MANIPULATING GENOMES
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
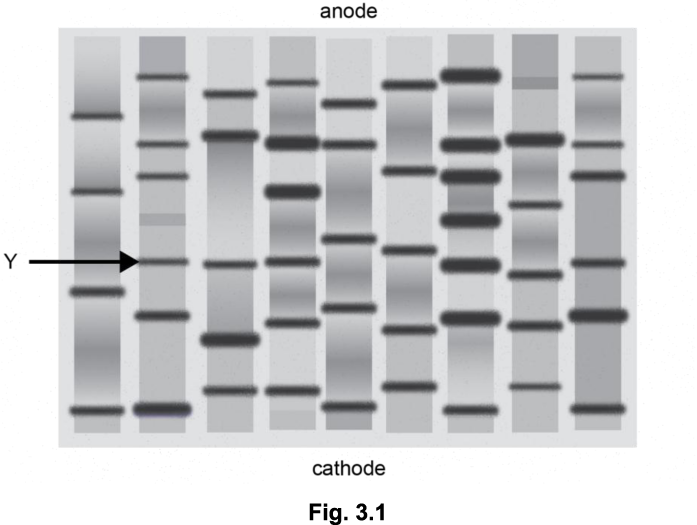
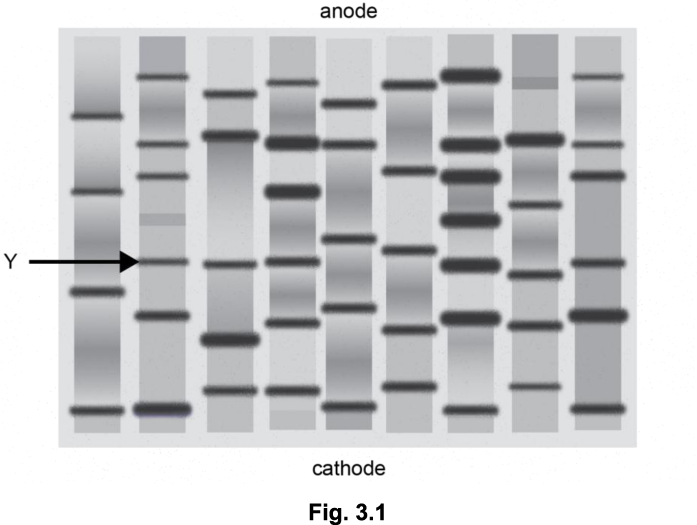
(i) Describe how DNA can be visualised after electrophoresis has been completed. (2)
(ii) Place a cross (X) on Fig. 3.1 to indicate the position of a fragment of DNA with a mass greater than the DNA band labelled Y.
(i) radioactive, labels / tags (1)
fluorescent, labels / tags (1)
UV, light / radiation (1)
(named) visible stain (1)
(ii) X placed on any fragment below Y (1)
Mixtures of proteins can also be separated by electrophoresis.
Proteins are heated before being placed in the electrophoresis gel.
The gel contains a substance called SDS, which has a negative charge. SDS binds to proteins.
Suggest why proteins are heated before being placed in the electrophoresis gel. (1)
denature / unfold, protein AND idea of exposes charges or hydrophobic region
(1)
Mixtures of proteins can also be separated by electrophoresis.
Proteins are heated before being placed in the electrophoresis gel.
The gel contains a substance called SDS, which has a negative charge. SDS binds to proteins.
(ii) Suggest why the binding of SDS to proteins is necessary for protein electrophoresis. (2)
idea that different proteins have different overall charges (1)
idea that (binding of) SDS makes all proteins negatively charged (1)
idea that proteins will be separated by, mass / length (1)
idea that proteins move in the same direction (1)
An Iron Age farm was excavated by archaeologists. Some DNA was recovered from the tooth of an animal thought to be a type of domesticated milk cow.
A farmer keeps rare breed cows similar to those farmed on the Iron Age farm. DNA from the cows was obtained.
What technique would you plan to use, to compare digested and amplified fragments from the two DNA samples? (1)
electrophoresis
Tissue traces from a crime scene often need to be identified. DNA from the tissue is ‘amplified’ by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to get samples large enough for further analysis.
