CSCI 113i LT 1
1/128
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Comprises Lectures 0–3 (Introduction to BI, Corporate Strategy and BI in the Value Chain, Data Lifecycle Management, Data Warehouse and OLAP)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
Business Intelligence
The set of techniques and tools for the transformation of raw data into meaningful and useful information for business analysis purposes
Data Driven Decision Making
Decisions based on data instead of instinct or heuristics
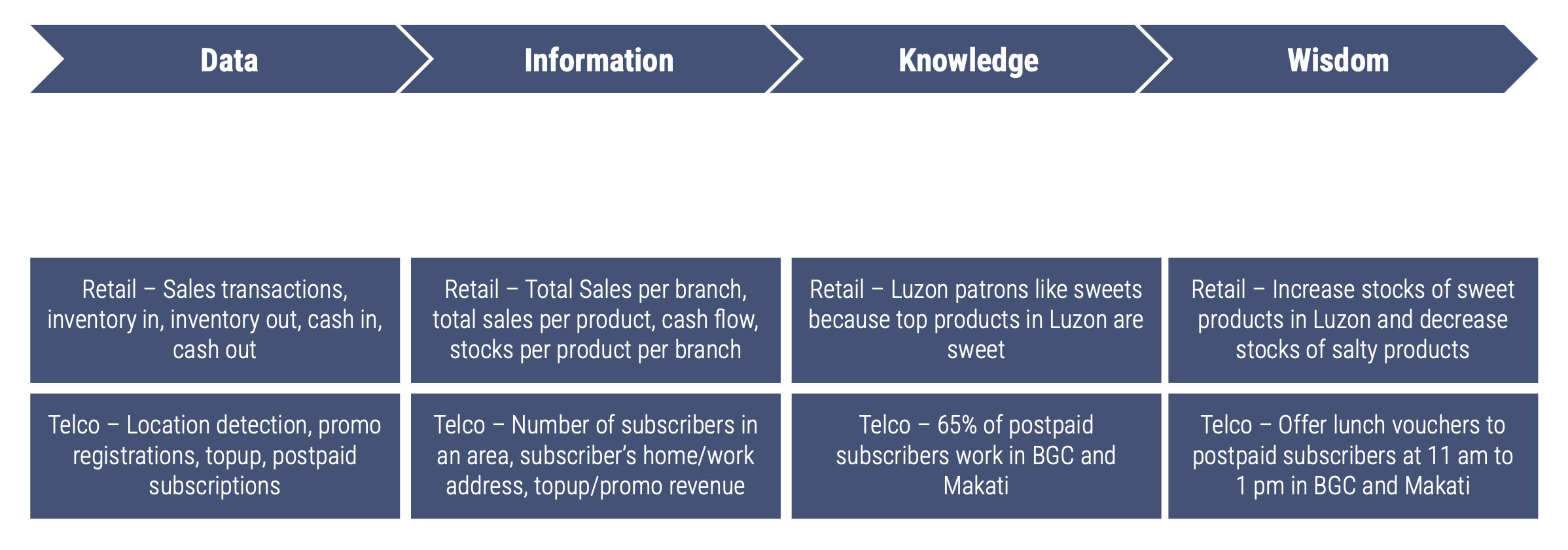
Data
Events captured by a business’ system
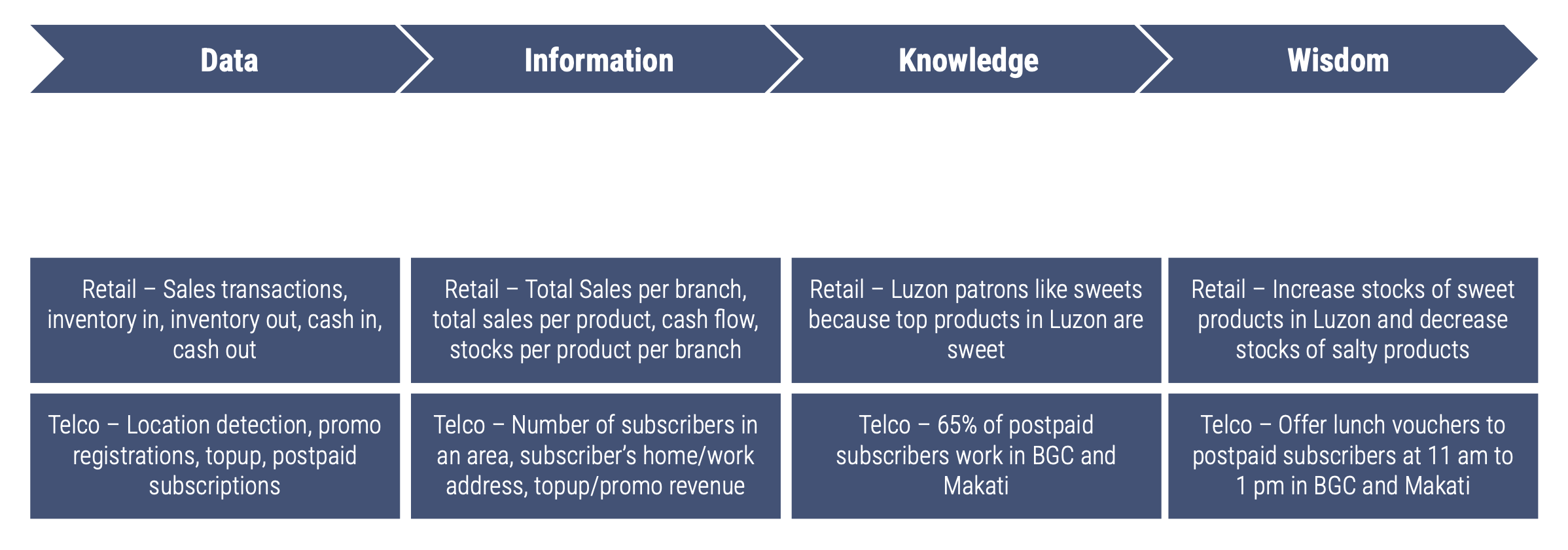
Information
Organized and categorized data usually in a data warehouse
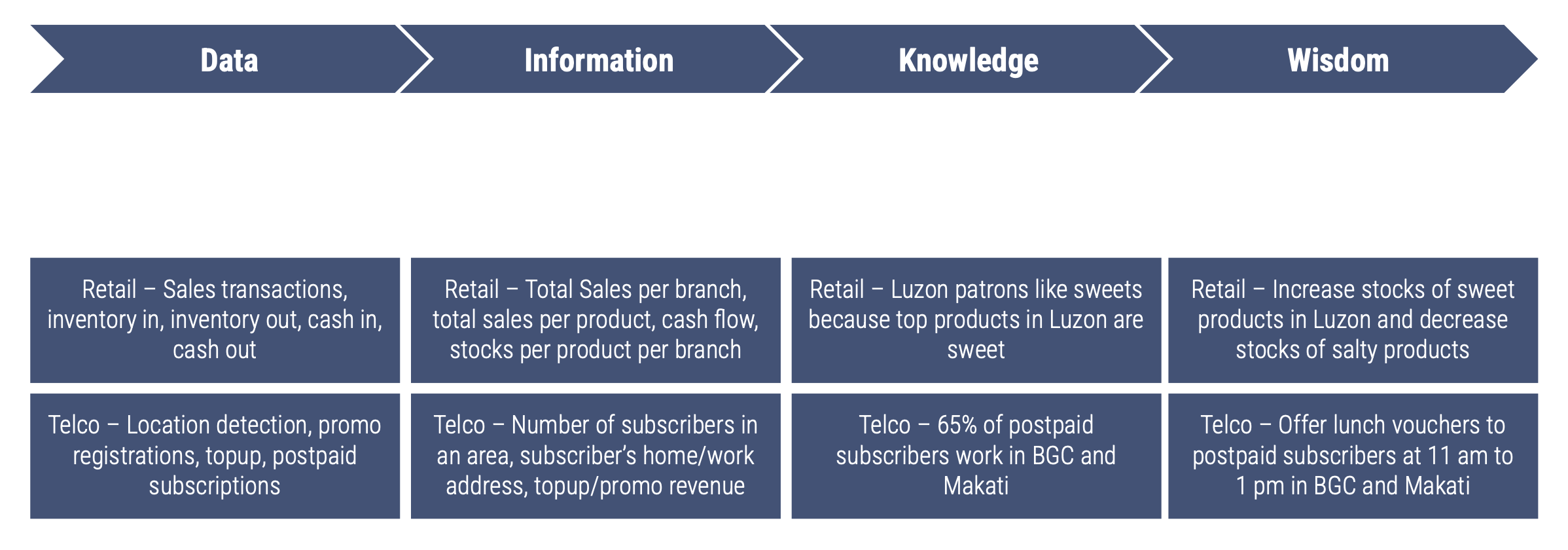
Knowledge
Patterns, context, and insights discovered from information
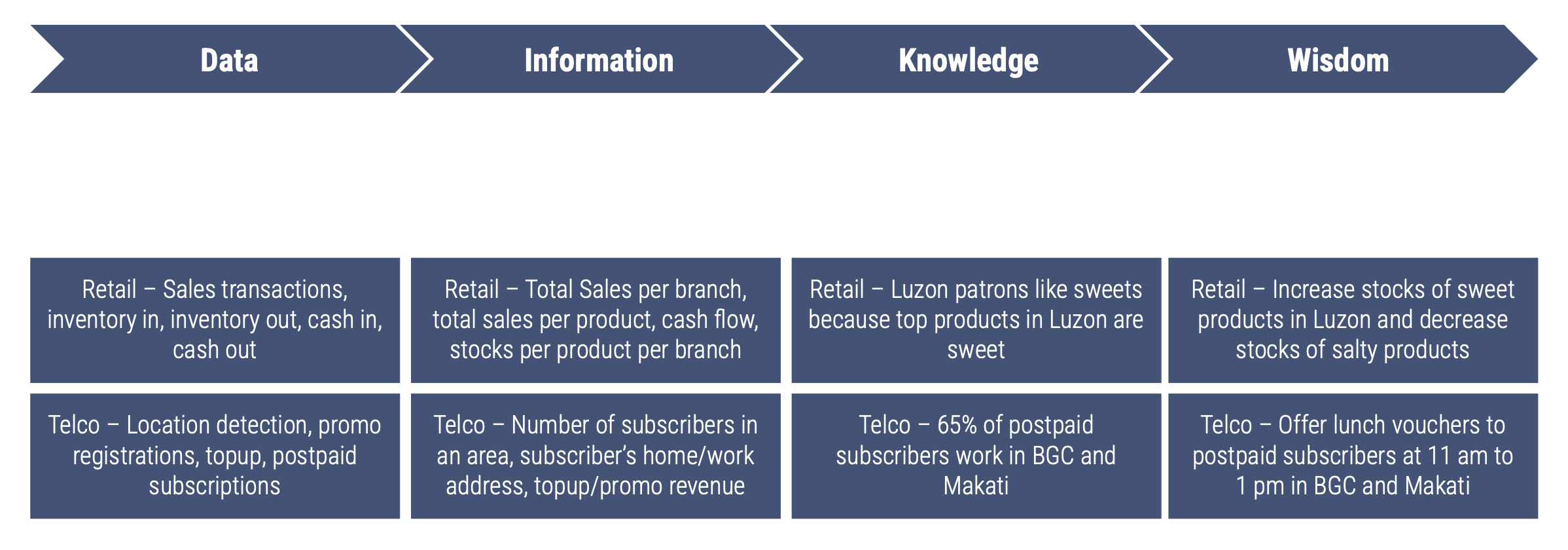
Wisdom
Application of knowledge to solve business problems
Data Mining
Sometimes referred to as exploratory data analysis due to analysis of large quantities of data using statistical, technical, and business knowledge
Knowledge
The goal of data mining
Data Science
A set of fundamental principles that guide the extraction of knowledge from data
Data Mining
The process of extracting knowledge from data, via technologies that incorporate data science principles
Hypothesis Testing
A general approach to data mining. For decisions that repeat, especially in a massive scale, to improve decision making accuracy.
Sense & Respond
Knowledge Discovery
A general approach to data mining. For decisions that discoveries need to be made from data.
Predict & Act
Mission
Why we exist
Vision
What we want to be
Values
What we believe in and how we will behave
Competitive Advantage
Traits or ways an organization has that keep them ahead of their competitors; these are traits that rivals desire.
Differentiation Advantage
A type of competitive advantage where customer’s perceived value is greater than its competitors
Low Cost Advantage
A type of competitive advantage where company’s profit margin is higher than its competitors
Value Chain
A series of activities in an organization’s operations that add value to its final product or service.
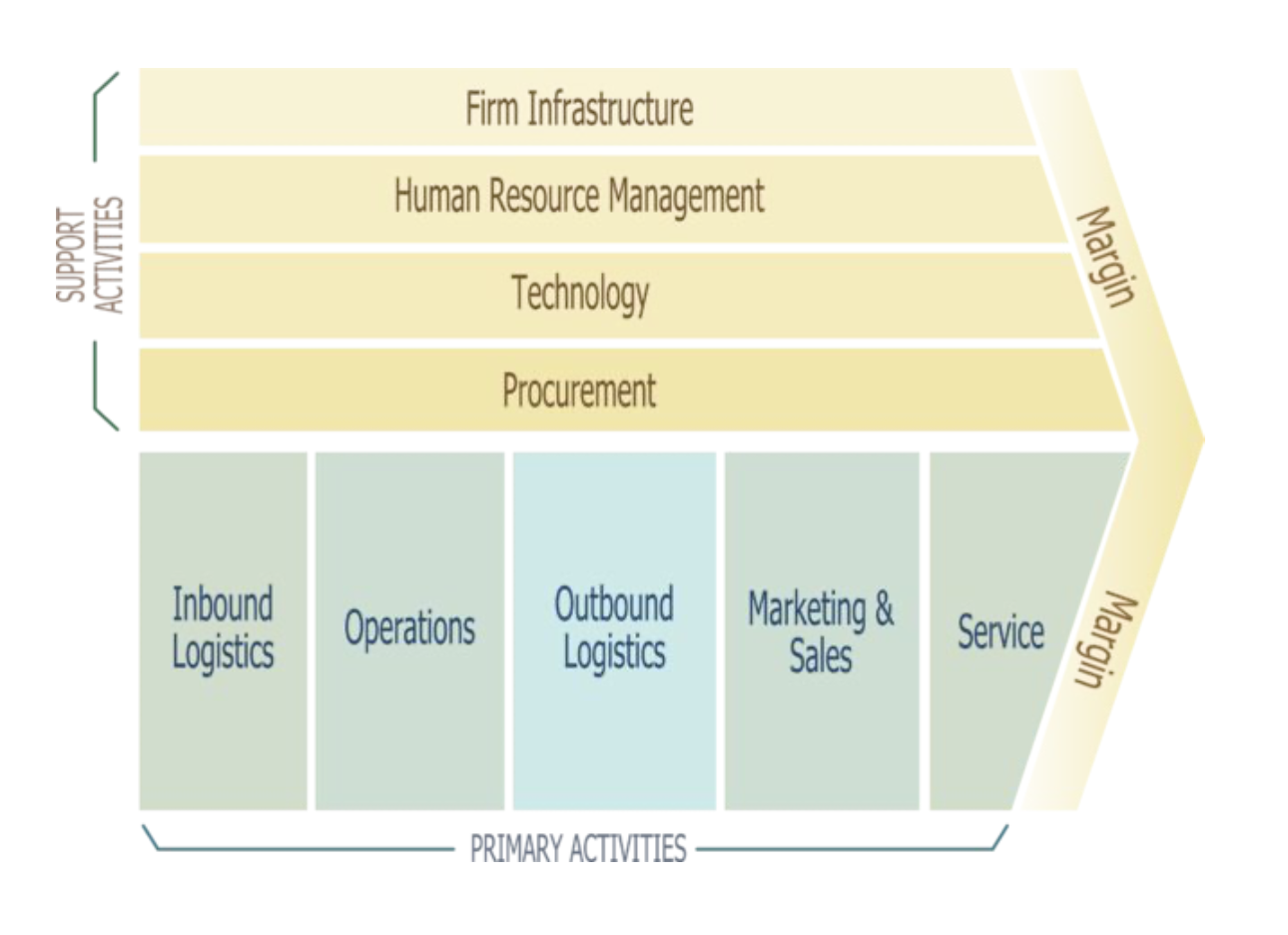
Inbound Logistics
A primary activity in the value chain. Receiving and storing of raw materials.
Operations
A primary activity in the value chain. Conversion of raw materials into finished goods.
Outbound Logistics
A primary activity in the value chain. Storing and distributing finished goods to customers.
