Hygiene principles (Kidney disease and dialysis)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Chronic kidney disease (CKD)
Progressive kidney disease aka this is progressive3 kidney disease that can result in reduced renal funtion, with effects on multipke organ sytems. Potential manifestations include anemia, abnormal bleeding, electrolyte and fluid imbalance, hypertension, drug intolerance, and skeletal abnormalities that can affect the delivery of dental care. In addition, patients who have severe and progressive disease may require artificial filtration of the blood throuh dialysis or kidney transplantation.
3 months
CKD or chronic kidney disease is defined as the progressive loss of renal function that persists for — months or longer. It results from direct damage to nephrons. CKD results in uraemia and kidney failure and can lead to death.
Stage 1
The National Kidney Foundation defines a five-stage classification system for CKD based on the glomerular filtration rate (GFR). This stage is chatacterized by: normal or only slightly increased GFR associated by some degree of kidney damage.
Stage 2
The National Kidney Foundation defines a five-stage classification system for CKD based on the glomerular filtration rate (GFR). This stage is chatacterized by: mildly decreased GFR.
Stage 3
The National Kidney Foundation defines a five-stage classification system for CKD based on the glomerular filtration rate (GFR). This stage is chatacterized by: a moderately decreased GFR, with loss of 50% or more of normal renal function.
Stage 4
The National Kidney Foundation defines a five-stage classification system for CKD based on the glomerular filtration rate (GFR). This stage is chatacterized by: a severely decreased GFR.
Stage 5
The National Kidney Foundation defines a five-stage classification system for CKD based on the glomerular filtration rate (GFR). This stage is chatacterized by: renal failure, wherein 75% or more of the approximately 2 million nephrons have lost function.
ESRD (end stage renal disease)
This is caused by conditions that destroy nephrons. The 4 most common known caused of —.—.—.—. Are diabetes mellitus (37%), hypertension (24%), chronic glomerulonephritis (16%), and polycystic kidney disease (4.5%). Other common causes, in decreasing order, are systemic lupus erythematous (SLE), neoplasm, urologic diseases, and acquired immunodeficiency.
3
There are few signs and symptoms until CKD progresses to stage —. At this stage and beyond, patients may complain of a general ill feeling, fatigue, headaches, nausea, loss of appetite, and weight loss. With further progression, anemia, leg cramps, insomnia, and nocturia often develop. The anemia produces pallor of the skin and mucous membranes and contributes to the symptoms of lethargy and dizziness. Hyperpigmentation of the skin is characterized by a brownish-yellow appearance, caused by the retention of carotene-like pigments normally excreted by the kidney.
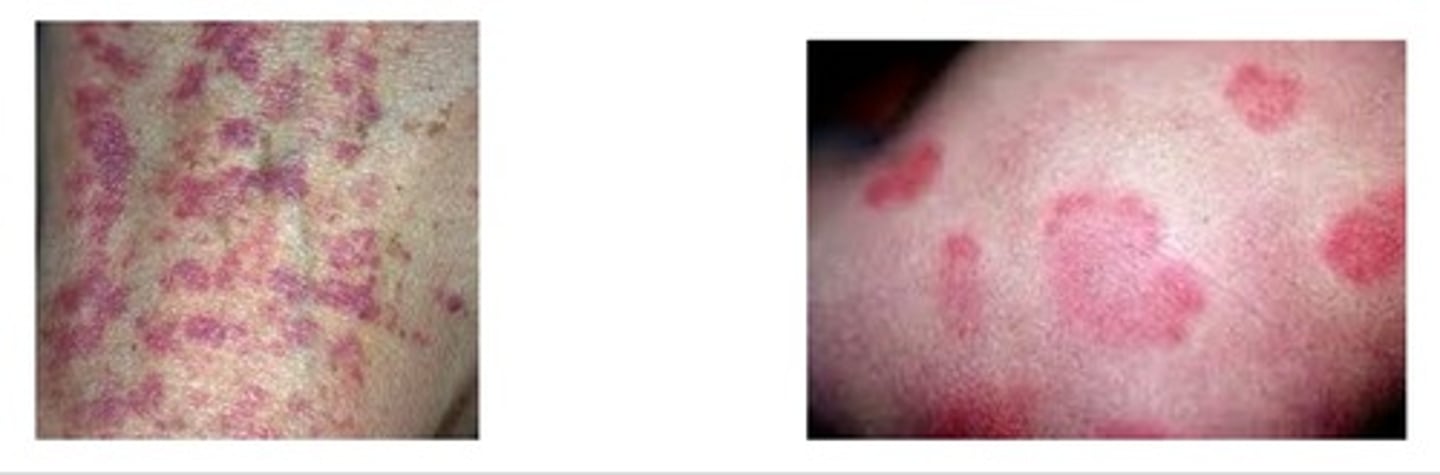
Ecchymoses, petechiae, and purpura
What's are these 3 skin manifestations of CKD?
