Streams & Floods
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Streams + rivers
concentrated flows of water in channels
erodes, transports, then deposits sediments
transfers mass from continents to ocean basins
Uses of stream flow
gathering water, growing food, drinking, transporting, gaining energy (electricity)
Hyrdrologic Cycle
condensation from clouds falls (rain), flows down through channels into ocean, evaporates back into clouds
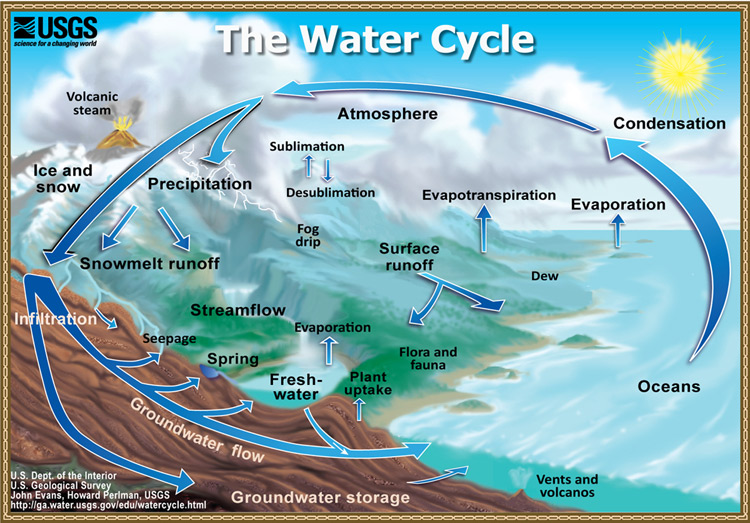
Stream Bank
along the edges of the channel, kinda the surface
parts of a stream
Streambed
floor of the channel, deepest part of the stream
parts of a stream
Reach
a defined length of the channel, prob in a unit
parts of a stream
Runoff
sheet-like flow over the land surface
happens if a stream is not in a channel
Efficiency of erosion
depends on:
velocity of flow, steepness of the slope, type of soil or rock present, and presence of vegetation
Downcutting
process where water flowing in a channel cuts into the substrate and deepens the channel
basically digging into the ground, making a deep crevice
