independent segregation + crossing over
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
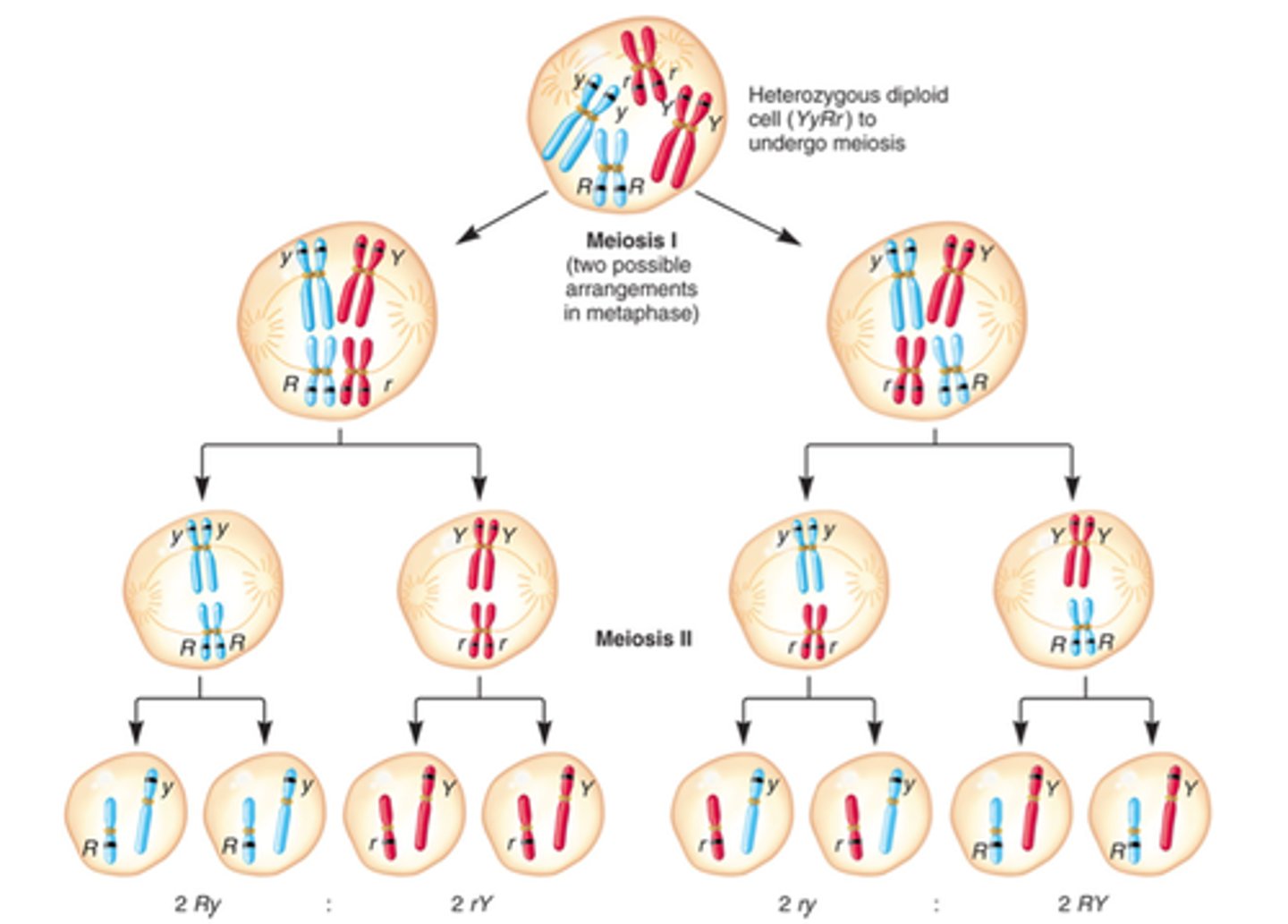
independent segregation
in meiosis 1, homologous pairs of chromosomes line up opposite each other at the equator of the cell.
it is random which side of the equator the paternal + maternal chromosomes from each homologous pair lie.
these pairs are separated, so one of each pair ends up in a daughter cell.
this creates a large number of possible combinations of chromosomes in the daughter cells produced.
over 8 million different combinations of chromosomes can be made.
