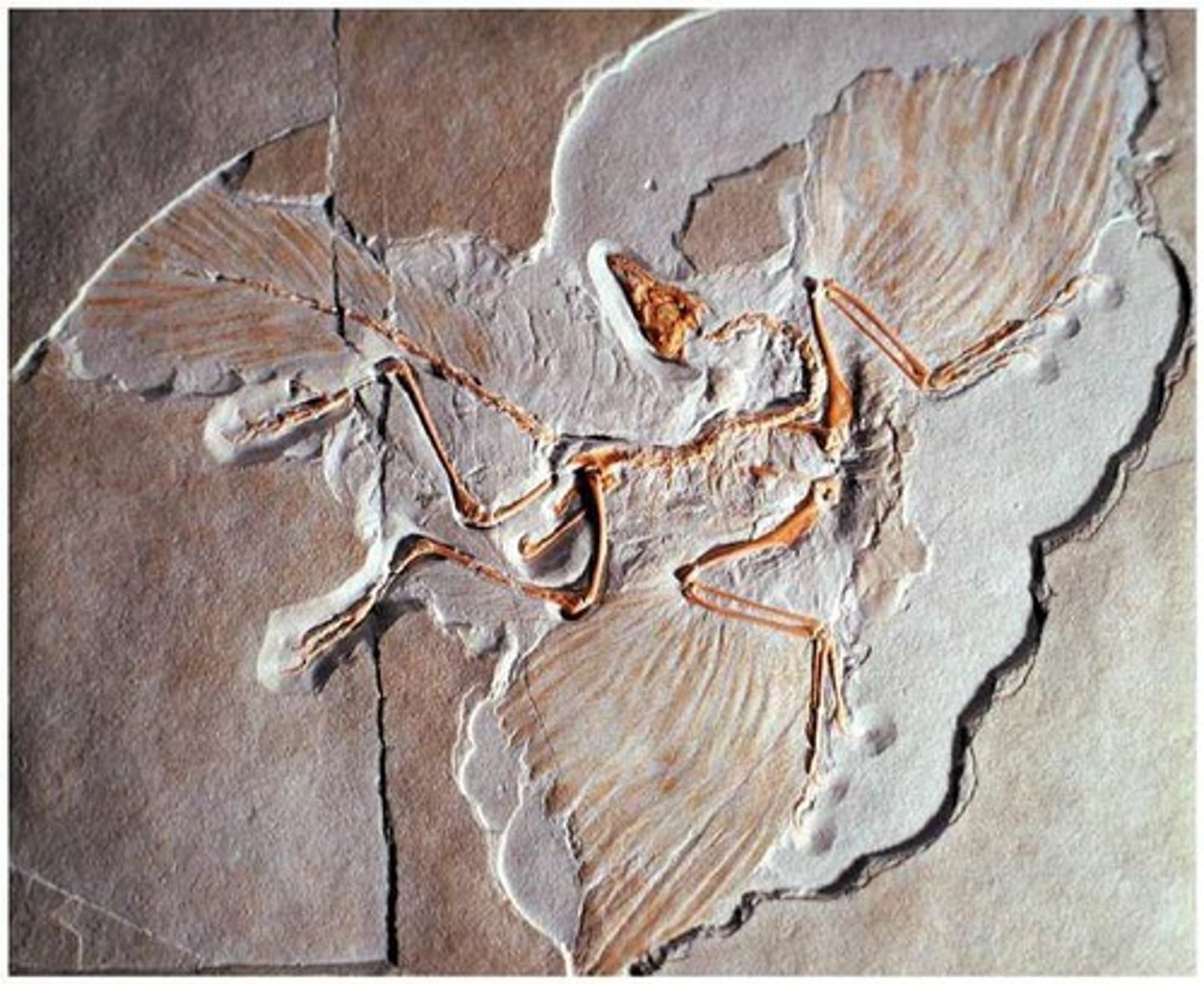

What features does Archaeopteryx possess?
features of both dinosaurs (bony tail, teeth) and birds (wings, feathers).