as _____ continues, channel depends and surrounding land begins to slope down towards channel
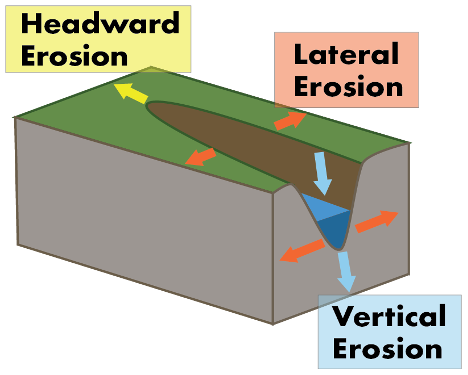
Headward erosion
process in which river water erodes in an upstream direction, lengthening the river valley
lengths it more forwardly
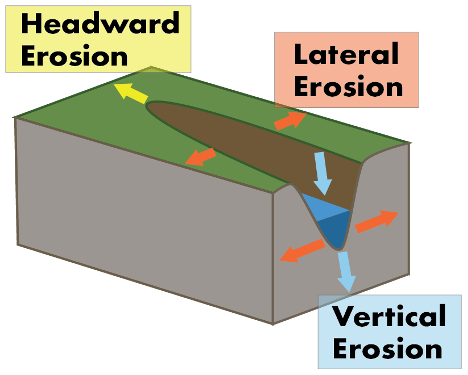
Lateral Erosion
process in which river water erodes laterally, widening the river valley
Tributary
a smaller stream that flows into a larger stream
Dendritic
branching or tree-like
common in regions of uniform material
Type of Drainage Pattern
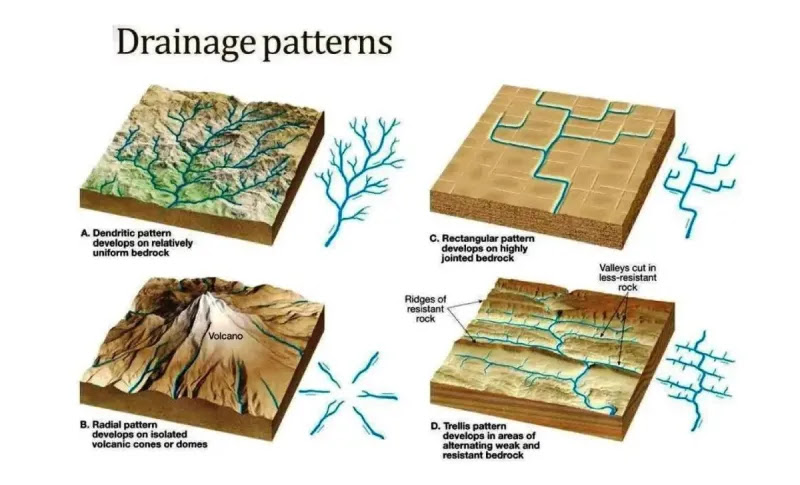
Radial
Draining in all directions away from a point (mountains, hills)
Type of Drainage Pattern
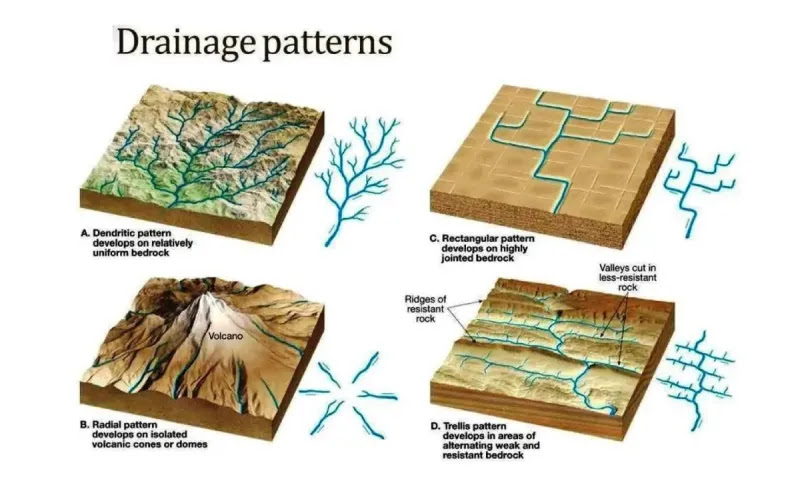
Rectangular
channels aligned primarily in two directions
follows fractures in rock, looks like a puzzle piece
Type of Drainage Pattern
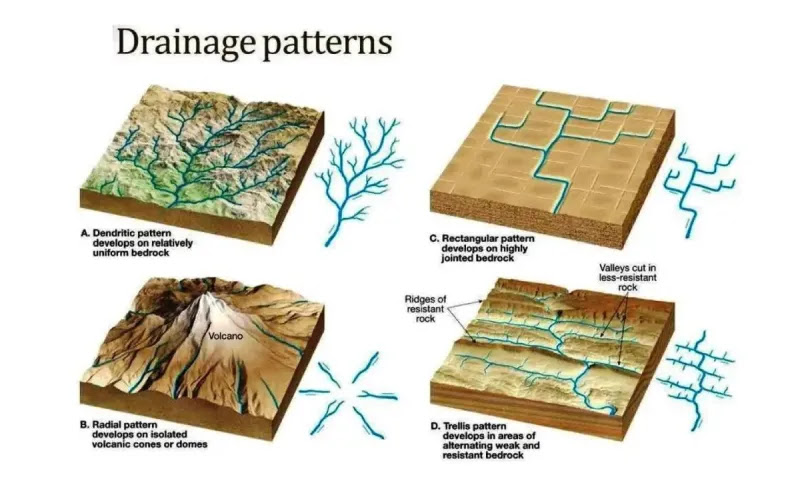
Trellis
develops across parallel valleys and ridges
surface alternates between erodible and resistant materials
basically said idgaf im going through all these valleys
Type of Drainage Pattern
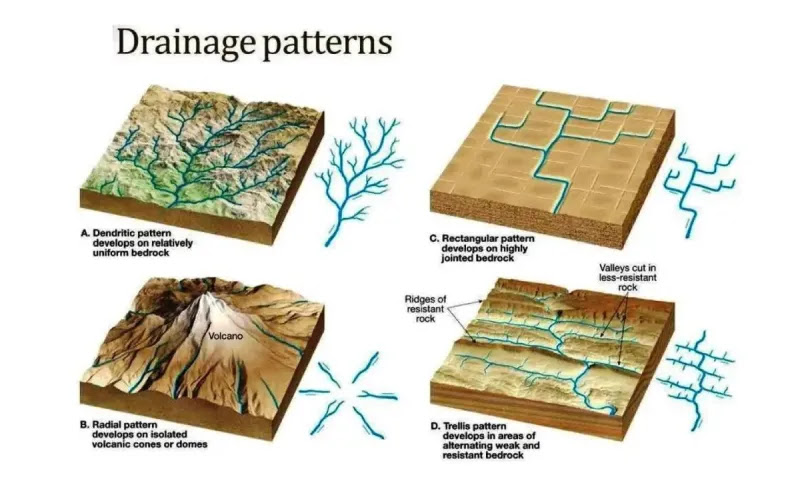
Parallel
