Wk 8/9 secondary prevention
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
lvls of prevention
primary → general population
seocndary → at risk
tertiary → has diagnosis
major approaches to secondary prevention
Behavior change (also in primary prevention
Screening (what health issues may require screening)
early intervention (what health issues can benefit from early intervention)
Behavior change
focus on long term positive health behaviors
What are some long term positive health behaviors?
Transtheoretical Model (Stages of Change)
Widely used model for changing negative behaviors on a
continuous basis.THE STAGES OF CHANGE MODEL
Stage 1: PRECONTEMPLATION
Stage 2: CONTEMPLATION
Stage 3: PREPARATION
Stage 4: ACTION
Stage 5: MAINTENANCE

stage 1
There is no intention to change behavior in the foreseeable future.
precontemplation
stage 2
Combines behavioral criteria with a problem. Aware a problem exists.
Contemplation
stage 3
Makes a plan for change. Initiates the change process.
Preparation
stage 4
Individuals modify their behavior, experiences, or environment to overcome their problems.
action
stage 5
Has made behavior change for 6 months. Work to prevent relapse
maintenance
ASPECTS OF THIS STAGES OF CHANGE APPROACH
Five stages that people go through in the process of behavioral change
People go through distinct processes of change
Stages are associated with cognitive changes
Stages are associated with levels of self-efficacy
Interventions should be linked to the stage a person is at
pre-contemplation → contemplation
Consciousness raising: Increasing information about self and problem; observations, confrontations, interpretations.
Dramatic relief: Experiencing and expressing feelings about one’s problems and solutions: psychodrama, grieving losses, role playing.
Environmental reevaluation: Assessing how one’s problem affects the physical environment; empathy training, documentaries.
contemplation → preparation
Self-reevaluation: Assessing how one feels and thinks about oneself with respect to a problem:
values clarification
Imagery
corrective emotional experience
preparation → action
Self liberation: Choosing and commitment to act or belief in ability to change: decision-making therapy, New Year’s resolutions, commitment enhancing techniques.
action → maintenance
reinforcement management: Rewarding oneself or being rewarded by others for making changes: contingency contracts, overt and covert reinforcement, self-reward.
Helping relationships: Being open and trusting about problems with someone who cares: therapeutic alliance, social support, self-help groups.
Counter conditioning: Substituting alternatives for problem behaviors: relaxation, desensitization, assertion, positive self-statements.
Stimulus control: Avoiding or countering stimuli that elicit problem behaviors: restructuring one’s environment (e.g., removing alcohol or fattening foods), avoiding high risk cues, fading techniques.
STAGES OF CHANGE PROS/ CONS
Strengths
Useful tool for tailoring interventions for individuals or targeting for groups
Theory of behavior change, not just behavior
Organizational tool for thinking about types of interventions
Weaknesses
Time periods are arbitrary (e.g., why 6 months?)
Stages are not qualitatively different or mutually distinct
Stages may not be sequential
Apply properly, don’t abandon stage models
EXAMPLES OF HEALTH BEHAVIORS STUDIED...
Smoking behavior
Quitting cocaine
Weight control
Safer sex
Condom use
Physicians’ preventive practices
Adolescent delinquency
Sunscreen useRadon gas exposure
High fat diet
Exercise acquisition
Mammography screening
EARLY INTERVENTION METHODS
Most popular methods...
Harm Reduction
Risk and Protective Factors Model
Harm Reduction Approach (HRM)
Idea: high-risk individuals have multiple problems and difficult situations → may not be possible to change all of them
Focus on problem behaviors that pose the greatest public health threat
In short-term do not address other risky or unhealthy behaviors
May serve as a building block for changing other behaviors through the buildup of trust and rapport, not being judged
THERE MUST STILL BE HARM LEFT TO COUNT
HRM pros and cons
Yay
2 or more conditions
Reduce harm
Controversial
Maybe culturally bound
Nay
One health condition
Eliminated harm
Behavior change or treatment
Universally applied
Side effects or complications
condoms for high school students vs. condoms for sex workers
condoms for high school students is behavior change intervention because risk of STDs, early pregnancies, etc. are reduced. All risk reduced, no harm behavior left.
Condoms for sex workers reduce STDs, accidental pregnancies, etc. but even w/ the intervention, sex work is still illegal in the U.S. so there is still harm.