What is a 'transitional form' in paleontology?
an organism that exhibits traits of both ancestral and derived species, such as Archaeopteryx.
What is Microraptor?
four-winged dino-bird that may have had capabilities for gliding or powered flight.
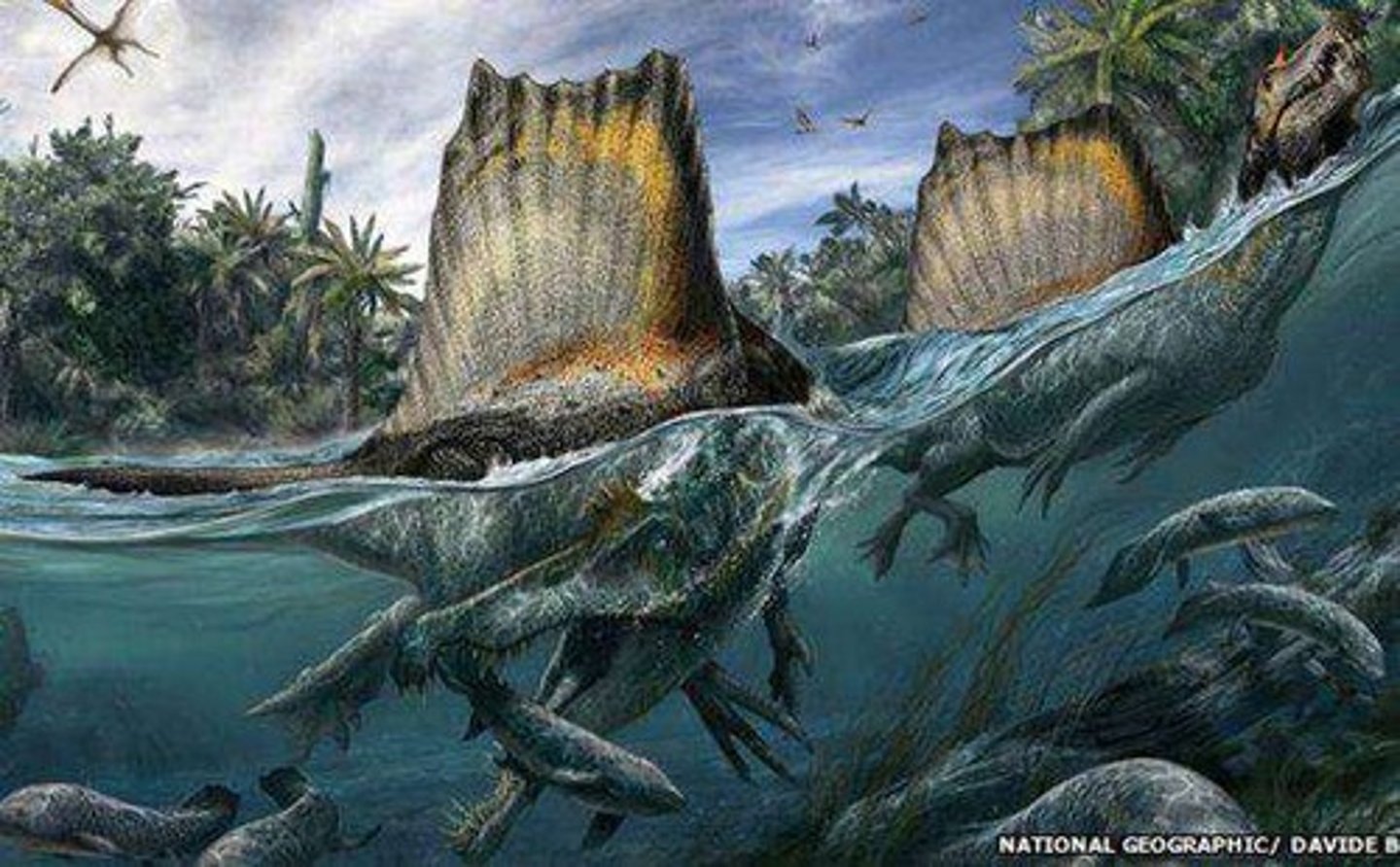
What adaptations did Spinosaurus have for a semi-aquatic lifestyle?
flat feet for paddling, retracted nostrils, dense bones for buoyancy, and a broad tail for steering.

