PCOL LEC midterms - ANTIPSYCHOTIC AGENTS AND LITHIUM
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
What hypothesis?: Schizophrenia is caused by a relative excess of dopamine in specific neuronal tract in the brain
DOPAMINE HYPOTHESIS
DOPAMINE HYPOTHESIS
Antipsychotic drugs blocks _____
Dopamine agonist drugs (____) exacerbate schizophrenia
_____ density of dopamine receptors detected in certain brain regions of untreated schizophrenic
dopamine receptors (D2 receptors)
Amphetamine, Levodopa
Increased
What hypothesis?
● Discovery of hallucinogens such as lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) and mescaline that are serotonin agonist lead for the search for endogenous hallucinogen (schizophrenia)
SEROTONIN HYPOTHESIS
What hypothesis?
● 5-HT2a receptor blockage is a key MOA for second generation antipsychotics
SEROTONIN HYPOTHESIS
SEROTONIN HYPOTHESIS
Discovery of hallucinogens such as ______ and _____ that are serotonin agonist lead for the search for endogenous hallucinogen (schizophrenia)
_____ is a key MOA for second generation antipsychotics
lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) and mescaline
5-HT2a receptor blockage
What hypothesis?
Hypofunction of NMDA receptors, located on GABAergic interneurons, leading to diminished inhibitory influences on neuronal firing → contributed to schizophrenia
GLUTAMATE HYPOTHESIS
What DOPAMINERGIC PATHWAY?
Controls motor function
(Deficiency can lead to parkinsonian symptoms)
NIGROSTRIATAL
What DOPAMINERGIC PATHWAY?
Hyperactive in schizophrenia
(positive symptoms)
MESOLIMBIC
What DOPAMINERGIC PATHWAY?
Underactive in schizophrenia
(negative symptoms)
MESOCORTICAL
What DOPAMINERGIC PATHWAY?
Controls prolactin secretion
(Dopamine inhibits prolactin release)
TUBEROINFUNDIBULAR
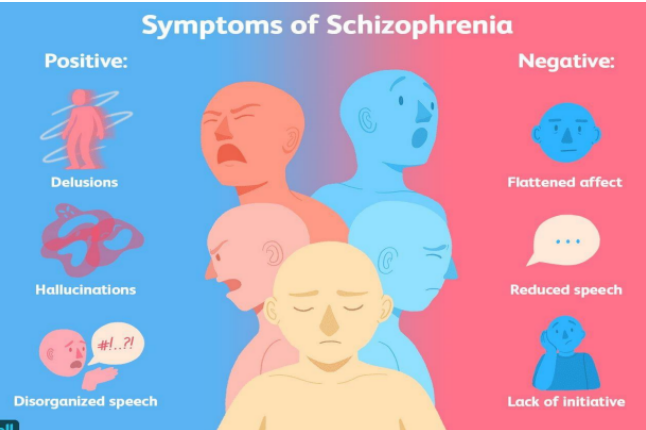
Positive Symptoms of Schizophrenia (HIDES)
● Hallucination
● Illusion
● Delusion
● Excitement
● Suspiciousness
Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia
(4 Bl An Av An)
● Think of depression
(Blunt affect, anhedonia, avolition, anergia)
What type of Anti-psychotics:
Can only address the positive symptoms of schizophrenia
TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS
What type of Anti-psychotics:
Can be classified into
High potency (Haloperidol, Trifluoperazine, Fluphenazine) and
Low potency (Chlorpromazine, Thioridazine)
TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS
TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS
Can be classified into
High potency (3____) and
Low potency (2____)
Haloperidol, Trifluoperazine, Fluphenazine
Chlorpromazine, Thioridazine
TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS
High potency typical antipsychotics → Higher chances of causing ____
Low potency typical antipsychotics → Lower chance of causing EPS more likely to cause ____ and ____
extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS)
sedation and postural hypotension
What type of Anti-psychotics:
Blocks D2 receptors >> 5-HT2 receptors
TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS
What type of Anti-psychotics:
Can address both positive and negative symptoms
ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS
What type of Anti-psychotics:
Lesser chances of EPS but higher chance to cause metabolic derangements (weight gain, endocrine problems)
ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS
What type of Anti-psychotics:
Blocks 5-HT2 receptors >> D2
ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS
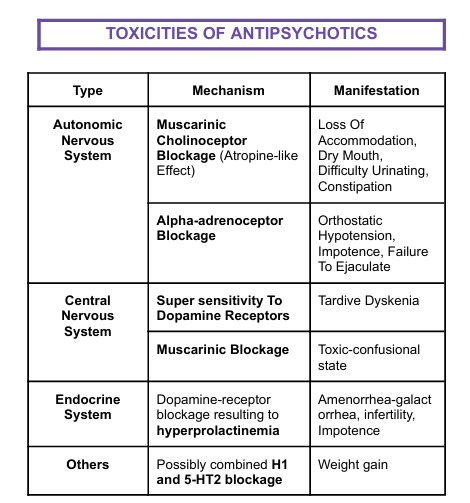
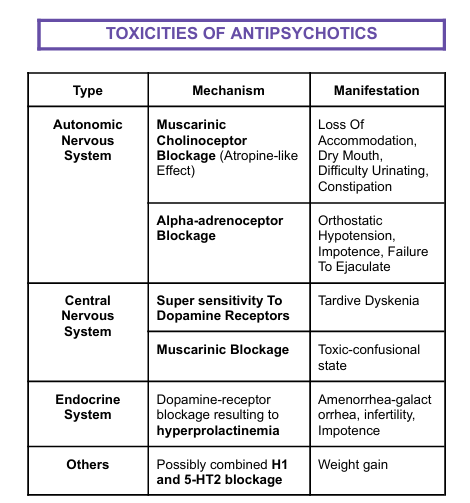
TOXICITIES OF ANTIPSYCHOTICS:
Mechanism and Manifestation of Autonomic Nervous System
Mechanism: Muscarinic Cholinoceptor Blockage (Atropine-like Effect)
Manifectation: Loss Of Accommodation, Dry Mouth, Difficulty Urinating, Constipation
Alpha-adrenoceptor Blockage
Orthostatic Hypotension, Impotence, Failure To Ejaculate
TOXICITIES OF ANTIPSYCHOTICS:
Mechanism and Manifestation of Central Nervous System
Mechanism: Super sensitivity To Dopamine Receptors
Manifestation: Tardive Dyskenia
Mechanism: Muscarinic Blockage
Toxic-confusional state
TOXICITIES OF ANTIPSYCHOTICS:
Mechanism and Manifestation of Endocrine System
Mechanism: Dopamine-receptor blockage resulting to hyperprolactinemia
Manifestation: Amenorrhea-galact orrhea, infertility, Impotence
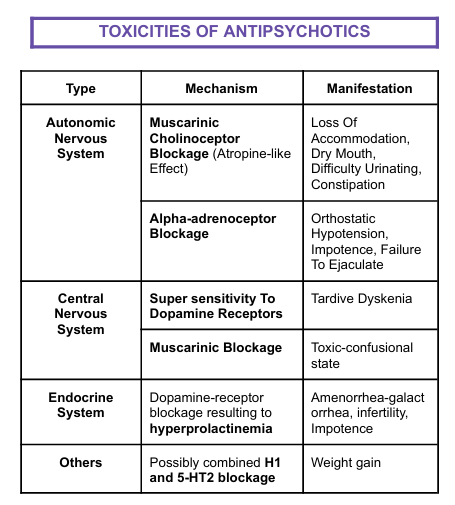
TOXICITIES OF ANTIPSYCHOTICS:
Mechanism and Manifestation of OTHERS
Mechanism: Possibly combined H1 and 5-HT2 blockage
Manifestation: Weight gain
TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS (3)
PHENOTHIAZINE
PIPERIDINE
BUTYROPHENONE
PHENOTHIAZINE examples (4)
Chlorpromazine, Levomepromazine, Prochlorperazine, Promethazine
Chlor,Levo,Pro,Pro
PIPERIDINE examples (3)
Thioridazine, Fluphenazine, Trifluoperazine
Thi,Flu,Tri
BUTYROPHENONE examples (3)
Haloperidol, Droperidol
MOA of what antipsychotic drug:
● Blocks D2 receptor >> 5-HT2 receptors
TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS
USES of a typical antipsychotic:
Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders, Manic phase of bipolar disorder
Anti-emetics (Promethazine and Prochlorperazine)
PHENOTHIAZINE (Chlorpromazine, Levomepromazine, Prochlorperazine, Promethazine)
SE/AE of a typical antipsychotic:
● Postural hypotension, failure of ejaculation, contact dermatitis
● Sedation
● Extrapyramidal symptoms, Tardive dyskinesia, Hyperprolactinemia
● Corneal and lens deposit
● Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
PHENOTHIAZINE (Chlorpromazine, Levomepromazine, Prochlorperazine, Promethazine)
PHENOTHIAZINE notes: Prototype of all antipsychotics?
