3.8 Operant Conditioning
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What does the law of effect state?
Behaviors followed by favorable outcomes are more likely to be repeated, while behaviors followed by unfavorable outcomes are less likely to be repeated
A type of learning in which behavior is strengthened or weakened by consequences, such as reinforcement or punishment:
Operant conditioning
Things we naturally like, such as food or water:
Primary reinforcers
Things we learn to like because they're connected to primary reinforcers or other things we like:
Secondary reinforcers
Examples of secondary reinforcers:
Money, praise, grades in school, points, applause, trophies, medals
An operant conditioning procedure in which reinforcers guide behavior toward closer and closer approximations of the desired behavior:
Shaping
Reinforcement vs punishment:
Increases vs decreases likelihood of behavior happening again
Positive vs negative in operant conditioning:
Adds vs removes a stimulus
Reinforcing a behavior every time it occurs:
Continuous reinforcement
Pro of continuous reinforcement:
Establishes behavior quickly in early stages
Con of continuous reinforcement:
Behavior extinguishes quickly when reinforcement stops
Example of continuous reinforcement:
Dog given treat for successfully performing trick every time
Reinforcing a behavior only some of the time it occurs:
Partial reinforcement
Pro of partial reinforcement:
Slower extinction
Con of partial reinforcement:
Less consistent responding
Does continuous or partial reinforcement lead to learnt behaviors being more resistant to extinction?
Partial
Meaning of fixed in operant conditioning:
Stay the same or constant
Meaning of variable in operant conditioning:
Change or vary
Responses reinforced by intervals are based on what?
Time
What does interval refer to in operant conditioning?
The passage of time between reinforcements
Responses reinforced by ratios are based on what?
Responses
What does ratio refer to in operant conditioning?
Number of responses required for reinforcement
Graph showing no. of responses vs time for variable ratio, fixed ratio, variable interval, and fixed interval:
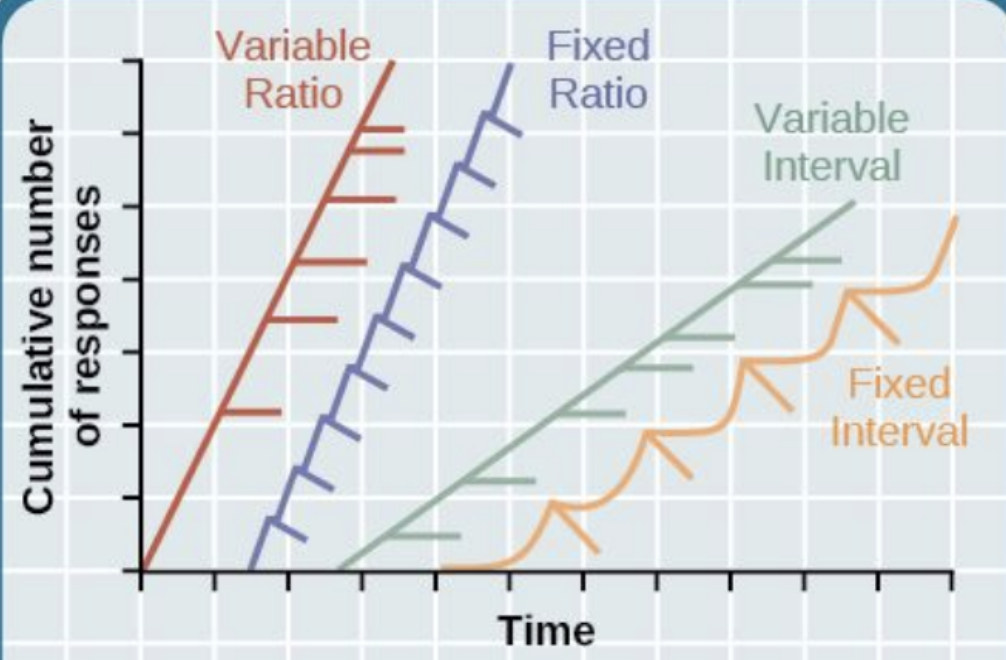
What pattern does fixed interval exhibit on no. of responses vs time graph?
Scalloped pattern
What is response like after a reward is given for fixed interval reinforcement?
Little to none
Why is there little to no response after a reward is given for fixed interval reinforcement?
Additional responses won’t lead to immediate reinforcement
How does response rate change as time for next reward approaches for fixed interval reinforcement?
Increases
When does response rate peak for fixed interval reinforcement?
Just before reward becomes available
For fixed interval reinforcement, subjects optimize their efforts based on what?
Expected timing of rewards
Describe curve of variable interval reinforcement on no. of responses vs time graph:
Gradual increase
What is the slope of variable interval reinforcement on no. of responses vs time graph similar to?
Slope of fixed interval reinforcement
When is reinforcement given for variable interval reinforcement?
After unpredictable time intervals
What pattern does fixed ratio reinforcement exhibit on no. of responses vs time graph?
Step pattern
What happens to response after reward for fixed ratio reinforcement?
Pauses
What happens to response as reward nears for fixed ratio reinforcement?
Rapidly increases
What is break-and-run dynamics typical of?
Fixed ratio schedules
Describe curve of variable ratio reinforcement on no. of responses vs time graph:
Steep increase
How are responses accumulated for variable ratio reinforcement?
Rapidly
For variable ratio reinforcement, what is reinforcement given after?
Unpredictable no. of responses
Response rate for variable ratio reinforcement:
High and steady
Why does variable ratio reinforcement result in a high and steady response rate?
Because next reward is always potentially one response away
Nature of classical vs operant conditioning:
Involuntary, reflexive responses vs Voluntary, chosen behaviors
Basis of classical vs operant conditioning:
Association linking two stimulus events vs associating behavior with a consequence
Role of stimulus for classical vs operant conditioning:
Neutral stimulus becomes meaningful vs Behavior is strengthened or weakened by consequences
Key elements in classical vs operant conditioning:
NS, US, UR, CS, CR vs Reinforcer and punisher
Purpose of classical vs operant conditioning:
Predicts the occurrence of a significant event vs Increases or decreases the likelihood of behavior