BIOL 242 Practical Test #1 Study Guide
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
anterior pituitary gland
glandular tissue that secretes: ACTH, PRL, GH, TSH, FSH, LH
posterior pituitary gland
nervous tissue that secretes: ADH and Oxytocin
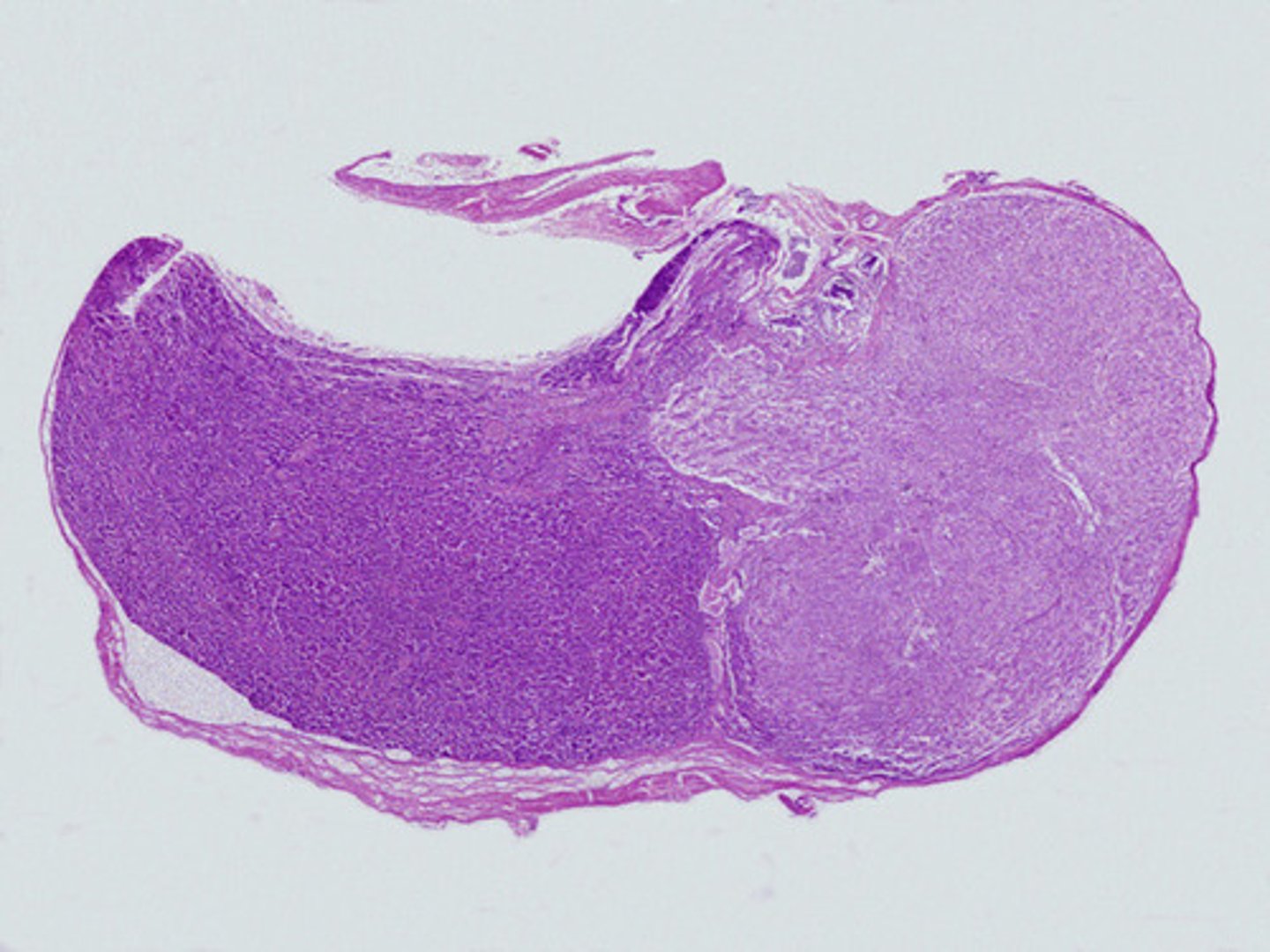
pituitary gland
entire gland, glandular tissue on the left and nervous tissue on the right.