develops steep, uniform streams with parallel courses
goes like:
I I I I
Type of Drainage Pattern
Drainage Basin (watershed)
land areas draining into the main stream or body of water
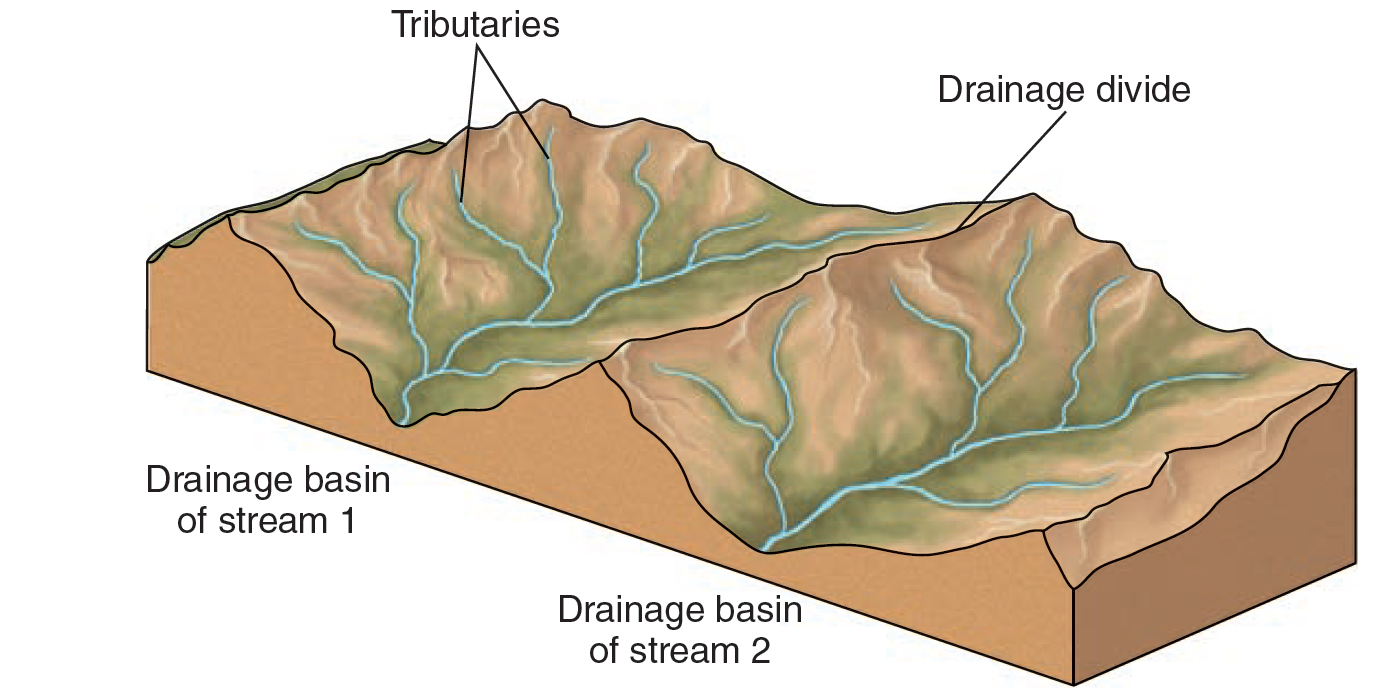
Drainage Divide
A ridge separating two drainage basins
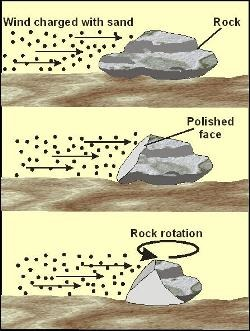
Abrasion
the “sandblasting” of rock by particles in fast-moving water
Type of erosional process
Scouring
removal of loose fragments of sediment (HM: dissolution and breaking and lifting)
Type of erosional process
Sediment load
material moved by running water
affected by water velocity + the sediments being transported
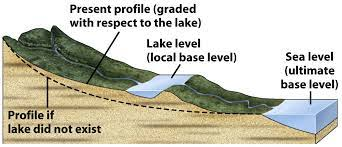
Base Level
the lowest point to which a stream can erode
stream loses all potential energy, so velocity drops to zero when it reaches base level
gradient is nearly flat, discharge is high, sediments are fine, meandering channels, velocity may be slower
Headwaters
most rivers start near a headwater, which may contain a patch of snow that starts it
gradient is steep, discharge is low, sediments are coarse and younger, channels are mainly straight, velocity may be higher