Modern PCR technique uses DNA polymerase from the bacterium Thermus aquaticus. Why is this enzyme chosen? (2)
thermostable
OR
does not, denature / AW, at 95 °C (during DNA strand separation) (1)
so PCR can be cycled repeatedly without stopping (to reload with enzyme) (1)
In order to sequence the whole genome of an organism it may be necessary to sequence billions of nucleotides.
The human genome is approximately 3.2 billion nucleotides long.
Sequencing DNA requires a series of steps.
Place the following steps in the correct sequence. The first and last ones have been done for you.
A place sections in order by matching overlapping regions
B cut DNA into sections of varying length
C sequence short sections of DNA
D amplify the DNA (create many copies)
E extract samples of DNA from cells
E _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ A
B, D, C (1)(1)
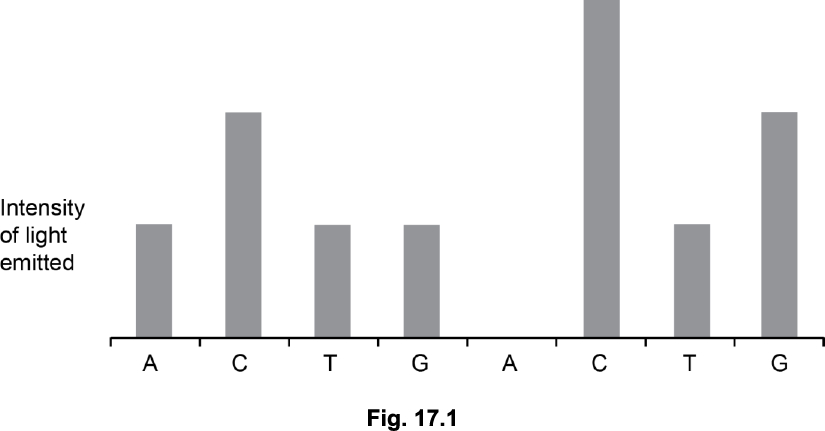
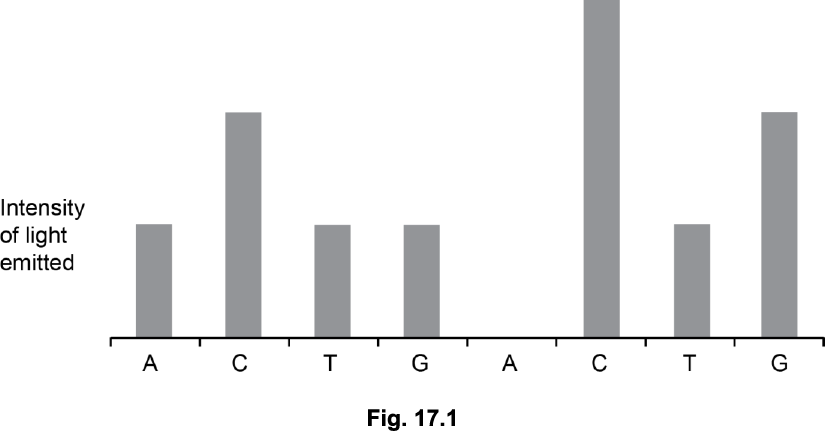
Roche pyrosequencing relies on building a chain of nucleotides against a template. It involves the following steps:
Nucleotides are washed over the template in a specific order.
When the correct nucleotide is present it joins the new chain.
The addition of a nucleotide to the chain releases energy.
The energy is used to activate a protein called luciferin.
Light released by luciferin is detected.
If two identical nucleotides are added together then the intensity of the light emitted is doubled.
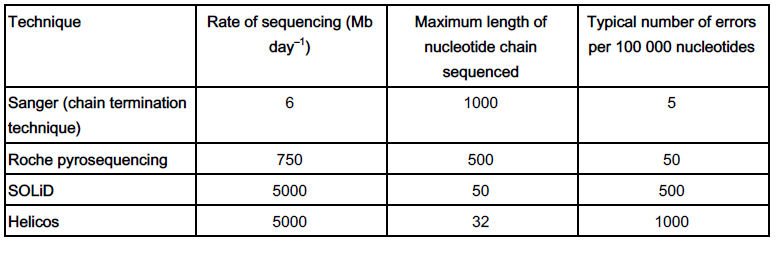
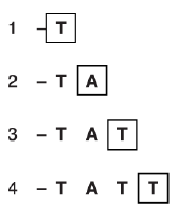
Fig. 17.1 shows a readout from a pyrosequencing machine. Read off the sequence of bases in the length of DNA.
