APES unit 3 populations
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
generalist species
A species that exists under a broad range of conditions
specialist species
a species that exists under a narrow range of conditions
Intrinsic growth rate
the number of offspring an individual can produce in a given time period, minus the deaths of the individual or its offspring during the same period
biotic potential
Under ideal conditions with unlimited resources available, every population has a maximum potential for growth
k-selected species
a species with a low intrinsic growth rate that causes the population to increase slowly until it reaches the carrying capacity of the environment
Carrying capacity
the limit to the number of individuals that can be supported by an existing habitat or ecosystem, denoted as “k”
r-selected species
a species that has high intrinsic growth rate and a population that increases rapidly and experiences population overshoots and diebacks.
Overshoot
When a population becomes larger than the environment’s carrying capacity
Dieback
A rapid decline in a population due to death
Survivorship curve
A graph that represents the distinct patterns of species survival as a function of age
Type 1 survivorship curve

A pattern of survival over time in which there is high survival most of the life span, but then individuals start to die in large numbers as they approach old age (k-specialist)
Type 2 survivorship curve
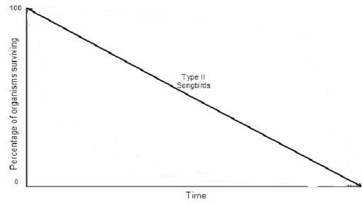
A pattern of survival over time in which there is a relatively constant decline in survivorship throughout most of the life span (rodents, birds)
Type 3 survivorship curve
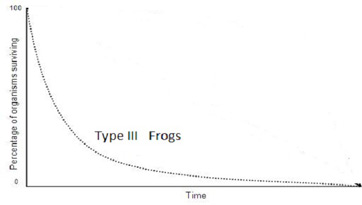
A pattern of survival over time in which there is low survivorship (high death rate) early in life with few individuals reaching adulthood (r-selected species, frogs, seeds)
Density-dependent factor
A factor that influences an individual’s probability of survival and reproduction in a manner that depends on the size of the population
Density-independent factor
A factor that has the same effect on an individual’s probability of survival and reproduction at any population size
population growth models
mathematical equations that can be used to predict the population size at any moment in time (exponential and logistic growth)
fecundity
The ability to produce an abundance of offspring
Exponential growth model
A growth model that estimates a population’s future size after a period of time based on the biotic potential and the number of reproducing individuals currently in the population (J-curve)
Logistic growth model
A growth model that describes a population whose growth is initially exponential, but slows as the population approaches the carrying capacity of the environment (S-curve)
Limiting resource
A resource that a population cannot live without and that occurs in quantities lower than the population would require to increase in size
Demography
The study of human populations and population trends
Demographer
A scientist in the field of demography
Immigration
the movement of people into a country or region from another country or region
emigration
the movement of people out of a country or region
crude birth rate
The number of births per 1000 individuals per year
crude death rate
The number of deaths per 1000 individuals per year
global population rate equation
(CBR-CDR)/10
Net migration rate
the difference between immigration and emigration in a given year per 1000 people in a country
National population growth rate equation
((CBR+immigration)-(CDR-emigration))/10
life expectancy
the average number of years that an infant born in a particular year in a particular country can be expected to live, given the current average life span and death rate in that country
Infant mortality
The number of deaths of children under age 1 per 1000 live births
Child mortality
The number of deaths per children under age 5 per 1000 live births
Environmental justice
The study of the disproportionate exposure to environmental hazards experienced by people of color, recent immigrants, and people of lower socio-economic backgrounds
Age structure diagram
A visual representation of the number of individuals within specific age groups for a country, typically expressed for males and females
Population pyramid
an age structure diagram that is widest at the bottom and smallest at the top, typical of developing countries
developing countries
countries with relatively low levels of industrialization and income
developed countries
countries that have relatively high levels of industrialization and income
population momentum
continued population growth after growth reduction measures have been implemented
Total fertility rate (TFR)
An estimate of the average number of children that each woman in a population will bear throughout her childbearing years
family planning
the regulation of the number or spacing of offspring through the use of birth control
replacement rate fertility
the total fertility rate required to offset the average number of deaths in a population in order to maintain the current population size
(2, to offset 2 parents)
doubling time
the number of years it takes for a population to double
rule of 70
A method which dictates that by dividing the number 70 by the percentage population growth rate we can determine a population’s doubling time
doubling time (years)= 70/growth rate %
Theory of demographic transition
A theory that states that a country moves from high to lower birth and death rates as development occurs and that country moves from a preindustrial to an industrialized economic system
IPAT equation
A conceptual representation of the 3 major factors that influence environmental Impact: Population of humans, Affluence, Technology
Impact= population*affluence*technology