What is the significance of the fossil record in paleontology?
it is complex and constantly changing, reflecting the evolving understanding of prehistoric life.
What is plate tectonics?
theory that Earth's outer shell is divided into lithospheric plates that move and interact.
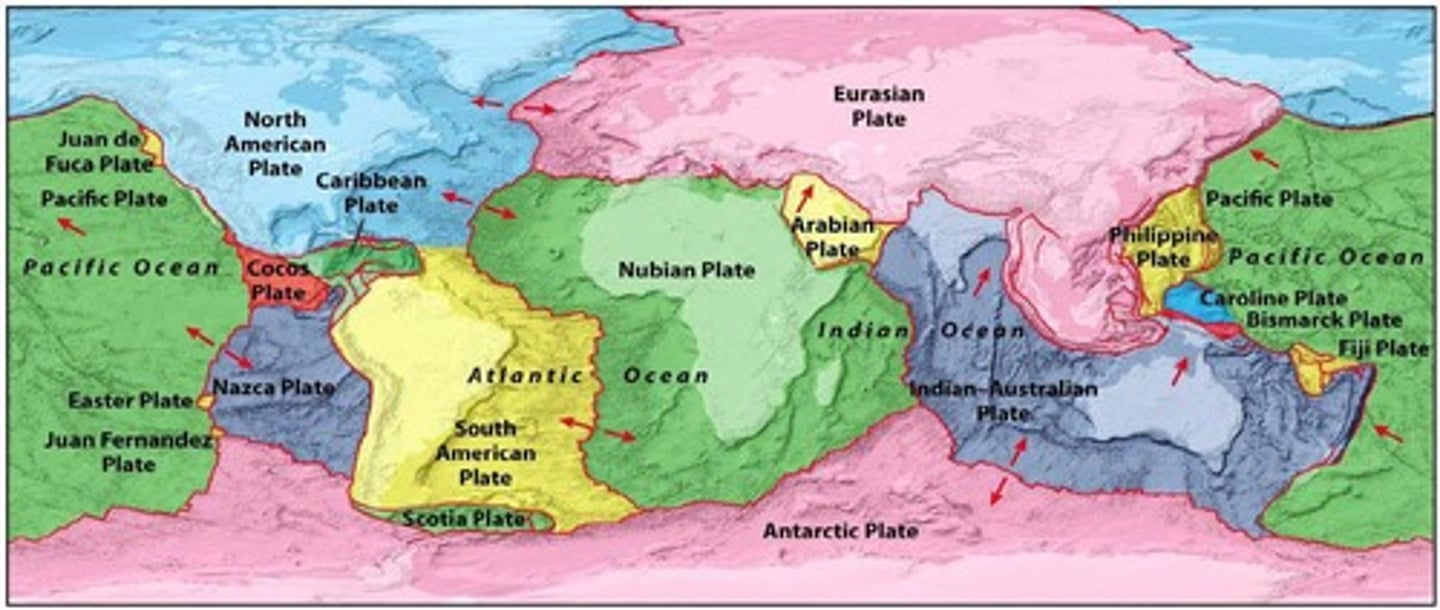
What are the two types of crust in Earth's structure?
continental crust (thick, rich in Si and Al) and oceanic crust (thin, rich in Fe and Mg).
What is the composition of the Earth's core?
The core is metallic, while the crust and mantle are dominated by silicate minerals.
What are the three main layers of the Earth?
crust, mantle, and core.
What is the lithosphere?
composed of the rigid uppermost mantle and the crust.
What are the three types of plate boundaries?
divergent (plates move apart), convergent (plates move together), and transform (plates slide past each other).