Marketing & Sales
A primary activity in the value chain. Making the customers aware of the product or service and provides them with an opportunity to buy.
Service
A primary activity in the value chain. Activities after the point of sale (training, installation, support).
Firm Infrastructure
A supporting activity in the value chain. Organizes a firm for it to function.
Human Resource Management
A supporting activity in the value chain. Supports all concerns related to staffing.
IT
A supporting activity in the value chain. Supports the organization’s IT infrastructure.
Procurement
A supporting activity in the value chain. Supports purchasing of materials used for production.
Business Intelligence
Provides historical, current, and predictive views of the business
Corporate Strategy
An organization’s game plan. Consists of a goal, scope, and means.
Business Motivation Model
A framework used to define and align a company’s goals and strategy to its overall vision.

Strategy
What our competitive game plan will be. Consists of objective (ends), scope (domain), and advantage (means).
Objective
A basic element of a strategy statement that corresponds to ends
Scope
A basic element of a strategy statement that corresponds to domain
Advantage
A basic element of a strategy statement that corresponds to means
Balanced Scorecard
How we will implement and monitor the game plan
Measures
A unit-specific term used to describe business objects or entities (e.g. 1M USD in revenue, 1000 monthly sales)
Metrics
A quantifiable measurement used to track and assess the performance of a business process (e.g. 10% increase in month on month sales, 5% increase in subscriber growth)
KPI
A subset of metrics used to measure how well a business is achieving its goals (e.g. after migrating from on-premise services to cloud servers, there is a 30% cost reduction in IT operations)
Measure
Classify as measure, metric, or knowledge: 3,273 new postpaid subscribers for the month of January
Knowledge
Classify as measure, metric, or knowledge: 1% growth on new postpaid subscribers for the month of January as compared to January last year
Measure
Classify as measure, metric, or knowledge: 20,000 km distance traveled by a sedan
Measure
Classify as measure, metric, or knowledge: 51 degrees celsius average CPU temperature
Metric
Classify as measure, metric, or knowledge: 51 degrees celsius average CPU temperature when playing Valorant vs 42 degrees celsius average CPU temperature when idle
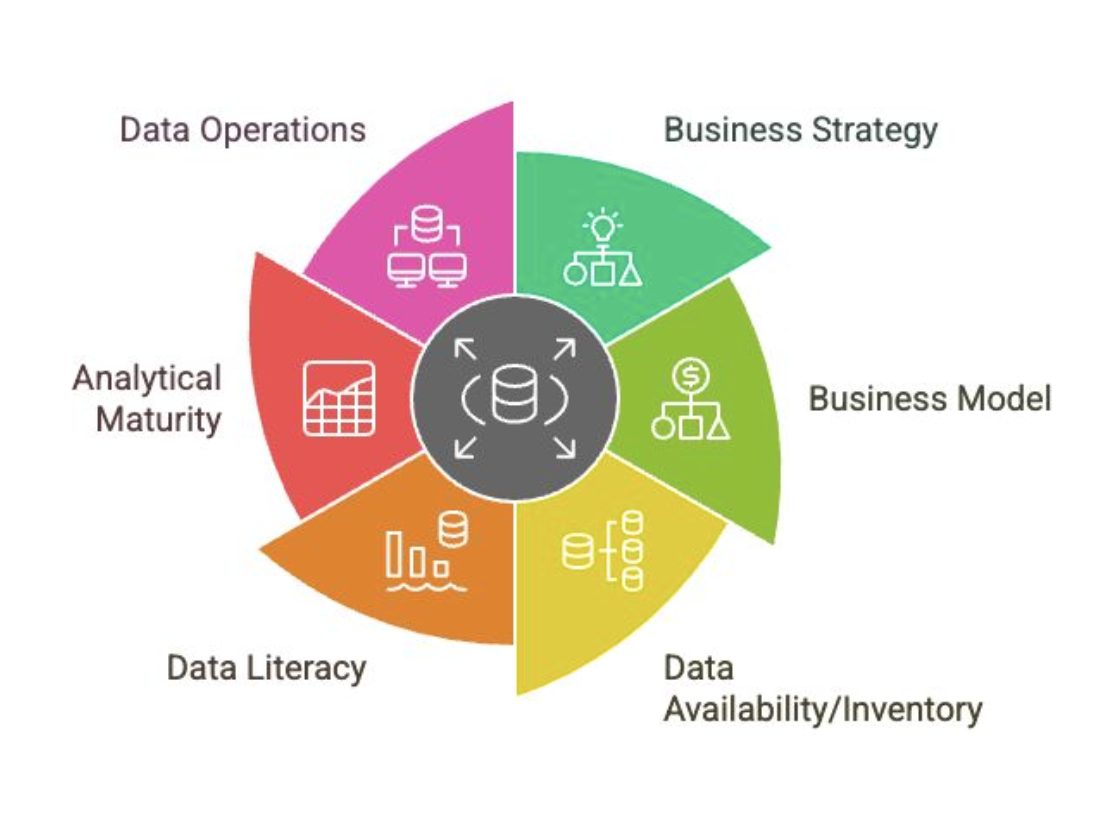
Data Strategy
A subset of the corporate strategy that is specifically focused on data
Data Strategy
Creates the necessary alignment across the organization to create more value from data and ideally leads to improved decision-making and operational efficiency
Business Strategy
Influences on Data Strategy
What are your goals for this strategy?
What is your scope?
What are your advantages or means for this strategy to materialize?
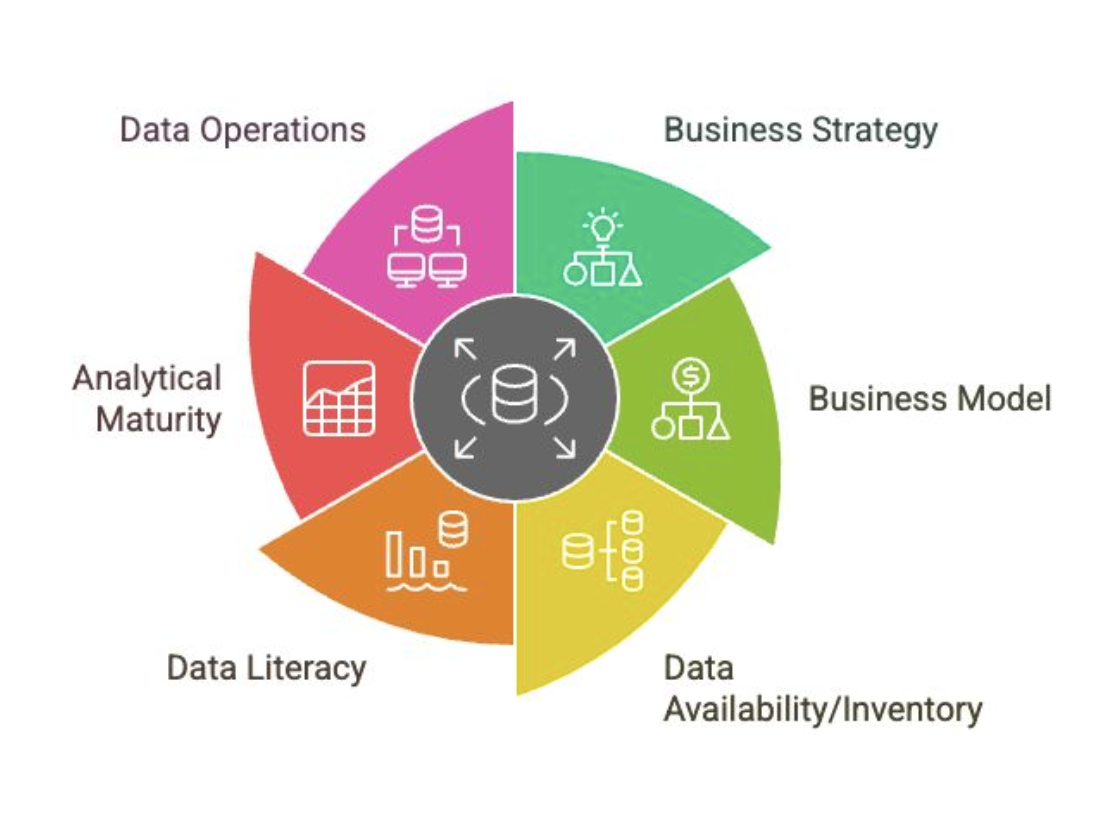
Business Model
Influences on Data Strategy
How does your company operate?
How do you earn (or what are your different revenue streams?)
How can your customers purchase your products?
What’s your value proposition?
What’s your cost structure?
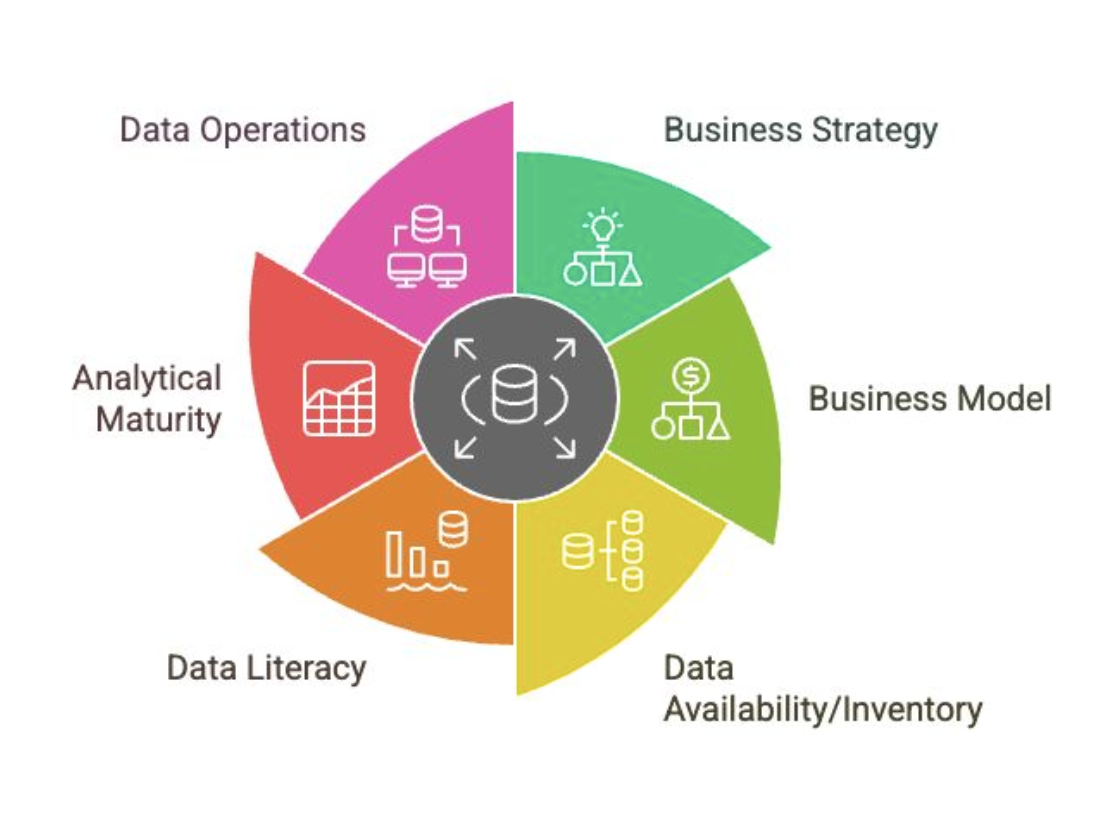
Data Availability/Inventory
Influences on Data Strategy
What data is available?
Which activities in the value chain produce data?
Which data are relevant to the data strategy?
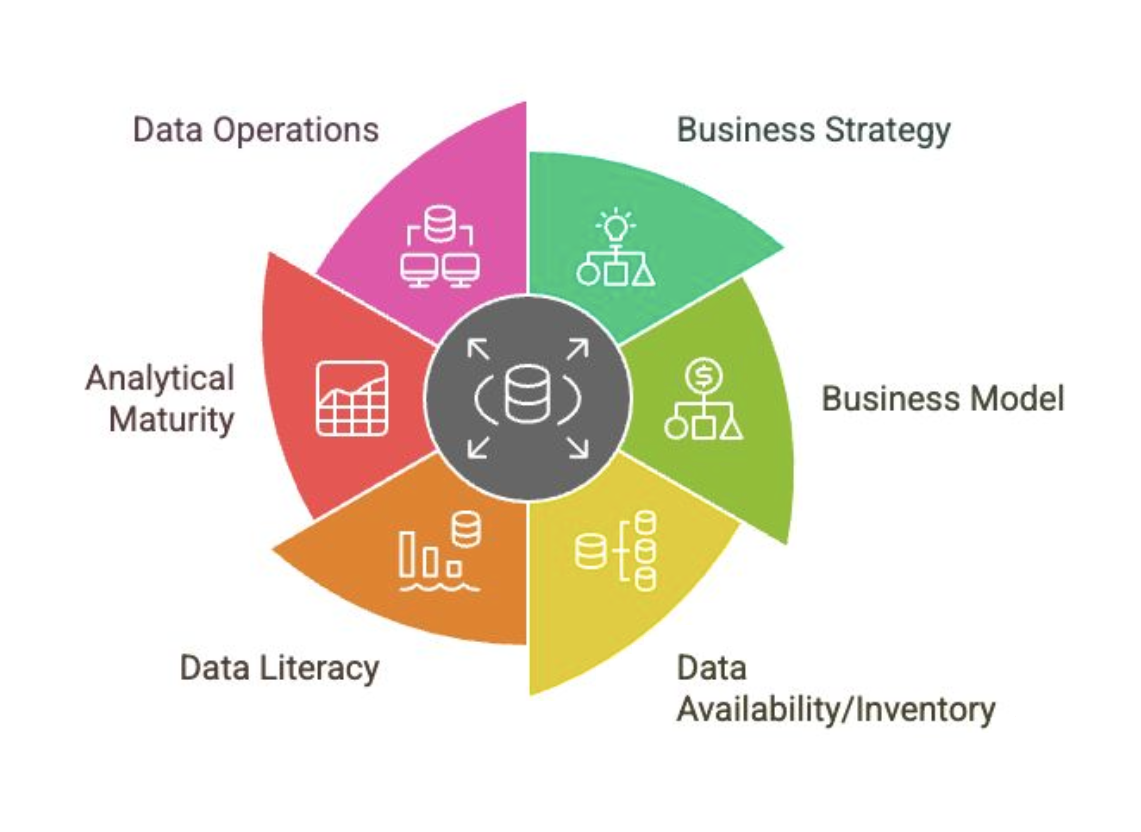
Data Literacy
Influences on Data Strategy
How well do your business functions understand data?
How well do your business functions understand statistical/mathematical principles?
How well do your business functions understand YOUR data?
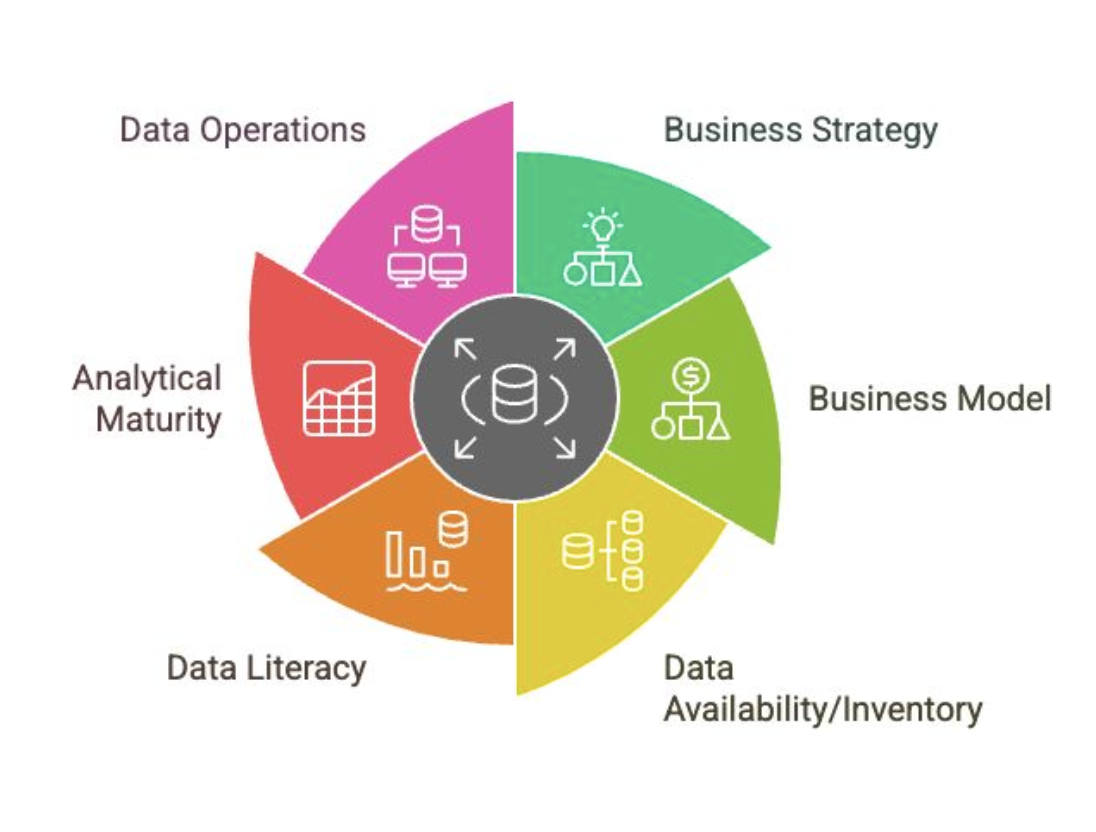
Analytical Maturity
Influences on Data Strategy
Where are you in the (business intelligence) curve?