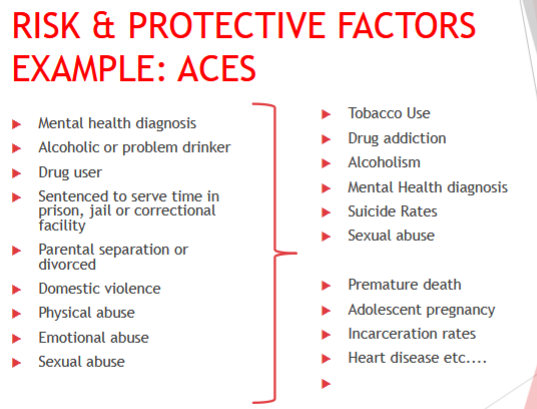
RISK AND PROTECTIVE FACTORS MODEL
Developed by Hawkins, Catalano, et al 1999
Sets up overall predictive relationship
“epidemiological exposure model”
level of exposure to risk/protective factors affects the
outcomeMultiple risk factors mean more than the “sum”
Most often used children & adolescents
Applied less among adults and elderly population
Actual risk & protective factors vary by TOPIC & POPULATION
RISK FACTORS
Individual: biological & psychological dispositions, attitudes, values, knowledge, skills, problem behaviors
Peer: norms, activities, attachment
Family: function, management, bonding, abuse/violence
School: bonding, climate, policy, performance
Community: bonding, norms, resources, poverty level, crime, awareness/mobilization
Society/environmental (sometimes): norms, policy/sanctions
Protective
Not as well-specified
Individual: gender, intelligence, temperament
Social bonding: attachment/ commitment to positive, pro-social individuals and groups
Healthy beliefs: low valued associate with bad behaviors
Clear standards for behavior: in families, schools, communities
risk and protective factors model critique
Edberg’s critique:
Still focuses on an output of behavior
Ignores world view in an ecological or meaning context
Difficult to translate into a program/intervention
Does not lend itself to typical research/planning/evaluation designs
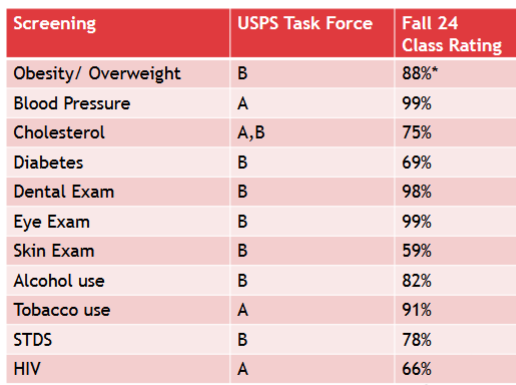
screening
Goal: Early identification
Mechanism: screening process – usually for those suspected of or at high risk
Screening followed by....
➢ Initiation of early treatment
➢ Focus on behavior change
➢ Other risk modification
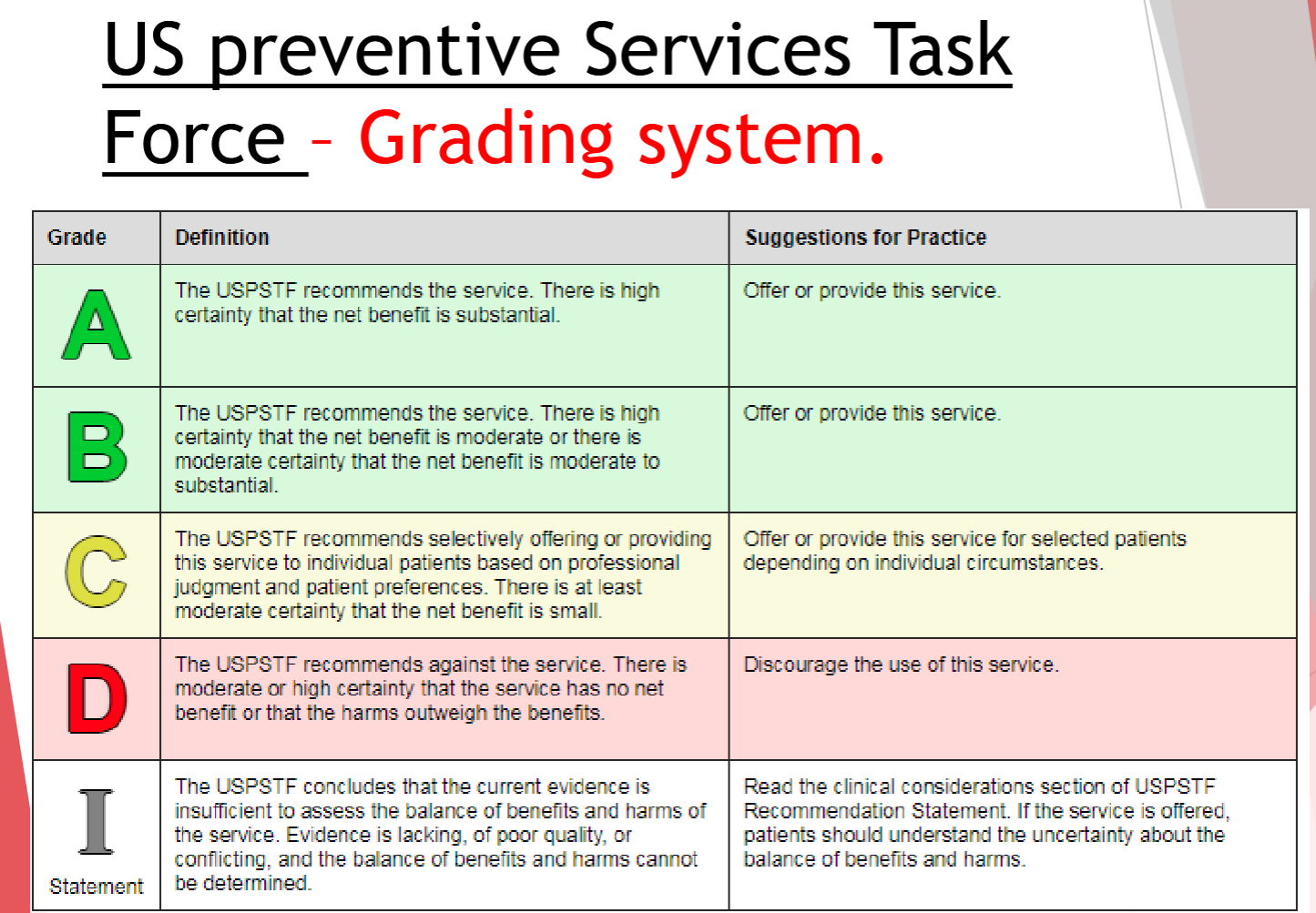
screening US preventitive Service Task Force