6. Heating and cooling liquid and solid food (DONE)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
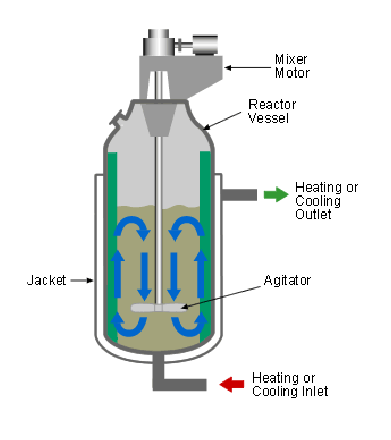
Batch heating in industry
contains agitator that stirs liquid in vessel
used to make soup for example
Sensible vs latent heat
Sensible: heat you can feel (temperature)
Latent: Heat you cannot feel (heat needed for phase transitions)
How fast heating takes place formula
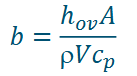
Types of heat exchangers: plate system
only works for low viscosity products.

Types of heat exchangers: tubular system
for more viscous products
usually pretty long for there to be enough residence time

Types of heat exchangers: tube in shell
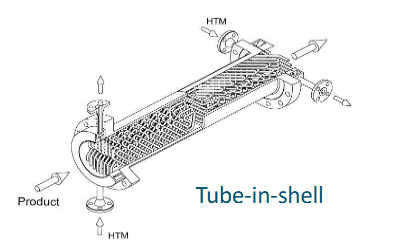
Types of heat exchangers: scraped surface
For cooling
Can remove crystals