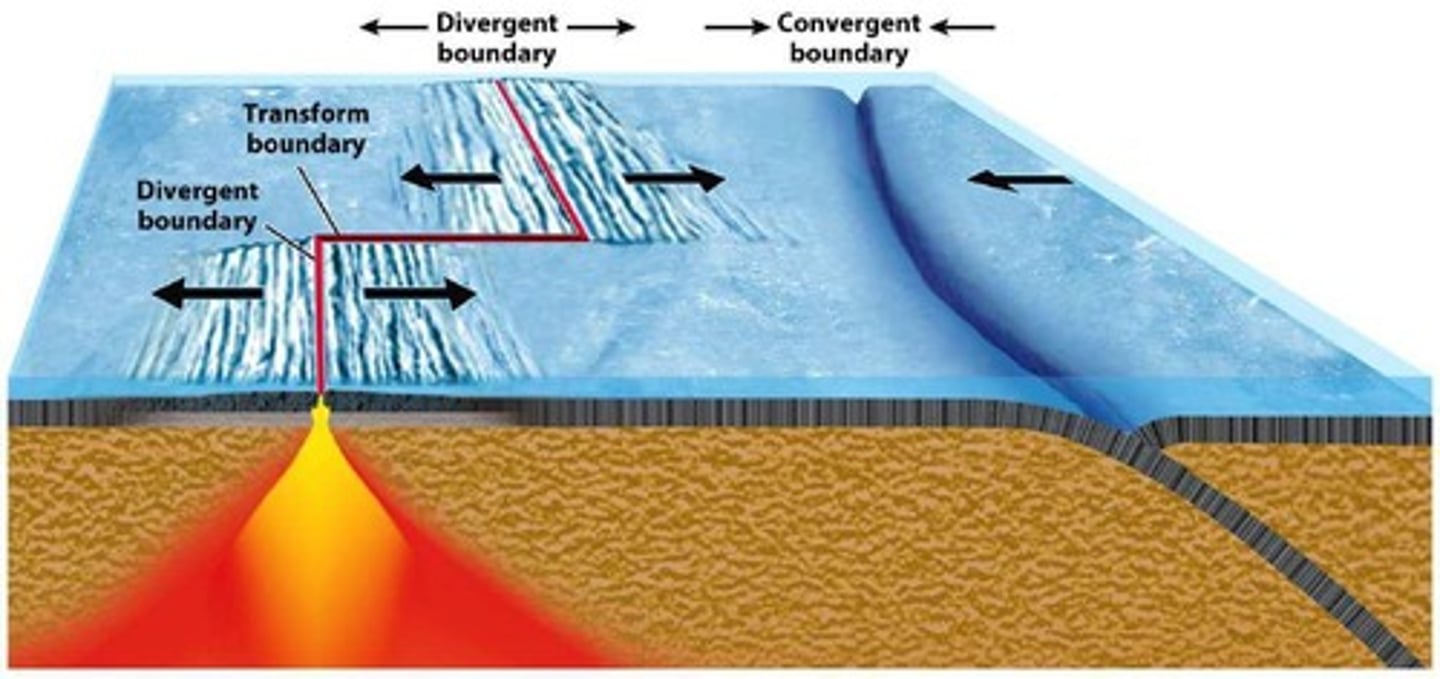
How do divergent boundaries create new oceanic crust?
At divergent boundaries, hot rocks rise, melt, and fill gaps, creating new oceanic crust as plates move apart.
What happens to rocks as you move away from a mid-ocean ridge?
Rocks get older as you move perpendicular away from the ridge due to the continuous formation of new crust.
What drives the movement of tectonic plates?
Tectonic plates move in response to forces within the Earth, typically at rates of ~0-10 cm/year.
What is the difference between the uppermost mantle and the asthenosphere?
uppermost mantle is rigid and brittle, while the asthenosphere is a ductile solid.
What is the role of pressure, temperature, and density in Earth's layers?
Pressure, temperature, and density increase with depth, leading to differences in phase and mechanical behavior of Earth's layers.
Where do we find dinosaur fossils?
found on every continent because dinosaurs lived on land.
What is the takeaway message about the science of paleontology?
it is complex and always changing, reflecting ongoing research and discoveries.
What is the significance of the term 'missing link' in paleontology?
refers to a transitional form that provides evidence of evolutionary change between groups.
