Cancer
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
what are the 4 most common types of cancer?
breast
lung
prostate
bowel
what is lenalidomide?
Binds to cereblon protein (CRBN) - Induces ubiquitination of IKZF1 and IKZF3 by CRL4/CRBN → Stimulates apoptosis
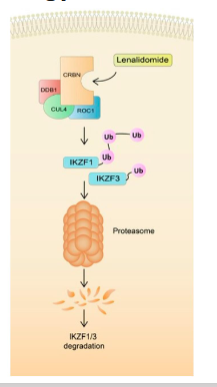
what is the treatment of lenalidomide?
Multiple Myeloma - Cancer of antibody producing plasma cells. bone pain, bleeding, infection and anaemia (teratogenic)
Lenalidomide with dexamethasone (50% patient survival after 5-years)
what is proto-oncogenes?
Normal genes that help cells grow/divide/stay alive.
what is oncogenes?
Mutated proto-oncogenes that have the potential to cause cancer. i.e. Gain of function/activity.
Mutations often have a dominant effect (Single mutations)
what are tumour suppressor genes?
Normal genes that regulate cell division, DNA repair and apoptosis.
Loss of function can lead to cancer.
Mutations often have a recessive effect (Requires multiple mutations
how do tumour progress?
what is the definition of cytotoxic drugs?
in cancer therapy inhibit cell division
what are the cytotoxic drug groups?
inhibitors of cell division
inducers of dna breakdown
inhibitors of dna synthesis
what is the log kill model?
each does kills a fraction of cells
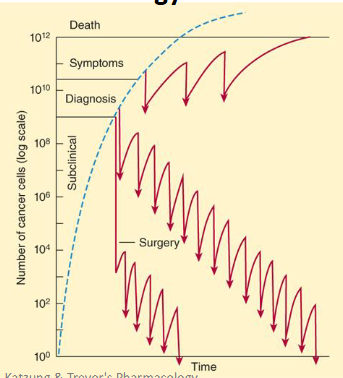
what is the main problem with the log kill model?
intermittent dosing reduces adverse effects but allows cancer regrowth and resistance
what are common side effects of cytotoxic drugs?
Bone marrow toxicity
Loss of hair
GI tract epithelial damage
Impaired wound healing
Sterility
Teratogenicity
Carcinogenicity
Kidney damage - Rapid cell destruction with precipitation of purines and urate in renal tubules
Severe nausea and vomiting
what does chemotherapy target?
Cell cycle control (Signalling) - e.g. Tyrosine kinases inhibitors
Apoptosis
Cellular invasiveness, metastasise or de-differentiate
Senescence/immortalisation - e.g. Telomerase inhibitors
De-differentiation
Invasion and metastasis
Angiogenesis
Tumour metabolism
Molecular chaperones and degradation
DNA packaging - e.g. Histone deacetylase inhibitors
what are tyrosine kinase inhibitors?
Inhibit cell signalling
Regulate transcriptional control of genes crucial for cell survival, proliferation, cell cycle progression and critical events in invasion, angiogenesis and metastasis
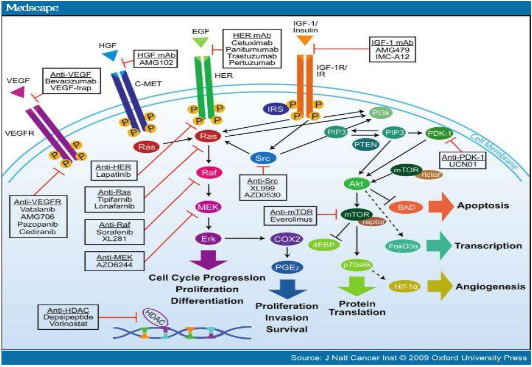
what are examples of EGFR inhibitors?
gefitinib (Iressa), lapatinib (Tykerb) and erlotinib (Tarceva)
what are examples of multikinase inhibitors?
Sunitinib (Sutent) - GI stromal tumours and renal cell carcinoma
Targets: VEGFR, Flt-3, PDGFR, c-kit, stem cell factor receptor
Sorafenib (Nexavar)- Targets VEGFR and Raf (None receptor)
Pazopinib - VEGFR1,2,3
Vandetanib - VEGFR2, EGFR and RET
Leflunomide (Arava) - PDGFR and antirheumatic in inflammatory disease
what are the two main examples of monoclonal antibodies that target erb82 receptor family?