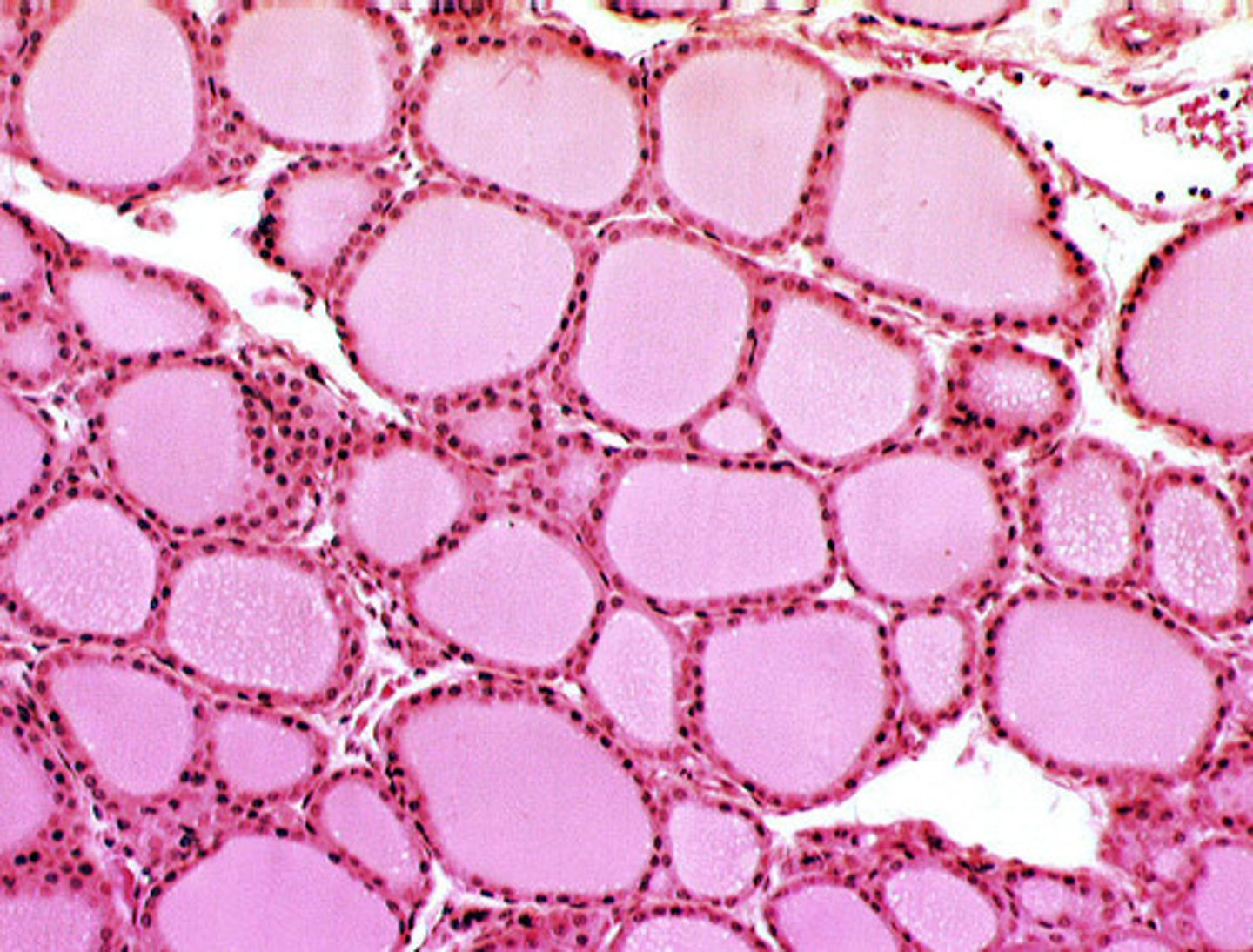
thyroid gland
glandular tissue with follicles that secrete T3 and T4
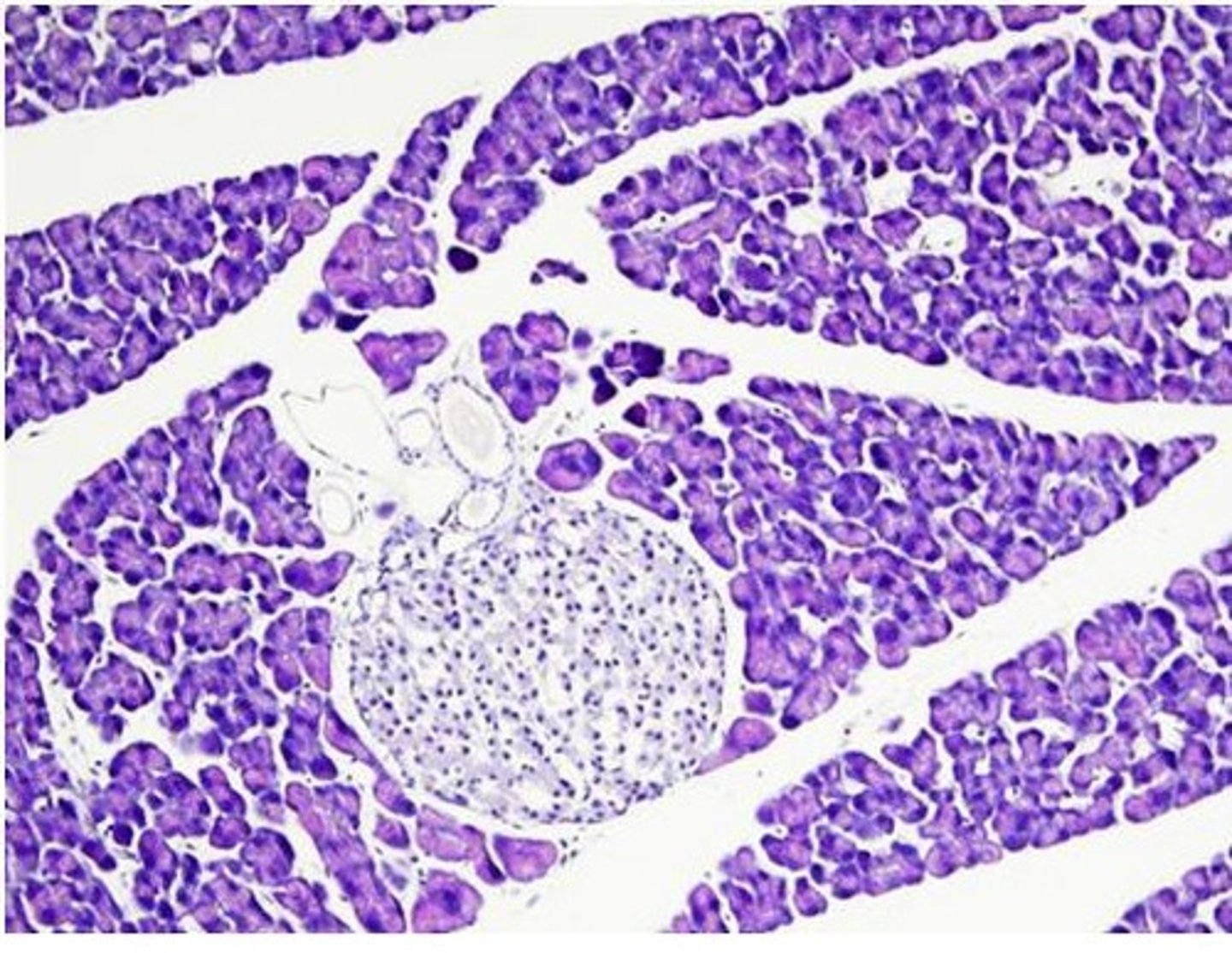
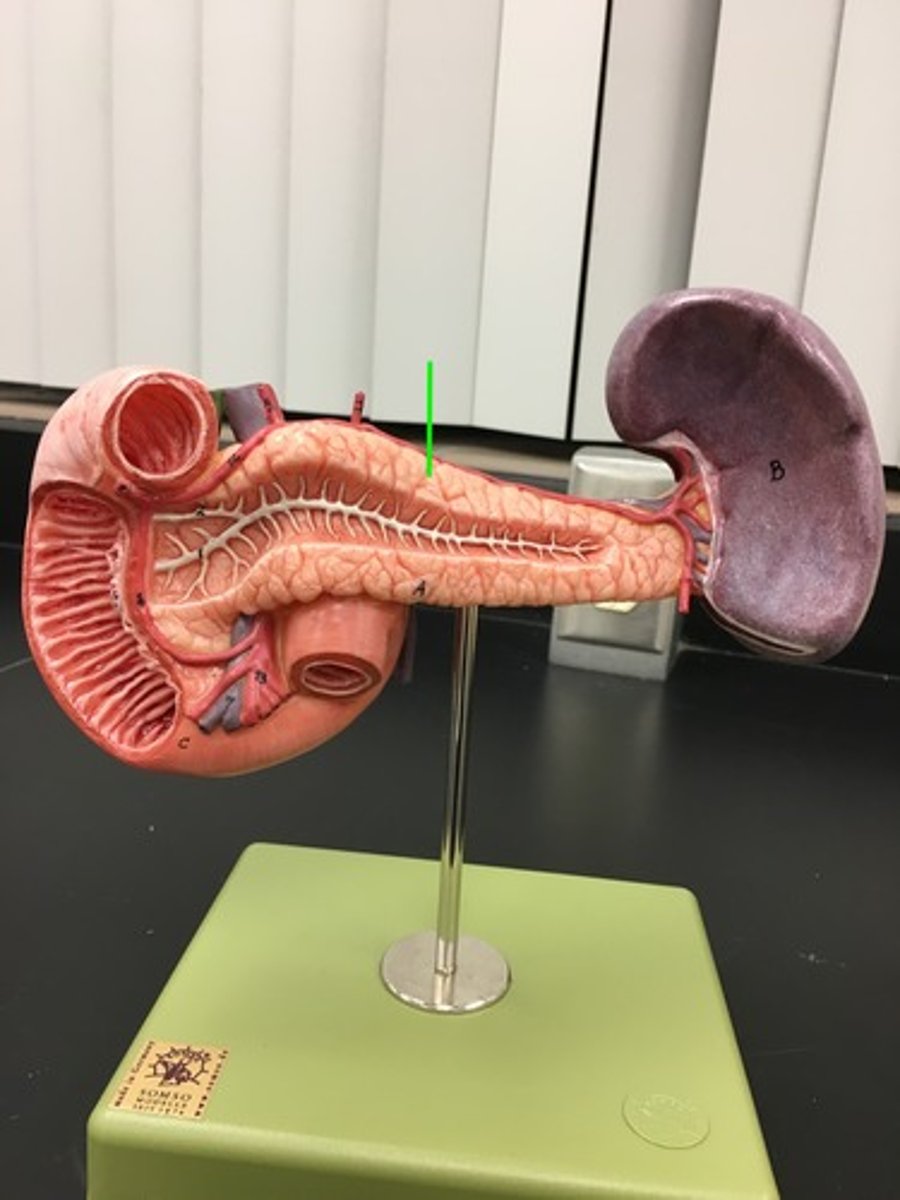
pancreas
mixed gland. Ducts (shown) that secrete digestive enzymes and ions (exocrine function)
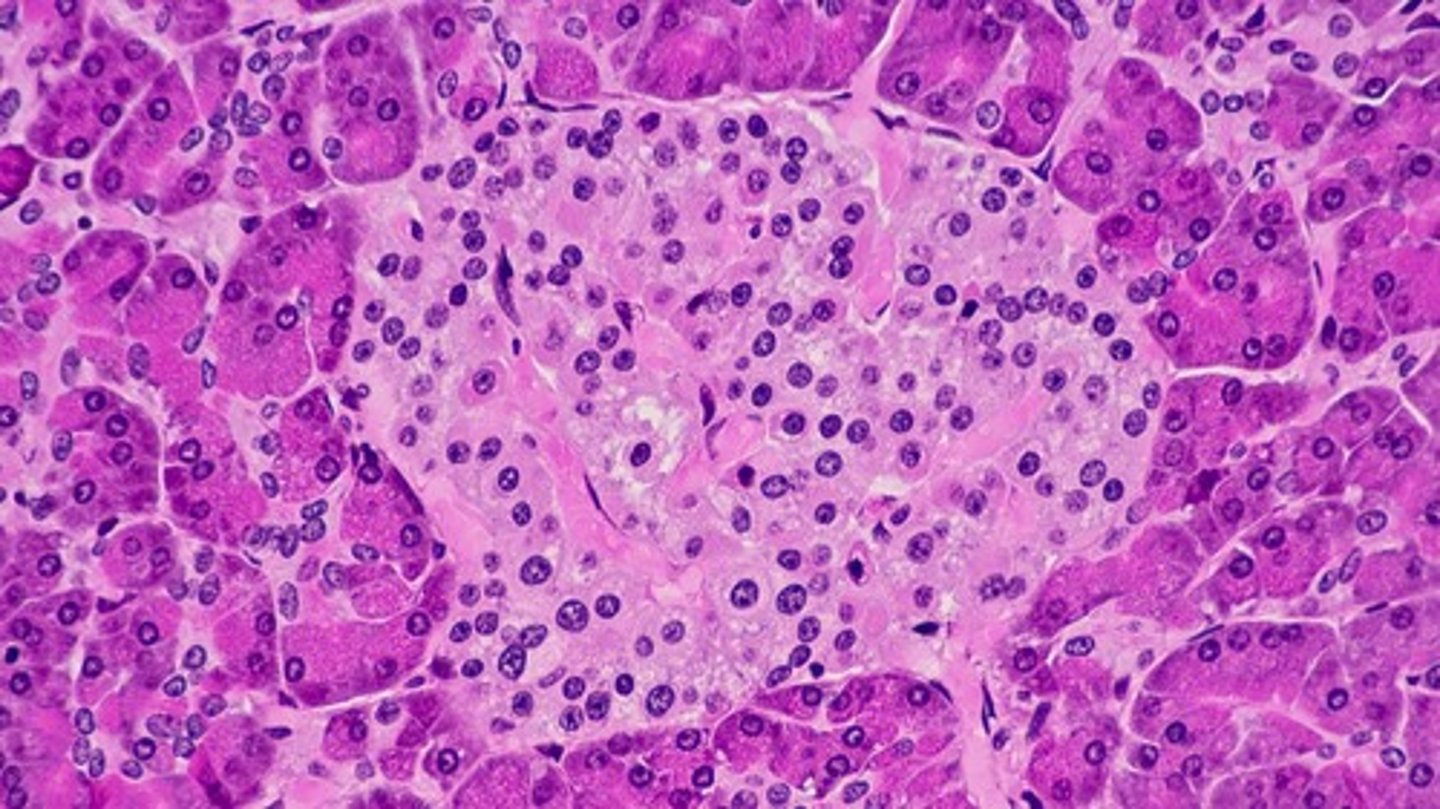