A C C T G C C C T G G
To identify an allele that causes a genetic disease it must be sequenced accurately so that differences from
the healthy allele are clear.
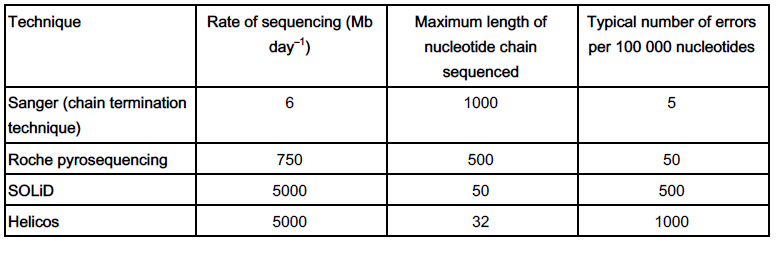
Using the information in Table 17.1 decide which technique is best to use when sequencing a human gene
that causes a genetic disease.
Explain your choice. (2)
Sanger / chain termination technique (1)
Only 5 errors per 100 000 nucleotides compared to, 50 in Roche pyrosequencing
/ 500 in SOLiD / 1000 in Helicos (1)
(iii) Suggest how the interdisciplinary field of bioinformatics may be useful in determining whether a newly sequenced allele causes a genetic disease. (2)
base sequence of normal allele and (known) alternatives held (in database) (1)
computational analysis allows rapid comparison of sequences with newly sequenced allele (1)
amino acid sequence / protein structures, also held (in database) (1)
DNA profiling uses techniques to separate lengths of DNA to produce a profile that is unique to each individual.
Explain why only selected sections of non-coding DNA are used when profiling a human. (3)
in most people, the genome is very similar / most genes the same (1)
using coding sequences would not provide unique profiles (1)
(parts of) non-coding DNA contains variable numbers of, short tandem repeats / repeating sequences (1)
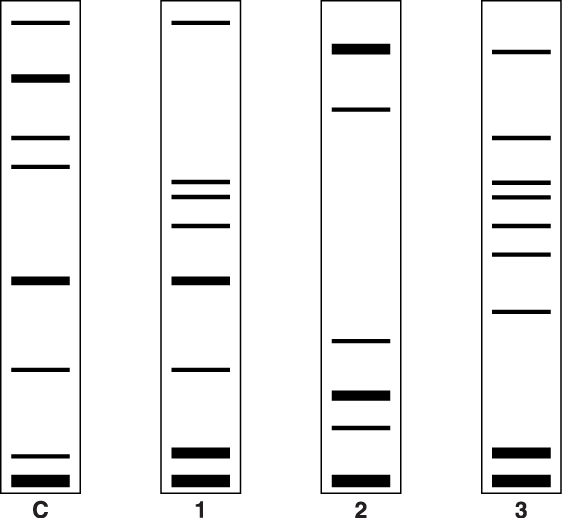
Samples of DNA were taken from frogs A, B, C and D.
Mitochondrial DNA from the frogs was sequenced.
State, giving a reason, which of the frogs A, B and C would have a mitochondrial DNA sequence identical to D. (1)
cytoplasm / mitochondria, came from A
or
mitochondria / (mitochondrial) DNA, in cytoplasm of A;
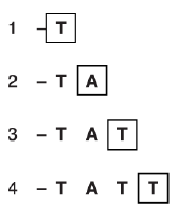
Explain how the automated sequencing machine orders the DNA fragments from the PCR reaction into the
size order shown in Fig. 3.2.(3)
electrophoresis;
(negatively-charged DNA) moves towards, positive electrode / anode;
smallest/smaller (fragments) move, fastest/ faster;
Asthma in children may be treated with drugs. One of the most commonly used drugs is salmeterol.
Salmeterol acts by binding to protein receptors in the lining of the bronchioles. However, in approximately 14% of children with asthma, salmeterol is not very effective. This is thought to be the result of a genetic mutation in these children.