Trastuzumab (Herceptin) - EGFR/HER-2
Cetuximab (Erbitux) - EGFR/HER-2
what are mitotic spindles?
Targeted by vinca alkaloids, taxanes (and epothilones)
Inhibit by interacting with microtubule components
what are vinca alkaloids?
Bind β-tubulin subunit at + end → self-association
Treat: leukaemias, lymphomas, bladder and testicular cancers
Pharmacokinetics: liver metabolism excretion in bile (reduce dose in liver disease
what are does limiting effects of vinca alkaloids?
Vinblastine - myelosuppression
Vincristine - neurotoxicity (motor weakness, loss of reflexes, abdominal pain, constipation)
Vinorelbine - advanced breast and non-small cell lung cancer
what are texanes?
Bind β-tubulin at interior of microtubule → self-association
Treat: Metastatic ovarian, breast, prostate, lung, GI, genitourinary, head and neck cancer
Pharmacokinetics: liver metabolism (CYP2C8)
what is paclitaxel?
Low solubility cremophor
Hypersensitivity reactions (antihistamines/steroids), bone marrow neutropenia (day 8-11), myalgia, stocking-glove neuropathy (Feet/hands)
what is docetaxel?
More soluble, less hypersensitivity reactions, greater neutropenia, less neurotoxicity, leg oedema (oral steroid cover required)
what are glucocorticosteroids?
Induces retinoblastoma protein (Rb1) dephosphorylation → G1 Phase arrest
Reduce drug hypersensitivity and nausea
what are examples of glucocorticosteroids?
Prednisolone
Methylprednisolone
Dexamethasone
Hydrocortisone
what is palbocicilib?
CDK4/6 inhibitor → Stops cell cycle in G1 → apoptosis
Oestrogen +ve, HER -ve breast cancer
Used with aromatase inhibitor
21 day schedule/7 day recovery
what are the adverse effects of palbociclib?
neutropenia, infections, pneumonititis
what treatments can nitrogen mustards be used for?
Non-Hodgkins lymphoma - cyclophosphamide/ doxorubicin/vincristine/prednisolone (CHOP)
Bladder cancer - cyclophosphamide/doxorubicin/cisplatin (CISCA)
Breast cancer - doxorubicin/cyclophosphamide (DC)
what treatment can chlorambucil tablets be used for?
chronic lymphocytic leukaemia
what can ifosfamide treat?
Testicular cancer - Etoposide/ifosfamide/cisplatin (VIP) + MESNA
Head & neck cancer - Paclitaxel/ifosfamide/cisplatin (TIP) + MESNA
what can melphalan treat?
Multiple myeloma - melphalan/prednisolone (MP)
what can nitrosoureeas treat?
Carmustine (BICNU) via IV - Brain cancer - Carmustine and XRT
Lomustine (CCNU) - Brain cancer - lomustine/procarbazine/vincristine (PCV)
what can alkyl sulphonate treat?
Busulphan (Myeleran) - Chronic myelogenous leukaemia (not in “blast” crisis)
Thiotepa - Breast, ovarian and bladder cancers
what are platinum coordination complexes and what do they treat?
Form reactive intermediates that bind DNA → cross-links double helix e.g Cisplatin, carboplatin and oxaliplatin
Treatment: Nonsmall cell lung cancer - Etoposide/cisplatin (EP)
Head and Neck - cyclophos/doxorubicin/cisplatin (CAP)
what are antitumour antibiotics?
Derived from microorganisms (S. caespitosus or S. lavendulae)
Intercalate between DNA/RNA base pairs → Inhibit DNA &/or protein synthesis
Some inhibit Topoisomerase I and II
Some cell cycle independent → Useful in slow growing tumours
what are examples of antitumour antibiotics and what do they treat?
Dactinomycin (Actinomycin D) - Ovarian cancer - vincristine/actinomycin D/cyclophosphamide (VAC)
Doxorubicin - Head and Neck - cyclophos/doxorubicin/cisplatin (CAP), Gastric/pancreatic cancer - 5FC/doxorubicin/mitomycin (FAM)
Mitomycin C - Cervical cancer - bleomycin/vincristine/mitomycin/cisplatin (MOBP)
Bleomycin - Testicular/ovarian - bleomycin/etoposide/cisplatin (BEP) and MOBP
what are anthracyclines?