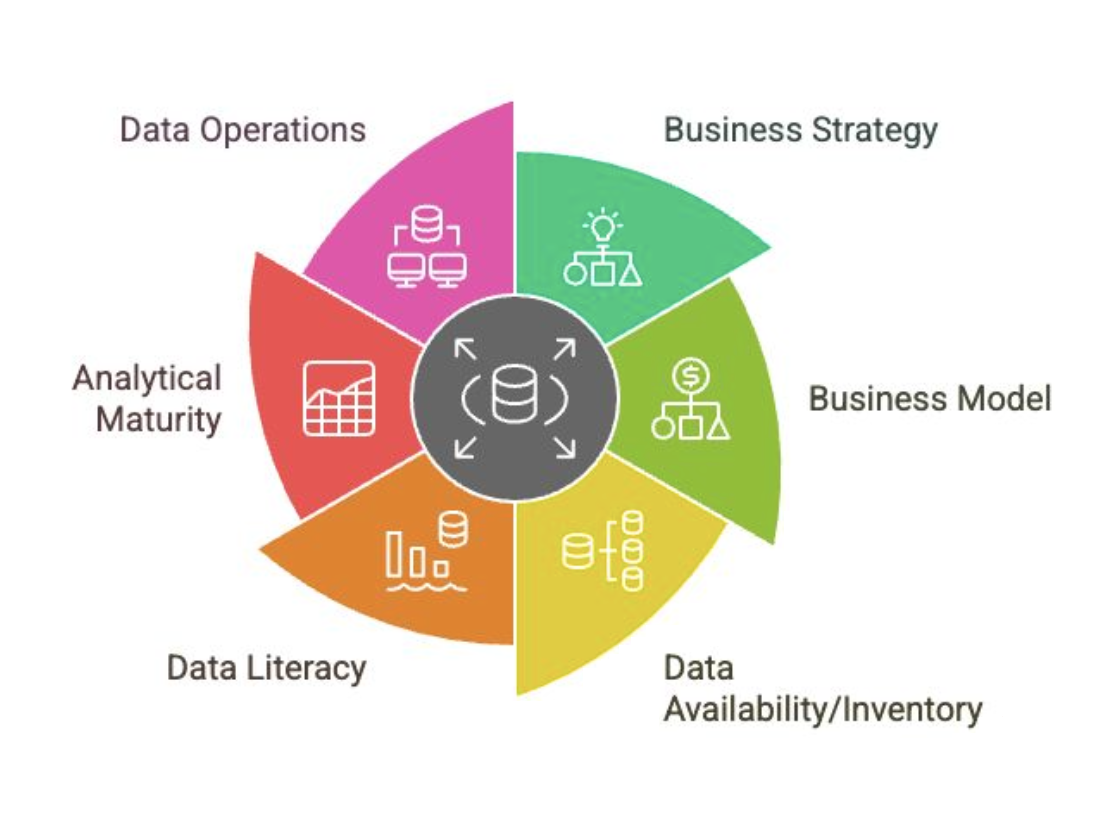
Data Operations
Influences on Data Strategy
Do you have a proper data platform?
Can your IT infrastructure support your data platform?
How mature is your data platform?
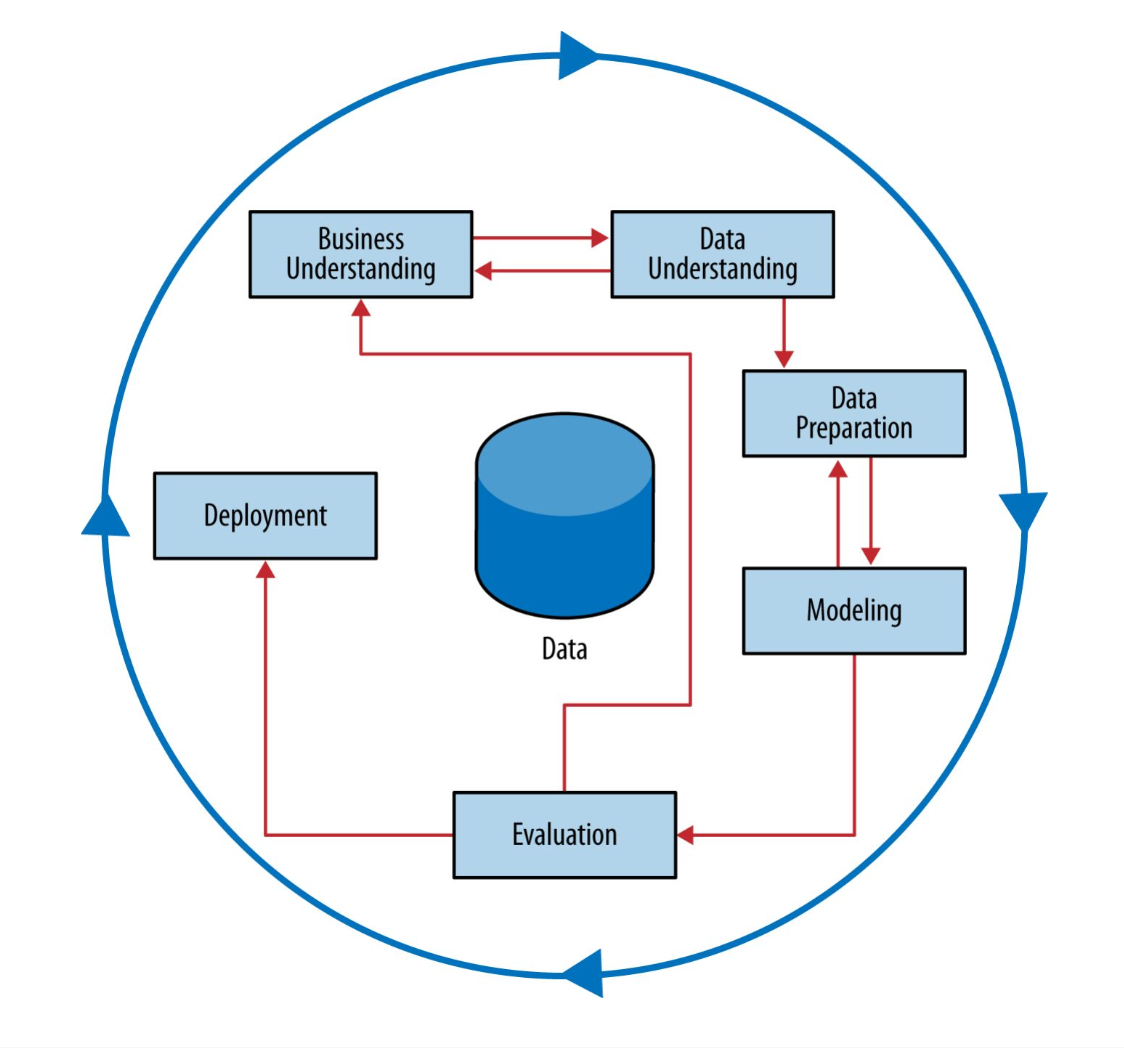
Business Understanding
The first phase of formulating a data strategy
Data Understanding
The second phase of formulating a data strategy
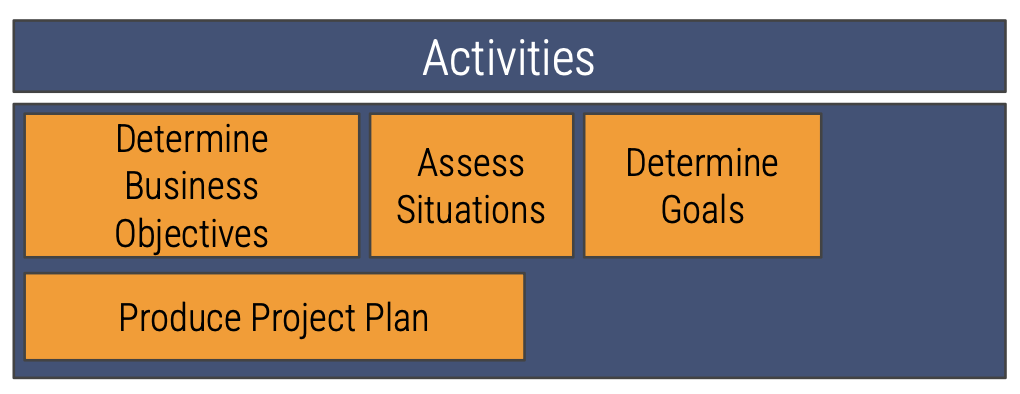
Determine Business Objectives
The first activity in the business understanding phase of formulating a data strategy
Outputs
Background
Business Objectives
Business Success Criteria
Assess Situations
The second activity in the business understanding phase of formulating a data strategy
Outputs
Inventory of Resources
Requirements, Assumptions, and Constraints
Risk and Contingencies
Terminology
Cost and Benefit
Determine Goals
The third activity in the business understanding phase of formulating a data strategy
Outputs
Data Science Goals
Data Science Success Criteria
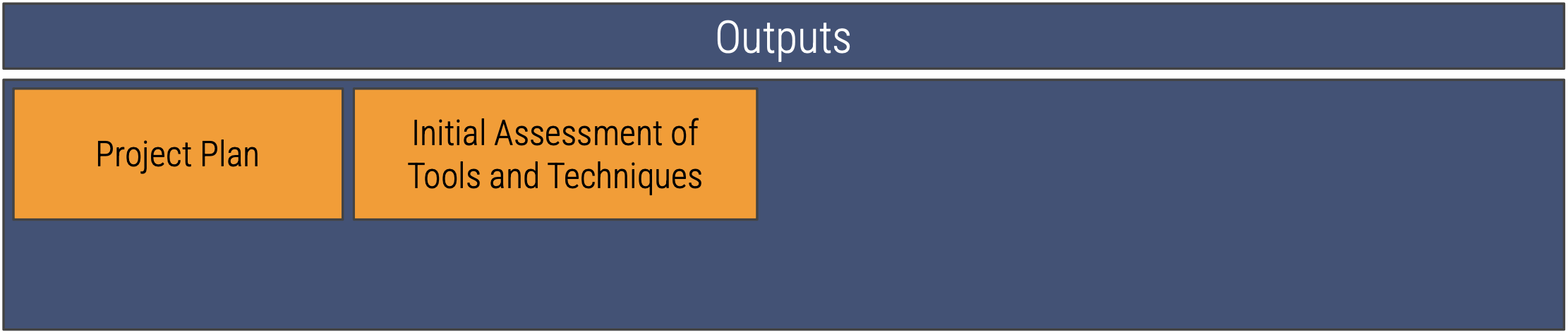
Produce Project Plan
The fourth activity in the business understanding phase of formulating a data strategy
Outputs
Project Plan
Initial Assessment of Tools and Techniques
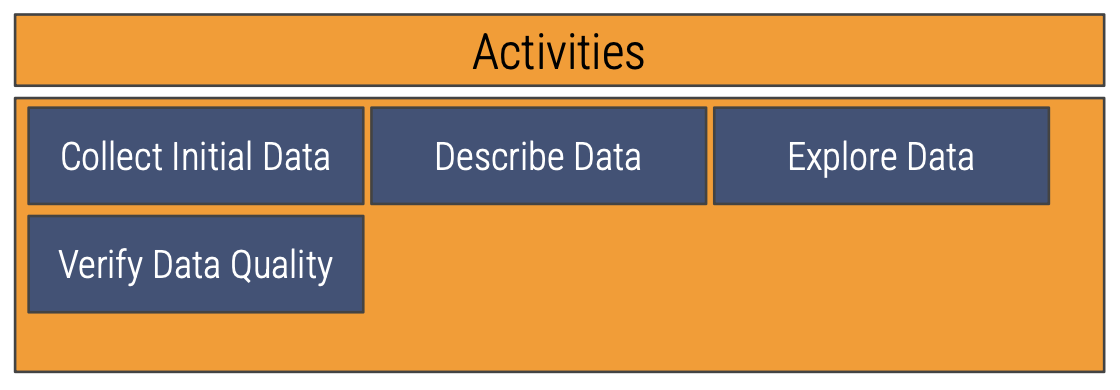
Collect Initial Data
The first activity in the data understanding phase of formulating a data strategy
Outputs
Datasets acquired
Data sources
Methods used to acquire the datasets
Any problems encountered and solutions (if existing)
Describe Data
The second activity in the data understanding phase of formulating a data strategy
Outputs
Format of the data
Quantity of data (no. of records and fields)
Identities of the fields
Any other surface features of the data that have been discovered
Explore Data
The third activity in the data understanding phase of formulating a data strategy
Outputs
First findings or initial hypothesis and their impact on the remainder of the project
If appropriate, include graph and plots
Verify Data Quality
The fourth activity in the data understanding phase of formulating a data strategy
Outputs
List of results of the data quality verifications
If quality problems exist, list possible solutions
Data Management
The development, execution, and supervision of plans, policies, programs, and practices that deliver, control, protect, and enhance the value of data and information assets throughout their life cycles
Data Governance and Stewardship
A knowledge area of data management that corresponds to the exercise of authority, control, and shared decision-making (planning, monitoring, and enforcement) over the management of data assets.
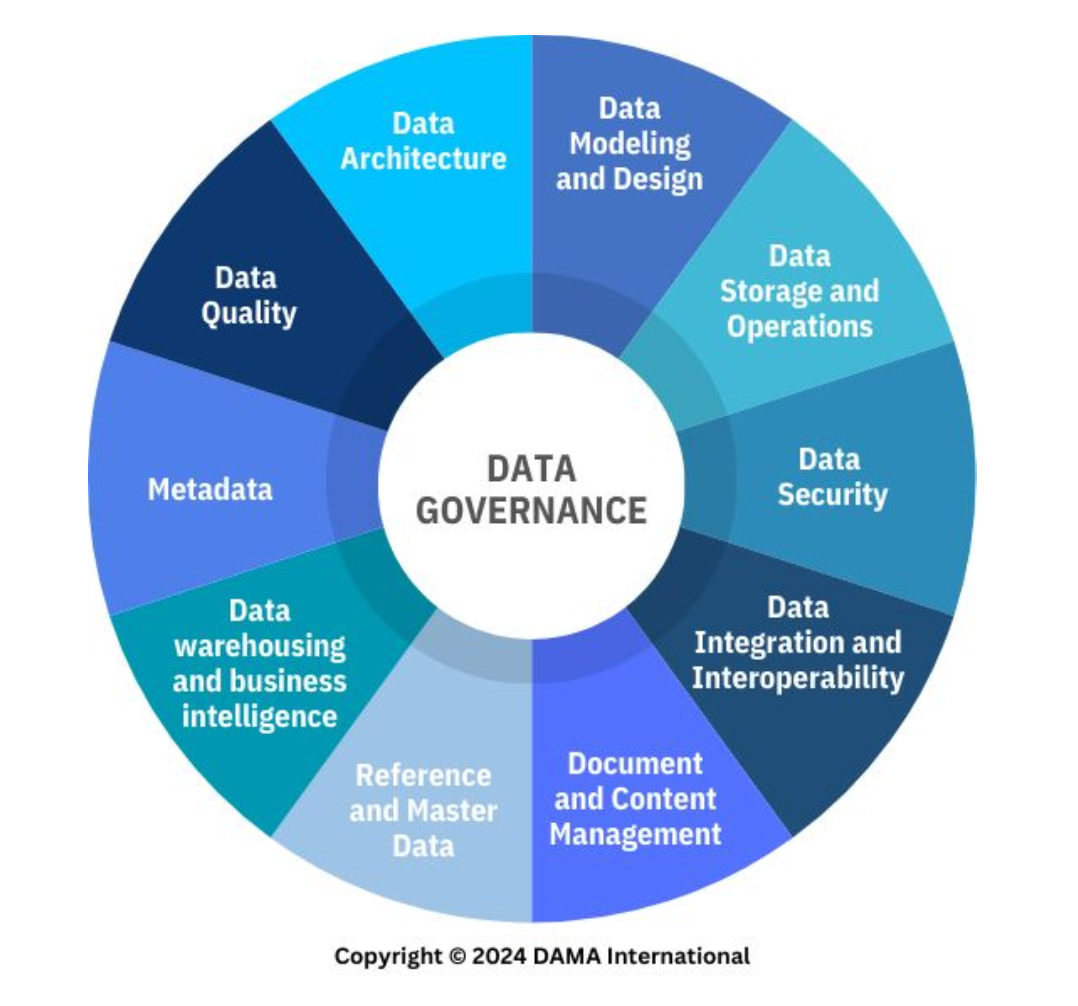
Data Architecture
A knowledge area of data management that corresponds to identifying the needs of the enterprise (regardless of the structure) and maintaining the master blueprints to meet those needs.