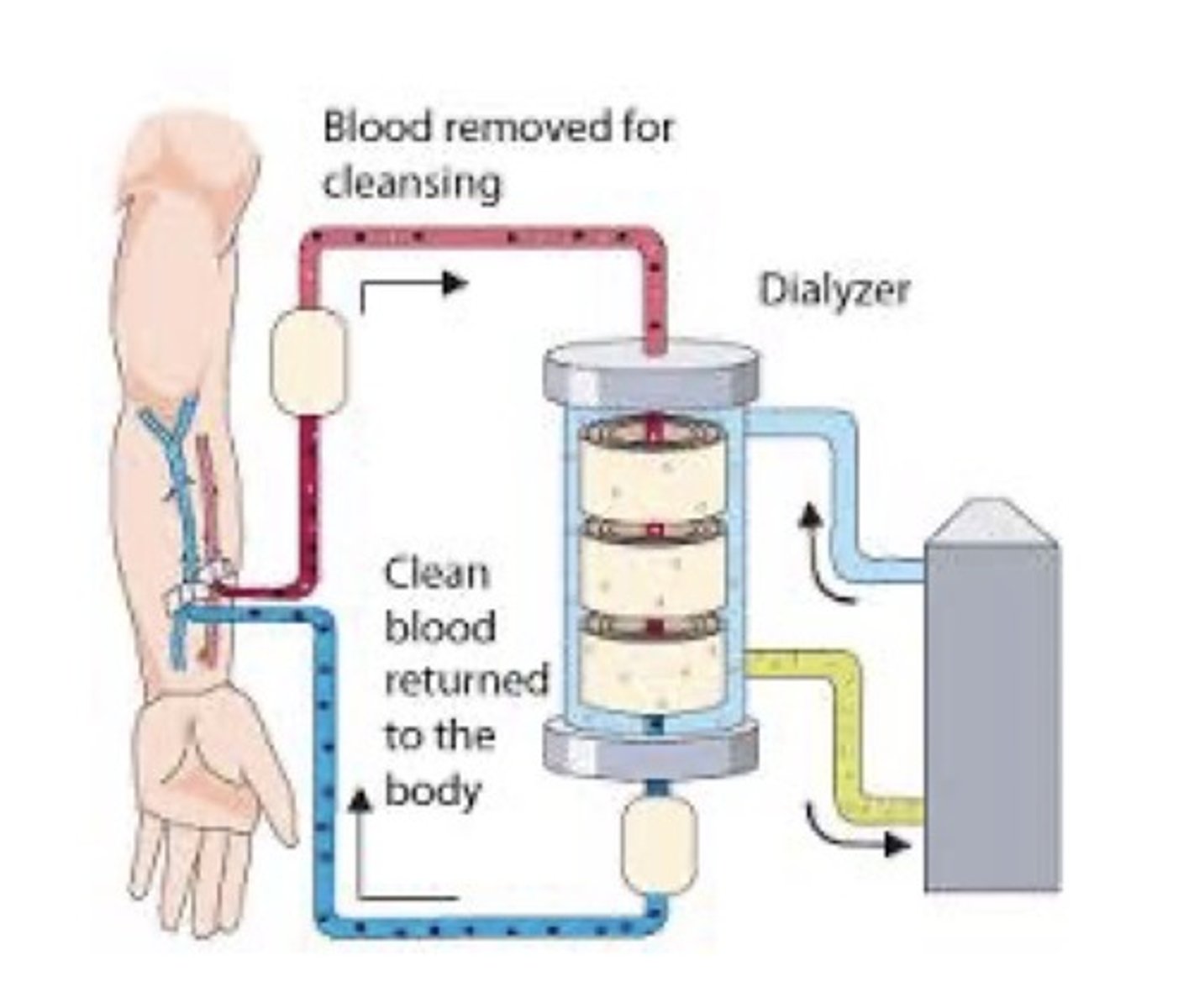
Dialysis
A medical procedure that artificially filters blood. Dialysis becomes necessary when the number of nephrons diminishes to the point that azotemia is unpreventable or uncontrollable. The procedure can be accomplished by peritoneal ——————— or hemodialysis. A graft or fistula is usually placed in the forearm and pts are "plugged in" to the hemodialysis machine at the fistula or graft site, and blood is passed through the machine, filtered, and returned to the patient. Heparin is usually administered during the procedure to prevent clotting.
hemodialysis
Most dialysis patients (80%) in the US receive this type of dialysis. —————————— is the method of choice when azotemia occurs and dialysis is needed on a long-term basis. Treatments are performed every 2-3 days and usually 3-4 hours is required for each session.
Hepatitis B, C, and HIV
The risk of these 3 infections is increased because dialyzers usually are disinfected, not sterilized, between uses.
Staphylococcus aureus
This bacteria is the most common cause of vascular access infection and related bacteremia in dialysis patients.