What is the relationship between dinosaurs and modern birds?
Modern birds are considered avian dinosaurs, sharing a common lineage with non-avian dinosaurs.
What geological feature is produced by seafloor spreading?
A continuous row of subsea volcanoes called the mid-ocean ridge.
Where is Thingvellir National Park located?
Iceland, on the boundary of two tectonic plates pulling away from each other.
What are the likely geologic hazards at divergent boundaries?
Volcanic activity and earthquakes.
What happens at an ocean-continent convergent boundary?
The oceanic plate is subducted beneath the continental plate, forming a deep trench and volcanic arcs.
What is formed as a result of oceanic crust being subducted?
An arc of volcanoes occurs on land above the subducting plate.
What mountain range was formed by the subduction of the oceanic plate beneath the continental plate?
The Canadian Rocky Mountains.
What occurs at an ocean-ocean convergent boundary?
Two oceanic plates collide, with the older, colder, denser plate subducting and forming an arc of volcanic islands.
What is produced by continent-continent convergence?
Very large mountains, such as the Himalayan Mountains.
What is the height of the Himalayan Mountains?
Approximately 9000 m above sea level.
What characterizes a transform boundary?
Side-to-side movement with no crust created or destroyed.
How do transform boundaries commonly form?
Along spreading centers to relieve stress.
What is an example of a transform fault?
The San Andreas Fault.
What drives the movement of tectonic plates?
Heat from the Earth's interior causes convection currents in the mantle.
What happens to water when it is heated from below?
It expands, becomes less dense, and rises.
What causes plates to move down into trenches?
The relatively high density of oceanic lithosphere and the weakness of the asthenosphere.
What evidence supports the theory of continental drift?
Similarity of fossils and rocks on different continents.
What was the name of the supercontinent proposed by Alfred Wegener?
Pangaea.
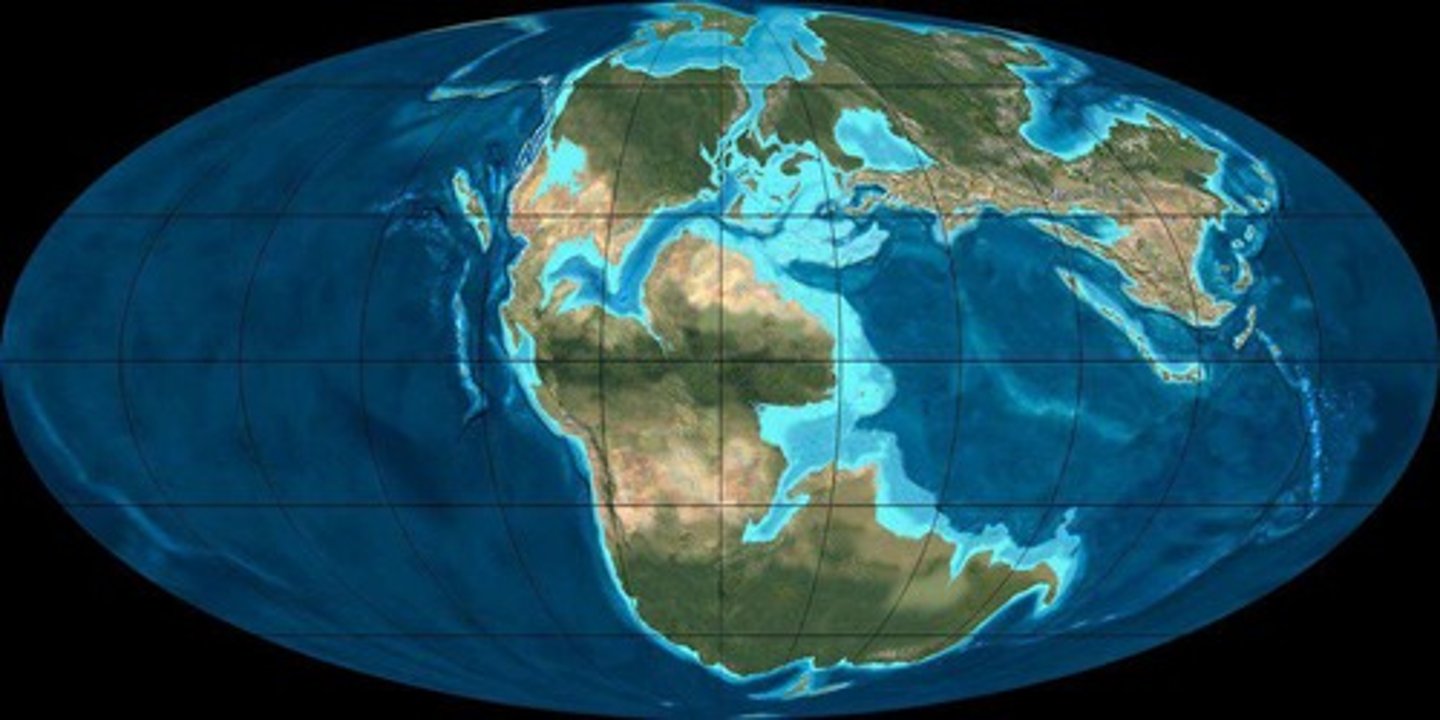
What type of evidence shows that continents were once connected?