Example: Doxorubicin (Adriamycin)
Formation of free radicals and DNA crosslinks
Intercalation
Topoisomerase I and II inhibition (enzyme sticks) → Inhibit transcription
what are epipodophyllotoxins?
Topoisomerase II inhibitors
Induce single- and double-strand breaks
what can etoposide treat?
Testicular cancer - bleomycin/etoposide/cisplatin (BEP)
Non-small cell lung, testicular - EP
Small cell lung cancer - etoposide/carboplatin (EC)
Multiple myeloma - Induction therapy (Rapid)
what can teniposide treat?
Neuroblastoma - cisplatin/teniposide (Pt/VM)
what are camptothecin analgoues?
Topoisomerase I inhibitors
Prevent resealing of single-strand breaks → Replication fork breakage (S-phase dependent) → cell death
what can topotecan treat?
Small cell/non-small cell lung cancers - Single agent therapy
what can irinotecan treat?
Colon cancer - Single agent therapy
what are quinone derivatives?
Undergo one- or two-electron reduction
Act as an alkylating agent when activated by enzymes (CYP450, NADH dehydrogenase, xanthine oxidase) → unstable semiquinone radicals → Bind DNA/RNA
what can mitomycin treat?
Upper gastro-intestinal cancers (e.g. esophageal carcinoma), anal cancers, and breast cancers and superficial bladder tumours
what are antimetabolites?
Analogues of DNA precursors
Interfere with DNA building blocks
Activity is greatest in S-phase
what is methotrexate?
Folic acid analogue (orally or IV)
Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) inhibition → Decrease THF needed for thymidylate in pyrimidine synthase
what can methotrexate treat?
Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
Bladder cancer - cisplatin/methotrexate/vinblastine (CMV)
Breast cancer - cyclophosphamide/methotrexate/fluorouracil (CMF)
what can pemetrexed treat?
Lung cancers e.g. pleural mesothelioma, non-small cell lung cancer
what is 6-mercaptopurine?
Hypoxanthine analogue
Activated by hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (HGPRT)
incorporated into nucleotides
Inhibits:
Glutamine-PRP Amidotransferase
IMP dehydrogenase
Adenyl succinase
what are pyrimidine analogues?
Inhibit enzymes in DNA/RNA synthesis
Incorporation into DNA
what can fluorouacil treat?
Gastric cancer - Fluorouracil/doxorubicin/mitomycin (FAM)
Colon cancer - fluorouracil/methyl CCNU/vincristine (FMV)
Breast cancer - CMF
what are the side effects of fluorouacil?
palmar-plantar syndrome
what is capecitabine and its treatment?
Prodrug of fluorouracil
Thymidylate synthase inhibition
Treatment: Breast and bowel cancers resistant to doxorubicin and paclitaxel
what is gemcitabine?
Inhibits ribonucleotide reductase
Treatment: Non-small cell lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, bladder cancer - single agent therapy
what are the side effects of gemcitabine?
Side effects: Inhibits DNA repair enzymes, increases toxicity of radiotherapy
what is combination drug chemotherapy?
more successful than single-drug treatment in most of the cancers for which chemotherapy is effective
what are the advantages of combination drug chemotherapy?
Maximal cell killing within the range of tolerated toxicity
- Effective against a broader range of cells in the heterogenous tumour population
- May delay the development of resistant cell lines
what is the major limiting adverse effects of combination drug chemotherapy?
Cytotoxic agents with same toxicities can only be combined by reducing the doses of each
Cytotoxic agents with different toxicities and different mechanisms combined at full doses
Adverse effects minimised by cytoprotectant drugs i.e. folic acid with methotrexate
what is non-hodgkin’s lymphoma treatment?
R - Rituximab
C - Cyclophosphamide
H - Hydroxydaunorubicin (doxorubicin)
O - Oncovin (vincristine)
P - Prednisolone
what is cell cycle non-specific drug combinations?
Quiescent non-replicating cells
Effect all phases
what is cell cycle specific drug combinations?
Drugs which effect different stages of the cell cycle work well in combination
Treat mixed cell populations at different stages