Caroline Dalton
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
What does innate immunity include ? (proteins)
Compliment
Cytokines
What are the 6 beneficial molecules in plasma?
Clotting factors
Antibodies
Compliment proteins
Nutrients
Lysozymes
Transferrin
when does plasma leakage occur?
During inflammation
What allows plasma leakage occur?
Capillary permeability allows plasma to leak into tissues
Benefits of plasma leakage? (6)
Clots form localising the infection
Antibodies enter the tissue
Activation of complement pathways
Nutrients enter tissue
Lysozymes enter the tissue and degrade microbes
Transferrin enters to deprive microbes of iron
What is complement?
Biochemical cascade that helps antibodies to clear pathogens or mark them for destruction.
What is special about compliment (2)
Composed of 30 small plasma proteins
Can be activated independently of antibodies
Functions of complement (5)
recruits inflammatory cells
Chemotactically attracts phagocytes
opsonisation of pathogens
Disrupts plasma membrane of infected cells
Clearance of antigen-antibody complexes
what are the 3 complement pathways?
classic
Alternate
Mannose-binding lectin
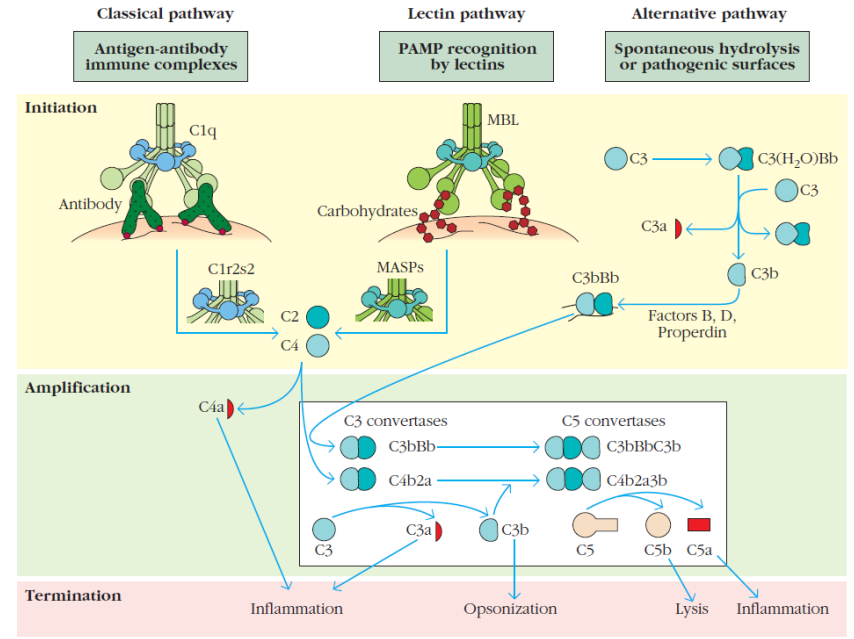
What do all complement pathways produce?
C3 convertase
How is the classic complement pathway activated?
By antibodies
How is the alternative complement pathway activated?
Activated by pathogens
How is the mannose-binding lectin pathway activated?
by mannose-binding lectin binding to mannose on the surface of a pathogen
What do the complement pathways do? (3)
Promotes opsonisation
Promote inflammatory responses
Membrane Attack Complex
What does the alternative complement and mannose-binding lectin pathway do?
Same as the classical pathway
What antibodies types activate the compliment pathway?
IgG or IgM
What is the first 2 steps of the classical compliment pathway?
Antibody binds to the subunits
C1q, C1r, C1s subunits combine to form the enzyme C1
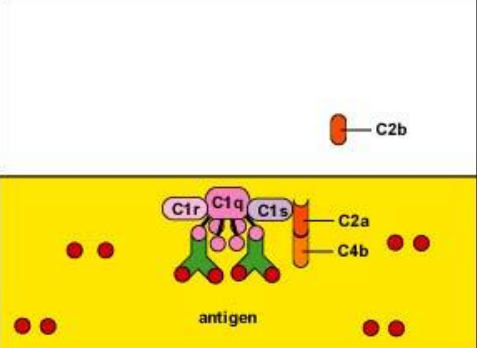
What does the C1 enzyme do (classic pathway) (2)
cleaves C4 into 2 subunits (C4a, C4b)
Cleaves C2 into subunits (C2a, C2b)
What does C4b and C2a do (2)?
Combine together and stick to the C1 enzyme complex
Functions as a C3 convertase
How many subunits does C4b2a (C3 convertase) cleave C3 into?
3 subunits
What does C3a do?
promotes inflammatory response
What does C3b do?
attaches antigens to phagocytes for opsonisation
What does C4b2a cleave apart from C3?
Cleaves C5 into 2 subunits
What is the most potent inflammatory compliment protein?
