Radioactivity
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is an isotope?
Atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons.
“Not all nuclei of elements are stable”. Explain what this means.
The ratio of protons and neutrons are imbalanced.
In order to regain this balance, radiation is emitted, releasing excess protons, neutrons or both.
List the types of radiactive emissions.
Alpha emission
Beta particle emission
Gamma rays
Positron decay
Electron capture
What is an alpha particle?
An alpha particle is equivalent to a helium nucleus with two protons and two neutrons.

What is alpha emission?
A type of radioactive decay, during which an atomic nucleus loses two protons and two electrons.
It reduces the atomic number by 2 and the mass number by 4, making the element more stable.
Give an example of an alpha emission equation.
Rules to remember:
The atom on the left side is the one that splits into two species.
One of the two atoms on the right is ALWAYS an alpha particle.
The other atom on the right ALWAYS reduces by 2 in the atomic number and 4 in the mass number.
Using the atomic number and a periodic table, find the chemical symbol of the element.

What is a beta particle?
A fast-moving electron.
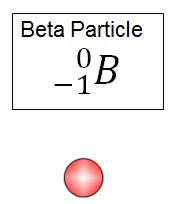
What is beta particle emission?
A type of radioactive decay where an electron is emitted from the nucleus of an atom.
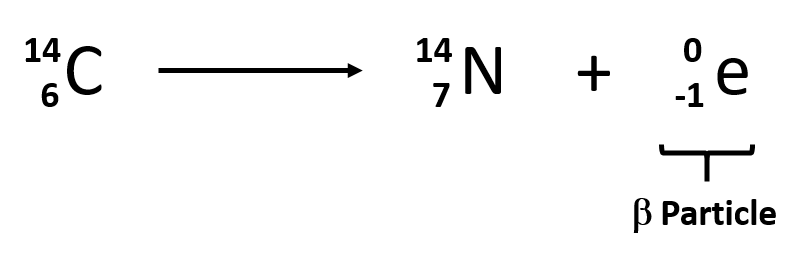
Give an example of a beta emission equation.
Rules to remember:
The atom on the left side is the one that splits into two species.
One of the two atoms on the right is ALWAYS a beta particle.
The other atom on the right ALWAYS has the same mass number and atomic number INCREASES by 1.
Explain another way in which beta particles can be formed.
Beta particles can also be considered as being formed when a neutron changes into a proton.
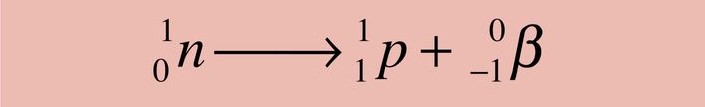
What are gamma rays?
Gamma rays are high energy electronmagnetic (EM) waves. They have no charge.
What is postrion emission (beta plus decay)?
When a proton is converted to a neutron, releasing a positron.
What is a positron particle?
The antiparticle to an electron- meaning it has the same mass but opposite charge, i.e. +1 charge.
Give an example of a positron emission equation.
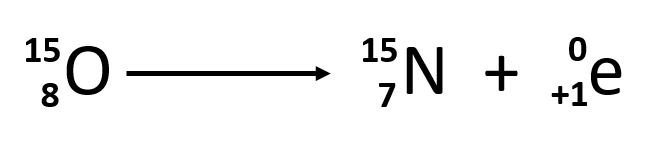
What is electron capture?
In electron capture, an electron from the closest energy level enters the nucleus, causing a proton to become a neutron.
This particle interaction occurs specifically within the nucleus.
Give an example of an electron capture equation.
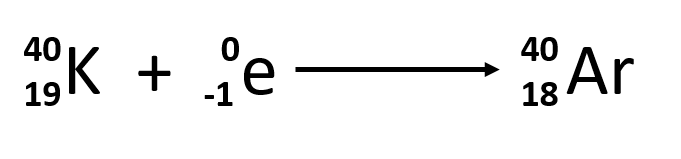
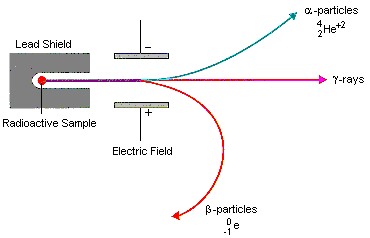
Describe the penetrating power of radioactive emissions.
Alpha particle- least penetrating radiation, stopped by a piece of paper.
Beta particle- stopped by a thin sheet of metal (0.5cm of aluminium).
Gamma rays- stopped by thick lead (may take more than 2cm).
State in ascending order the ionising power of radioactive emissions.
Least ionising- Gamma
Beta
Most ionising- Alpha
Describe the behaviour of radioactive radiation in an electric field.
Alpha particle-
Attracted to the negatively charged plate.
Deflected in one direction.
Beta particle-
Attracted to the positvely charged plate.
Deflected in the opposite direction to alpha radiation.
Gamma radiation-
Has no charge so it not attracted to either of the electrically charged plates.
Very high energy so cannot be deflected.
Why are beta particles deflected more than alpha particles within an electric field?
Alpha particles are heavier than beta particles.
Due to their lower mass, beta particles are deflected far more than alpha particles.
What is half-life?
Half-life is the time taken for half of the atoms in a radioactive isotope to decay.
What happens to living cells when exposed to radiation?
At lower doses, DNA can become damaged, which can cause mutations and cancerous cells.
At higher doses, the cell can be killed.
How are radioactive istopes used in health and medicine?
Cobalt-60 is used as a treatment for cancer in radiotherapy. The high energy rays are used to kill cancer cells and prevent a tumour from developing.
Technetium-99m is the most commonly used medical radioisotope. It’s used as a tracer by labelling a molecule which is taken preferentially up by the tissue to be studied.
How are radioactive istopes used in radio dating?
Carbon-14 has a half-life of 5570 years and is used to calculate the age of the remains of plants and animals. All living organisms must contain a small percentage of carbon-14 through absorption. This absorption stops when the animal dies, so the carbon-14 that is present will start to decay. The rate of decay decreases over the years and the activity that remains can be used to calculate the age of organisms.
Potassium-40 has a very long half-life of 1300 million years. It is used to estimate the age of rocks. It can change into argon-40 by the nucleus gaining an inner electron. Measuring the ratio of potassium-40 to argon-40 in a rock gives an estimate
How are radioactive istopes used in analysis?
Dilution analysis: Substances containing radioisotopes can be used to find the mass of substance in a mixture. This is useful when the substance can be extracted in its pure state from the mixture, but it can’t be extracted in such a way that its concentration cannot be determined.
How are radioactive istopes used in industry?
Thickness monitoring of metal strips or foil: The metal is rolled between two rollers in order to obtain the right thickness. A β-source is placed on one side of the metal with a detector on the other. If the metal comes out too thick, then the detector with sense a reduced amount of radiation, so the rollers will move closer together.