ch. 12: swine (omnivore) digestion
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
what is the pH of swine saliva?
7.4
is a pig a monogastric or ruminant?
monogastric
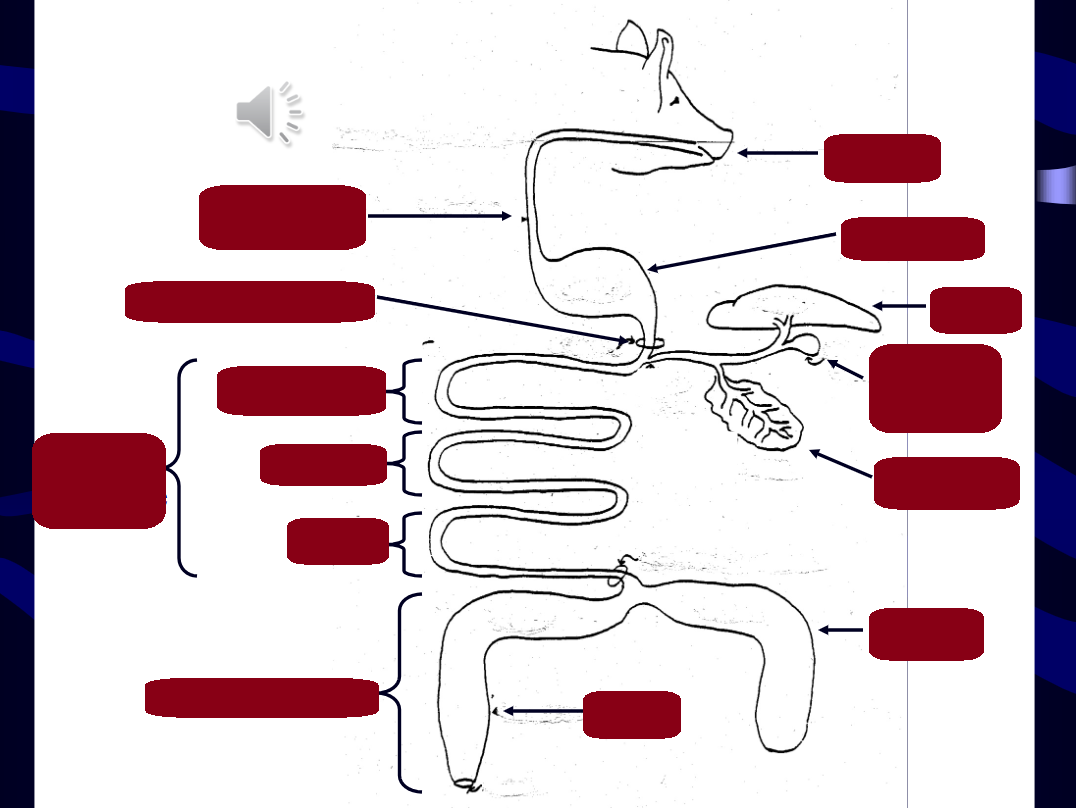
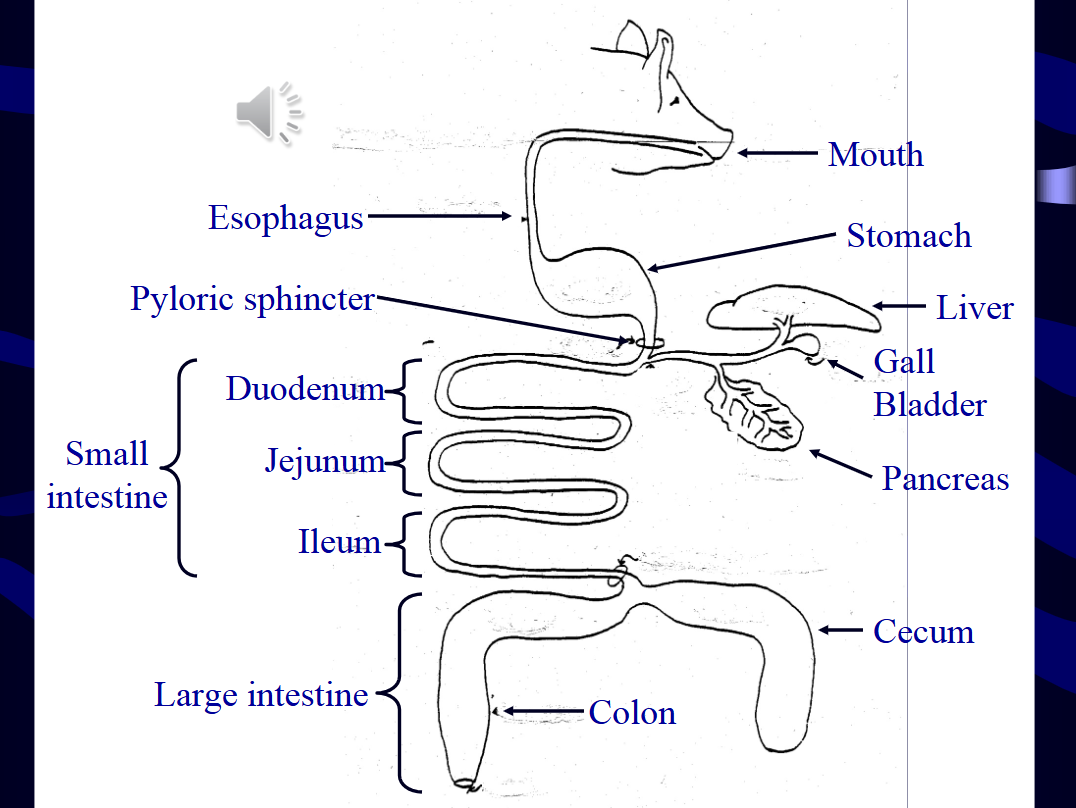
what type of digestion is the mouth primarily used for?
mechanical (grinding feed)
what 3 glands produce saliva
parotid, submandibular, and sublingual
what is ptyalin?
a salivary amylase (breaks down starch)
pigs are the only farm mammal with this enzyme
not really useful to pigs because feeds doesn’t stay in the mouth very long and the pH of the stomach is too low for it to work
what gastric juices are present in the pig’s stomach and what is their purpose?
mucin: made from neck cells; provide protective coating
HCl: made from parietal cells; denatures proteins, activates enzymes, provides acidic environment, kill bacteria
pepsinogen: made from chief cells; inactive form of pepsin (pepsin is a protease)
where does protein digestion start and finish?
starts in stomach and finishes in the small intestine
what is the function of the small intestine?
continue the process of digestion with:
pancreatic juice (enzymatic)
duodenal juice (enzymatic)
bile (chemical)
movement of the intestinal wall (mechanical)
what are the three ways that the pancreas contributes to digestion?
1) produces enzymes for protein, fat, and CHO digestion
