Biology 20Y - Motor Systems
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Skeletal Muscle
voluntarily controlled
multinucleated
striated
individual skeletal muscle cells: muscle fibres
attached to bones by tendon
carry out body movement
Smooth Muscle
involuntarily controlled
not striated
mononucleated
smooth myocotes (smooth muscle cells)
blood vessels, digestion, respiratory tract
Cardiac Muscle
involuntarily controlled
striated
mononucleated
cardiomyocytes (muscle tissue)
the heart
functions of muscular tissues
producing body movement
stabilizing body positions
storing/moving substances throughout body (blood circulation, respiration, etc)
generating body heat (using ATP to do work, shivering)
the four muscle functions stem from…
the fact that muscles can contract (tensile forces)
properties of muscle tissue
electrical excitability
contractility
extensibility
elasticity
electrical excitability
ability to respond to stimuli by generating electrical impulses
muscle cells primarily contract when they are stimualted by action potenial
action potential
electrochemical impulse travelling down nerve cell
contractility
ability to contract forcefully when stimulated by action potential. Contraction produces tension to attachment site (overcomes resistance)
extensibility
ability to stretch without damage
elasticity
ability to retain shape after being stretched out
smooth and cardiac muscles more elastic than skeletal
Components of Skeletal Muscle Tissue
muscle cells are called myocytes
skeletal myocytes are muscle fibers
cytoplasm: sarcoplasm (glycogen and myoglobin)
smooth endoplasmic reticulum: sarcoplasmic reticulum (store and release Ca ions to regulate muscle)
cell membrane: sarcolemma
myoglobin
protein that binds oxygen in muscle cells, aiding in energy production.
T system
system of T-tubules that run perpindicular to sarcoplasmic reticulum
electrical impulses travel through T-tubules
types of muscle fibers
slow twitch (type I)
fast twitch (type II)
Slow Twitch (Type I)
less power, dont tire easily, slow contraction, high myoglobin content (more O2)
Fast Twitch (Type II)
Type IIa: fast contraction, high myoglobin
Type IIb: fast contraction, low mitochondria, low myoglobin
generates explosive power, tires quickly
Myofibril
A long, thread-like structure found in muscle cells, composed of myofilaments that facilitate contraction.
made of myofilaments. Myofilaments are arranged in contracile units called sarcomeres
Actin Filaments
thin filament
Myosin filaments
Thick filament
Elastic filament
large protein called titin
Sarcomeres
composed on actin and myosin filaments and titin, boundaries are called Z-disks
muscular contraction
myosin and actin filaments silde over eachother to shorten length of muscular contraction
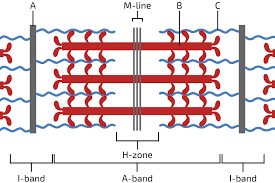
A band
extends entire length of thick filaments (myosin)
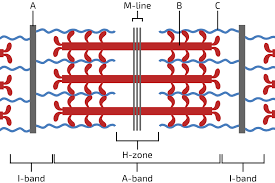
I Band
contains thin filaments (no thick)
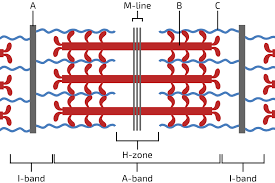
H zone
contains thick filaments (no thin)
Muscle Protein
a type of protein that makes up the muscle fibers and is essential for muscle contraction, including actin and myosin.
Troponin
Ca 2+ ions bind to troponin ( change shape), released by sarcoplasmic reticulum
The Sliding filament model of muscular contraction
Myosin filaments walk actin filaments towards M-line
thin filaments move inwards towards center of sarcomere
casues sarcomere to shorten
filaments are not shortening: they slide over eachother (overlap)
Muscle Contraction cycle
action potential reaches sarcoplasmic reticulum
sarcoplasmic reticulum releases Ca 2+ ions into sarcoplasm
Ca 2+ ions bind to troponin
troponin changes shape, pulling on tropomyosin
tropomyosin moves (uncovering myosin binding sites on actin filament)
Steps of contraction cycle
ATP hydrolusis (into ADP + Pi), myosin head includes ATP and ATPase (enzyme)
Myosin heads bind to actin, forming cross-bridges. (ADP + Pi are released)
Power stroke: myosin heads pull actin filaments towards M-line
detachment of myosin from actin: cross bridge reemains intact until myosin head bind to ATP (detach from actin filament) - ATP come from mitochondria
Muscular dystrophy
A group of genetic disorders characterized by progressive weakness and degeneration of skeletal muscles. It results from mutations that disrupt the production of proteins needed for healthy muscle function.
Anyotophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
A progressive neurodegenerative disease affecting nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord, leading to loss of muscle control and eventual paralysis.
Myostatin Deficiency
A genetic condition resulting in reduced levels of myostatin, a protein that inhibits muscle growth, leading to increased muscle mass and strength.