Using master blueprints to guide data integration, control data assets, and align data investments with business strategy.
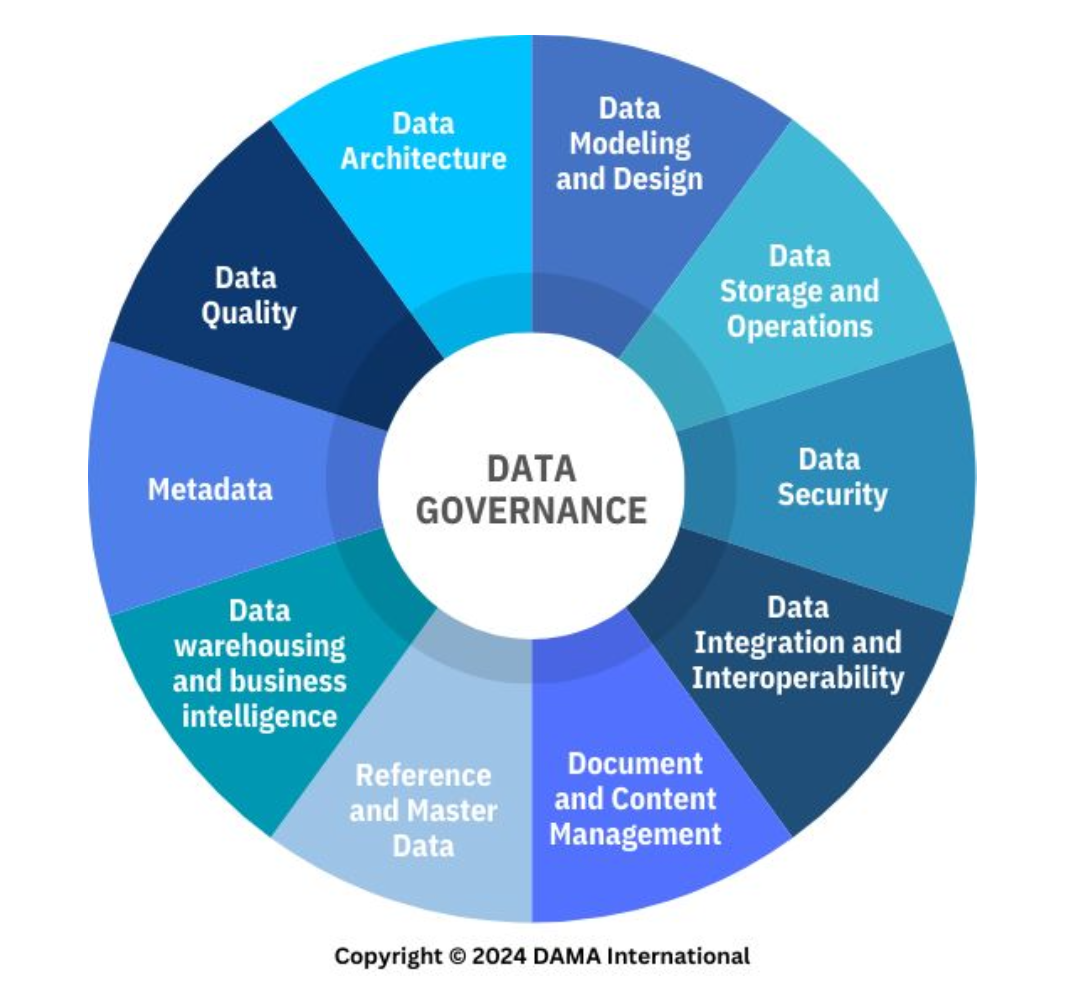
Data Modeling and Design
A knowledge area of data management that corresponds to the process of discovering, analyzing, and scoping data requirements, and then representing and communicating these data requirements in a precise form.
This process is iterative and involves conceptual, logical, and physical models.
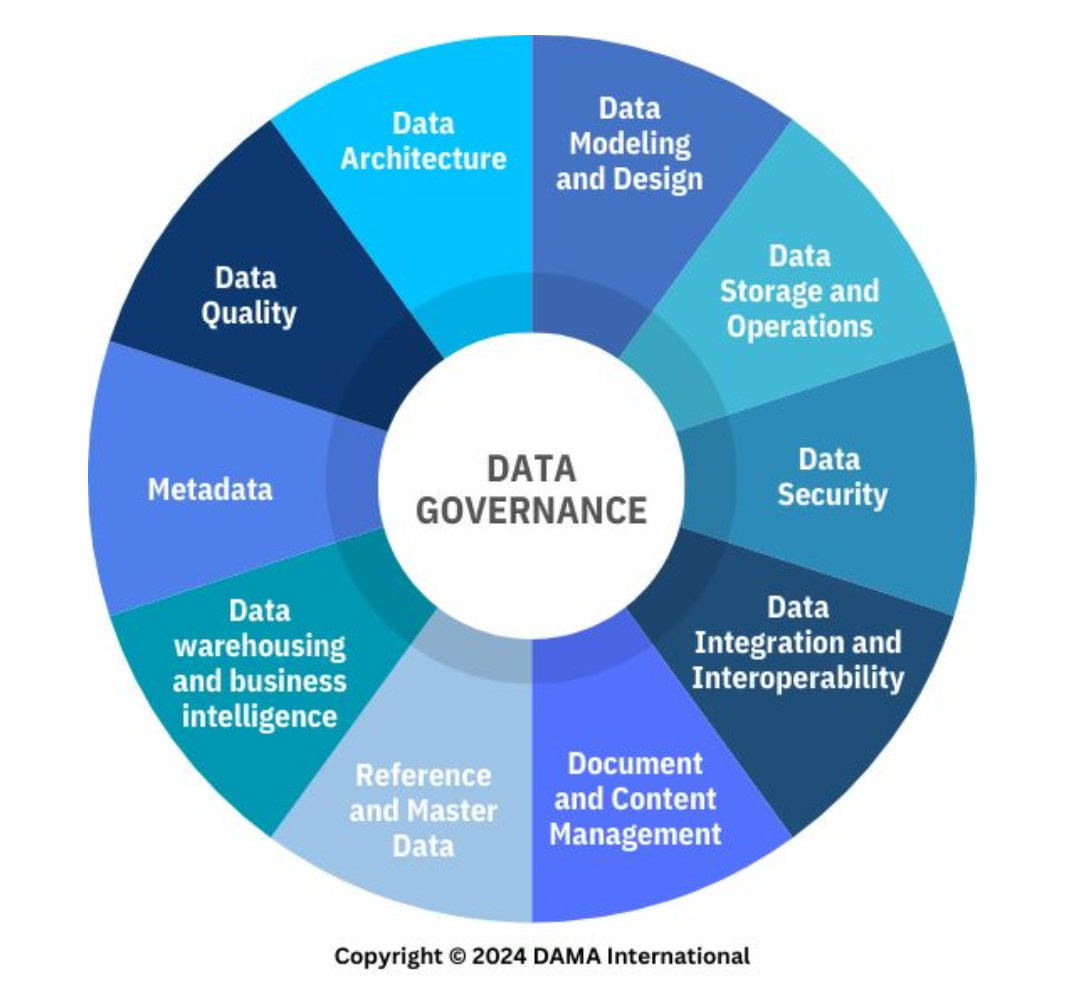
Data Storage and Operations
A knowledge area of data management that corresponds to the design, implementation, and support of stored data to maximize its value.
Data Security
A knowledge area of data management that corresponds to the planning, development, and execution of security policies and procedures to provide proper authentication, authorization, access, and auditing of data and information assets within cultural and regulatory consideration.
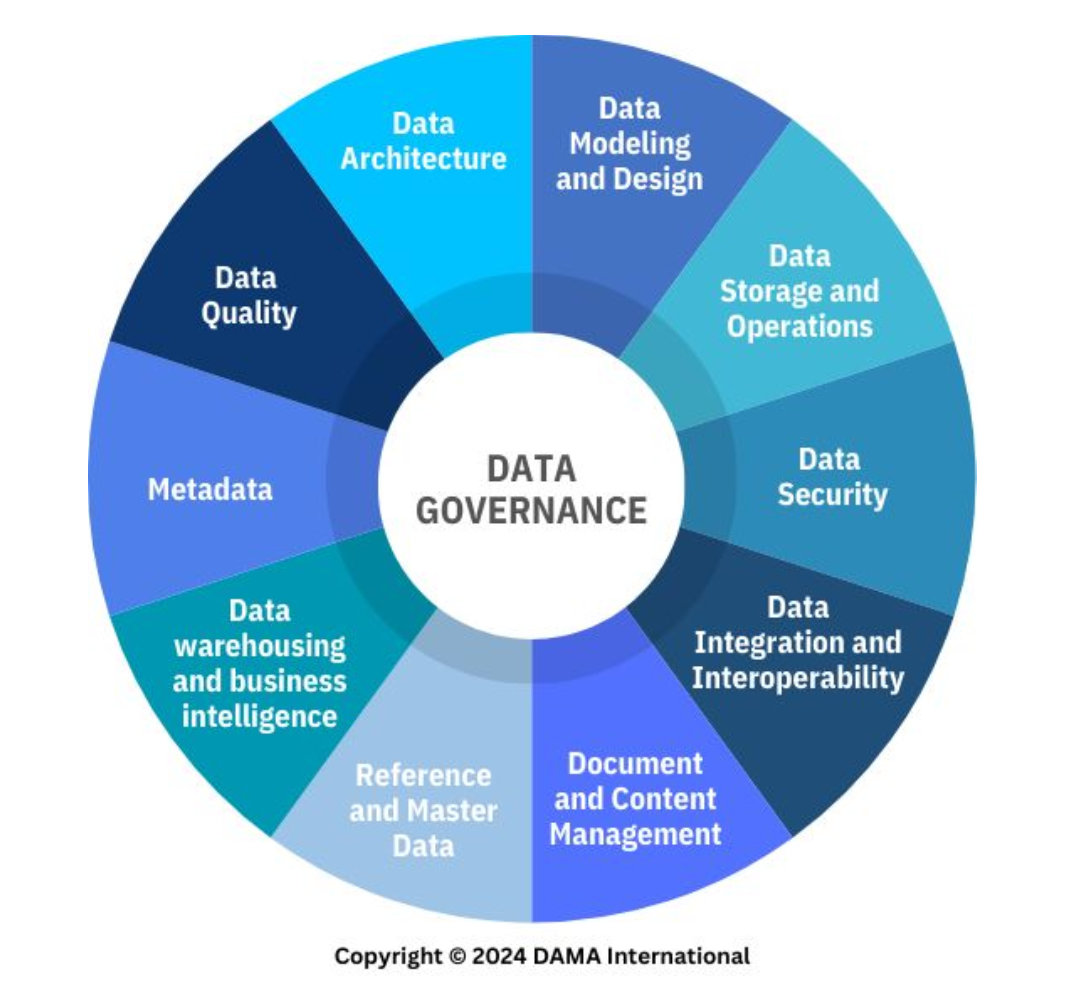
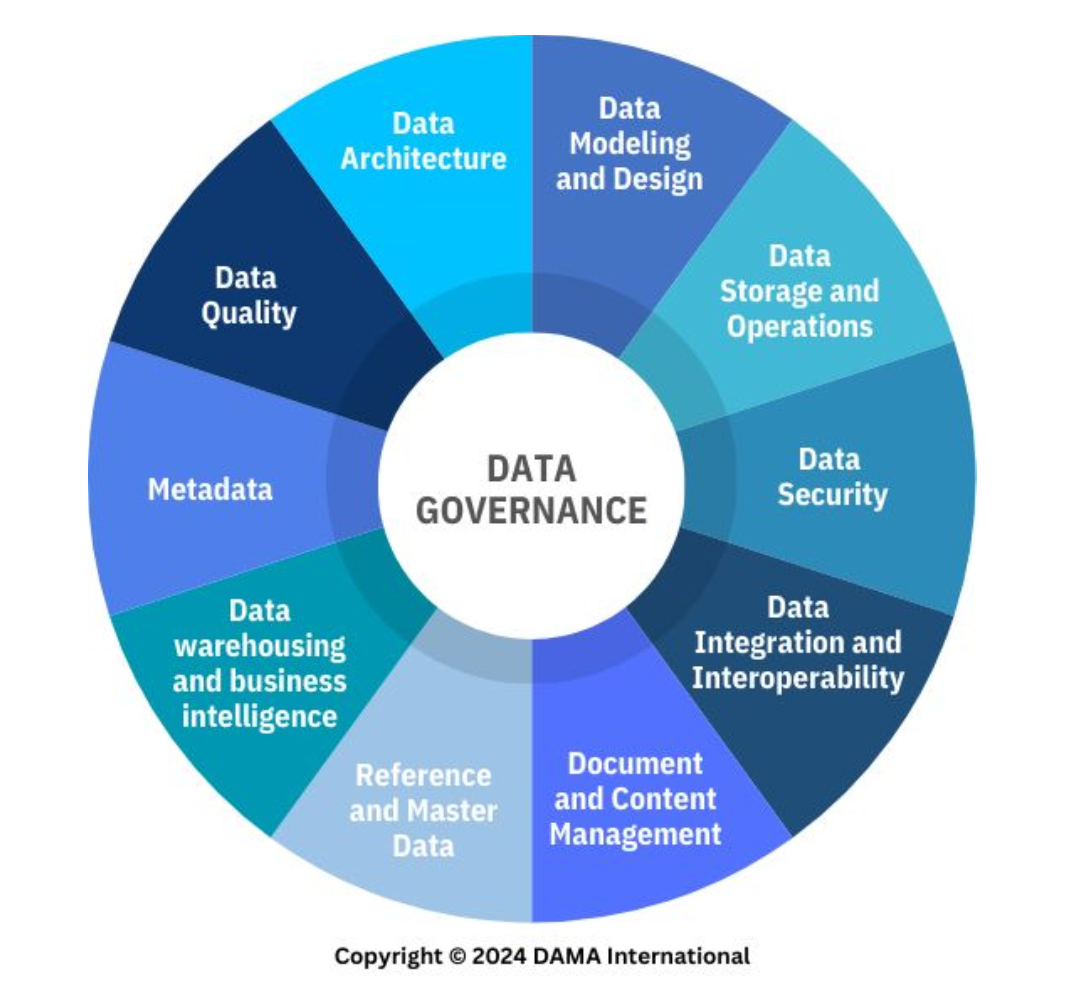
Data Integration and Interoperability
A knowledge area of data management. __________ is the movement and consolidation of data within and between data stores, applications, and organizations, while __________ is the ability for multiple systems to communicate.