C5a
What does C5a do (4)?
causes mast cells to release vasodilators
Promotes extravasation of leukocytes
Causes neutrophils to release toxic O2 radicals for extracellular killing
Chemoattractant for phagocytes
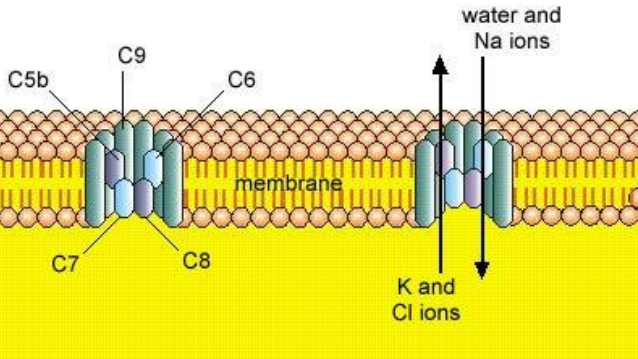
What does C5b do?
becomes part of the membrane attack complex
What is the membrane attack complex?
Forms a channel in the cell membrane changing osmolarity causing cell lysis
What is the first step in the Alternate pathway?
C3b binds to pathogen creating C3 convertase.
What happens to C3 when it binds to the pathogen in the alternative pathway?
B and D factors become stable after binding and then bind to properdin protein.
What are the first 3 steps in the Mannose-binding lectin pathway?
mannose binding lectin (MBL) in serum binds to mannose on surface of pathogen
Protease binds to this complex
The complex cleaves C4 and C2 into subunits that form C3 convertase.
What is a cytokine?
Small molecules used to communicate between immune cells.
What kind of bonds form between ligands and receptors?
Non-covalent bonds
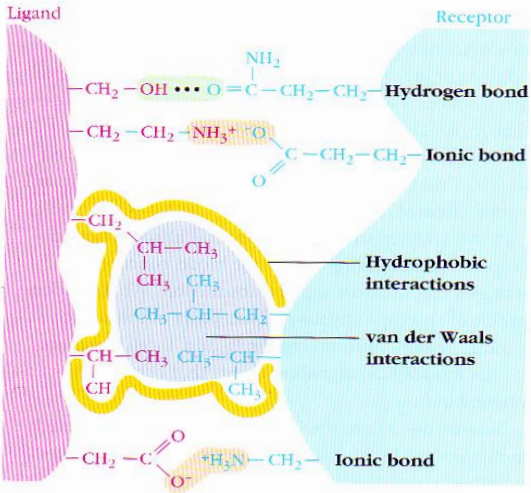
What does ligand-receptor binding cause?
A change in the receptor
A cascade of events
What is a multivalent receptor?
A receptor that has more than one ligand binding site.
What is a bivalent immunoglobulin?
Binds 2 identical antigens on the bacterial surface
How are IL-2 receptors expressed on lymphocytes (3)?
Antigens on pathogen bind to lymphocyte
Increase expression of third chain in cell-surface
Increase affinity of IL-2 receptor for IL-2, allowing it to bind.
What kind of pathway occurs after a ligand-receptor interaction?
Signal Transduction Pathway
What is a signal transduction pathways?
cascade of events leading to transcription factor binding and gene activation
What does the formation of a B-cell receptor complex result in?
Phosphorylation which activates downstream signalling
What do cytokines do? (2)
increase or decrease activity of enzymes
Change transcriptional activity
What are 4 cytokines?
IL-1 from macrophages
IL-2 from T-cells
Tumour necrosis factor
Interferons
What are cytokines?
All molecules that communicate between immune cells
What is a chemokine?
cytokines that mobilise immune cells
How do chemokines work?
Attract immune cells towards the area with the highest conc. of chemokines (chemoattractant)
What does pleiotrophic mean?
One cytokine can have different effects on different cells
How do cytokines have redundancy?
several cytokines have the same effect
What 3 methods of action can cytokines act in?
paracrine
autocrine
endocrine
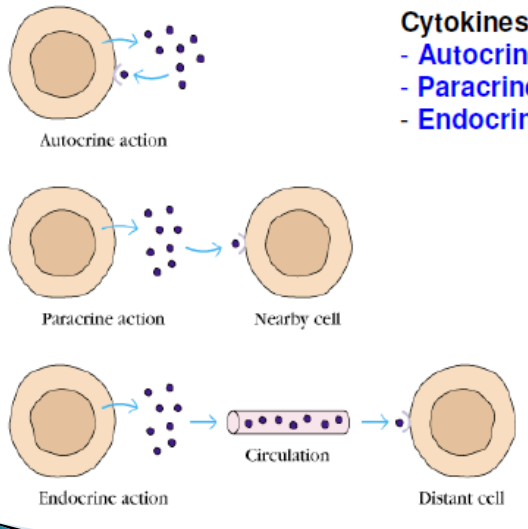
What does synergise mean?
When cytokines work together to enhance each other's effects. (summation)
What does antagonise mean?
When cytokines inhibit each other.
Where do soluble receptors bind to cytokines?
in solution
How are receptors secreted?
proteolytic cleavage releases the receptor from the cell membrane
Splicing out the transmembrane-encoding sequence results in a secreted protein
What is the role of soluble receptors? (3)
antagonist
receptor down-regulation
ligand bind to receptor then delivered to other cell to illicit the same response.