Bio Final Bullshit
1/197
Earn XP
Description and Tags
not
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
198 Terms
Scientific Method
way to solve problems/answer questions by experimenting.
Observations
info you gather using your senses, based around gathering DATA (Step 1)
Quantitative Data
data gathered through measuring/counting.
Qualitative Data
descriptive data; not numerical.
Hypothesis
A statement that predicts the answer to the research question (Step 2)
Independent Variable
What you are controlling, manipulating, changing.
Dependent Variable
What you are measuring. It depends on the independent variable.
Control Group
Does not receive the independent variable. You compare the experimental group results to the control group.
Experimental Group
Receives the independent variable
Theory
a logical explanation of WHY or HOW things work in nature based on observations and experimentation; supported by much evidence.
Engineering
using the scientific method to create solutions to real world problems; combines math and science.
Characteristics of Life
Qualities that we use to determine if something is alive or not.
Made of Cells
Organization
Use energy
Responds to stimuli
Growth
Maintain homeostasis
Reproduction
DNA
Metabolism
the chemical reactions that take place in your body.
Stimulus
input from the environment that causes an organism to react.
Voluntary Response
What a living thing chooses to do. In control of the response
Asexual Reproduction
only one organism’s DNA is used.
Sexual Reproduction
DNA from 2 organisms is combined.
Cell
the smallest unit that can carry out all the processes of life (i.e. take in nutrients, get rid of waste, etc). Performs functions with other cells that keep the organism alive, made of organelles
Unicellular
complete living thing made of only one cell.
Multicellular
a living thing made of more than one cell.
Cell membrane
surrounds the cell and controls what passes into and out of the cell.
Cytoplasm
the area between the membrane and the nucleus
Cytosol
gel-like fluid that surrounds organelles.
Tissue
a group of similar cells that carry out a common function, made of cells
Organ
a group of tissues that interact to perform a function(s). Made of tissues
Organ System
group of several organs working together to perform a series of related tasks.
Colonial Organisms
A group of genetically identical cells that live in a closely connected group, consisting of 500-6000 cells, and maintains individual existence, with some being specialized, carrying out specific tasks for the colony
Polar Compound
one end is positively charged and the other is negatively charged.
Hydrogen Bond
the bond between hydrogen and another atom.
Cohesion
same type of particles sticking together (water sticking to water).
Adhesion
water molecules sticking to solid surfaces (ex: water sticking to your window).
Surface Tension
surface film on water that requires force to break through.
Capillary Action
the ability of water to move upwards through a narrow tube.
Aqueous Solution
solution where water is the dissolver (solvent).
Solute
Stuff being dissolved
Acid Rain
acidic rain water results from air pollution; it can alter the pH of bodies of water and kill animals and plants, erode infrastructure.
Enzymes
Proteins that help speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy needed for the reaction to occur. They are called biological catalysts, help speed up catabolic and anabolic reactions, and are reusable
Lactose
sugar found in dairy products (disaccharide)
Coenzymes
Substance that attaches to the enzyme and makes the active site the correct shape
Enzyme Inhibitors
Bind and either change the shape of the enzyme or block the active site - keep the enzyme from working
Anabolism
join molecules to make polymers.
Catabolism
split polymer into monomers.
Macromolecules
Molecules present in living organisms that are needed for survival! LARGE and contain CARBON.
Monomer
a single building block/unit. A single molecule!
Polymer
A chain of building blocks. Multiple monomers bonded together form polymers!
Carbohydrates
Quick Energy (minimal storage), and forms structures of living things/protective. Made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Monomer is called a monosaccharide (simple sugar), with the other form being a disaccharide. Polymer is called a polysaccharide
Lipids
The functions of lipids include storage of Energy (long-term), and serving as structural and chemical messengers. Monomer is called fatty acid/glycerol. Polymer is called saturated fatty acid (has a lot of hydrogens, which is unhealthy fats), unsaturated fatty acid (Double bonds between carbons, which are healthy fats), waxes, and phospholipids
Unsaturated fat
Liquid at room temperature, decreases bad cholesterol and increases good
Saturated fat
Solid at room temperature, increases bad cholesterol and decreases good, leading to clogged arteries
Polypeptide
Chain - twists to make protein structure
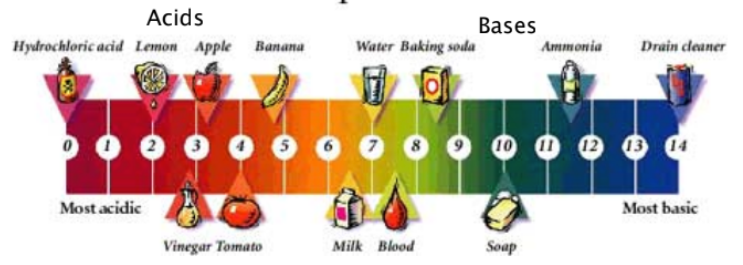
pH Scale
Measures how acidic or basic a solution is, measured from 0 - 14
DNA
Stores Genetic Info to make protein, it is the genetic code
All living thing have this to control the actions of the cells, as well as the ability to pass this on to their offspring
RNA
transmit genetic info and directly make protein
Proteins
The chain of amino acids fold into 3-D shape, which determines the protein’s job.