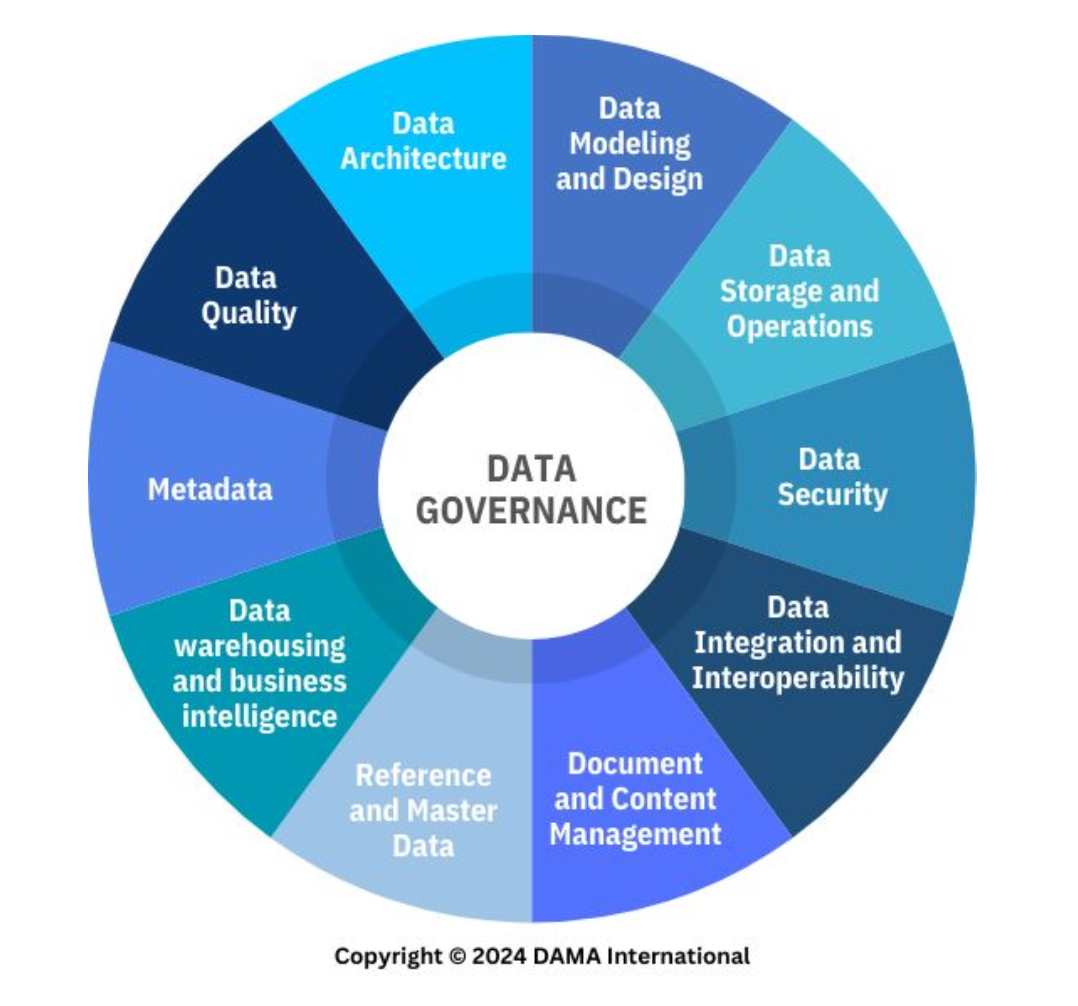
Document and Content Management
A knowledge area of data management that corresponds to controlling the capture, storage, access, and use of data and information stored predominantly relational databases.
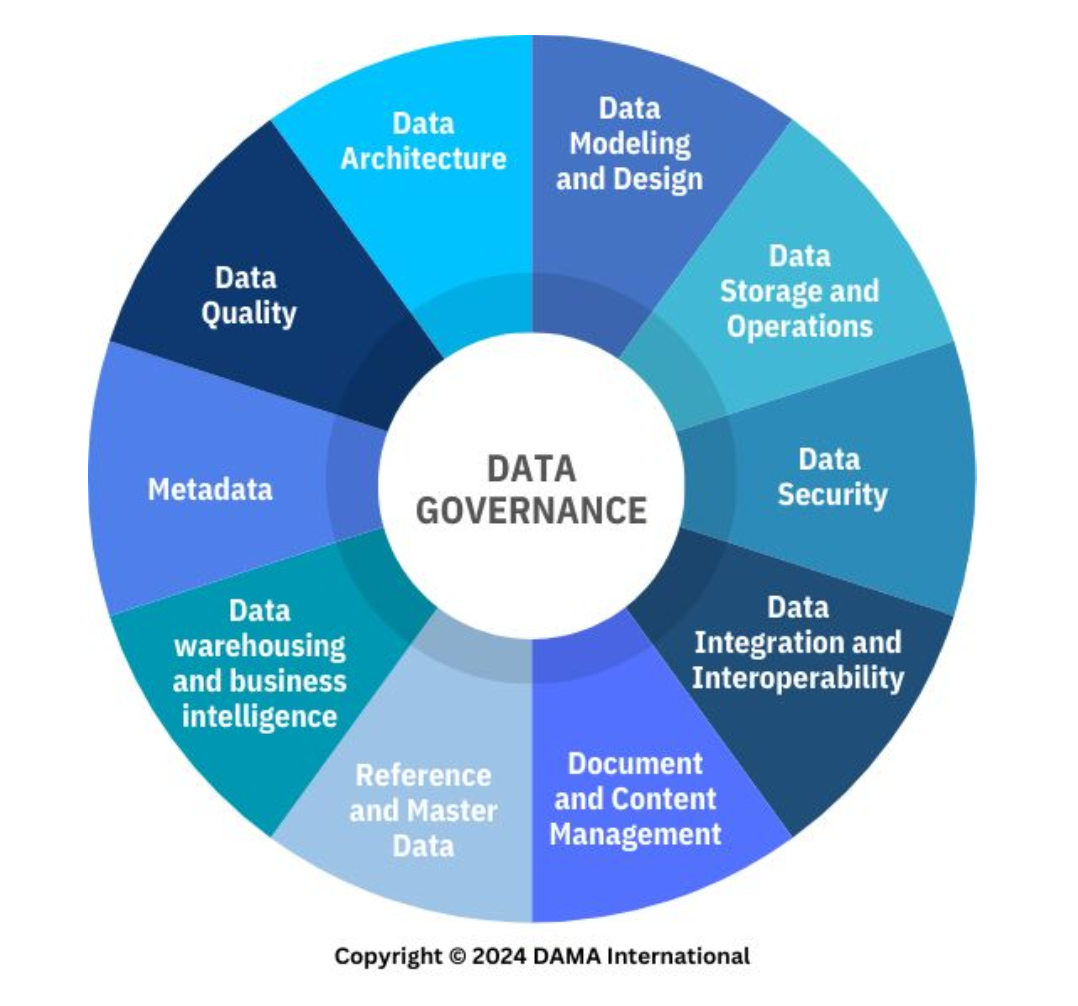
Reference and Master Data
A knowledge area of data management that corresponds to managing reconciled and integrated data through stewardship and semantic consistency in support of enterprise-wide needs to share its data assets.
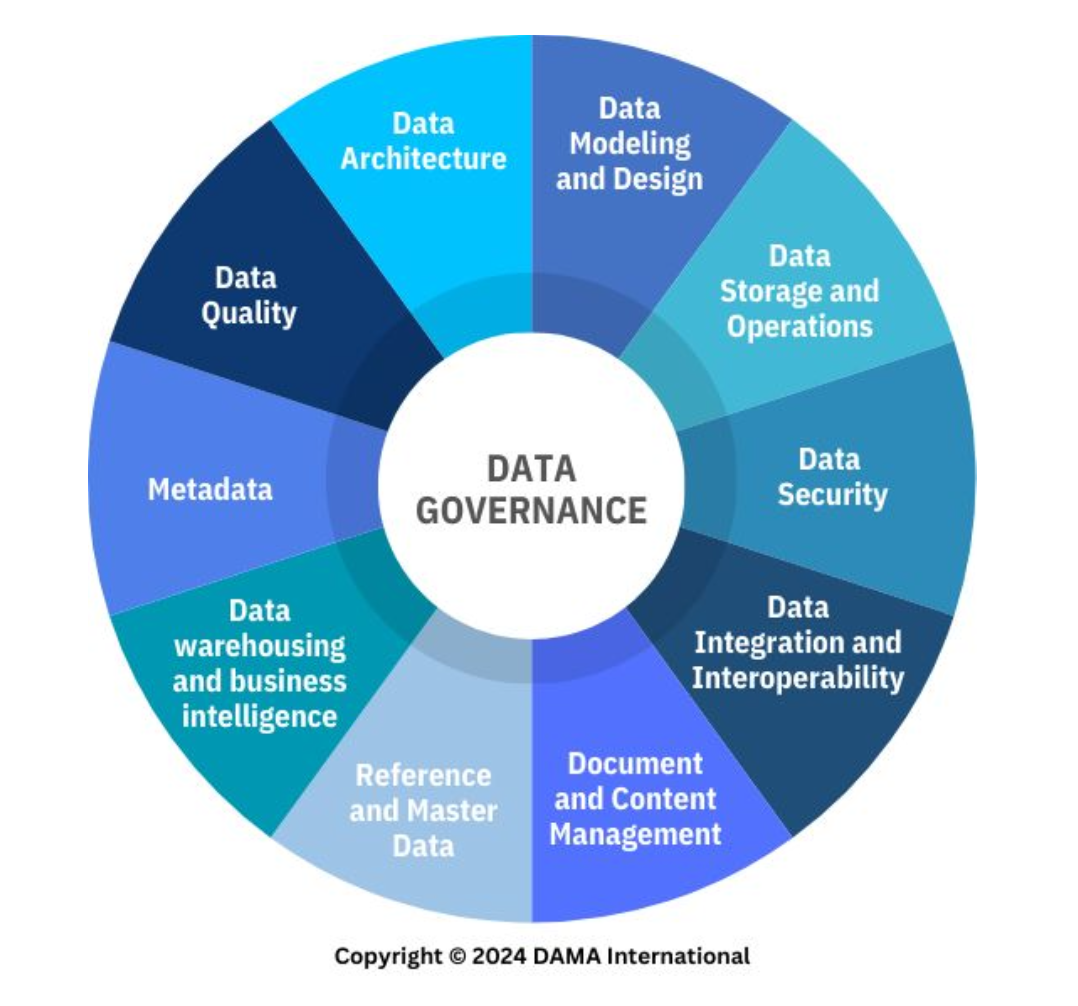
Data Warehousing and Business Intelligence
A knowledge area of data management that corresponds to planning, implementation, and managing an integrated data system to support knowledge workers engaged in reporting, query, and analysis.
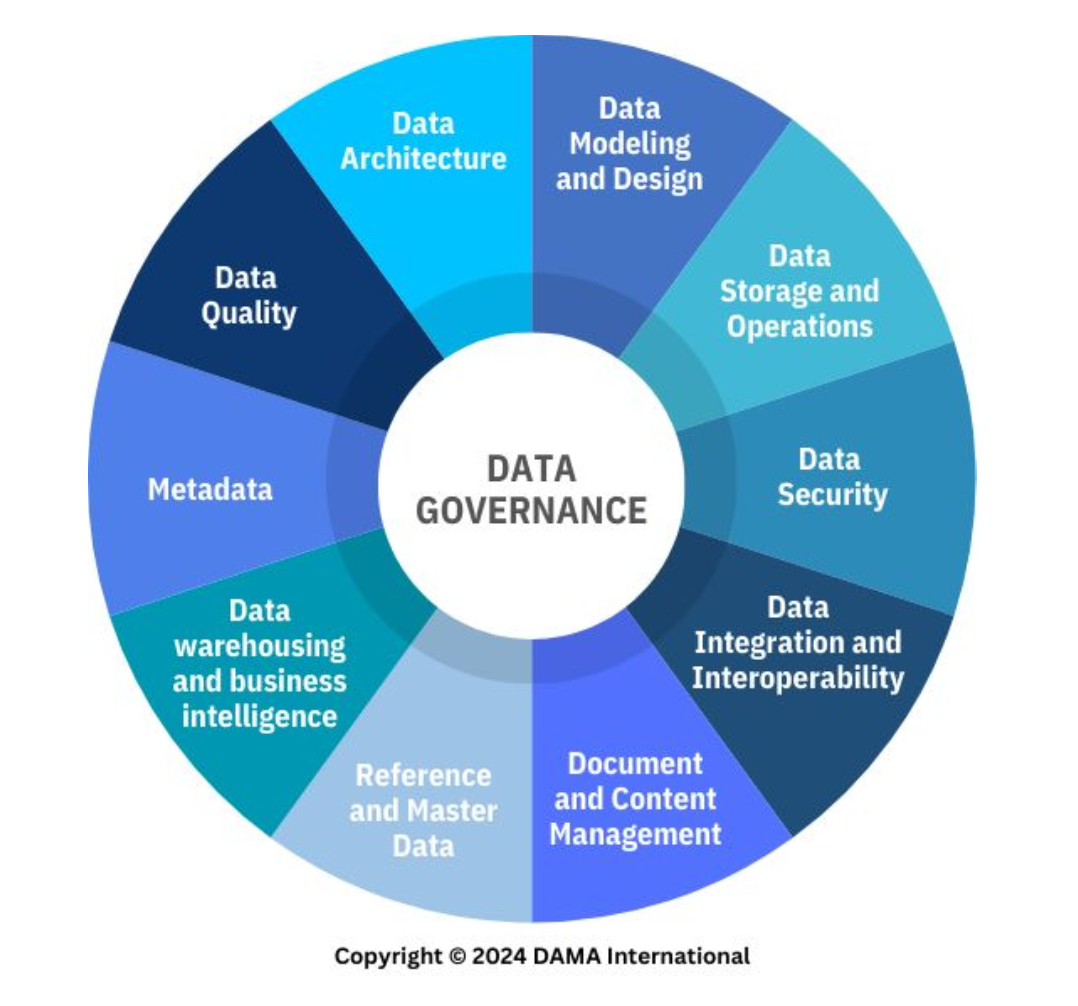
Metadata Management
A knowledge area of data management that corresponds to planning, implementation, and control of activities that contribute to the ability to process, maintain, integrate, secure, audit and govern other data.
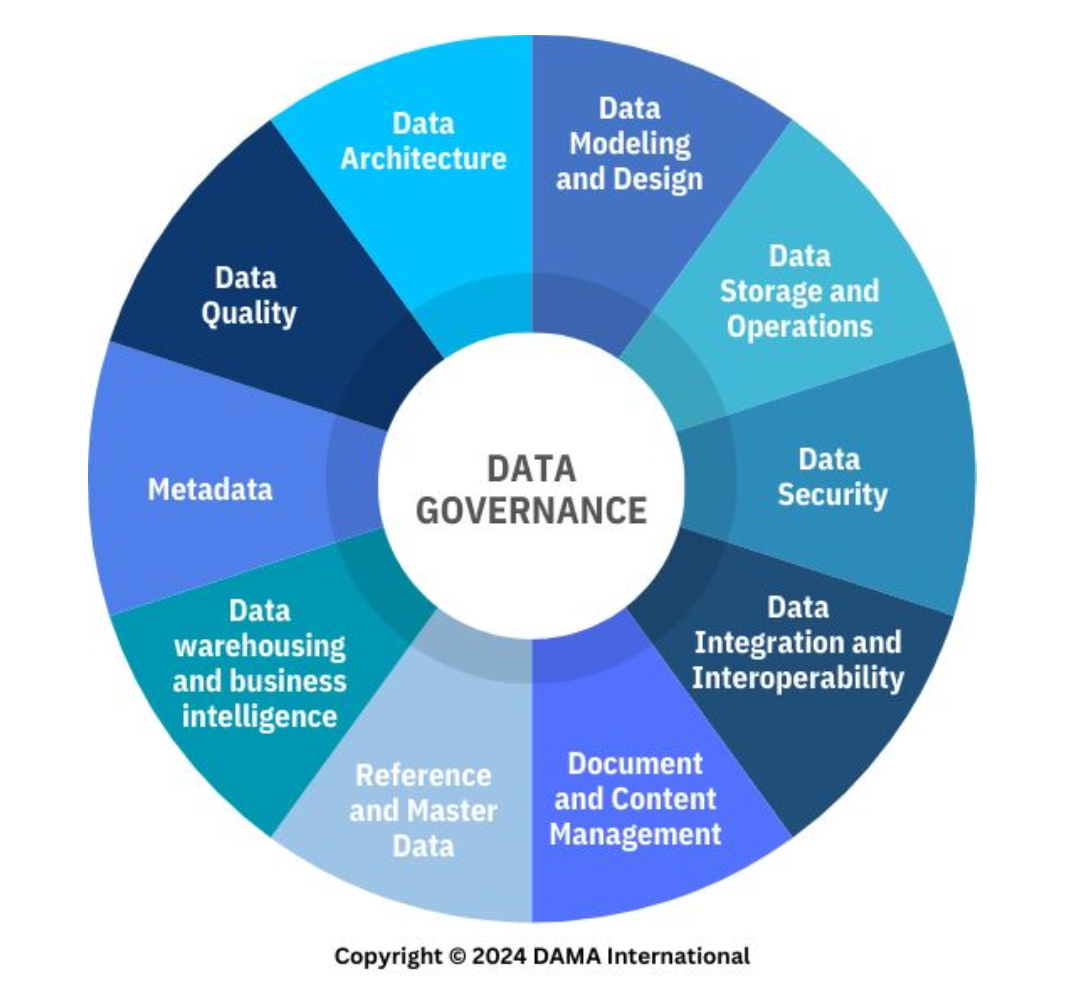
Data Quality Management
A knowledge area of data management that corresponds to the planning, implementation, and control of activities that apply techniques for collecting and handing data ensuring it addresses the needs of the enterprise and local consumer is fit for use.