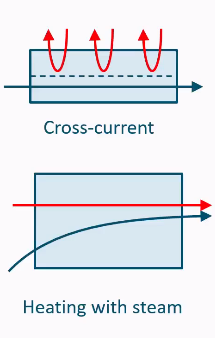
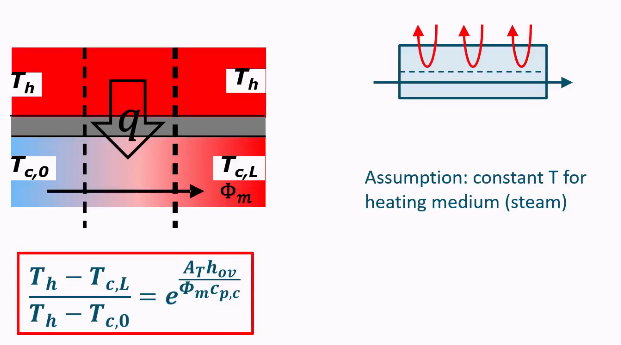
Temperature changes in streams for cross current
E.g. heating with steam, steam stays constant temperature but heats up other product.
Temperature changes in streams for co-current
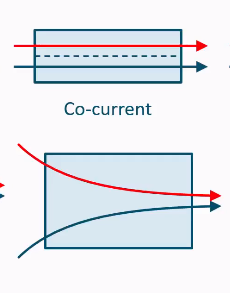
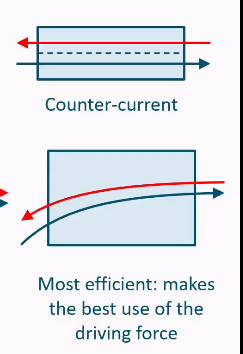
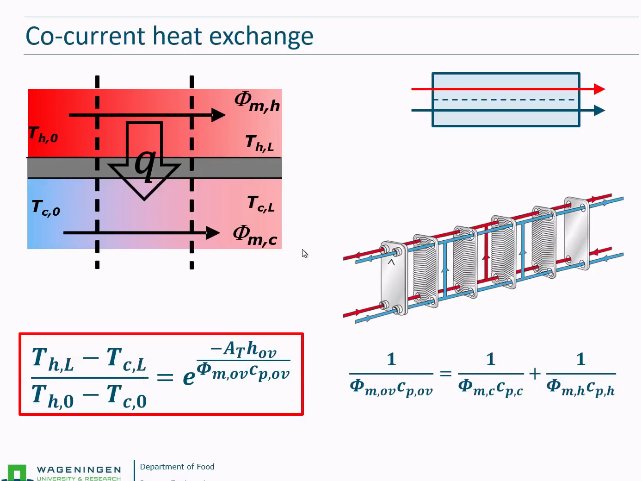
Temperature changes in streams for counter current
Most efficient
What does each part of the 1/hov equation represent?
1/hh = resistance for heat transfer at the heating medium
thickness/conductivity = resistance to heat transfer of the wall
1/hc = resistance in cooling medium
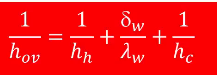
Cross-current heat exchange
Assumption: constant T for heating medium (steam)
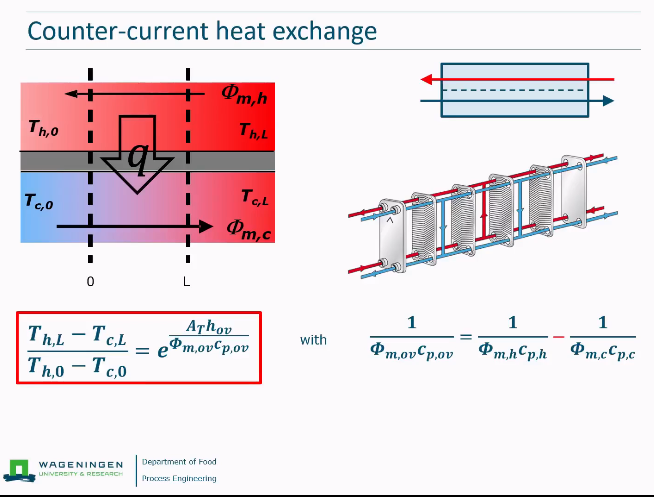
Co-current heat exchange
Counter-current heat exchanger
Options for heating of semi-solid food
Options:
First package, then heat
First heat than use aseptic packaging
Process for first packaging and then heating
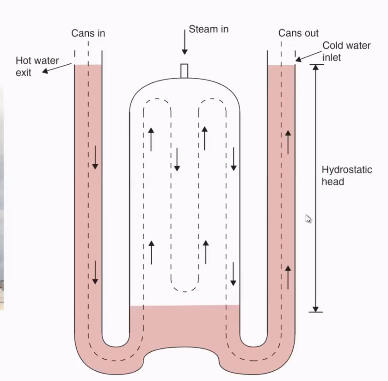
Batch system: autoclave
Solid products (cans/bottles): autoclave
Steam injection
High pressure at sterilization temperature
Cooling by spraying water
Residence time
Process for first packaging and then heating (continuous system)
Process for first heating and then packaging
Steam injection (direct heating)
continuous system + aseptic packaging
Semi solid foods
Biot number
A number to help you find out if resistance is inside limiting or outisde limiting
Bi>10 → resistance inside limiting
Bi<0.1 → resistance outside limiting
Resistance to heating of a solid product
For a solid product, outside the product there is convection.
Therefore, convection is limiting to the heating process
Inside the product there is conduction
Therefore conduction is limiting
How to find if inside or outside is resistance limiting
If inside is limiting, you want to make the can smaller
If outside the can is limiting, you want to make the can larger
Bi > 10 → resistance inside is limiting
Bi < 0.1 → resistance outside is limiting
Meaning of high and low Bi
Bi large → hext high and/or gamma low and/or dc large → high delta T
Bi small → hext low and/or gamma high and/or dc small → low delta T
What are the three “archetypal’’ forms of solid products?
Infinitive cylinder (don’t count top and bottom because its infinitive)
Infinitive slab
sphere
Dimensionless temperature Y
Y is always between 0 and 1
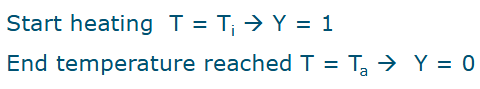
What is dc in bi and fo
One sided heating:
Dc is the whole thickness
Two sided heating:
Dc is the half thickness
All sided heating (sphere or cylinder)
Dc is the radius
How to find dimensionless temperature with two different shapes
Find them for each shape and multiply the dimensionless temperatures.