pancreas
mixed gland. Islet of Langerhans (shown) with Alpha Cells that secrete Glucagon and Beta Cells that secrete Insulin (endocrine)
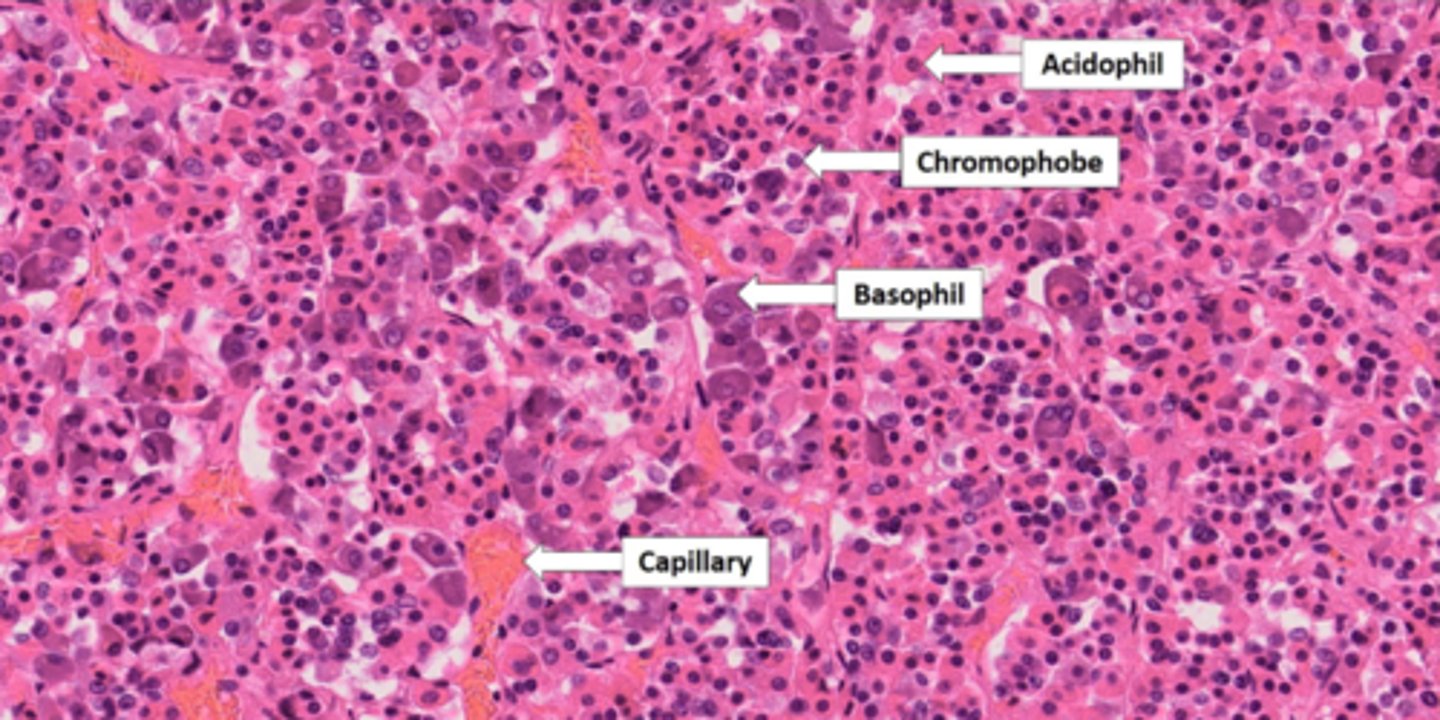
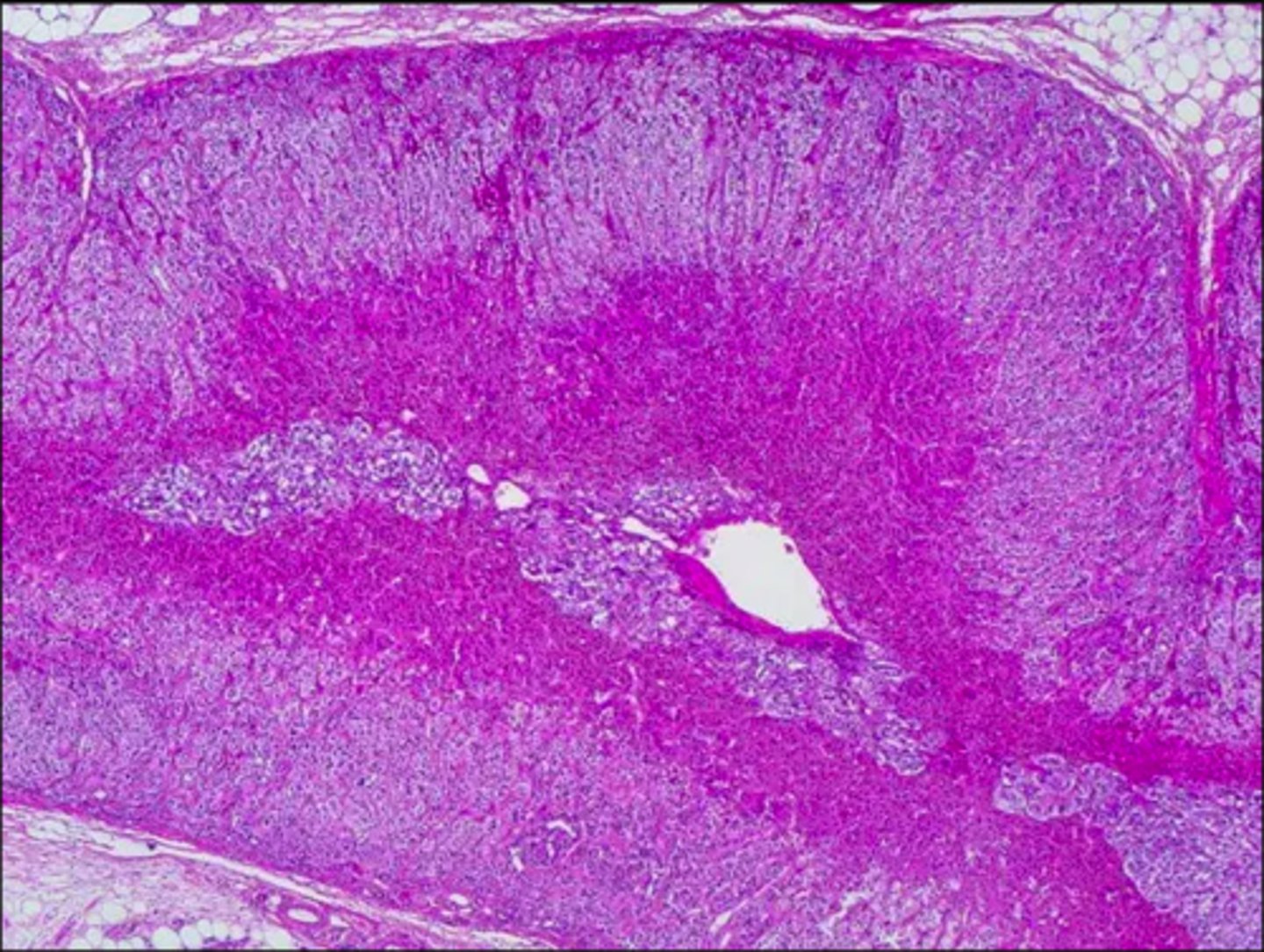
adrenal gland
entire gland. comprised of glandular tissue (outer layers) and nervous tissue (deepest portion).