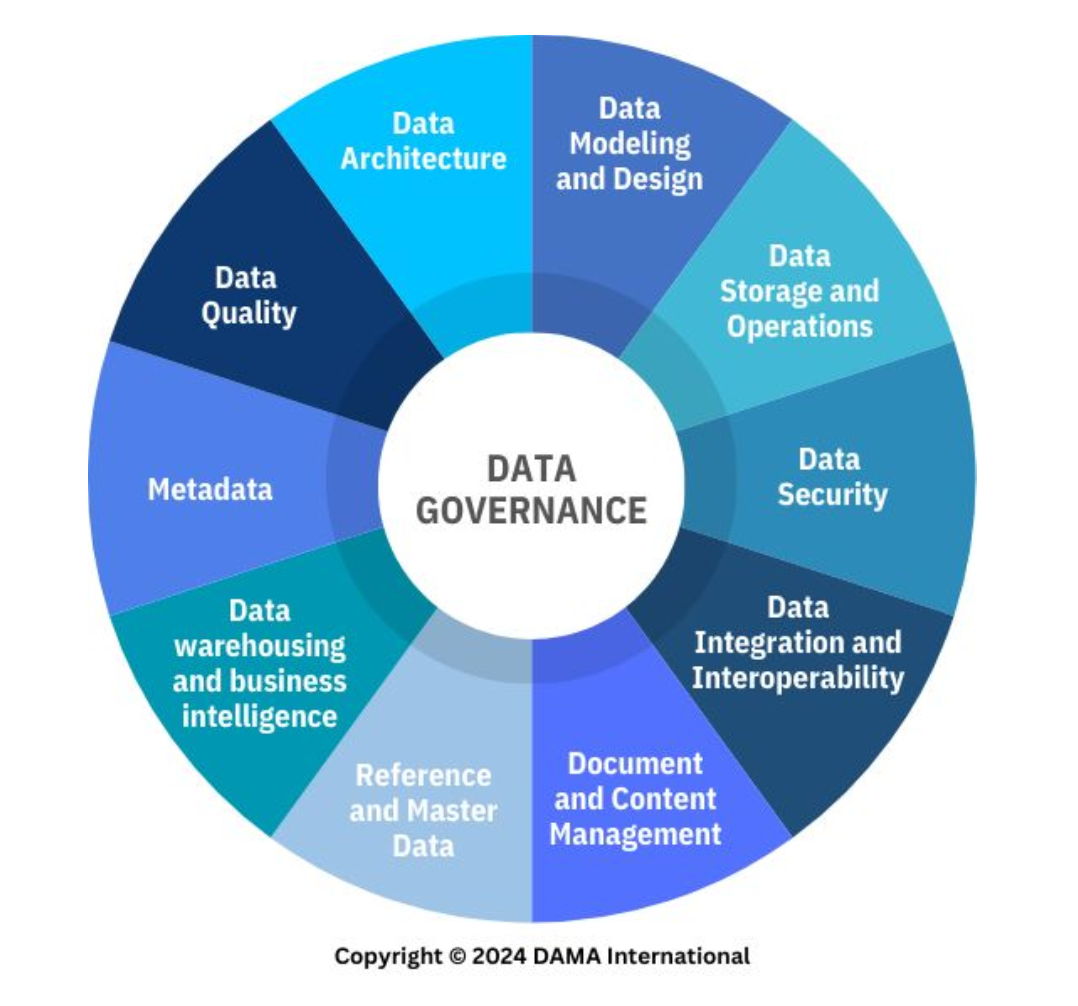
Data Lifecycle
Outlines the stages that a particular set of data goes through in analytics projects
Generation
A stage in the data lifecycle that comes in two forms: digital and analog data. Samples include sales transactions, promo subscriptions, cash in and cash out, stock in and stock out, and sensor generated data.
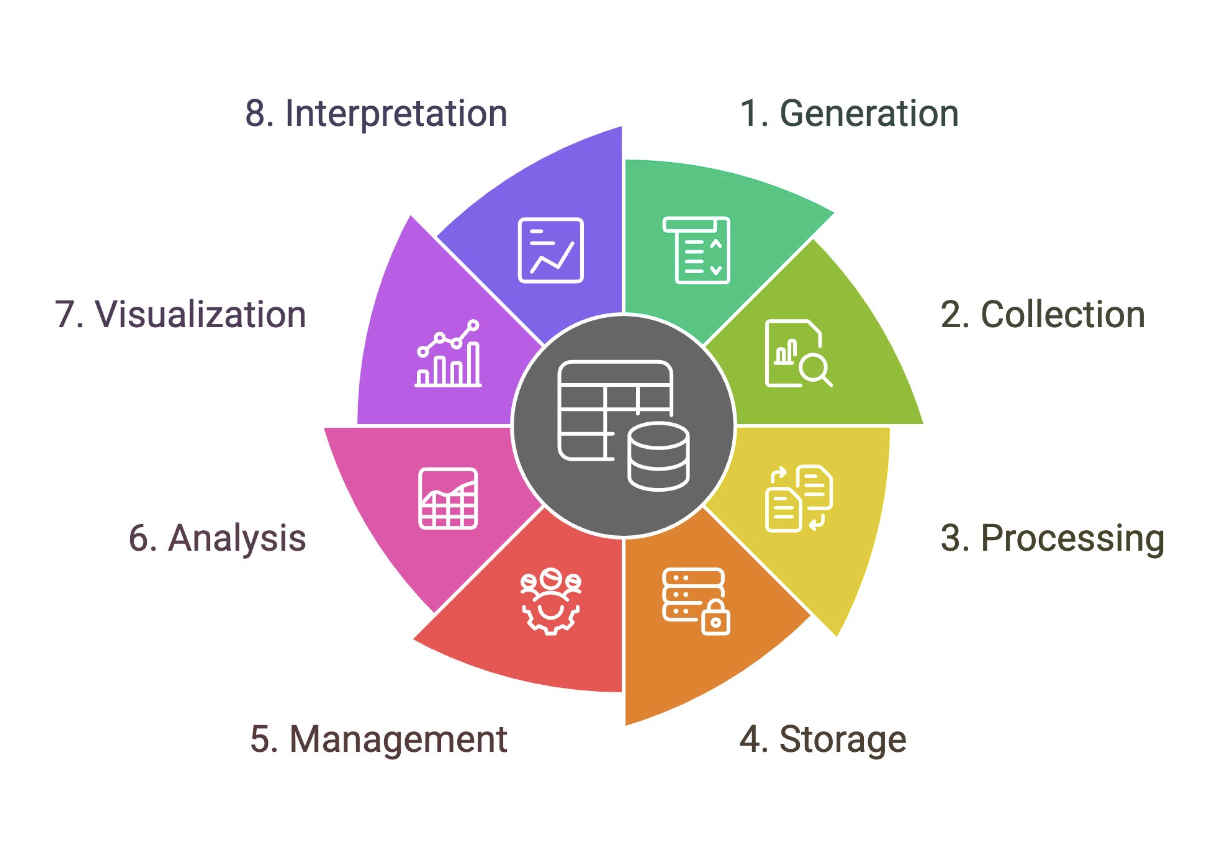
Collection
A stage in the data lifecycle that corresponds to the process of retrieving data from data sources and putting them into a single data platform. This is the “E” in ETL. Can be automated or manual.
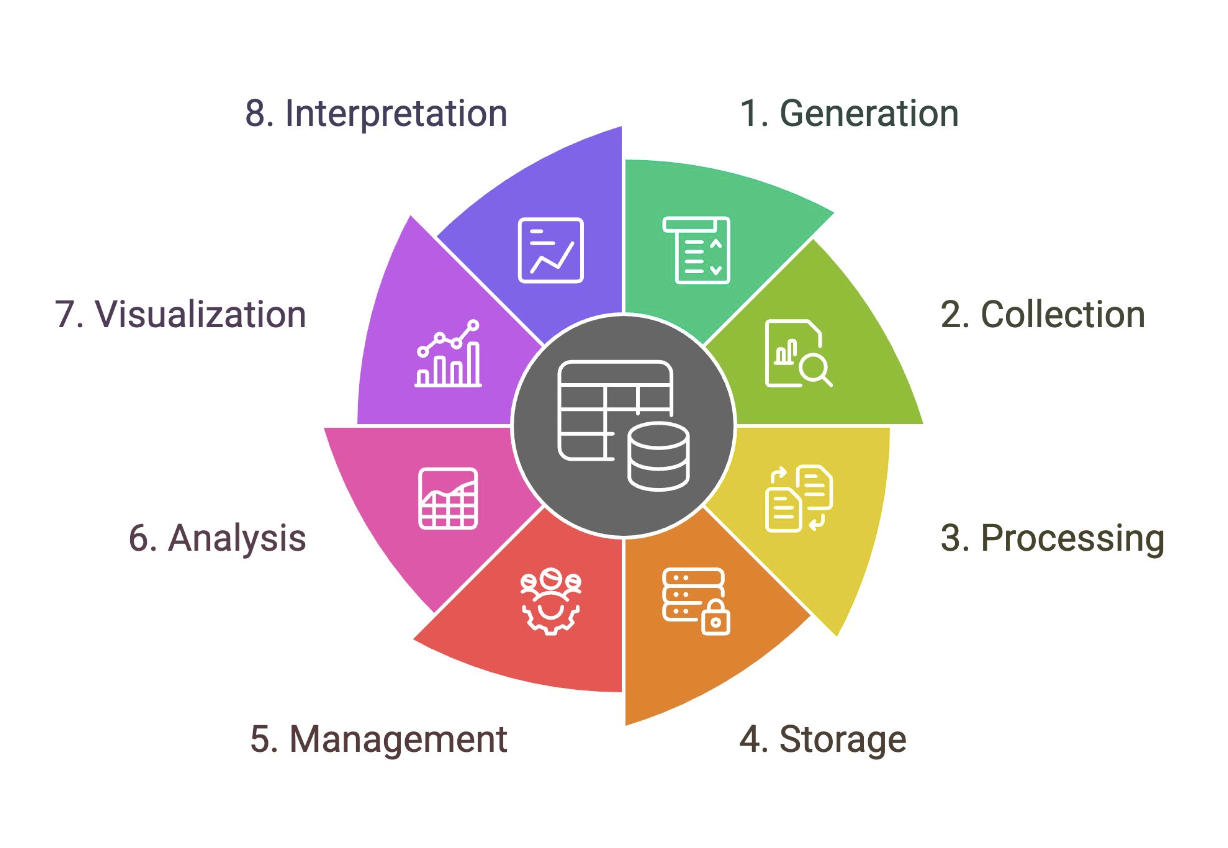
Processing
When data is collected, they may not be in the format that you need them to be. A stage in the data lifecycle that corresponds to the “T” in ETL. Sample activities include data cleansing, data transformations, computations, and data aggregations.
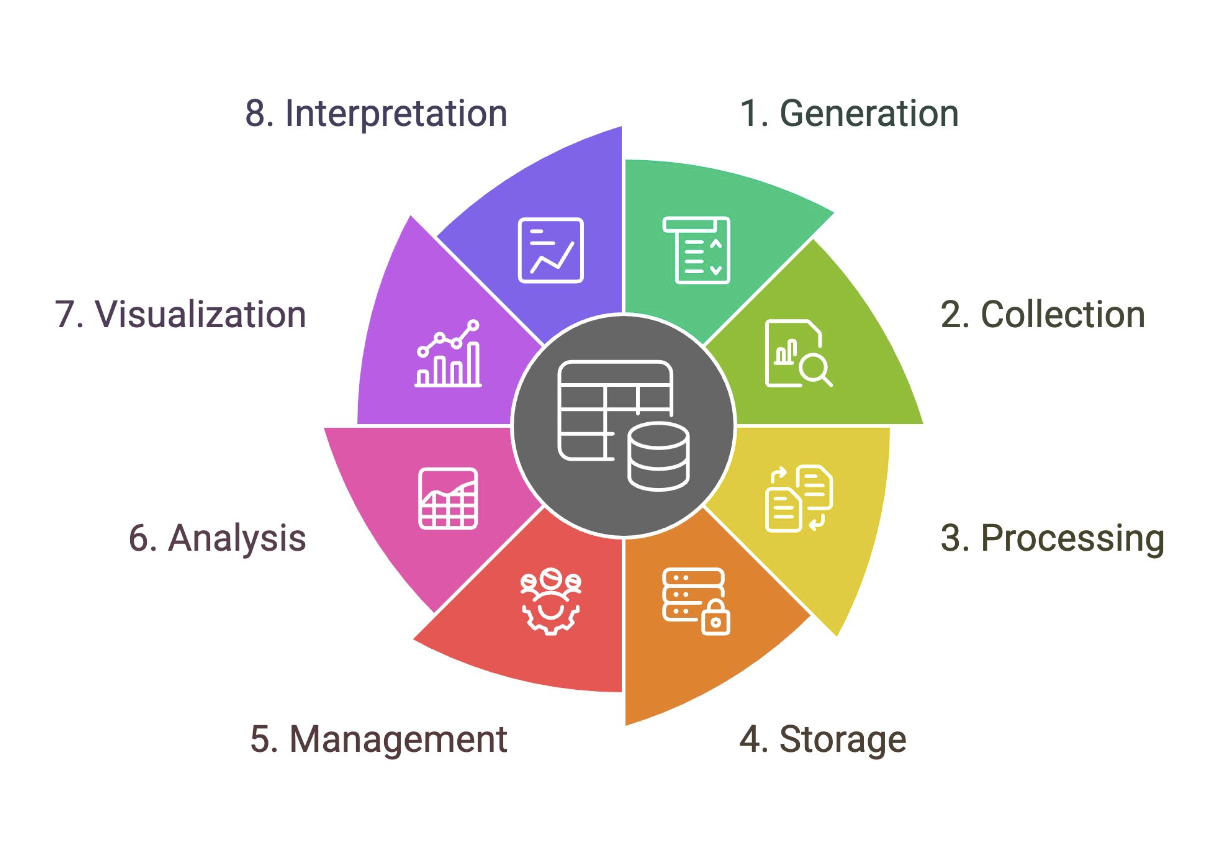
Storage
A stage in the data lifecycle that corresponds to where data is loaded into the data platform infrastructure. This is the “L” in ETL.
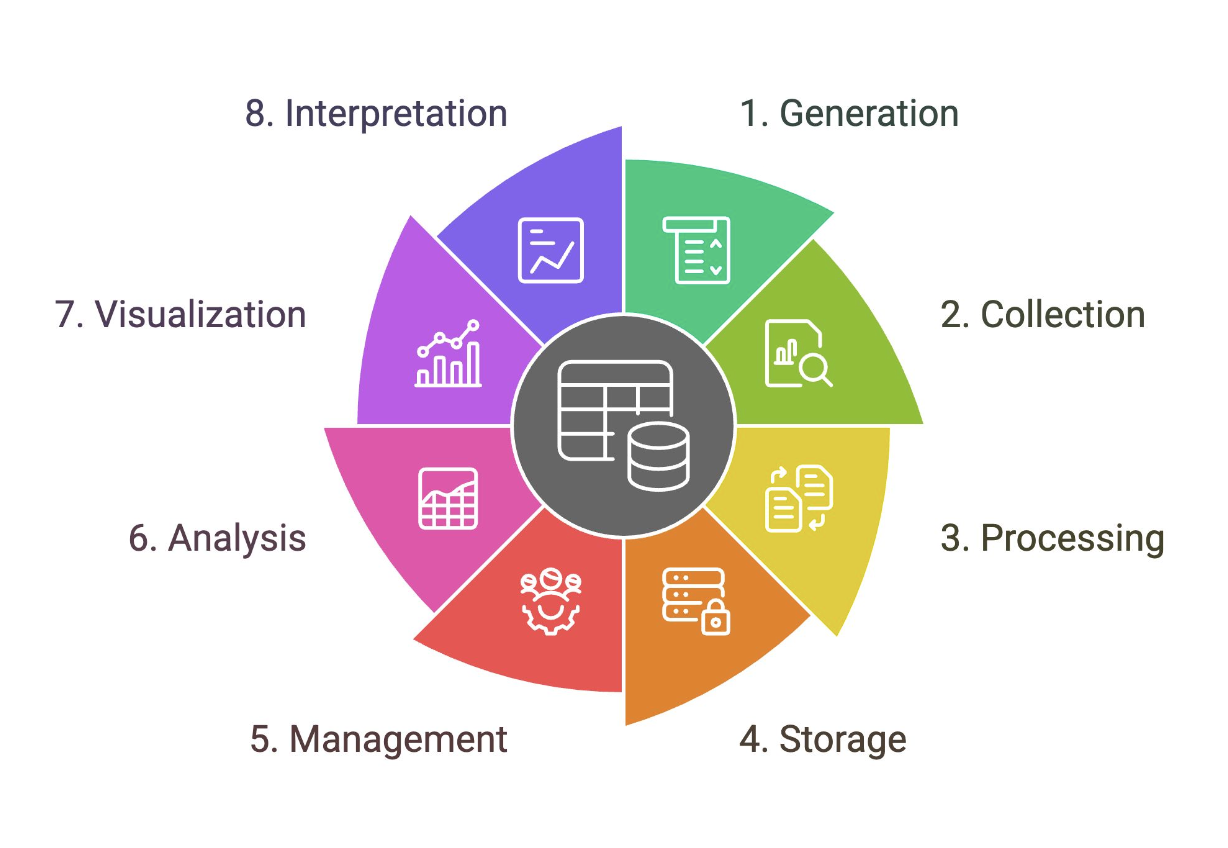
Management
A stage in the data lifecycle that corresponds to an ongoing process that involves, organizing, storing, and retrieving data as necessary over the life of a data project. Also includes encryption, access control, and other related functions that support the operations of the data platform.
