Activity 7 | Chemical Reactions and Chemical Equations
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Chemical equation
Shows the reactants (starting materials) on the left hand side and the products on the right hand side. An arrow is placed between the reactants and the products to show that the reactants are chemically changed into products. The arrow is pronounced “yields”
Coefficient
The number preceding the formula of each reactant and product. Represents the number of molecules (or moles) of each reactant and product used in the reaction
Precipitation Reaction
Form an insoluble product
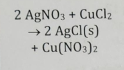
Acid-Base Neutralization
Acid + base form a salt + water
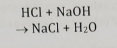
Non-redox Decomposition
Breakdown of one compound into 2 or more
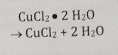
Non-redox Combination
2 substances combine to make one product
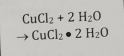
Oxidation-Reduction (Redox)
Involve electron transfer
Redox Decomposition
Breakdown of one compound into 2 or more. The oxidation state between the reactant and the product changes
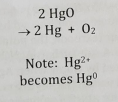
Redox Composition
2 substances combine to make one product. The oxidation state between the reactant and the product changes
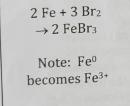
Combustion Reaction
React with O2; release heat/light
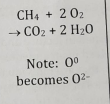
Disproportionation
Element is both oxidized and reduced
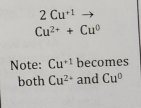
Displacement
Ion or atom in one compound is replaced by a different ion or atom
Hydrogen Displacement
Metal replaces H
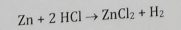
Metal Displacement
1 metal replaces another
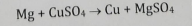
Halogen Displacement
1 halide replaces another
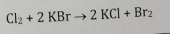
Balanced chemical equation
Shows the reactants and products, their physical states, and the appropriate stoichiometric coefficients
Complete ionic equation
Shows the reactants and products of the balanced chemical equations, with all of the aqueous salts written as the sum of their ions rather than as compounds. It shows the charge of each ion and it may contain spectator ions
Net ionic equation
The equation that results from removing the spectator ions from a complete ionic equation. It shows only the species that undergo a chemical change