adrenal cortex
capsule + All Three Zones (glandular tissue)
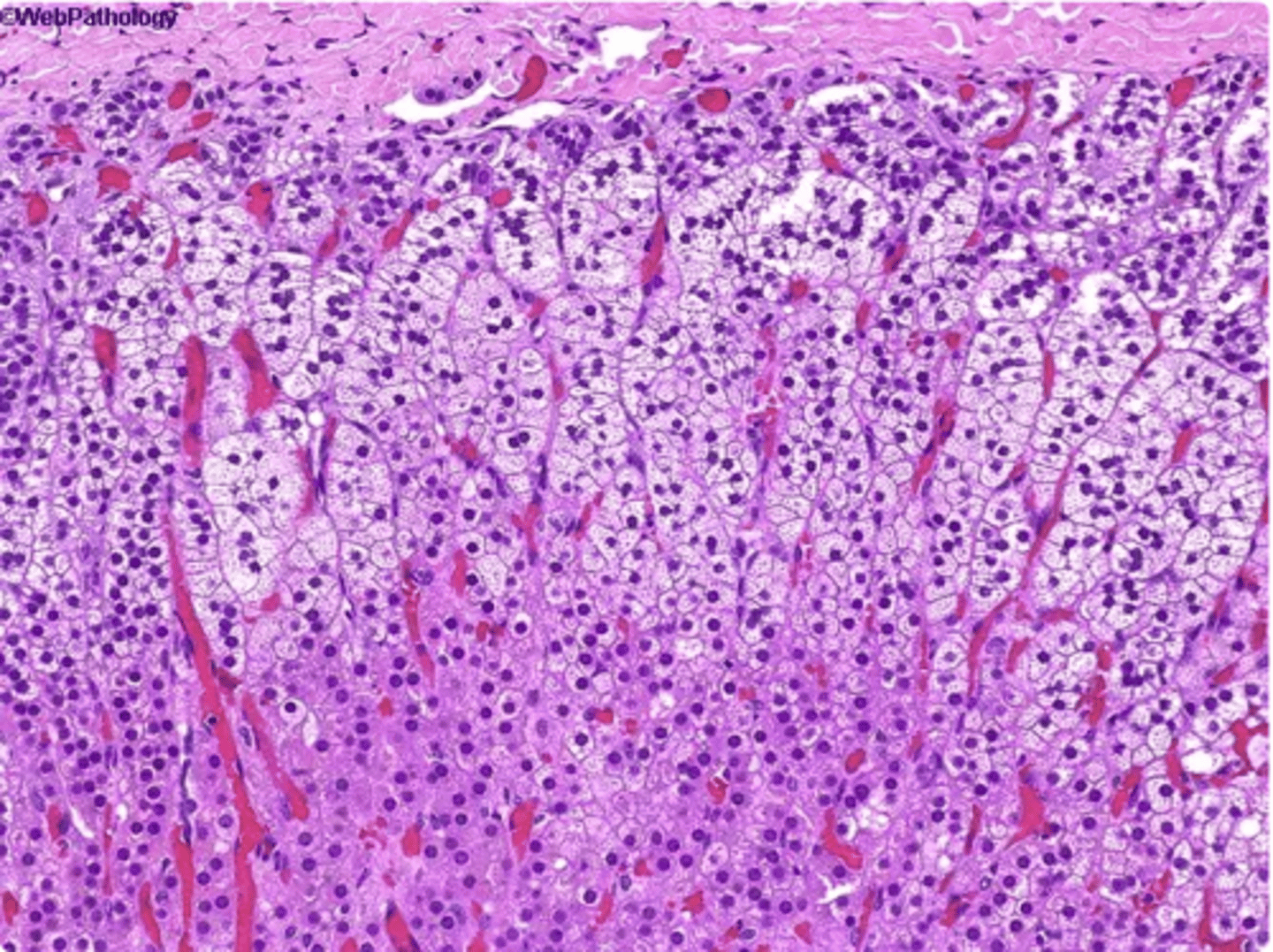
capsule of adrenal gland
connective tissue and the most superficial layer (not a glandular tissue) (generalized term used for a dense fibrous layer surrounding something)
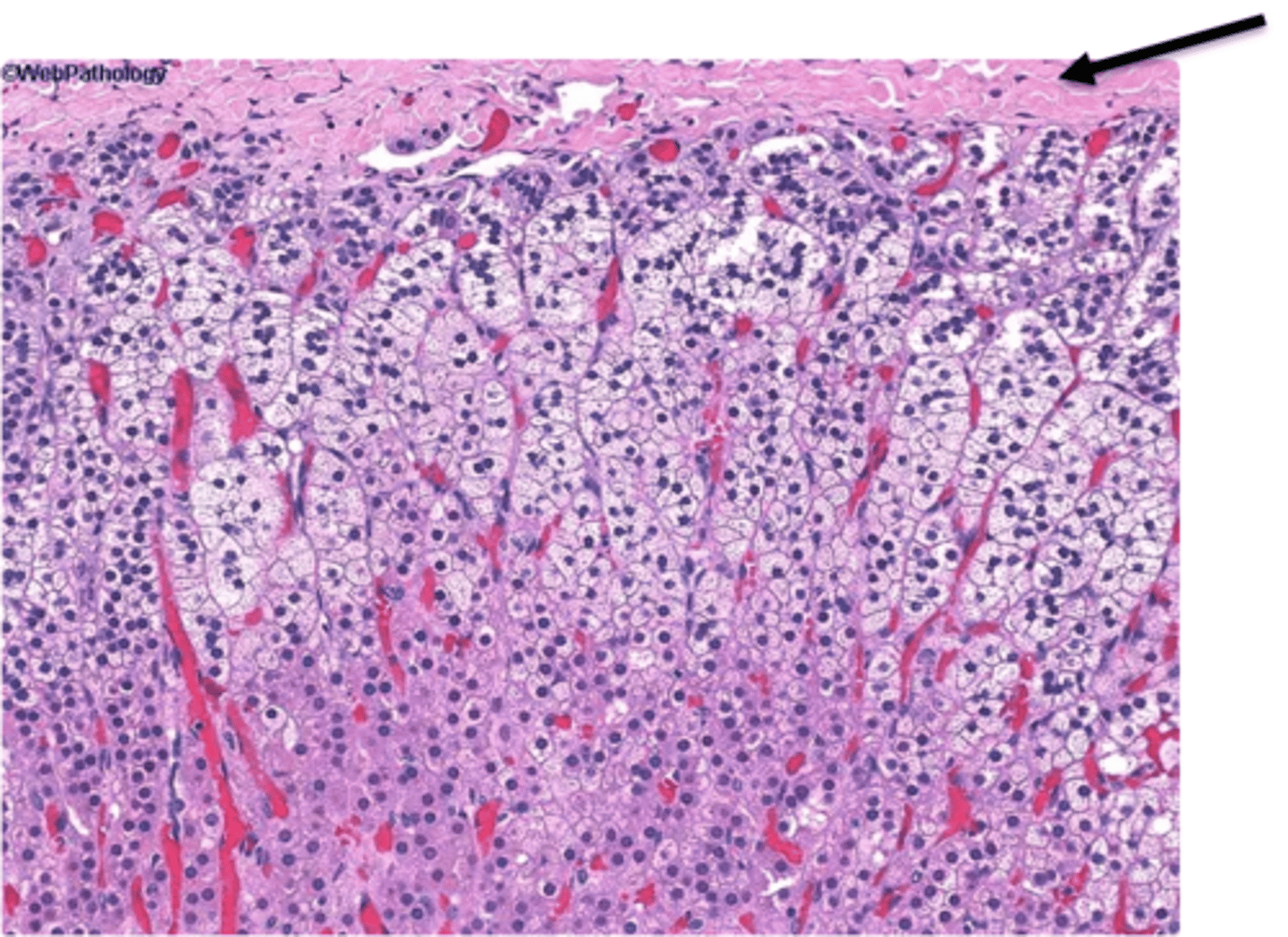
zona glomerulosa of adrenal cortex
outermost glandular tissue layer that secretes aldosterone
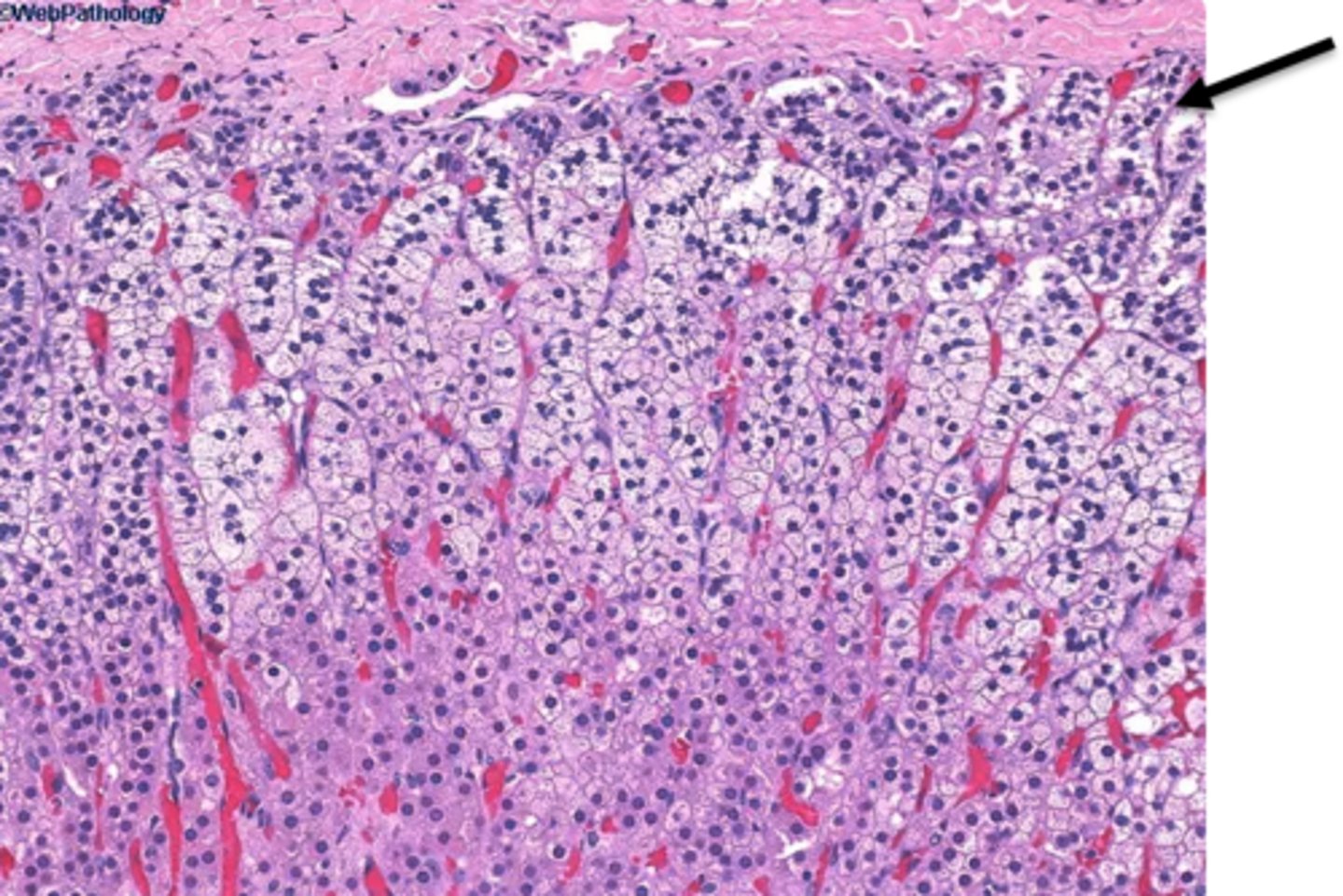