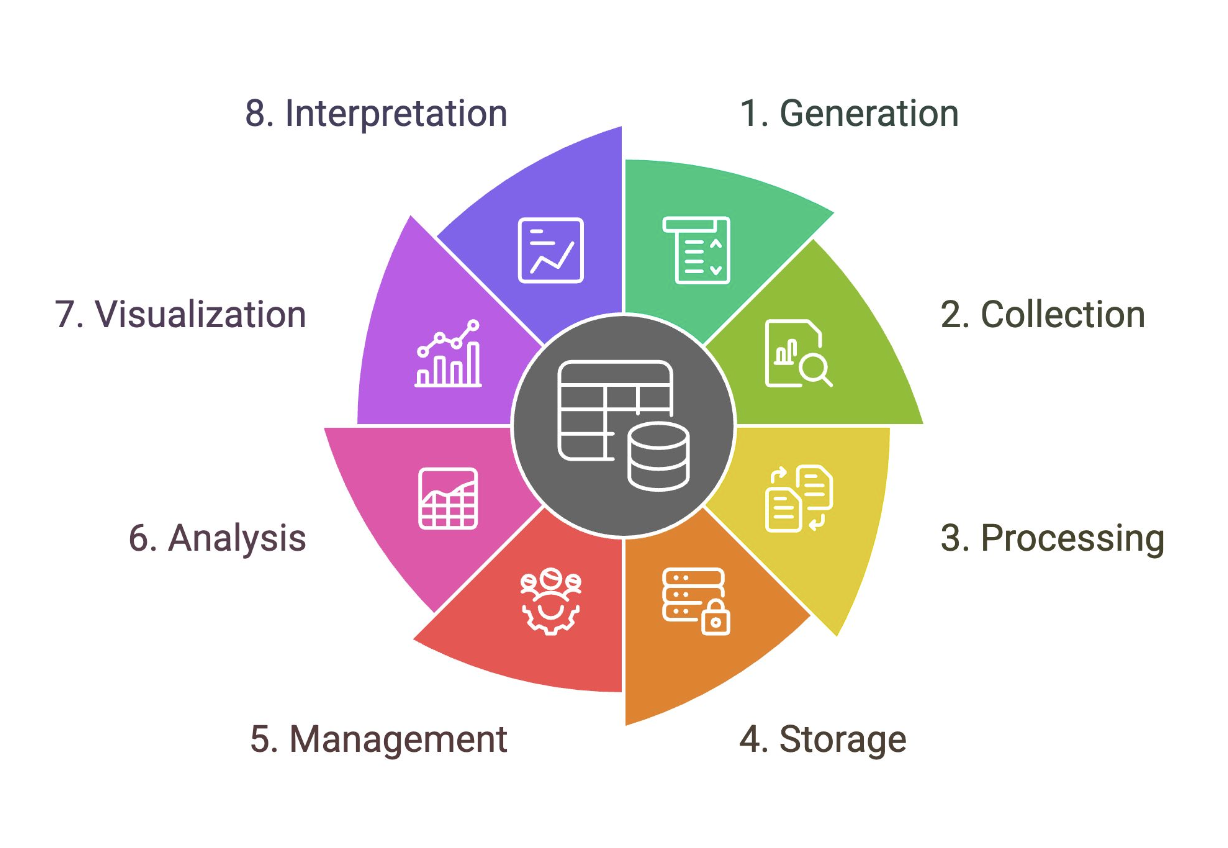
Analysis
A stage in the data lifecycle that corresponds to the processes that attempt to glean meaningful insights from raw data with the appropriate tools and strategies. Requires a question/challenge. Sample activities include statistical modeling, ad hoc analytics, artificial intelligence, data mining, and machine learning.
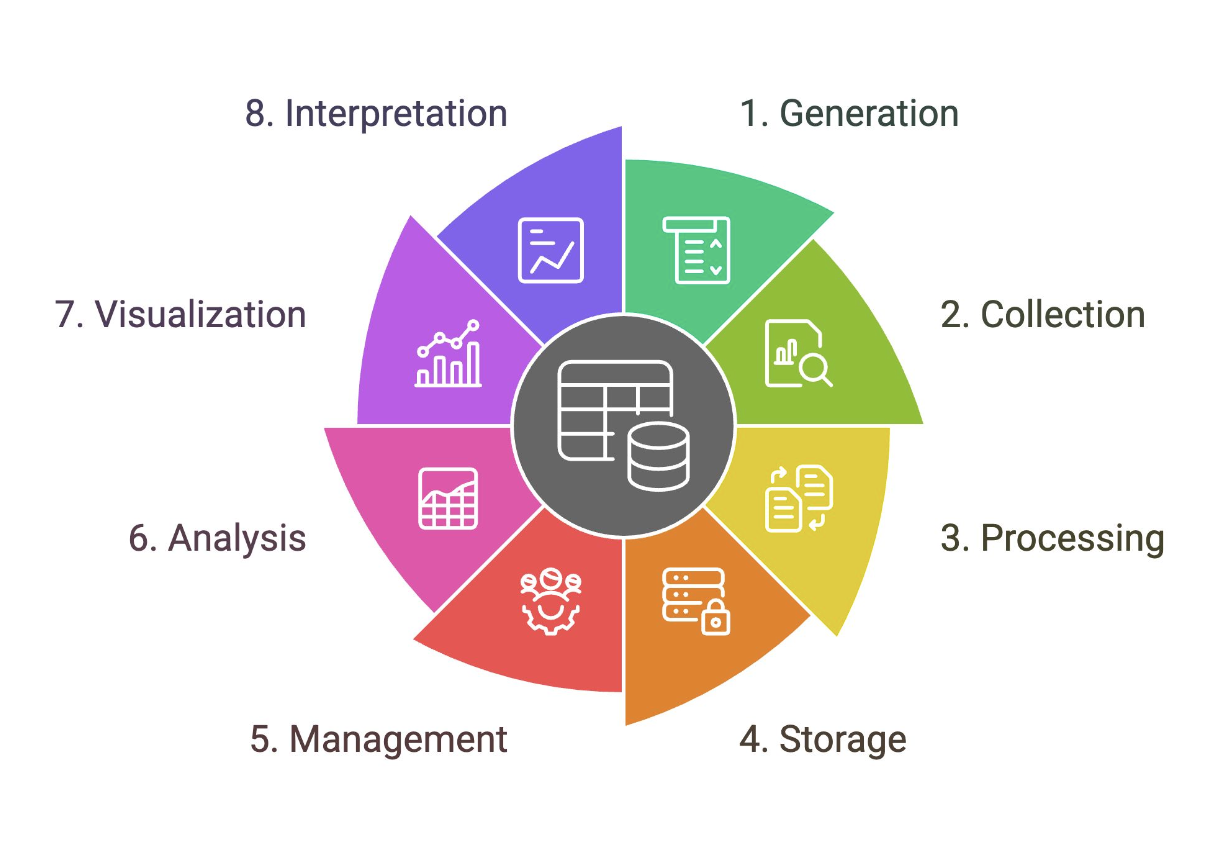
Visualization
A stage in the data lifecycle that corresponds to the process of creating graphical representations of your information or knowledge to quickly communicate your analysis. Should take audience and data story into account.
Interpretation
A stage in the data lifecycle that makes sense of your analysis and visualization and investigates it through the lens of your expertise and understanding (domain knowledge).
May include a description or explanation of what the data shows and the implications.
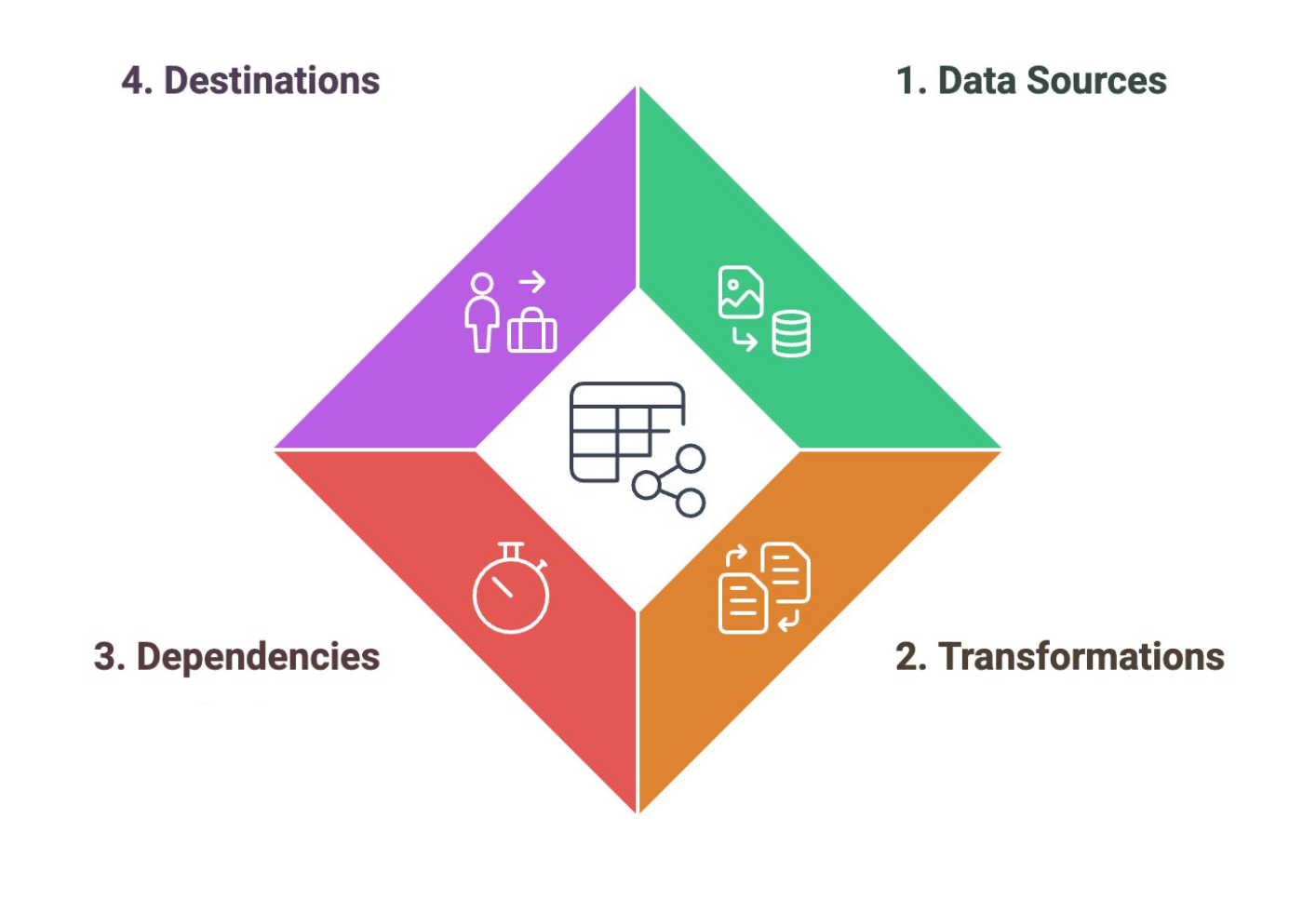
Data Pipelines
Support the Collection, Processing, and Storage stages of the Data Lifecycle. They are microservices that perform different tasks to prepare the data for analytics.
Data Sources
A component of the data pipeline that corresponds to the entry points for data into the pipeline, including applications and devices
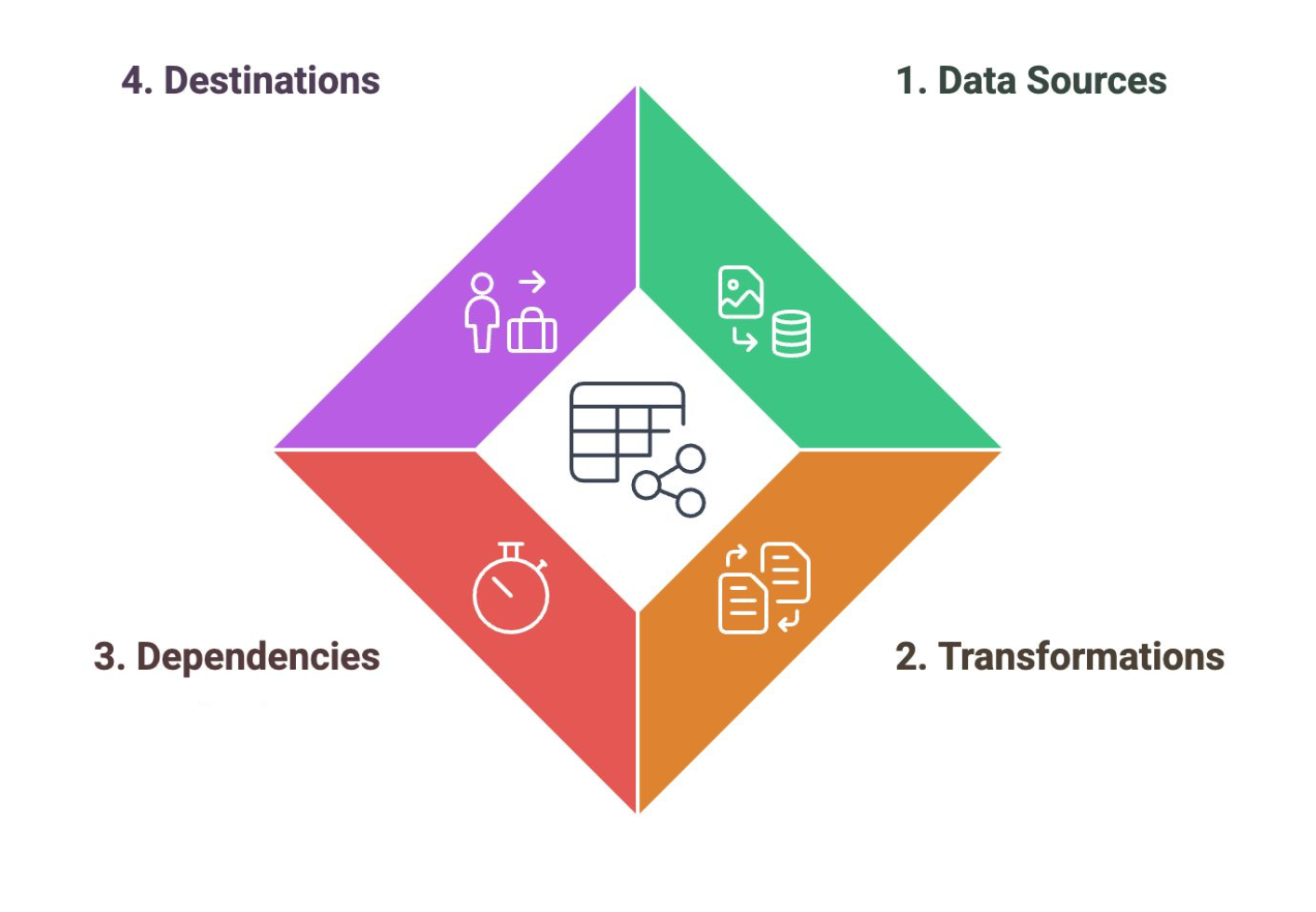
Transformations
A component of the data pipeline that corresponds to the operations that modify data to meet analysis requirements.