Suggest why this mutation reduces the effectiveness of salmeterol. (3)
(mutation) change in (DNA) nucleotide/ base, sequence; (mutation causes) change
in, amino acid sequence / primary structure (of protein); (1)
change in, tertiary structure/ 3D shape / binding site, of receptor;(1)
salmeterol unable to bind; (1)
idea that no response triggered in cell / no
second messenger system activated; (1)
In a recent medical trial, 62 children with this genetic mutation were studied.
Their asthma was not controlled well by salmeterol.
31 children continued using salmeterol and the remaining 31 were given an alternative drug, montelukast.
Montelukast is not routinely prescribed because salmeterol is far more effective for most children with asthma.
(i) After one year, the children taking Montelukast had better control of their asthma and were able to reduce their use of montelukast.
Suggest why these children responded better to montelukast than to salmeterol. (2)
(mutation resulted in) receptor having complementary shape to montelukast;
montelukast able to bind;
(whereas) salmeterol cannot;
montelukast may have a different receptor;
In a recent medical trial, 62 children with this genetic mutation were studied.
Their asthma was not controlled well by salmeterol.
31 children continued using salmeterol and the remaining 31 were given an alternative drug, montelukast.
Montelukast is not routinely prescribed because salmeterol is far more effective for most children with asthma
Comment on the reliability of the results of this medical trial. (1)
not reliable because, sample size too small
/ only 62 children in study;
or
could be reliable because 31 is quite a large sample;
It is proposed that a simple saliva test could identify those children who have the mutation.
What would be the source of the genetic material used in this test?(1)
(epithelial) cells lining cheek;
Name the enzyme that can be used to convert mRNA to single-stranded DNA.
reverse transcriptase;
Explain how the locations of the fluorescent spots on the DNA chip reveal which genes are most active. (3)
1 mRNA binds to, (gene) probes / cDNA / ssDNA, by complementary base pairing;
2 idea that the more active the gene the more mRNA produced;
3 during transcription;
4 more fluorescence indicates more mRNA
(bound);
Scientists have genetically engineered many different species of plant.
Aubergine plants, Solanum melongena, can suffer damage from moth larvae.
Scientists have produced a variety of aubergine that is resistant to moth larvae. To create the resistance,
scientists transferred a gene from the Bacillus thuringiensis bacterium.
Describe the process the scientists could have used to produce the pest-resistant aubergines. (6)
method for gene extraction from the bacterium (e.g. conversion of mRNA to
cDNA with reverse transcriptase, or removal of gene with restriction enzymes)
use of appropriate vector (e.g. Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens)
electroporation
use of DNA ligase
reference to marker genes and their purpose
electrofusion
Potatoes often suffer bruising, which reduces their value as a food crop.
A variety of crop potato that does not bruise has been developed using a technique called gene silencing.
Scientists carry out gene silencing by inserting small sequences of RNA into potato cells. These RNA
sequences are complementary to mRNA from genes responsible for bruising.
Use this information to suggest why the technique is called ‘gene silencing’. (2)
base sequence in genes is unchanged ✓
idea that mRNA is inhibited, therefore translation does not occur ✓
gene is not expressed ✓
When sequencing DNA, fragments of DNA are separated by electrophoresis.