zona fasciculata of adrenal cortex
The middle glandular tissue layer that secretes cortisol
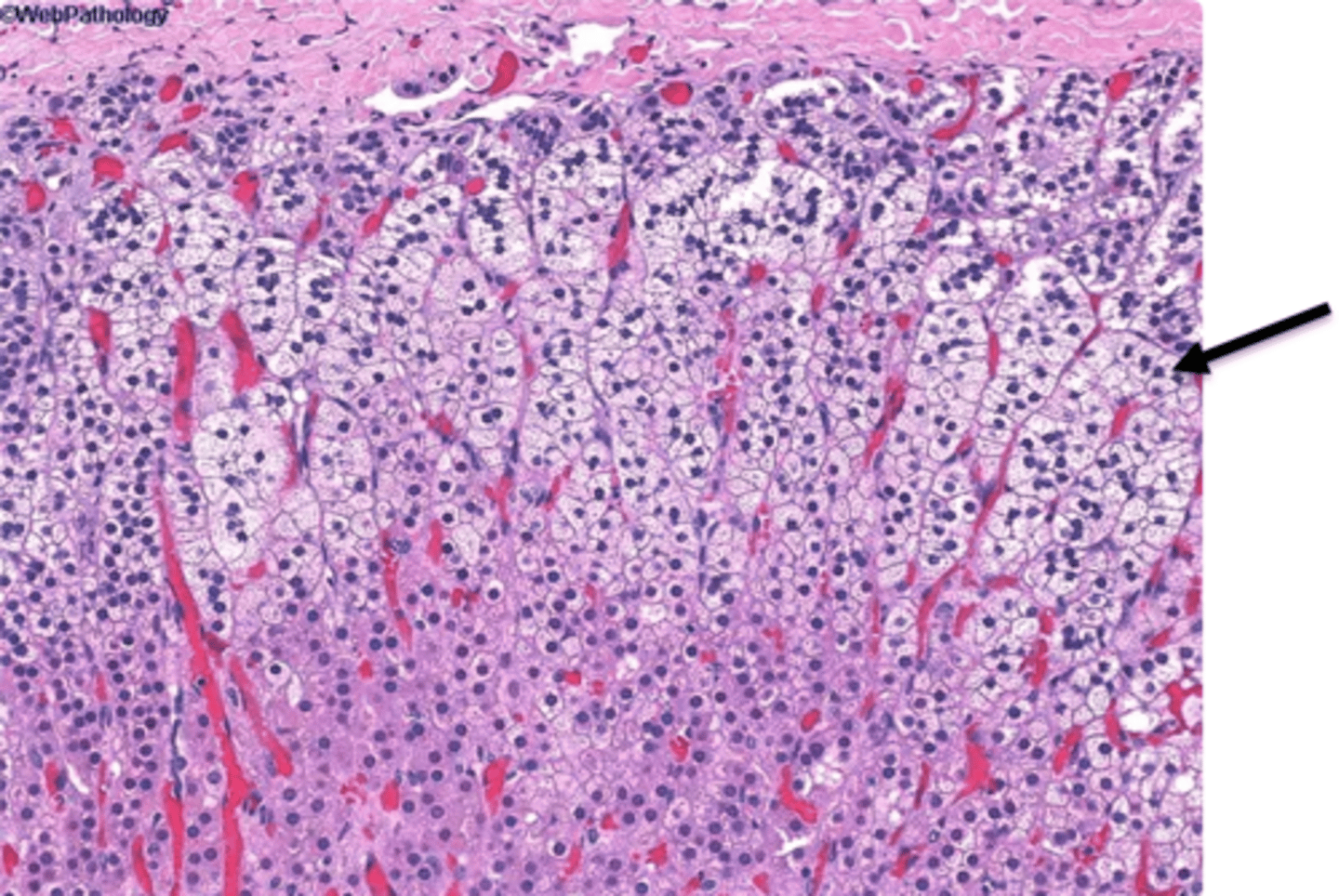
zona reticularis of adrenal cortex
deepest glandular tissue layer that secretes androgens (not to be confused with nervous tissue, and the deepest layer of the entire gland).
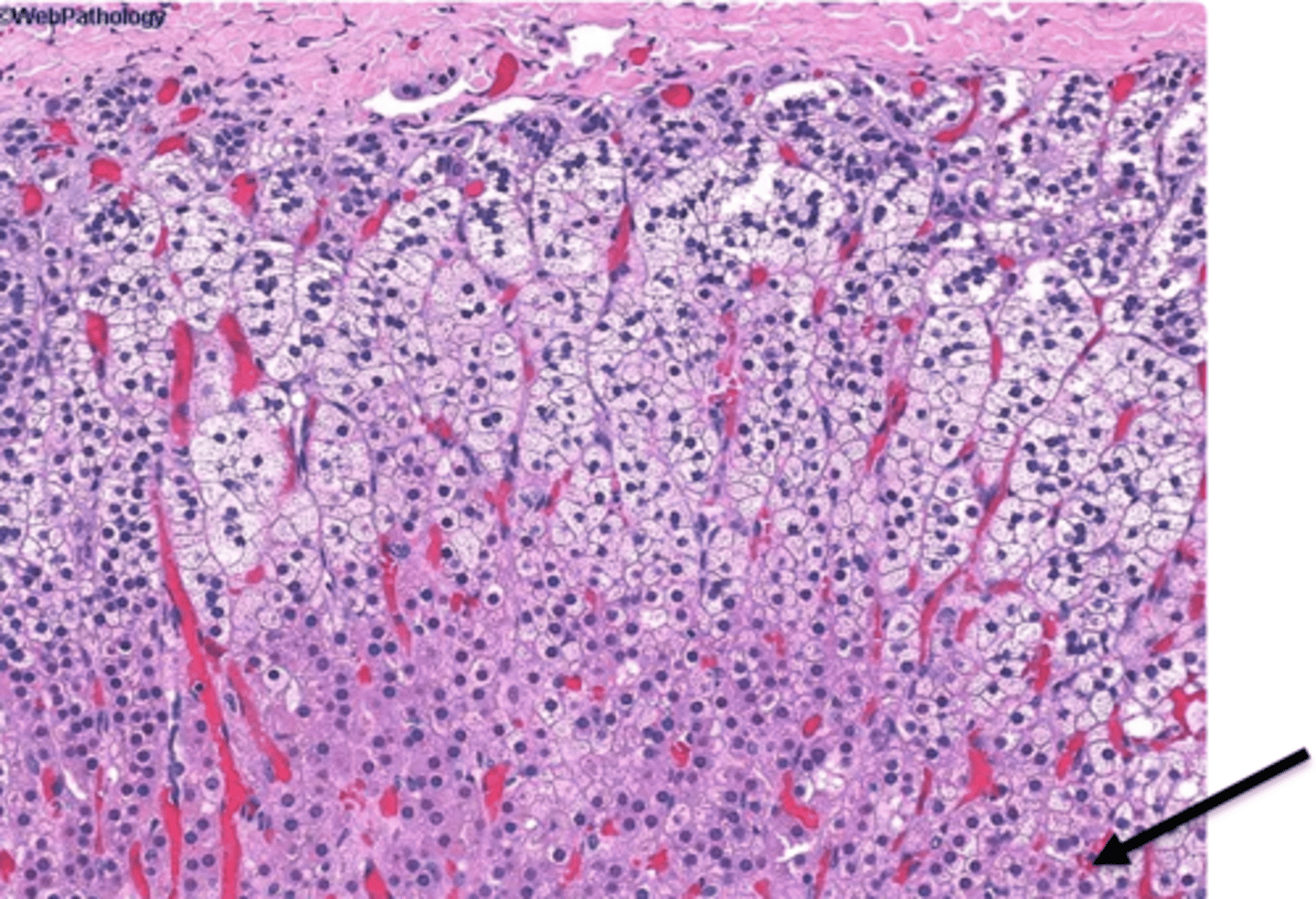
adrenal medulla
deepest nervous tissue layer that secretes epi & norepi. Under the control of the sympathetic nervous system.