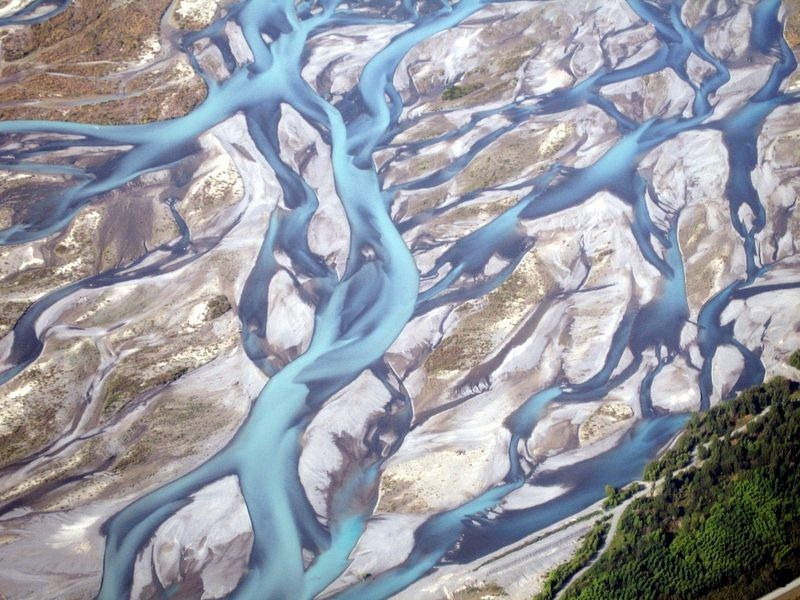
Braided Streams
trunk stream consisting of many channels
high sediment load, usually coarse sediments, channels weave back and forth between bars of sediment

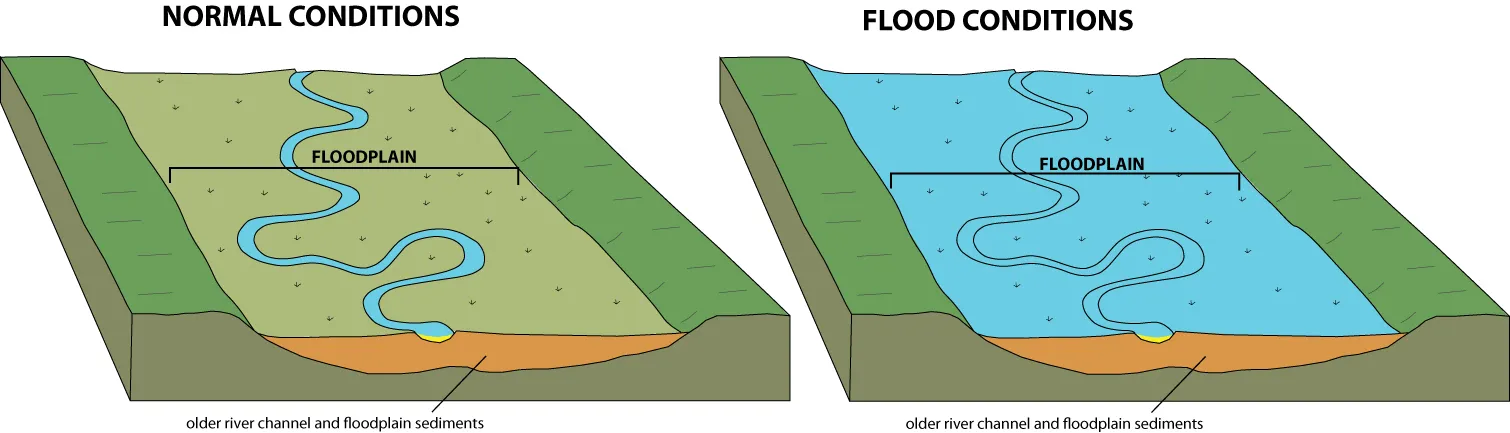
Floodplain
a relatively flat area in between hills or ridges, prone to flooding
Delta
forms when a stream enters standing water
think Nile River
spans out into the ocean, can form into different shapes
(triangle-shape forms where waves or offshore currents redistribute sediment entering the standing water)
Straighter-shaped delta
currents are stronger, less sediment accumulates so the edge becomes straight
Outward arc-shaped delta
currents are weaker, more sediment accumulates, causing edges of delta to arc outward
Delta Lobes
formed during different time intervals
lobes form when a stream’s given path over time starts to become too gentle of a slope, so a new one forms
Flood
occurs when volume of water flowing down a stream exceeds the volume of the stream channel
spreads over floodplain
triggered by torrential rains, rapid snowmelt, and/or failure of a dam or levee