2) produces sodium carbonate (NaCO3) and bicarbonate (HCO3) to work as buffer to the acidity of the stomach
3) produces insulin for CHO metabolism
what are the 4 proteases used for protein digestion, their inactive forms, and how are they activated?
1) trypsin
produced by pancreas as trypsinogen
activated by Ca ions and enterokinase from BB
2) chymotrypsin
produced by pancreas as chymotrypsinogen
activated by trypsin
3) carboxypeptidase
produced by pancreas as procarboxypeptidase
activated by trypsin
4) aminopeptidases
produced by brush border of duodenum
breaks small peptides down into single amino acids
go study the image on slide 7
yes chef o7
what are the 4 functions of bile in fat digestion
1) emulsifies fat (allows fat & water to interact)
2) works to digest and absorb fat
3) absorption of fat soluble vitamins
4) activates lipase
what is the function of pancreatic lipase in fat digestion?
1) breaks fat down into fatty acids and glycerol enzymatically
this is most effective after emulsification
what 4 enzymes are used in carb digestion?
1) pancreatic amylase (starch → maltose)
2) maltase (maltose → glucose)
3) sucrase (sucrose → glucose and fructose)
4) lactase (lactose → glucose and galactose)
what makes up the large intestine and what is its function?
made up of the colon and cecum before terminating as the rectum at the anus
function: absorb water, absorb VFAs, and act as a reservoir for waste materials
overall though, absorption is limited