4. Light Microscopy Basics
1/33
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Light microscopy
optical microscope
used to visualize structures and objects too small to be seen by the naked eye
LM input mode
visible light
LM Resolution and Magnification Limits
resolution to ~200nm
magnification to x2000
parts of LM microscope
a light source, condenser, objective lens, and eyepiece (ocular lens)
sample properties
refract, reflect, or absorb based on its properties
objective lens
collects and refracts the light to create a magnified image
ocular lens
eyepiece
Image Formation
image you see when looking in your microscope is NOT the same as what you would see with your eye
magnified, flipped, and blurred
Why is the image blurred?
point spread function and diffraction
The Point Spread Function (PSF)
response of an imaging system to a point source or point object
light passes through an aperture (hole)
diffraction causes it to spread out
causes light from closely spaced objects to overlap
lowering spatial resolution
forming a perfect point, it forms an airy disk (convolution, blurring)
diffraction limit
min distance between two points to be distinguishable
image will blur into one, appearing as a single point if closer than diffraction limit
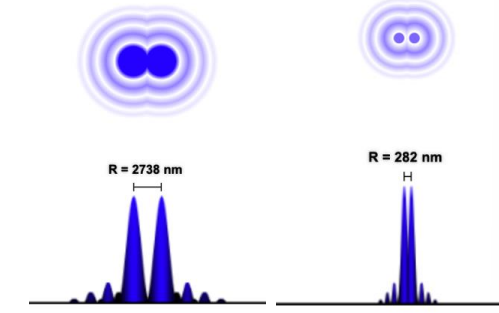
resolution
depends on the wavelength of light used
numerical aperture of the microscope’s objective lens
Abbe Resolution Criterion
0.5𝜆/NA
FOR OBJECTIVE LENS
Rayleigh Criterion (Refined)
0.61𝜆/NA
FOR OBJECTIVE LENS
numerical aperture equation
NA = n sin 𝛼
refractive index: nair = 1.0 and noil = 1.4
visible light wavelength (𝜆): 400nm to 700nm
FOR OBJECTIVE LENS
why add oil
improves resolution by improving numerical aperture by increasing the refractive index
how is resolution affected by Small Objective NA
poor resolution
how is resolution affected by Large Objective NA
excellent resolution
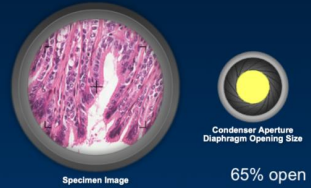
resolution if the condenser aperture
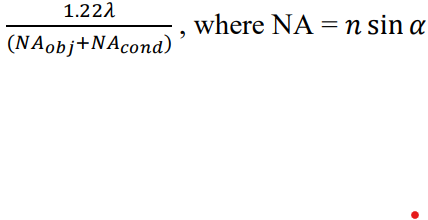
Total Magnification
= (Magnification of Objective) * (Magnification of Ocular Lens)
magnification of Ocular Lens
1X-30X (usually 10X)
magnification of Objective Lens
2X-200X (low 10X, high 40X, oil immersion 100X)
what contributes to image control
condenser and iris diaphram
Condenser
collects and focuses light from illuminator onto specimen, under stage
Iris Diaphragm
controls amount of light that reaches specimen, under stage
acts as a control for resolution and contrast IN LM
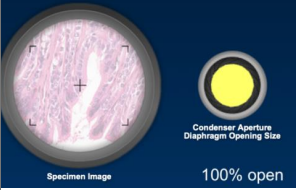
Opening the diaphragm too much
glare and loss of contrast
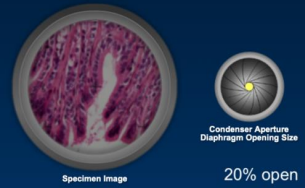
Closing the diaphragm too much
increased diffraction and loss of resolution
Intermediate position 60-90% opening
optimal resolution and contrast
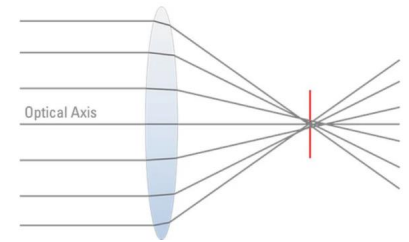
Aberrations
“distortion of an image” or “lens errors”
interaction of light with glass lenses
what are the two main types of aberrations
1) Geometrical or Spherical Aberrations
2) Chromatic Aberrations
corrective optics
aberations can be fixed using a series of optical lenses to counteract
Spherical Aberrations
blurring or distortion of image
light rays from the periphery of lens focusing at different points (before or after) those from the center
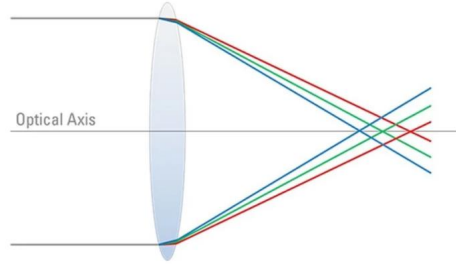
Chromatic Aberrations:
blurring or color fringing of images
component wavelengths (colors) focusing at different points
light path in LM
ocular lens → objective lens → speciman → condenser lans → diaphram