Non-parametric stats.
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
What are the parameters required to use a non-parametric test?
A nonparametric test should be used if...
You CANNOT assume a normal/Gaussian population/distribution
Variance is unequal
Have a very small sample
Have nominal or ordinal data
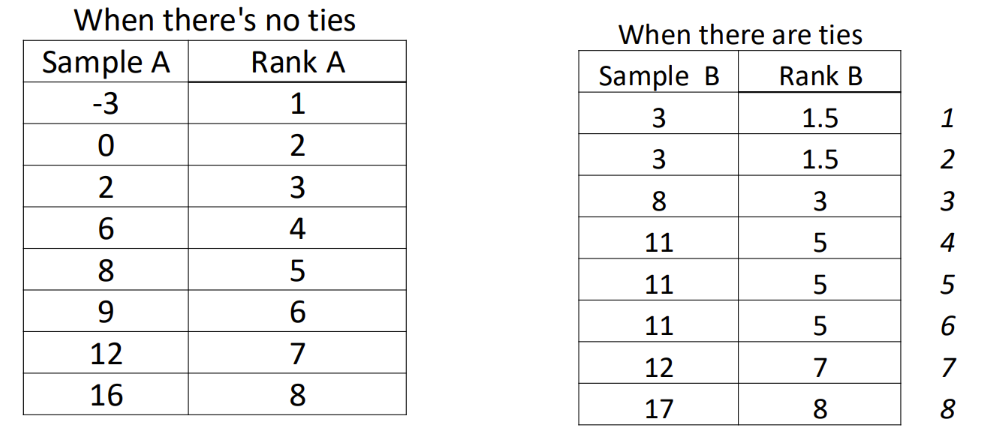
What is the ranking score concept used in non-parametric tests
Rank data out from smallest to largest
Smallest score = 1
Highest rank = n
If 2 or more scores have the same value, they’re given the average of the possible ranks
What is a non-parametric test
Less powerful because have a higher chance of type 2 error
BUT more powerful with non-normal populations
No outliers
Power only an issue if you DON’T get statistical significance (null not rejected)
Most involve ranking scores (rather than comparing precise metric changes)
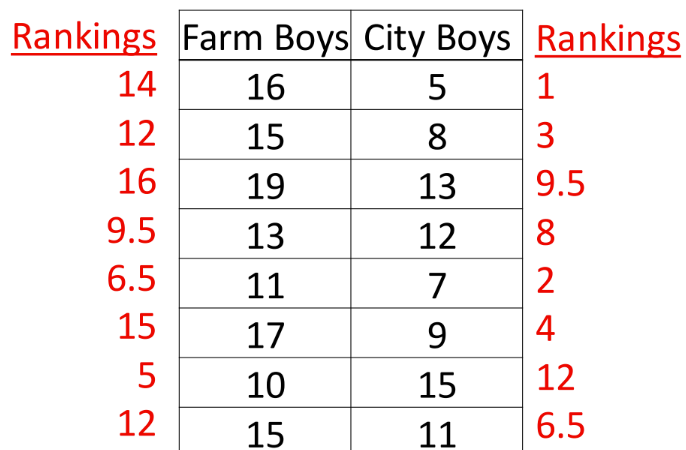
What is a Mann-Whitney U-test
non-parametric version of student’s t-test
Requires at least ordinal scale
Doesn't look at the mean because looking at the median is more accurate
Test determines if the difference in the medians is large enough to be significant
Procedure:
Combine both sets of scores and RANK them (farm boy example: ranked 1-20)
Separate the ranks by group and add ranks together from each group
Perform test
What is a Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA
non-parametric version of ANOVA
Assumes ordinal data
Three or more INDEPENDENT groups
Test determines if the differences in the mean of the ranks is large enough to be significant
Procedure:
Combine both sets of scores and RANK them
Separate the ranks by group and add ranks together from each group AND take average
Perform test
Ex: Only state vs private had a statistically significant difference

What is a Wilcoxon Matched pairs signed-ranks test
non-parametric version of paired t-test
Compares 2 paired groups (DEPENDENT)
Negative values are taken as the absolute version
What is a Friedman test
non-parametric version of a repeated-measures ANOVA
Compares 3 or more paired groups (DEPENDENT)
Followed with a post-test
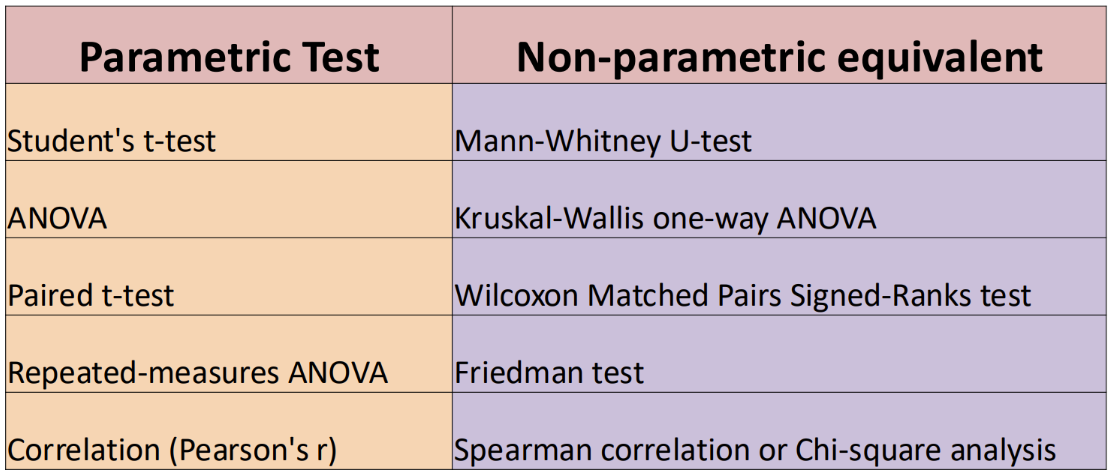
What is the non-parametric equivalent of each parametric test
Look at image