Describe three differences between the process of thin layer chromatography and the form of electrophoresis
used to sequence DNA. (3)
1. separates by (relative) , adsorption / solubility / interaction with the stationary
phase in TLC
and (separates) by size in electrophoresis ✓
2. TLC separates non - charged particles
and
electrophoresis (only) separates charged particles ✓
3. electricity, used for electrophoresis / not used for TLC ✓
4. buffer solution, used for electrophoresis / not used for TLC ✓
5. dyes used in TLC
OR
radioactive / fluorescent , tags /
nucleotides, used in electrophoresis ✓
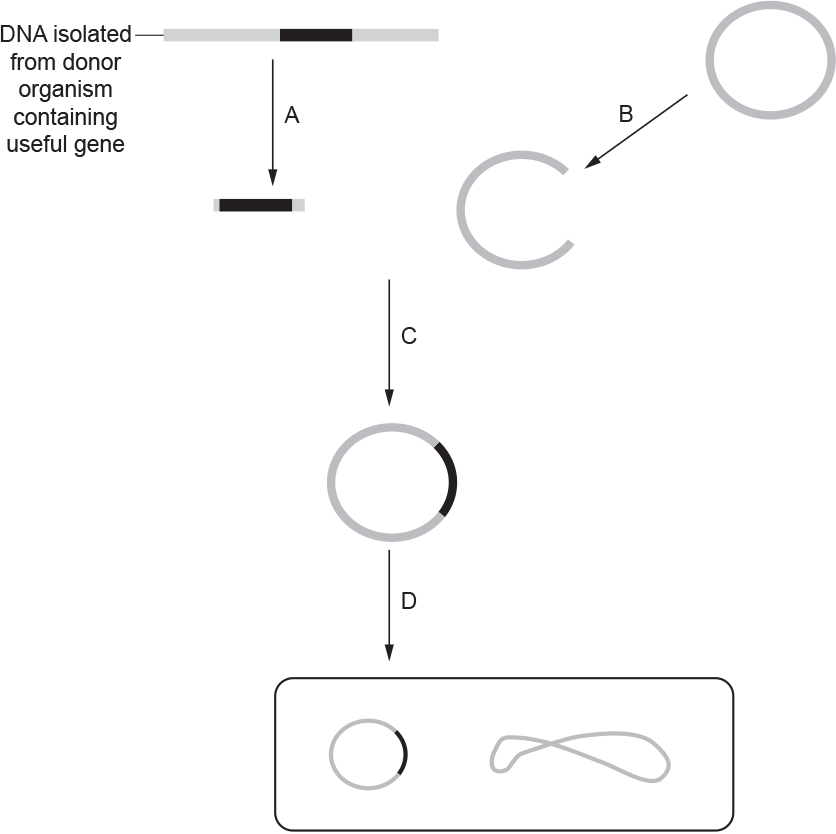
Fig. 21 shows some of the steps involved in producing a genetically modified bacterium.
The following passage describes steps A and B. Complete the passage using the most appropriate terms.
A gene is cut from the DNA of the donor organism using a ……………… …………………
The ………………………………………… enzyme is used to cut open a small piece of bacterial DNA so that the base sequences at the end of each piece of DNA are ……………………………… .
restriction, enzyme / endonuclease
same
complementary
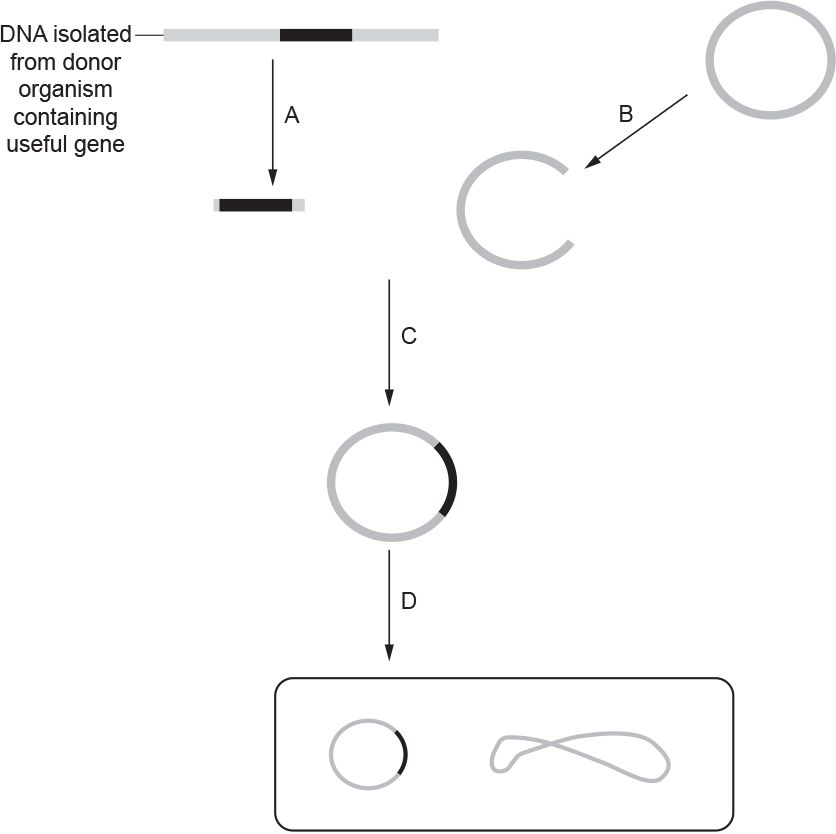
Describe the events that are taking place at the step labelled C.(3)
the gene / the DNA fragment, inserted into plasmid (1)
complementary bases (pair / anneal) (1)
formation of hydrogen bonds (1)
formation of phosphodiester bonds (1)
using (DNA) ligase (1)
Step D results in a transformed bacterium.