Geologic evidence such as rocks of the same age and type found on separated continents.
What occurred during the Late Permian period?
Pangaea existed as a single supercontinent with ice sheets over the South Pole.
What significant event happened during the Early Jurassic period?
Pangaea began to break apart, leading to rising sea levels and the formation of inland seas.
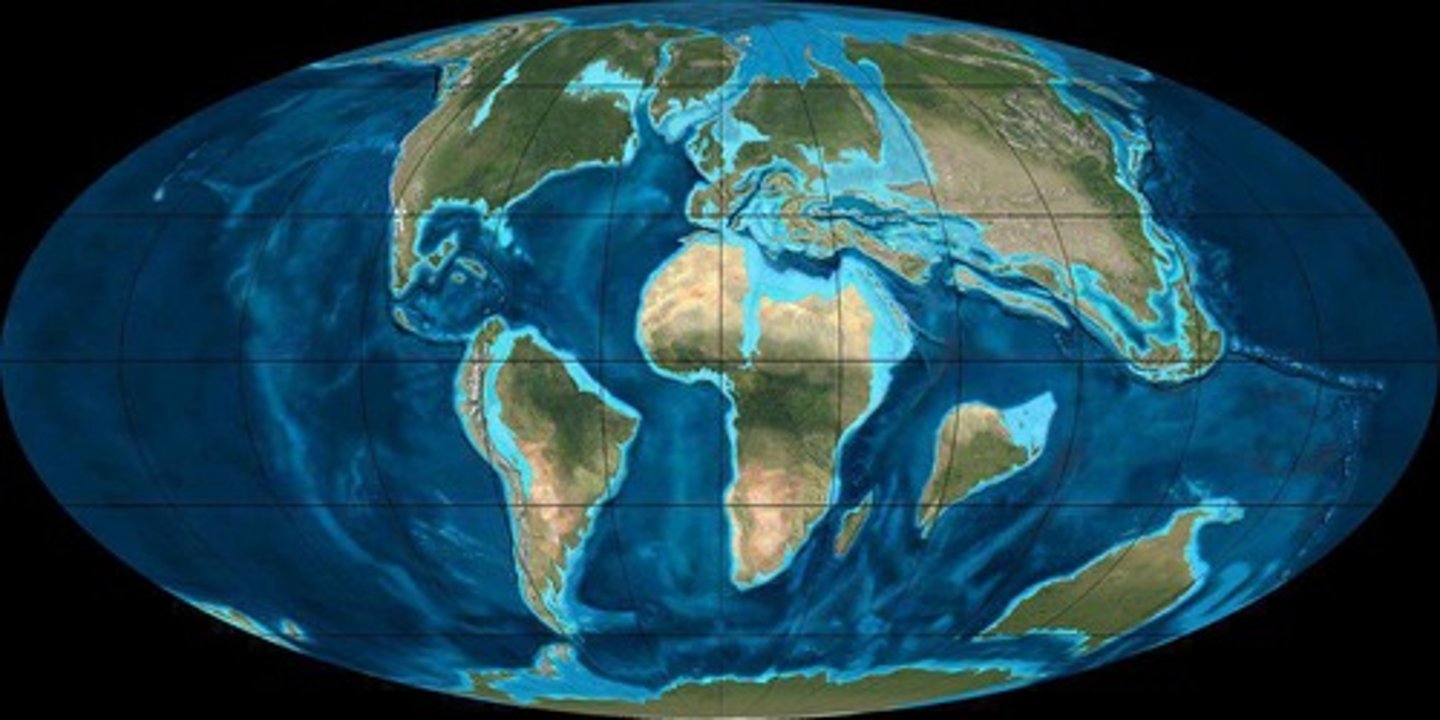
What were the two smaller supercontinents formed after Pangaea?