Chlorpromazine
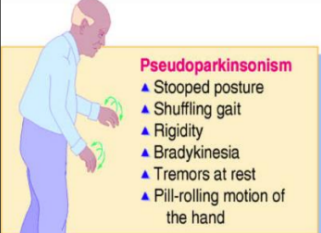
Stooped posture
Shuffling gait
Rigidity
Bradykinesia
Tremors at rest
Pill-rolling motion of the hand
Pseudoparkinsonism
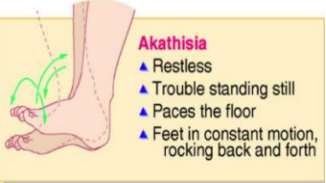
Restless
Trouble standing still
Paces the floor
Feet in constant motion, rocking back and forth
Akathisia
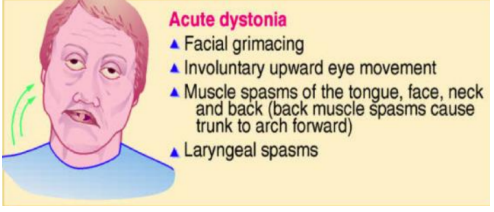
Facial grimacing
Involuntary upward eye movement
Muscle spasms of the tongue, face, neck and back (back muscle spasms cause trunk to arch forward)
Laryngeal spasms
Acute dystonia
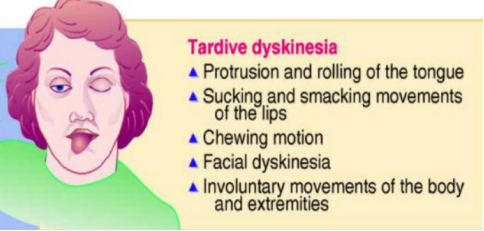
Protrusion and rolling of the tongue
Sucking and smacking movements of the lips
Chewing motion
Facial dyskinesia
Involuntary movements of the body and extremities
Tardive dykinesia
a life threatening reaction to antipsychotics characterized by fever, altered mental status, muscle rigidity, and autonomic dysfunction.
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
USES of a typical antipsychotic:
Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders
PIPERIDINE (Thioridazine, Fluphenazine, Perphenazine, Trifluoperazine)
SE/AE of a typical antipsychotic:
● Postural hypotension, failure of ejaculation, contact dermatitis
● Sedation
● Extrapyramidal symptoms, Tardive dyskinesia, Hyperprolactinemia
● Retinal deposits (Thioridazine)
● Cardiotoxicity – QT prolongation arrhythmia (Thioridazine)
● Decrease seizure threshold
PIPERIDINE (Thioridazine, Fluphenazine, Perphenazine, Trifluoperazine)
USES of a typical antipsychotic:
● Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders
● Bipolar disorder (Manic Phase)
● Tourette's syndrome
BUTYROPHENONE (Haloperidol, Droperidol)
SE/AE of a typical antipsychotic:
● Extrapyramidal symptoms, Tardive dyskinesia, Hyperprolactinemia
● Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
BUTYROPHENONE (Haloperidol, Droperidol)
NOTES: Less sedating among typical antipsychotics
BUTYROPHENONE (Haloperidol, Droperidol)
ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS examples (7)
Clozapine,
Olanzapine,
Quetiapine,
Resperidone,
Paiperidone,
Ziprasidone,
Aripiprazole
MOA of an antipsychotic drug:
Blocks 5-HT2 receptors >> D2 receptors
ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS
USES of an Atypical antipsychotic:
Schizophrenia (DOC for refractory and suicidal schizophrenia)
CLOZAPINE
SE/AE of an Atypical antipsychotic:
● Extrapyramidal symptoms, Tardive dyskinesia, Hyperprolactinemia (less), Postural hypotension
● Weight gain, Hyperglycemia, Hyperlipidemia
● Agranulocytosis
CLOZAPINE and OLANZAPINE
CLOZAPINE notes:
____ and ____ has the highest tendency to cause weight gain
Because of the risk of agranulocytosis, patients receiving clozapine must have a weekly blood count for ___
Clozapine and Olanzapine
6 week
USES of an Atypical antipsychotic:
● Schizophrenia
● Bipolar disorder, Anorexia nervosa, and Depression
OLANZAPINE
NOTES from an atypical antipsychotic
