IAL AS BIOLOGY
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
DEFINITIONS
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
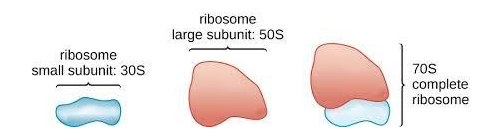
70S Ribosomes
The ribosomes found in the mitochondria and chloroplasts of eukaryotic cells and in prokaryotic organisms.
Consists of a 50S large subunit and a 30S small subunit and is essential for protein synthesis.
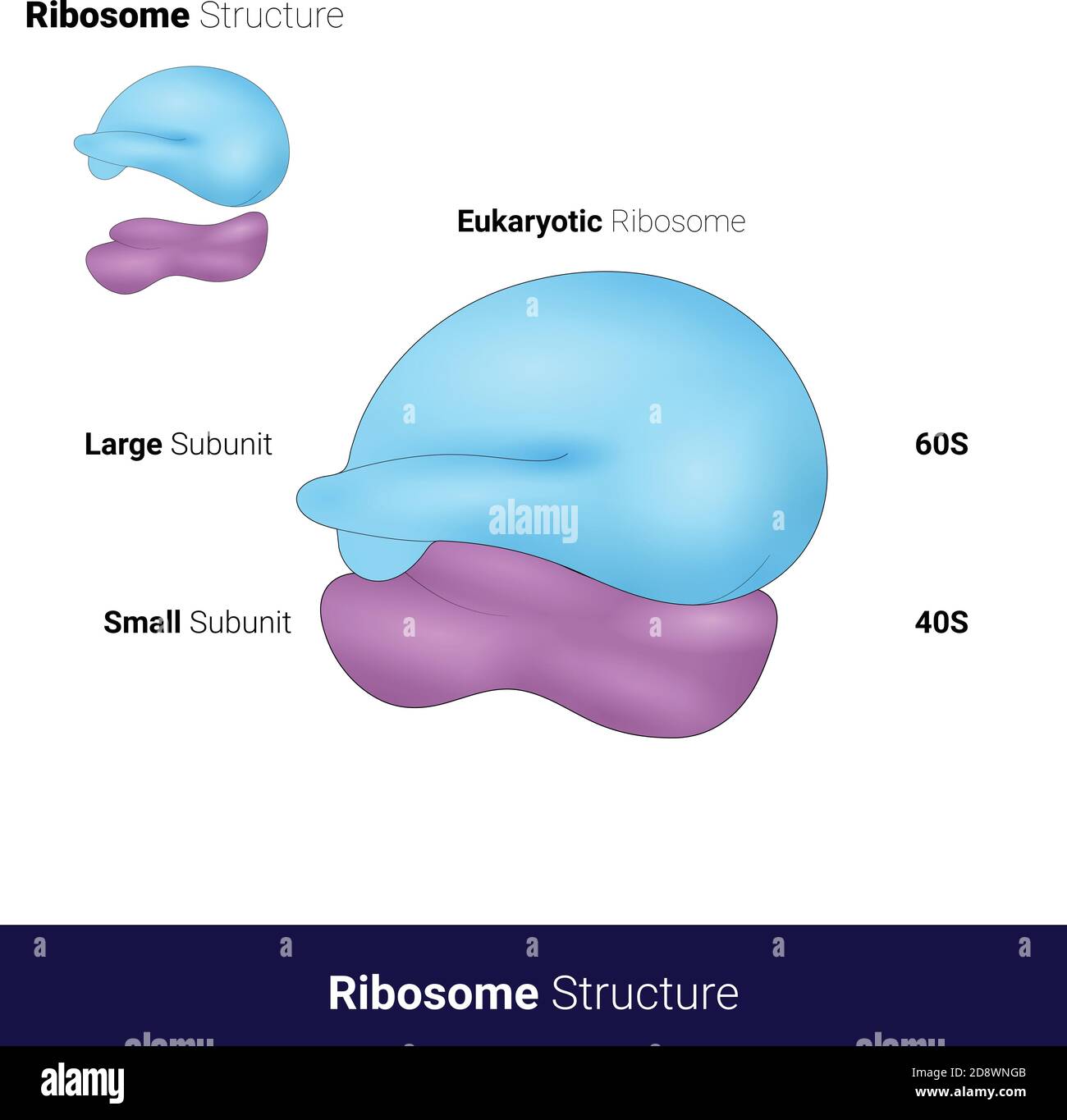
80S Ribosomes
Main type of ribosome found in eukaryotic cells, consisting of ribosomal RNA and protein.
Made up of 60s large subunit and a 40S small subunit and is the site of protein synthesis.
ACE inhibitors (Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors)
Drugs which block the production of angiotensin.
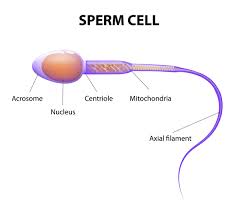
Acrosome
The region at the head of the sperm that contains enzymes to break down the protective layers around the ovum.
Acrosome Reaction
The reaction seen when the sperm reaches the oocyte and enzymes are released from the acrosome and digest the follicle cells and the zona pellucida.
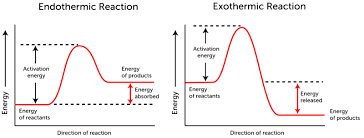
Activation Energy
The minimum energy needed for a chemical reaction to get started.
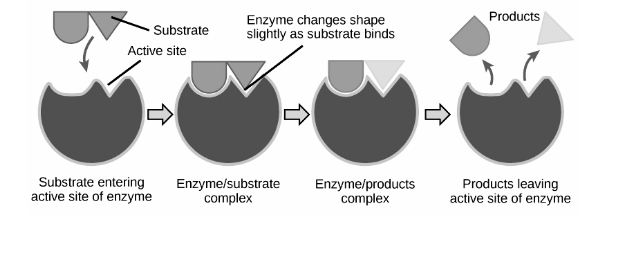
Active Site
The area of an enzyme that has a specific shape into which the substrate(s) of a reaction fit.
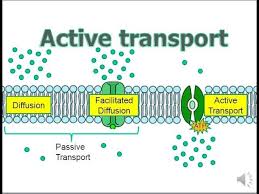
Active Transport
The movement of substances into or out of the cell using ATP produced during cellular respiration.
Adaptive Radiation
A process by which one species develops rapidly resulting in several different species which fill different ecological niches.
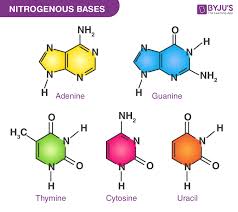
Adenine
A purine base found in DNA and RNA.
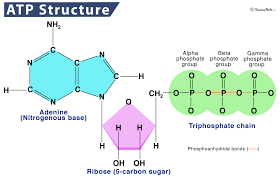
ATP (Adenosine triphosphate)
A molecule that acts as the universal energy supply molecule in cells; it is made up of the base adenine, the pentose sugar ribose and three phosphate groups.
Adult stem cells (Somatic stem cells)
Undifferentiated cells found among the normal differentiated cells in a tissue or organ, that can differentiate when needed to produce any one of the major cell types found in that particular tissue or organ.