Laurasia and Gondwana.
What is the significance of the Tethys Ocean?
It was an ocean that existed between Laurasia and Gondwana during the breakup of Pangaea.
What significant geological event occurred during the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous (120 Ma)?
India moved north at 15 cm/year and collided with Asia 40 million years later.
What happened to Africa and South America during the middle Cretaceous (105 Ma)?
Africa and South America split, while India continued to move north and Australia remained attached to Antarctica.
What was the state of sea levels during the Late Cretaceous (90 Ma)?
Africa, Europe, and India were flooded, leading to the formation of the Western Interior Seaway.
What marks the end of the Age of Dinosaurs?
The Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary (65.5 Ma) when continents were near their modern positions and sea levels began to drop.
How did the climate during the time of the dinosaurs differ from today?
The climate was alien compared to today, with significant variations in climatic and environmental conditions over time.

What impact did the supercontinent Pangaea have on climate?
Coasts were wet while interiors were arid, leading to stronger seasonal temperature swings.
What geological evidence indicates dry conditions during the time of Pangaea?
Desert sands and massive salt deposits formed in dry areas with little vegetation.
How do coal deposits relate to the climate during the time of the dinosaurs?
Coals formed in warm, wet coastal swamps near the equator from vegetation that fell into stagnant water and did not decompose.
What evidence suggests that the South Pole was once glaciated before the time of the dinosaurs?
The presence of glacial till near the South Pole indicates past glaciation.
What changes occurred in climate as Pangaea began to break up?
Temperature swings and aridity in the interior of continents became less extreme, and global temperatures warmed.
What was the global average temperature during the time of the dinosaurs compared to present?
The global average temperature was approximately 4 - 9°C warmer than present.
How did the temperature gradient between the equator and the poles change during the time of the dinosaurs?
The equator remained hot, but the poles were not as cold, resulting in a smaller temperature gradient.
What evidence exists regarding ice at the poles during the time of the dinosaurs?
There was likely no permanent ice at the poles, although it did snow.
What is the nature of climate change in relation to the time of the dinosaurs?
Climate change is a natural phenomenon, with a long record extending back billions of years.
Why is the climate record less reliable the further back in time we go?
The climate record becomes more incomplete and less reliable as we go further back in time.
Did humans coexist with dinosaurs?
No, humans were not present during the time of the dinosaurs.
What misconception do some people have about humans and dinosaurs?
A 2015 poll indicated that 41% of Americans believe humans and dinosaurs lived at the same time.
What was the public reaction to a controversial image of a hunter with a triceratops?
The image sparked outrage, with many expressing disappointment and calling for the hunter to be named and shamed.
What does the term 'supercontinent' refer to in the context of the time of the dinosaurs?
A supercontinent refers to all continents being assembled into a giant landmass, affecting climate and environmental conditions.
What climatic conditions were observed in coastal areas during the time of the dinosaurs?
Coastal areas were generally rainy due to the ocean's regulating effect on temperature.
What type of deposits indicate areas that experienced significant evaporation?
Salt deposits formed in lakes and restricted seaways where evaporation exceeded freshwater influx.
What is the significance of footprints of Minisauripus and raindrop impressions in understanding dinosaur climates?