___and ___ has the highest tendency to cause weight gain
Safe in pregnancy
Clozapine and Olanzapine
Olanzapine
USES of an Atypical antipsychotic:
Schizophrenia, Bipolar disorder
Sleep promotion and maintenance
QUETIAPINE
SE/AE of an Atypical antipsychotic:
● Extrapyramidal symptoms, Tardive dyskinesia, Hyperprolactinemia (less), Postural hypotension
● Weight gain, Hyperglycemia, Hyperlipidemia (less)
● Somnolence, Fatigue, Sleep paralysis, Hypnagogic hallucinations
● Cataracts, Priapism
● QT prolongation arrhythmia
QUETIAPINE
NOTES of an atypical antipsychotic
● ___ and ___ are amongst the atypicals that is least likely to cause tardive dyskinesia
Quetiapine and Clozapine
USES of an Atypical antipsychotic:
Schizophrenia Bipolar disorder, Tourette syndrome, Depression, Intractable hiccups
RISPERIDONE
SE/AE of an Atypical antipsychotic:
● Extrapyramidal symptoms, Tardive dyskinesia, postural hypotension(less)
● Hyperprolactinemia (marked)
● Weight gain, Hyperglycemia, Hyperlipidemia (less)
RISPERIDONE
NOTES of an Atypical antipsychotic:
● Highest propensity to cause hyperprolactinemia (amenorrhea, galactorrhea)
● Only antipsychotic approved for schizophrenia in the youth
RISPERIDONE
USES of an Atypical antipsychotic:
● Schizophrenia
● Bipolar disorder (Acute mania)
ZIPRASIDONE
SE/AE of an Atypical antipsychotic:
● Extrapyramidal symptoms, postural hypotension(less)
● QT prolongation arrhythmia
ZIPRASIDONE
NOTES of an Atypical antipsychotic:
Little to no tendency to cause hyperglycemia, hyperprolactinemia, or weight gain
ZIPRASIDONE
USES of an Atypical antipsychotic:
● Schizophrenia
● Bipolar disorder (Acute mania), Major depressive disorder, Autism
● Cocaine dependence
ARIPIPRAZOLE
SE/AE of an Atypical antipsychotic:
● Extrapyramidal symptoms, postural hypotension, Tremors
● GIT upset
● Hypersensitivity
ARIPIPRAZOLE
NOTES of an Atypical antipsychotic:
Less sedating and no atropine-like effects
ARIPIPRAZOLE
What antipsychotic drug?
Mood stabilizer
LITHIUM
MOA:
● Uncertain
○ Suppresses inositol signaling and inhibits glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3)
LITHIUM
Lithium: Suppresses _____ and inhibits ____
inositol signaling; glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3)
USES:
● Bipolar disorder (DOC)
● Recurrent depression
● Schizoaffective disorders
LITHIUM
SE/AE of this drug:
● Tremors (most common), Ataxia, Aphasia
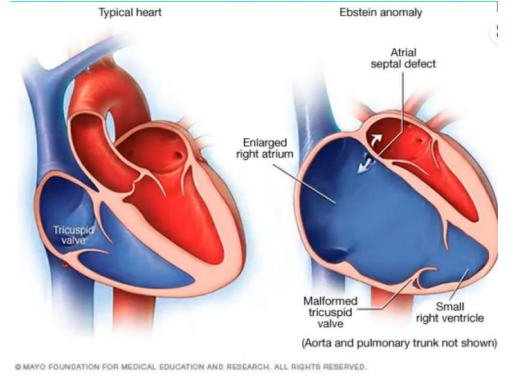
● Thyroid enlargement and subclinical hypothyroidism, Teratogen (Ebstein anomaly), Diabetes Insipidus
● LITHIUM (Low Thyroid hormone, Heart (Ebstein anomaly), Insipidus, Unintentional Movement (tremors)
LITHIUM
Side effects of lithium
mnemonic: LITHIUM
Low Thyroid hormone,
Heart (Ebstein anomaly),
Insipidus,
Unintentional Movement (tremors)
Notes of this drug:
● Narrow therapeutic window → Overdose is treated with hemodialysis
LITHIUM
LITHIUM:
Narrow therapeutic window → Overdose is treated with _____
hemodialysis