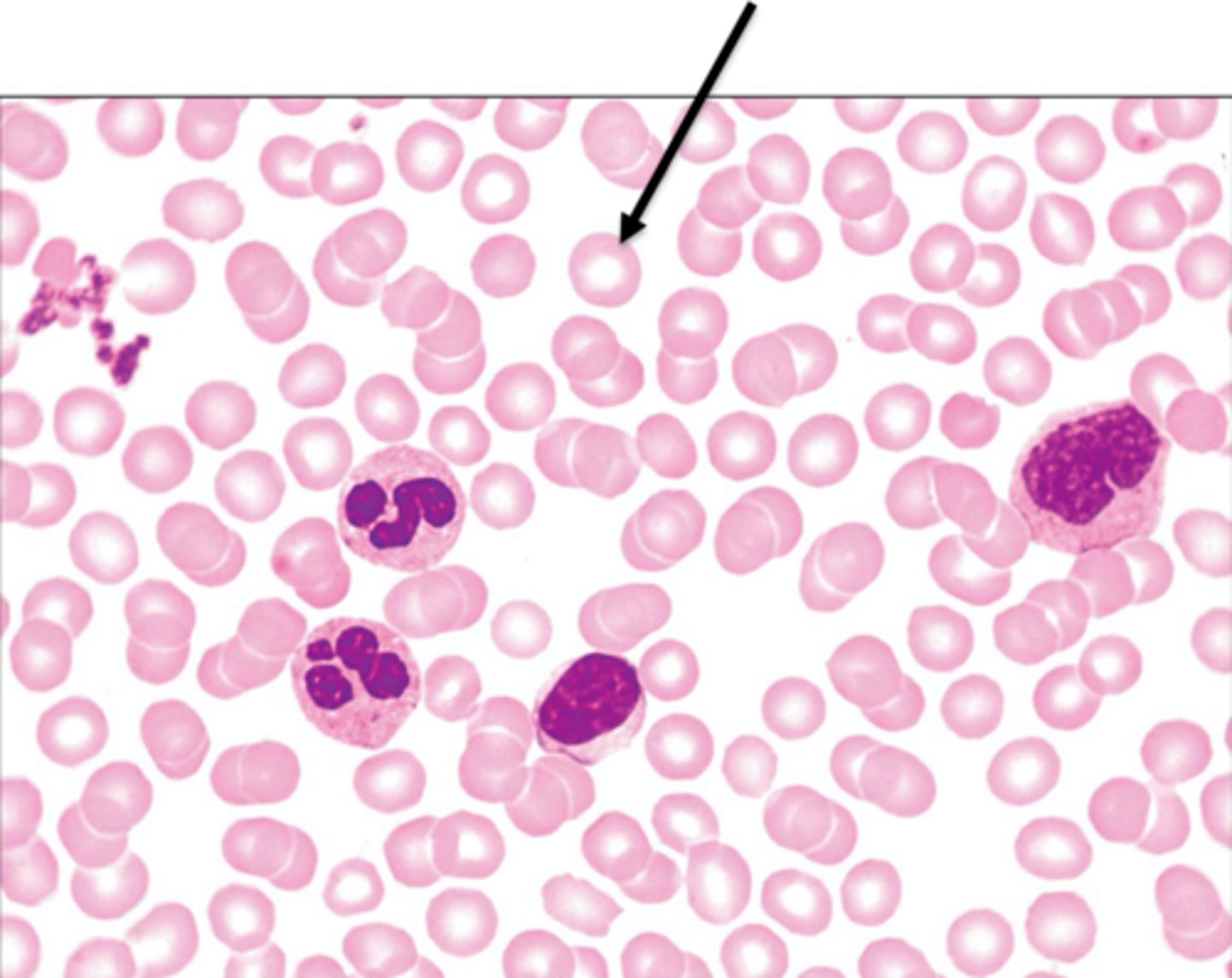
erythrocyte
biconcave shape, large surface area for gas exchange, filled with hemoglobin. AKA RBC.
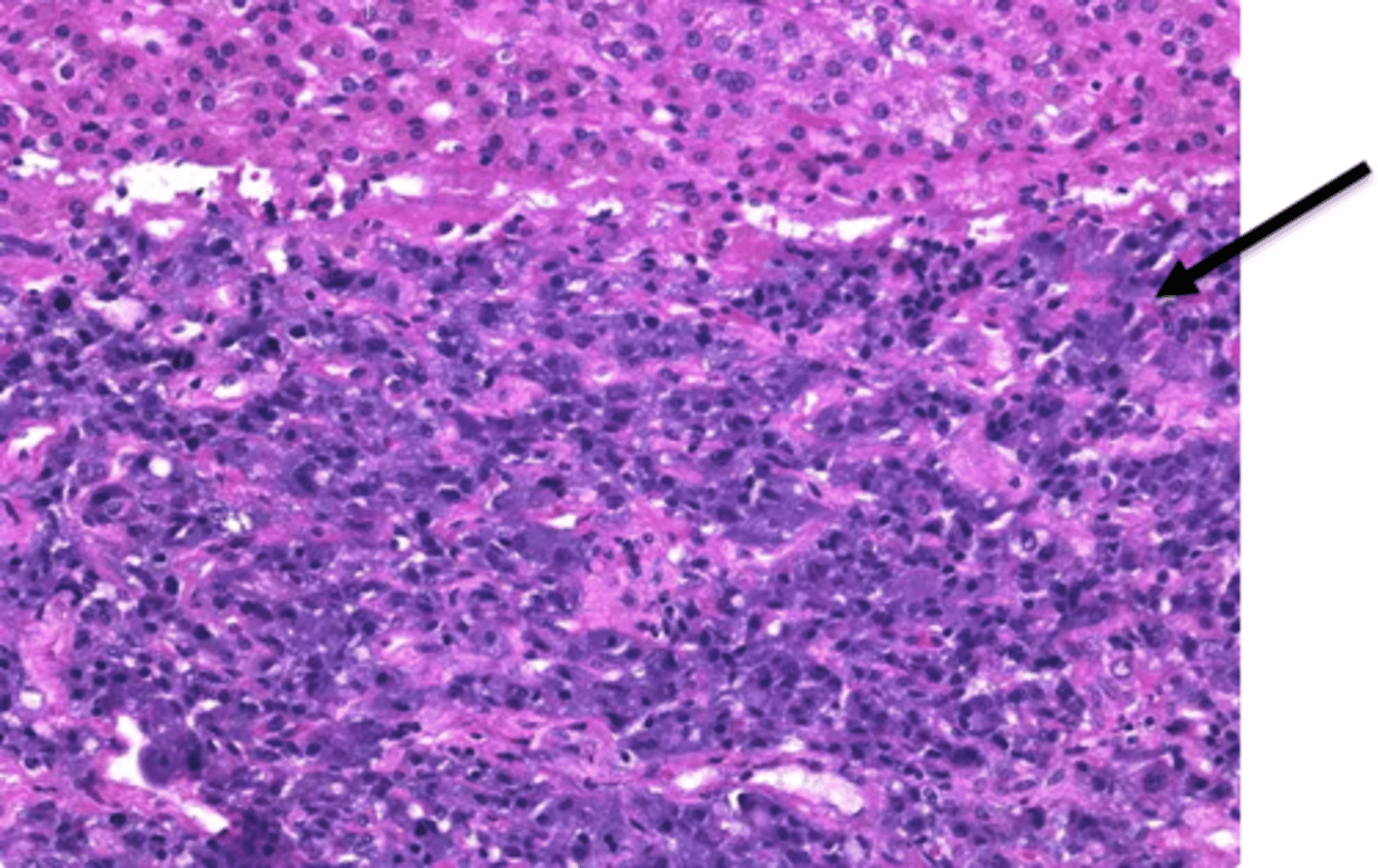
neutrophil
most abundant type of leukocyte AKA WBC, phagocytose bacteria, and have multi-lobed nucli
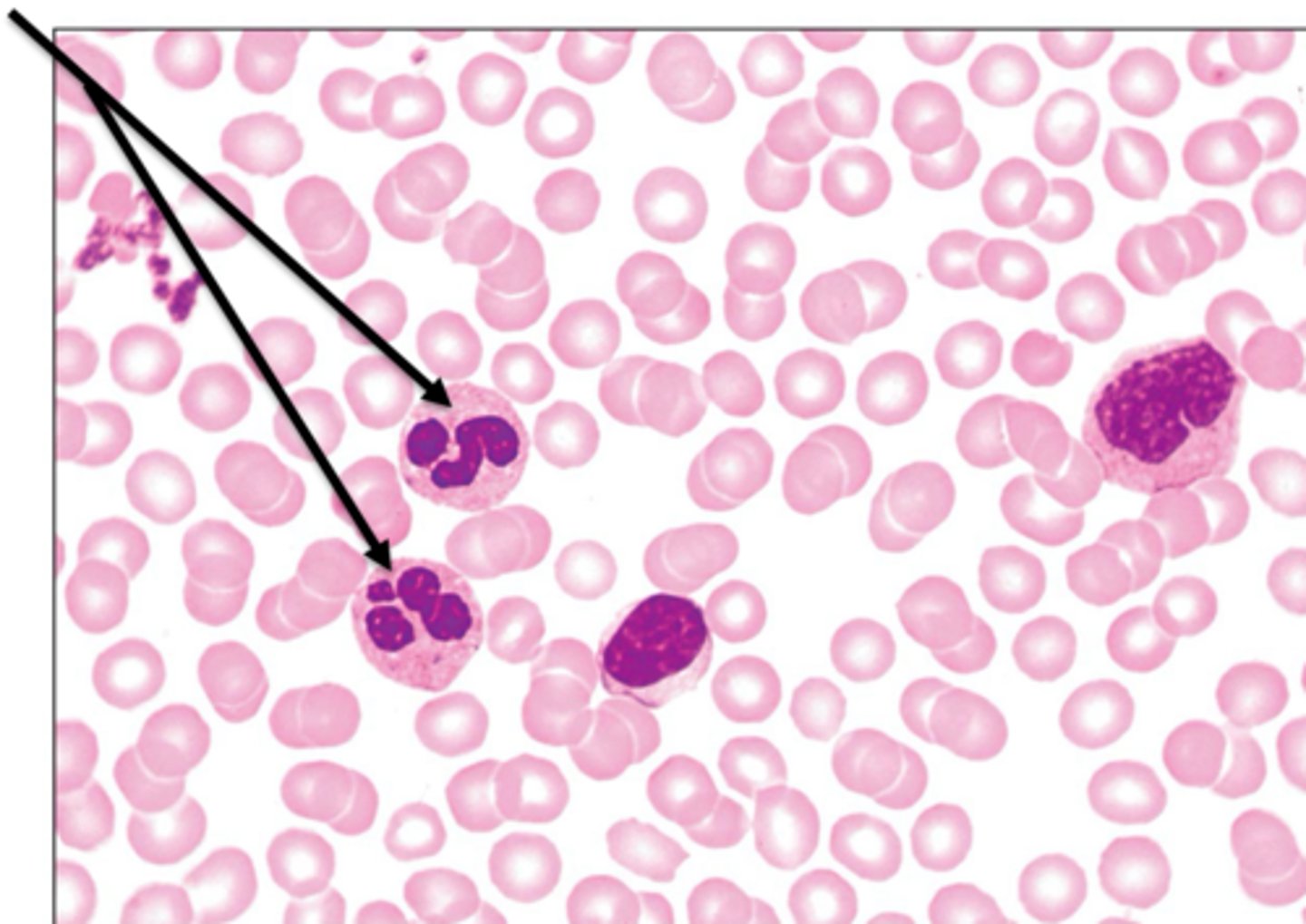
platelets
AKA Thrombocytes, form a temporary plug at damaged vessel sites, contain chemicals for clotting