Adrenal insufficiency
Taking large doses of corticosteroids, as often prescribed for medical management of ESRD, may lead to this condition.

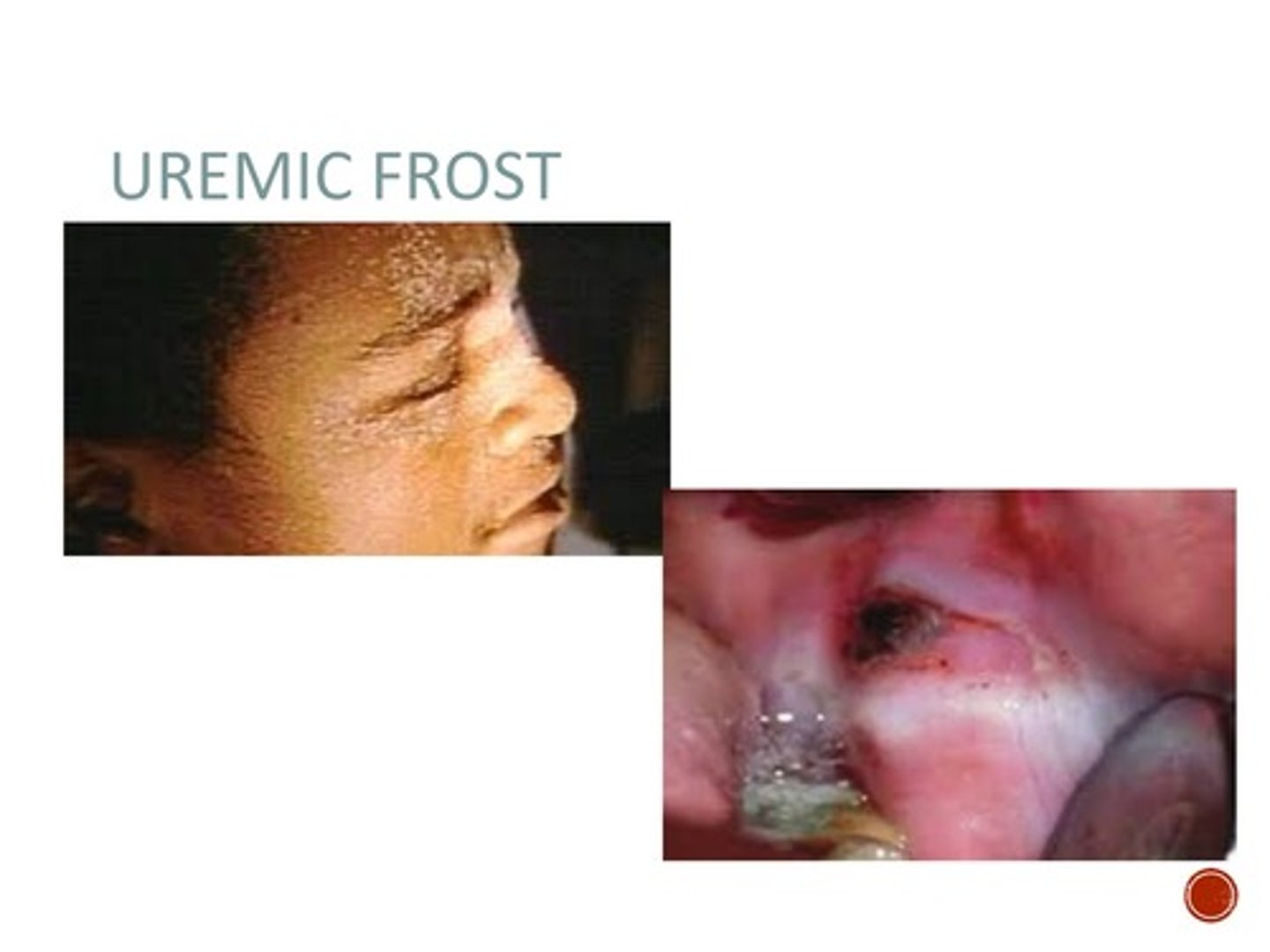
Uremic stomatitis
In severe renal failure, this type of stomatitis may be present. Early changes typically include red, burning, mucosa covered with grey exudates and later by frank ulceration. Adherent white patches called “uremic frost”, caused by urea crystal deposition, are more common on the skin but may be seen on the oral mucosa. Bleeding tendencies are evident as petechiae and ecchymoses on the labial and buccal mucosa, soft palate, and margins of the tongue, and is gingival bleeding.
Gingival enlargement
Patients with CKD who take calcium channel blocker hypotensive medication and renal transplant recipients who are taking cyclosporine may exhibit this oral manifestation:
Hyperparathyroidism
Secondary ————————————— along with the associated osseous changes in the jaws have been reported in up to 92% of patients receiving hemodialysis.