homologous chromosomes
chromosomes w/ exact same genes but diff alleles
number of possible combinations of chromosomes in the daughter cells produced =
2^n; n = number of homologous pairs
number of possible combinations of chromosomes in the daughter cells produced = HUMANS
2^23
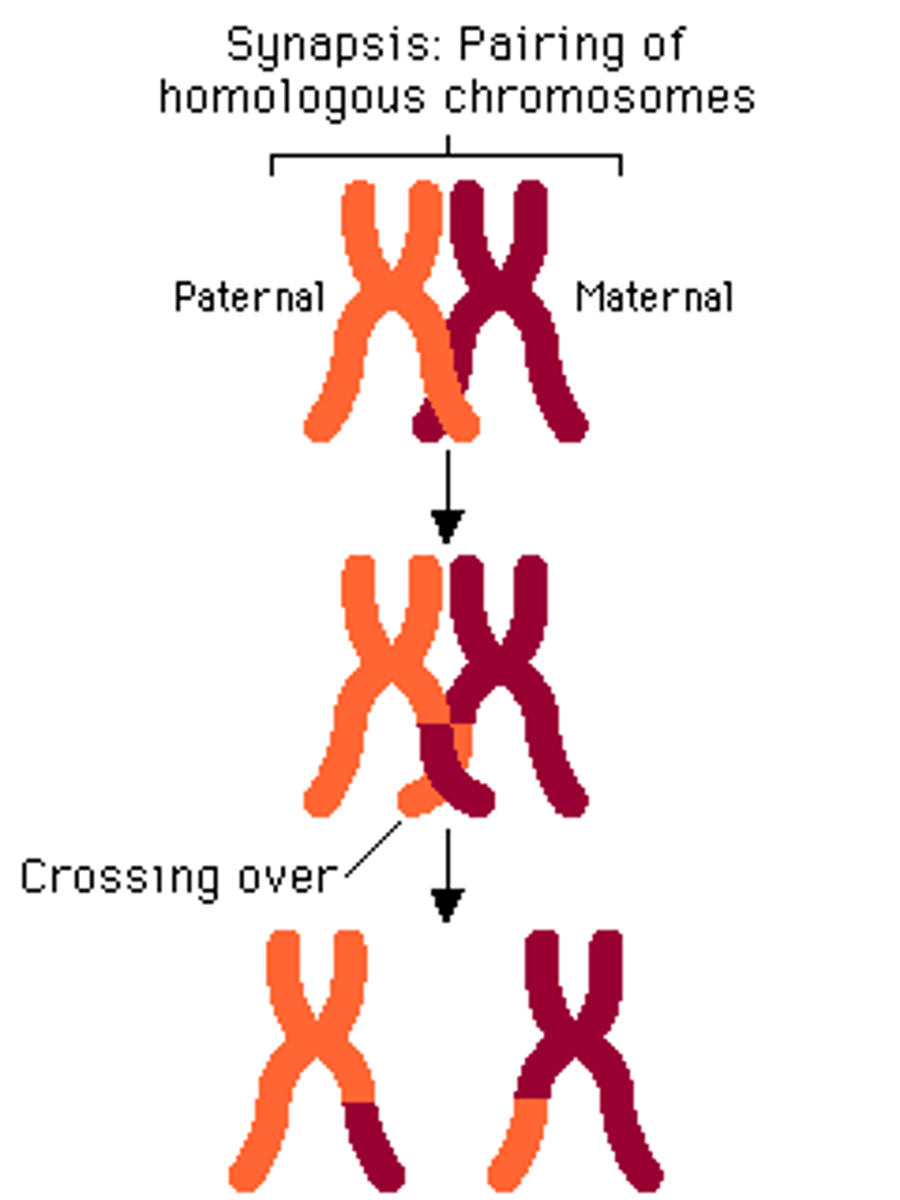
crossing over
in meiosis 1, homologous pairs line up opposite each other at the equator = parts of chromatids can become twisted around each other = puts tension on chromatids = chromatid pairs break off + broken parts of chromatid recombine w/ another chromatid = chromosome swap section of their chromatid = new combo of alleles
3 comparisions b/wn meiosis + mitosis
meiosis = 2 nuclear divisions; haploid cell; introduces genetic variation; mitosis = 1 nuclear division; diploid cells; creates genetically identically
random fusion of gametes
= new combo of alleles so the offspring are genetically different from their parents; (2^n)^2