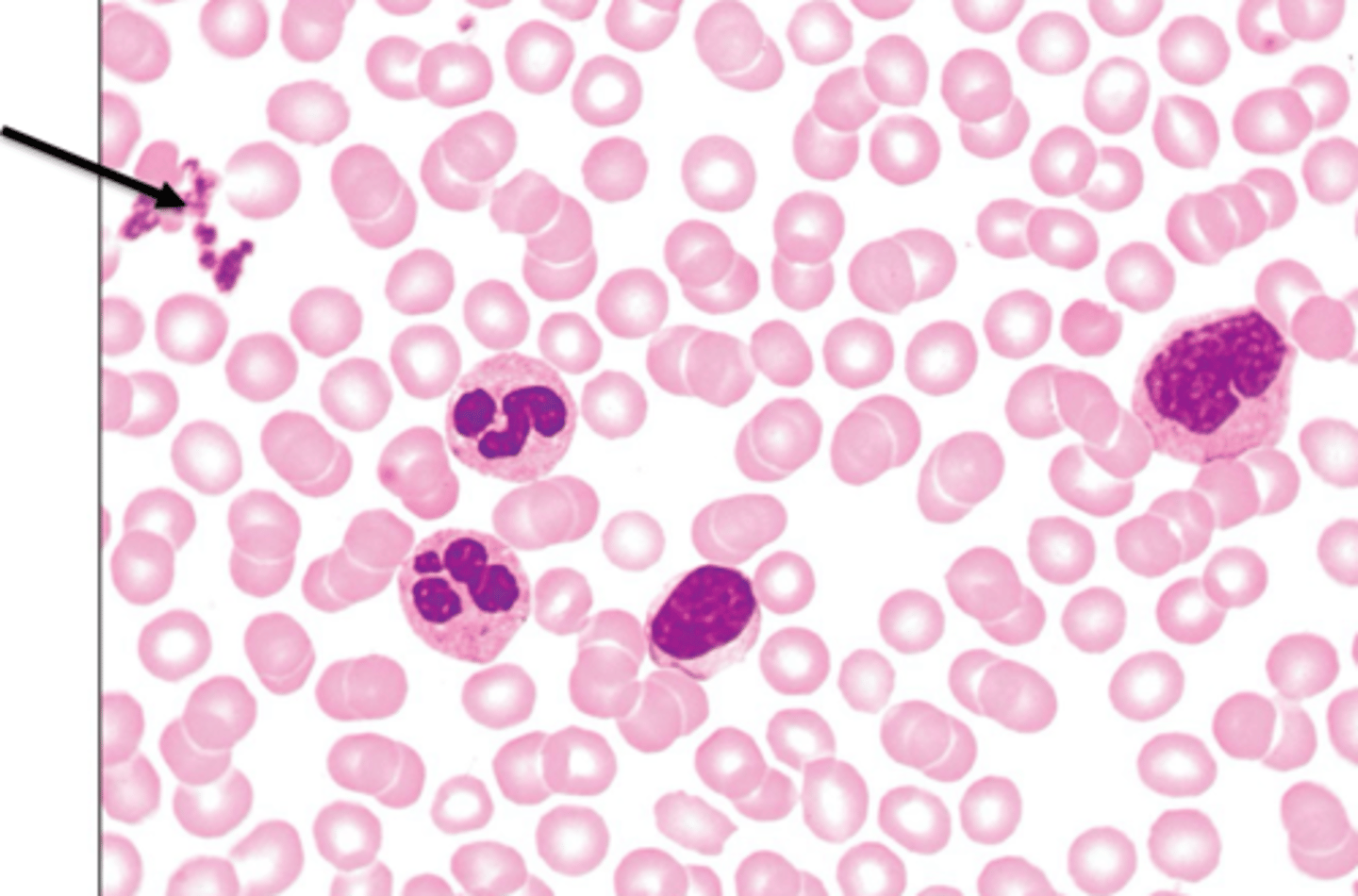
lymphocyte
second most abundant type of leukocyte AKA WBC, two sub types: b cells = make antibodies, t cells = fight infected cells, large nucli, little cytoplasm
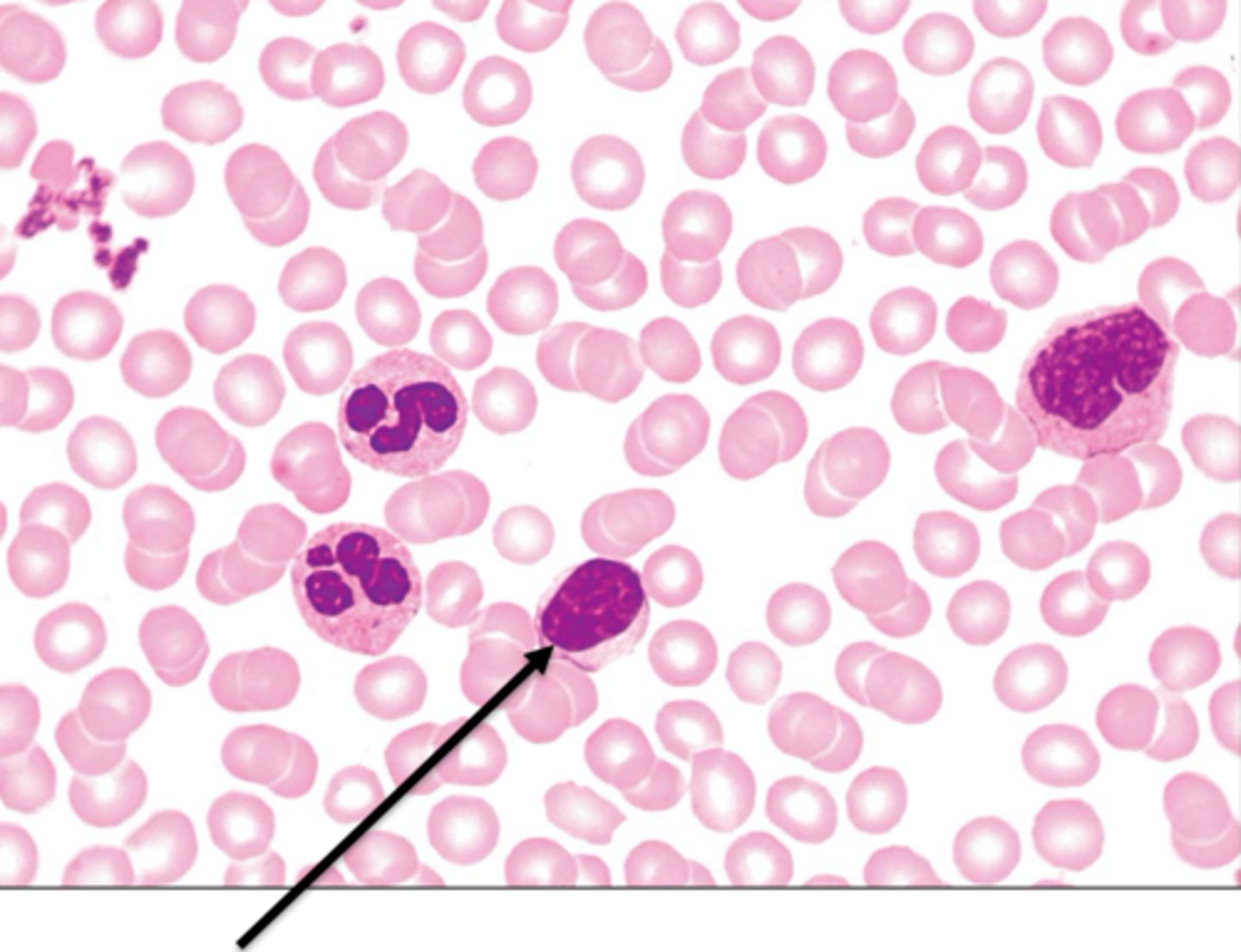
monocyte
largest leukocyte AKA WBC, phagocytose bacteria, viruses, dead cells, then leave circulation to become macrophages in the tissues, kidney shaped nucli