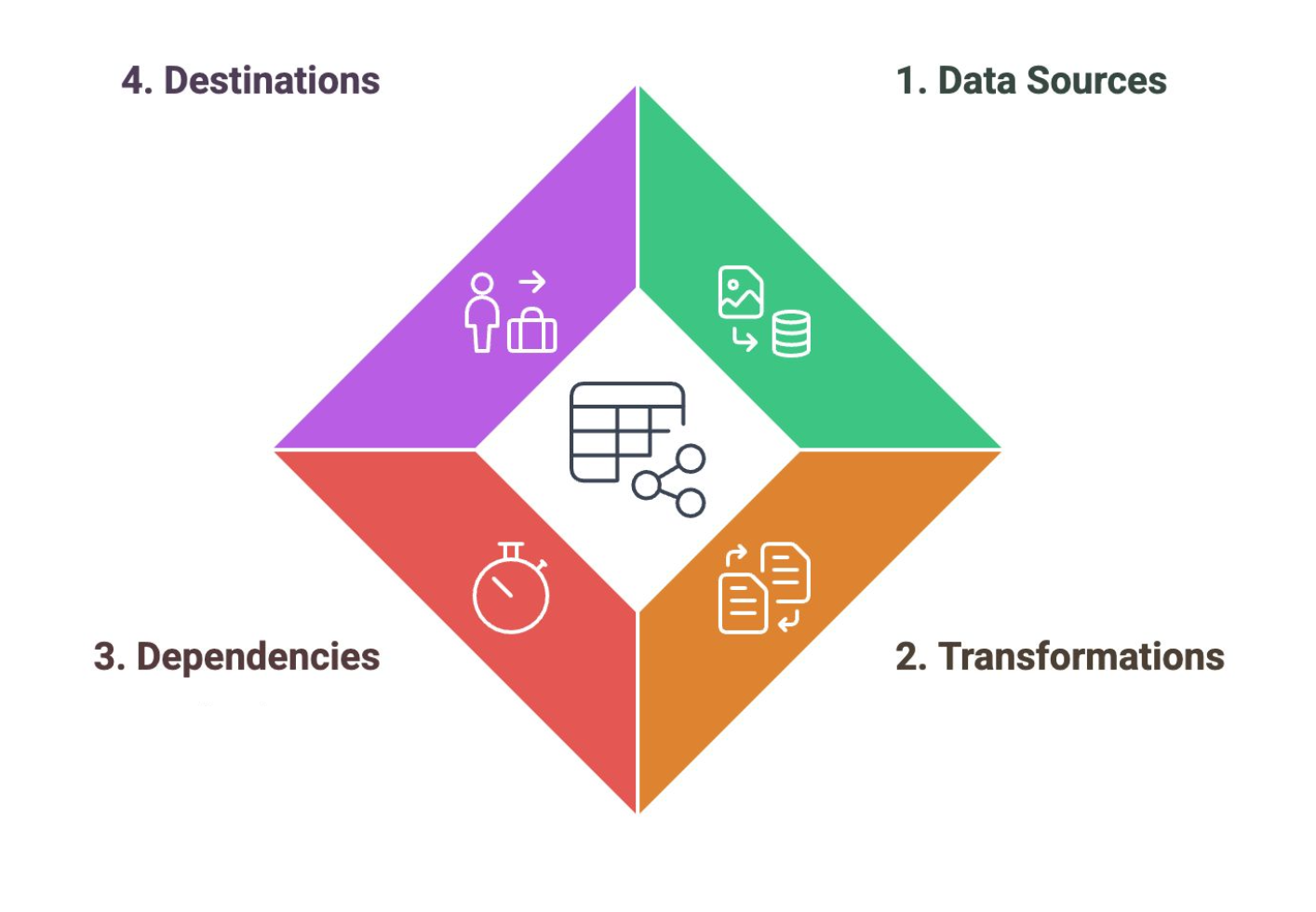
Dependencies
A component of the data pipeline that corresponds to the factors that determine the timing and progression of data processing.
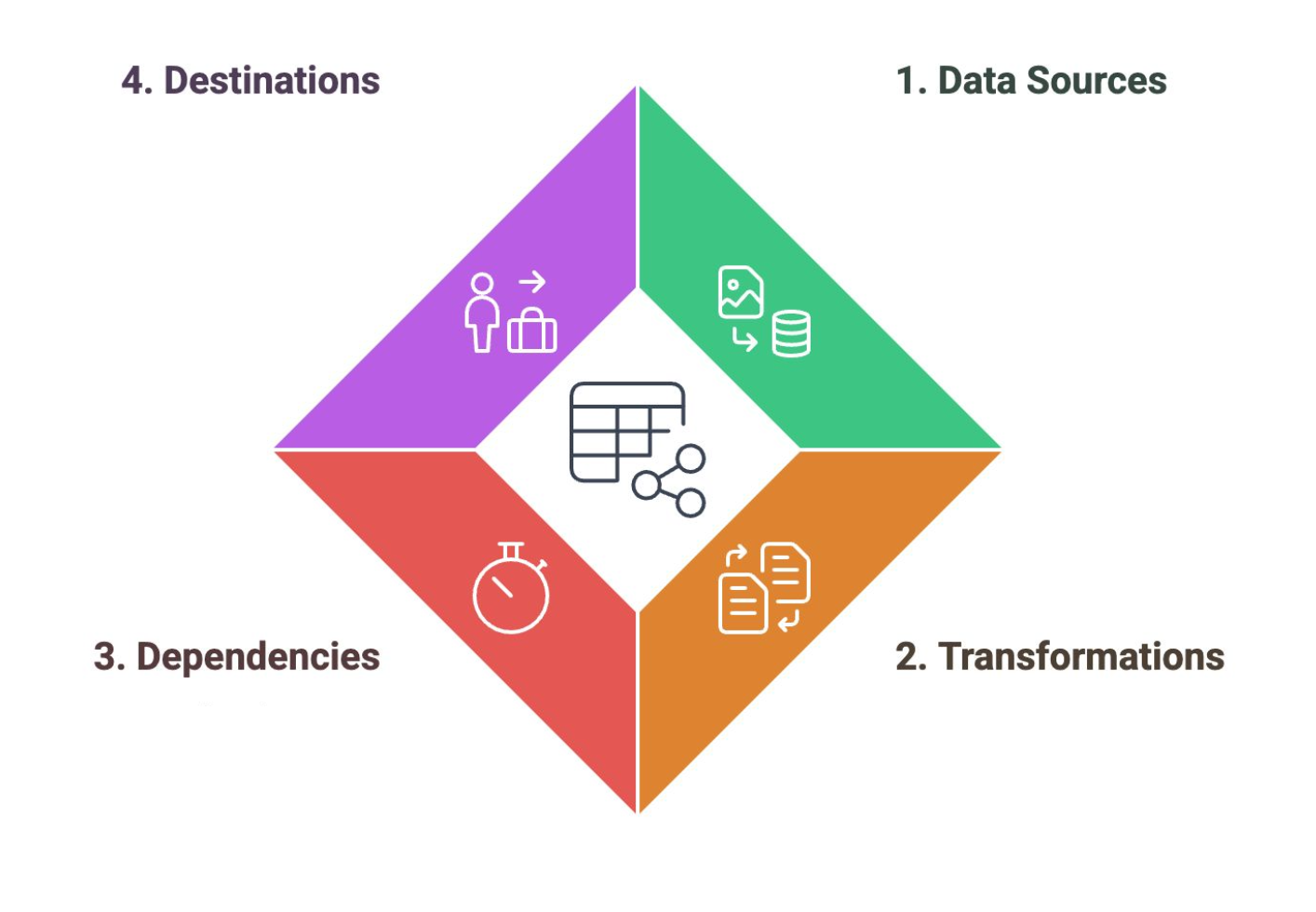
Destinations
A component of the data pipeline that corresponds to the final endpoints where data is stored or analyzed.
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load)
A special type of data pipeline that moves the data from a raw data source, transforms it to meet specific requirements, and loads it to a data storage. Not all data pipelines follow this sequence.
Batch
Data pipelines that are run on a specific schedule, and on specific intervals
Streaming
Data pipelines that are continuously running and ingesting data from one place to another
Cloud-Native
Data pipelines that use cloud managed services in performing their tasks. This can be batch or streaming
Batch
What kind of data pipeline operation is an API call?
Streaming
What kind of data pipeline operation is sensor generated data?
Streaming
What kind of data pipeline operation is data generated by IOT devices?
Data Analytics
Refers to the fundamental principles that guide analytics on business data. Commonly used interchangeably with data mining.
Data Engineering
The extraction of data from different sources
CRISP-DM (CRoss Industry Standard Process for Data Mining)
Provides a framework to structure our thinking about data analytics problems.
It is similar to the process on how data strategy is structured. The difference is the goal of each.
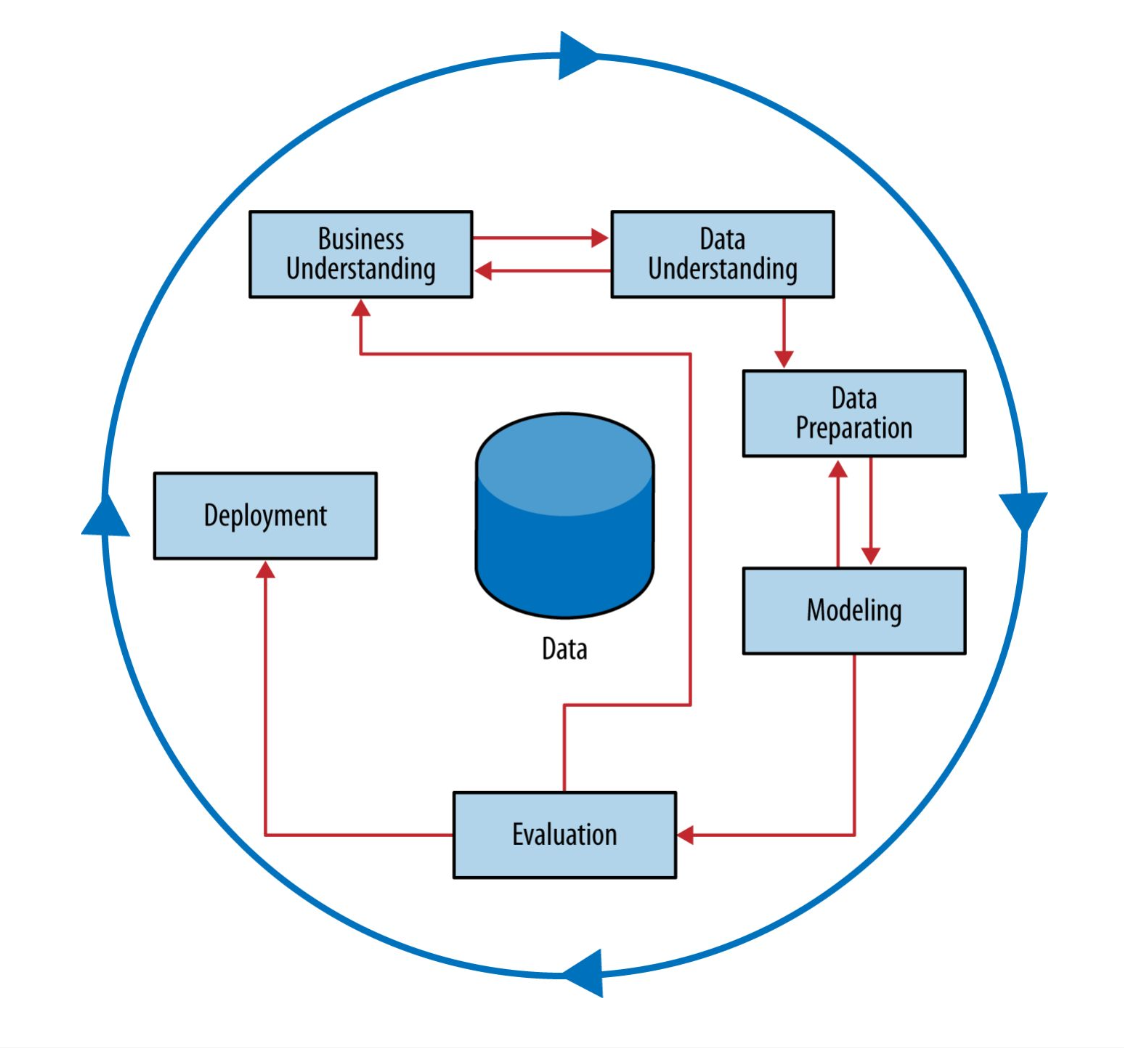
Business Understanding
Identify the CRISP-DM phase of this scenario: A game development company is looking to improve player retention in their mobile game. They need to identify the factors that contribute to player churn and create a model that will help predict when players are likely to stop playing. They meet with stakeholders to understand key business objectives, like increasing lifetime value and engagement.
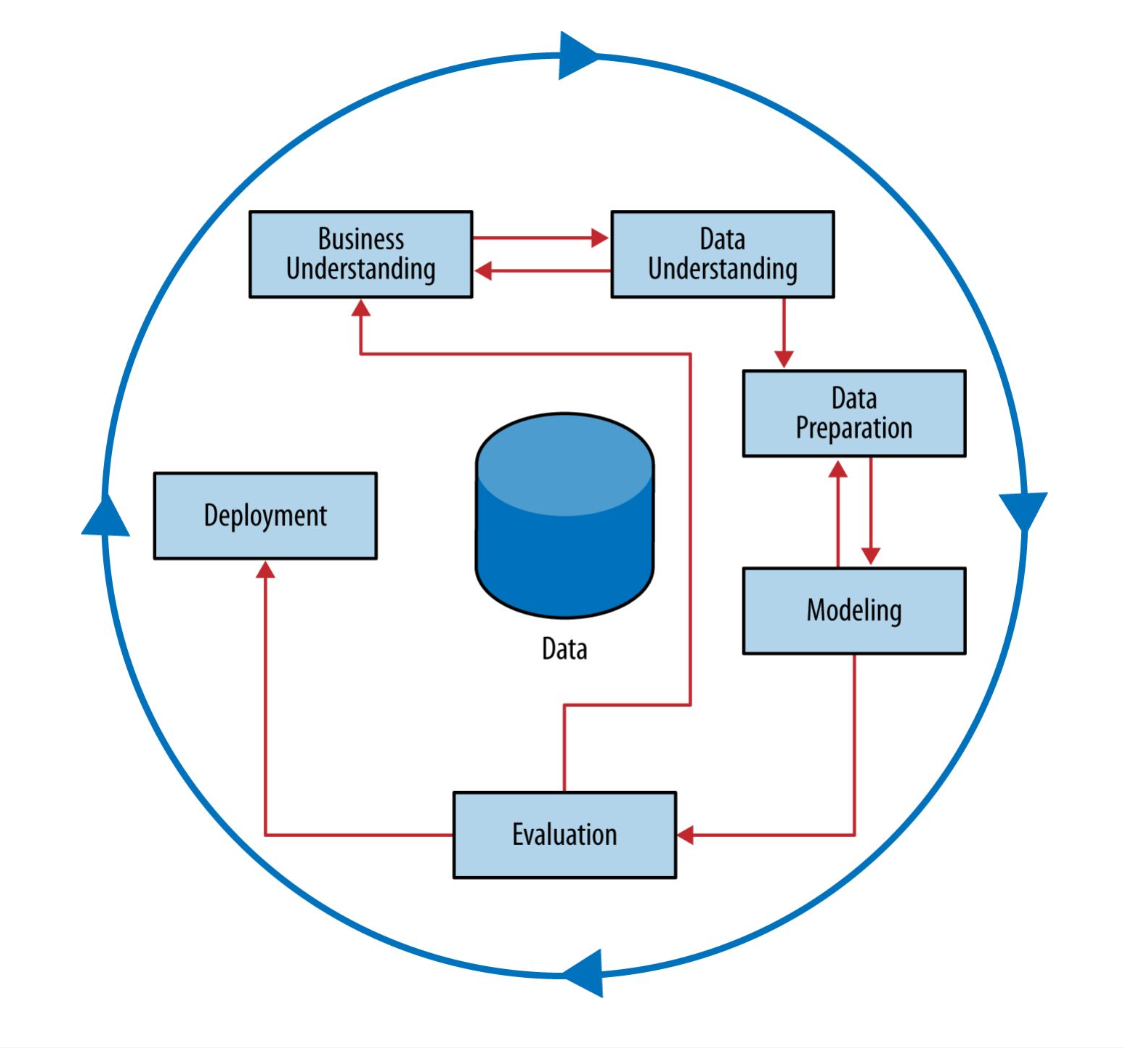
Data Understanding
Identify the CRISP-DM phase of this scenario: The game development team collects data on player behaviors, such as in-game purchases, session times, and level completion rates. They examine the raw data to identify trends, outliers, and patterns, such as whether players who reach higher levels tend to stay longer or if certain in-game events correlate with churn.