Makes the structures in living things, enzymes, transport, immunity, chemical messengers, controls traffic in/out of cells, and movement of muscles. Monomer is called an amino acid, polymer is called a polypeptide chain
Protein Pumps
Transport small molecules and ions up a concentration gradient (low to high), requires ATP
Plasmolysis
Cell shrinks away from cell wall and turgor pressure decreases
Positive Feedback Loops
The end result (output) causes an amplification (increase) of the stimulus (input) until the action is complete. Not common in biology and the best example is childbirth
Negative Feedback Loops
End results (output) stops/inhibits the stimulus (input); brings back to baseline.
Phospholipid Bilayer
Two layers of phospholipids and proteins
Selective
Picky about what can pass through.
Hydrophilic Head
Face the water, water loving
Hydrophobic Tail
Tails face each other, water hating
Osmosis
The diffusion of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of higher concentration of water to lower concentration of water until equilibrium is reached, and is used to maintain cellular balance
Hypotonic
The concentration of solute inside the cell is higher than the concentration of solutes outside the cell. Water moves INTO the cell. Animal cells SWELL and BURST
Isotonic
Cell and outside water are equal in concentration of solute
Hypertonic
The concentration of solute is higher on the outside of the cell than the concentration of solute inside the cell. Water moves OUT of the cell. Animal Cells will SHRIVEL
Tonicity
The state of concentration of a cell
Facilitated Diffusion
Molecules flow from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration but need the help of a channel protein
Active Transport
When molecules move against the concentration gradients and move from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. Requires energy in the form of ATP
Passive Transport
Molecules flowing down a concentration gradient (from high → low) is a natural process and does not require energy
ENDOcytosis
Vesicles move substances IN.
EXOcytosis
vesicles move substances OUT.
Homeostasis
A self-regulating process by which an organism can maintain internal stability while adjusting to changing external conditions, the state of biological balance.
Genome
refers to the entire DNA code for an organism.
DNA Replication
using a strand of DNA as a template, make two new strands of DNA.
Mutation
any change in the DNA sequence from its original sequence; may be spontaneous or due to exposure to environmental factors.
Gene Mutations
changes to a single gene (single DNA sequence).
Chromosome Mutations
changes to an entire chromosome OR the gain/loss of an entire chromosome.
Substitution
One nucleotide is replaced by another.
Deletion
a base is lost from the sequence, gene and chromosome mutations
Insertion/Addition
a base is added to the sequence.
FRAMESHIFT MUTATIONS
Causes a new codon sequence to be read at the ribosome (the bases to be read out of the original order).
Cancer
A disease of the cell cycle, uncontrolled cell division.
Gene expression
Molecules/Chemicals can turn certain genes on (expressed) or off (not expressed).
Activator
proteint that recruits RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter (turn gene on)
Repressor
protein that blocks RNA polymerase from binding to the promoter (turn gene off)
Transcription
the process in which segments of DNA serve as templates to produce complementary RNA molecules
Endergonic
Require energy
Exergonic
Release heat/energy
Anabolic
The process where the energy is used to form a bond.
Catabolic
The process where the bond is broken down to release energy.
Promoters
signals/areas in DNA molecules that show RNA polymerase exactly where to begin and there are similar regions that serves as stop codes
Translation
when mRNA is read by tRNA to create an amino acid chain (polypeptide chain) which turns into proteins.
mRNA
Messenger RNA - Carries instructions for polypeptide synthesis from the nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm
tRNA
Transfer RNA - Carries amino acids to the ribosome and matches them to the coded mRNA message
Codons
the genetic code is read in three-letter groupings
Crossing Over
When homologous chromosomes pair up and swap like segments
Bioethics
The idea of whether a scientific act is morally responsible or not.
Selective Breeding
Choosing the “best” traits for breeding.
Transgenic Organisms
Organisms that contain genes from more than one species (or inserted genes).