Many individual bacteria are not transformed successfully during this procedure. Explain how scientists can
determine the success of step D in this procedure.(3)
use of marker (gene) (1)
(genes for) fluorescence / colour change (1)
(examine fluorescence under) UV, light /
radiation (1)
antibiotic resistance (gene) (1)
(then) grow on agar containing antibiotic (1)
Some people are concerned about genetic modification.
State one valid concern that people have about the genetic modification of bacteria.(1)
(increase in antibiotic) resistance
Fred Sanger developed an effective DNA sequencing technique in 1977.
Define the term DNA sequencing. (1)
working out the sequence / AW , of
nucleotides / bases ✓
DNA sequencing can be used to determine the genome of an entire organism.
The first organism to have its entire genome sequenced was a virus.
Ebola is a virus that caused the death of over 11 000 people in West Africa between 2014 and 2016. The DNA of ebola virus has a rapid rate of mutation.
Since the first outbreak in 2014 scientists have been working to develop an effective vaccination against ebola.
Other scientists have developed a portable nanopore sequencing technique that could be used to sequence rapidly the entire ebola genome.
Outline how DNA sequencing and bioinformatics could be used to increase the effectiveness of a vaccination programme against ebola.(4)
sequencing
(high) mutation (rate) means many ,
strains / AW , of virus exist ✓
can predict (viral) , strain / protein /antigen ✓
(so) vaccine contains correct antigen ✓
bioinformatics
facilitates access to large amount of
data ✓
facilitates access to data on DNA
and proteins ✓
idea that format (of information) is
universal ✓
can identify source of outbreak ✓
can identify vulnerable populations ✓
vaccination program can target certain, area/ individuals✓
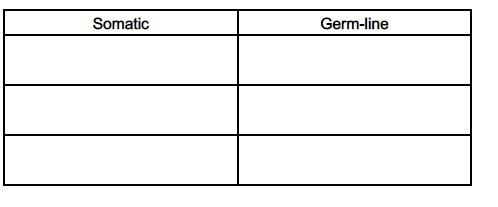
The treatment of cystic fibrosis is described as somatic gene therapy. Another type of gene therapy is known
as germ-line gene therapy.
Complete the table below to show three differences between somatic gene therapy and germ-line gene
therapy.
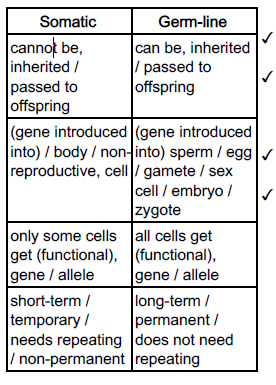
CF occurs when individuals have two copies of a recessive allele.
Huntington’s disease is a lethal disease caused by a dominant allele that codes for the protein huntingtin.
Suggest why gene therapy is unlikely to work as a treatment for Huntington’s disease.
(Huntington’s) protein / Huntingtin, still, synthesized / present ✓
A technique called quantitative PCR is used to check that the E. coli population is growing on the mice liver tumours rather than on healthy tissue.
Suggest how the scientists could use PCR to compare E. coli growth rates on cancerous liver tissue and healthy tissue.(2)
idea of extract DNA from cancerous liver and (named) healthy tissue ✓
choose primers for, E coli / β-galactosidase, DNA ✓
idea of comparing rate of DNA amplification ✓ e.g. ‘compare amount of DNA after 30 cycles of PCR’
Some people think that the genetic engineering of certain organisms is unethical.
However, there are very few ethical concerns about the genetic engineering of bacteria such as E. coli.
Suggest why there are very few ethical concerns about the genetic engineering of E. coli. (1)
idea of safety of genetic engineering (in bacteria) has been established ✓
idea of few animal rights issues to consider ✓