They provide evidence of weather conditions during the time of the dinosaurs.
What are the main causes of climate change?
Changes in solar radiation, greenhouse gas concentrations, and Earth's distance from the sun.
What are the four main climate archives used to understand ancient climates?
Sediment, Ice, Coral, and Tree Rings.
How do climate archives serve as proxies for climate change?
They respond in specific and predictable ways to climatic and environmental changes.
What is the Principle of Uniformitarianism?
Natural processes have been uniform through time, and studying modern geologic processes helps understand past events.
What does the phrase 'The present is the key to the past' mean in geology?
Current geological processes can provide insights into historical geological events.
What evidence do sedimentary rocks provide about past climates?
Different rocks form in different environments, indicating past climatic conditions.
How do ice cores provide information about ancient climates?
Ice traps atmospheric gases, which reveal past concentrations of greenhouse gases.
What information can tree rings provide about past climates?
The thickness of tree rings indicates favorable growth conditions, and the number of rings can determine the tree's age.
How can fossils indicate past climates?
Certain plants and animals are restricted to specific habitats, revealing climatic conditions of their time.
What role do isotopes play in understanding climate change?
The ratio of light to heavy isotopes in fossils and sediments varies with temperature, allowing inference of past climate changes.
What was the average temperature during the Time of the Dinosaurs compared to today?
It was several degrees warmer, with carbon dioxide levels 2X to 5X higher than today.
What geological event contributed to increased greenhouse gases during the Time of the Dinosaurs?
The breakup of Pangea caused intense sea-floor spreading and extensive volcanism.
How did volcanism contribute to climate change during the Mesozoic?
Volcanoes released large amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
What humorous factor contributed to greenhouse gas emissions during the Mesozoic?
Dinosaurs, especially herbivorous ones, produced methane gas.
What trend among dinosaurs may have contributed to global warming?
A trend towards gigantism, resulting in vast herds of large grazing dinosaurs.
What is the significance of the temperature difference (T) in climate records?
It is presented as the difference in temperature relative to the 1960-1990 average, indicating climatic changes.
What is the role of coral in climate archives?
Coral can provide records of past ocean temperatures and conditions.
How do different climate archives vary in their responses to change?
Each archive has different resolutions (seasonal, annual, longer) and provides records for different time intervals.
What is the significance of comparing different climate archives?
Comparisons must account for differences in response and resolution to accurately interpret climate changes.
What climatic conditions are indicated by coastal sedimentary rocks?
They indicate environments with evaporation and coastal processes.
What climatic conditions are indicated by swampy sedimentary rocks?
They indicate environments rich in plant life and wet conditions.
What climatic conditions are indicated by glacial ice?
They indicate cold environments where ice formation occurs.
What does the presence of certain fossils in specific habitats tell us?
It indicates the climatic conditions that allowed those organisms to thrive.
What happens to sea levels during low periods?
The coastline is situated near the break in slope between the continental shelf and slope, leading to erosion of the shelf by waves.
What occurs during high sea level periods?
The shallow shelf is flooded by up to 100 m of water, leading to deposition of marine sediments on the shelf.
What evidence indicates that sea levels were generally high during the Time of the Dinosaurs?
Extensive marine deposits found on continental shelves, such as the white chalk cliffs in England and France, which are made up of tiny skeletons of marine animals.
What are the two main causes of sea level rise?
Tectonic activity and climatic factors.
How does tectonic activity affect sea level?
It changes the size of the ocean basin; a smaller basin causes sea level to rise, while a larger basin causes sea level to drop.
What is the relationship between ocean basin size and sea level?
The volume of water remains constant, but the space it occupies changes with the size of the ocean basin.
How can tectonic activity change the size of the ocean basin?
By colliding or separating continents and changing the size of mid-ocean ridges.
What happens to sea level during continent-continent collisions?
It creates larger ocean basins, leading to a drop in sea level.
How did the separation of continents during the Time of the Dinosaurs affect sea level?
It would have kept sea level higher than it is today.
What is the average depth of mid-ocean ridges?
The crests of the ridges occur 2500 m below sea level.