Flood Prevention
expensive and only temporary (ultimately futile)
levees + flood walls prevent overflow for floodplains
**levees: can be man-made or sometimes created naturally through sediment deposition
Permanent Stream
water flows all year at or below the water table
humid or temperate climate
sufficient rainfall, lower evaporation
Ephemeral Stream
Dries up part of the year, above the water table, found in drier climates, flows intermittently
lower rainfall, high evaporation
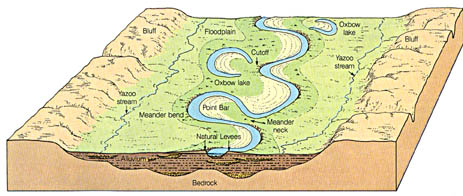
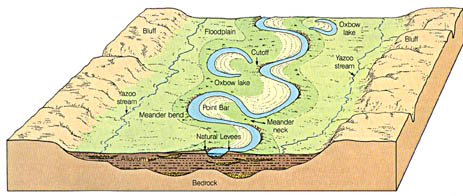
Cut Bank
High velocity flow where erosion takes place
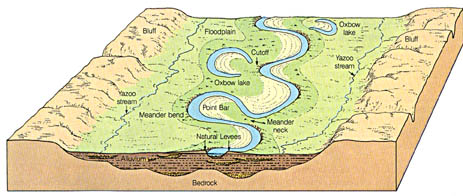
Point Bar
Place of low velocity where deposition occurs
Oxbow Lake
Remnant of a meander that has been cut off from the flow of a river
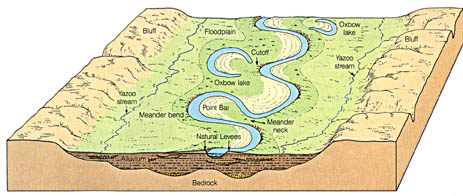
Meandering Streams
sinuous, looping curves
low gradient
broad floodplain
Discharge of a Stream
“volume per some given time”
ex:
width = ___m
depth =___m
velocity =____m/sec
discharge = ____m³/sec
Gradient (slope)
“drop in elevation over distance flowed”
△E/D
△E= ___ft
D = ____ mi
Grad=____ft/mi