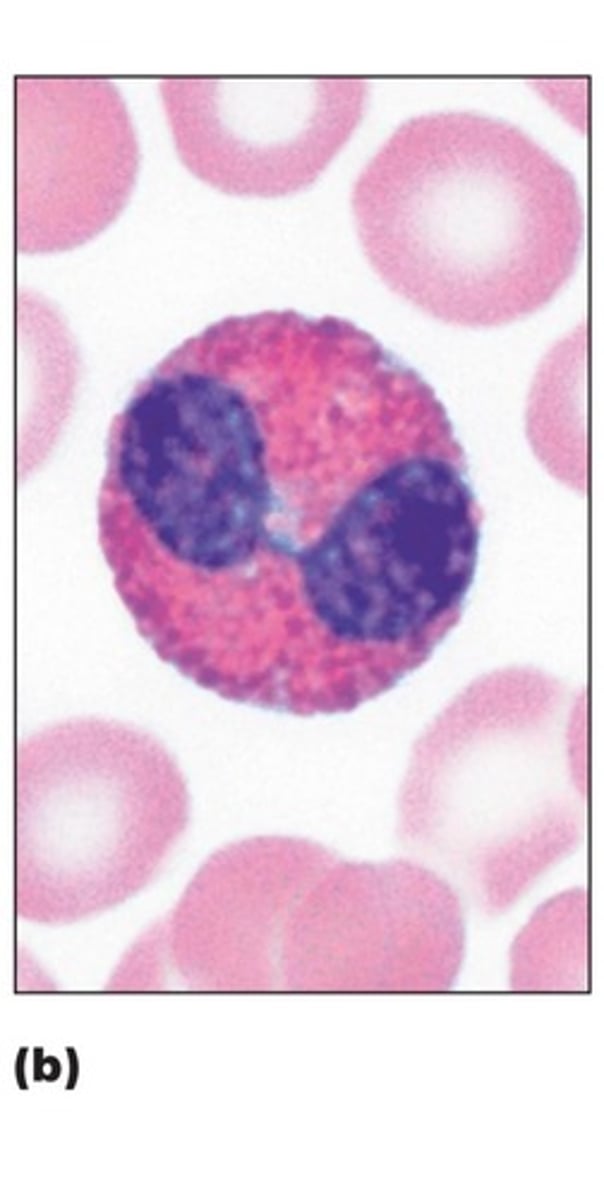
eosinophil
red staining granules, bilobed nucli, attack parasites and also involved in allergies and asthma and plays a role in modulating immune responses.
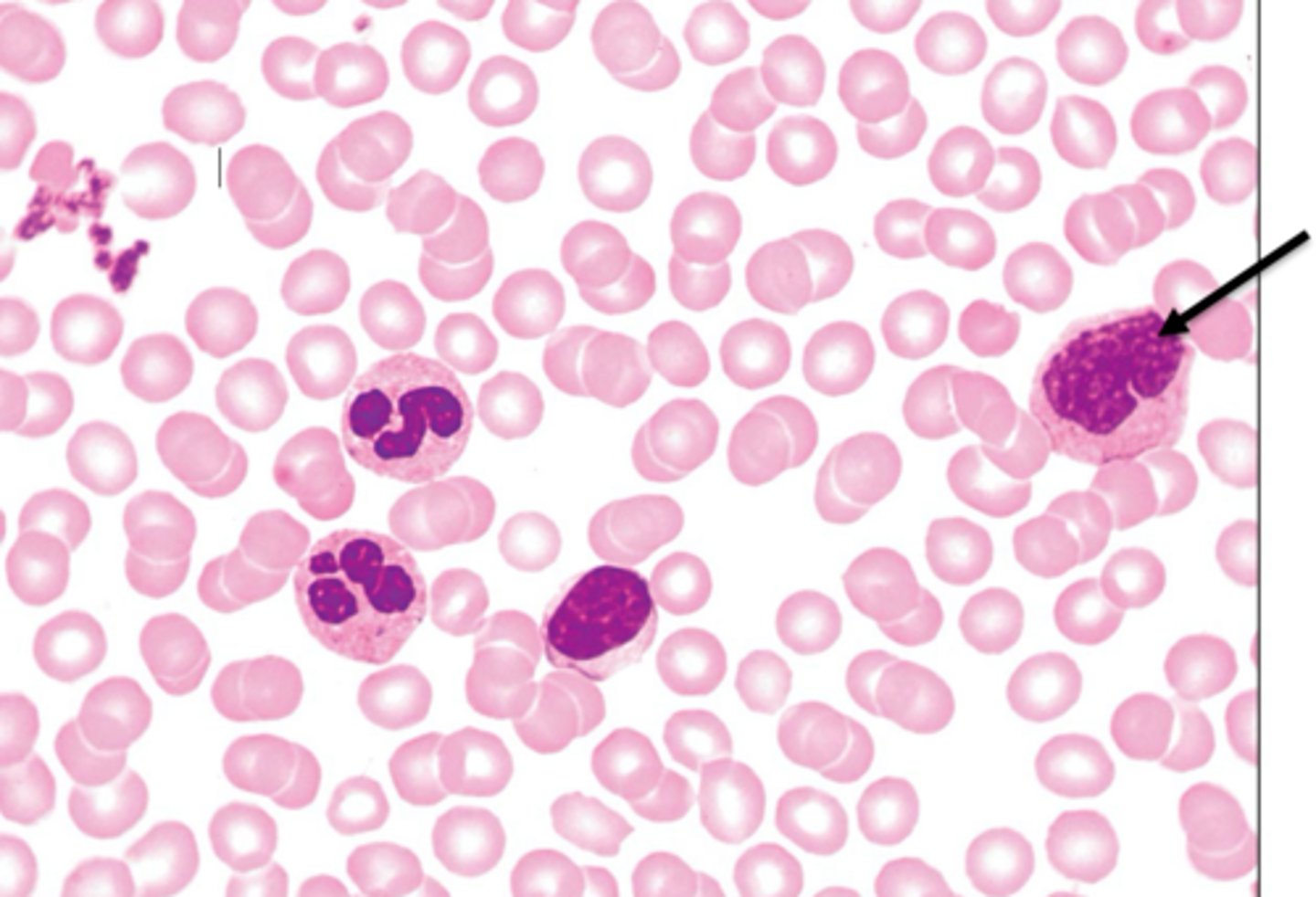
basophil
rarest leukocyte AKA WBC, bilobed nucli but deep purple granules that contain histamine and heparin, promotes inflammation and allergic reactions
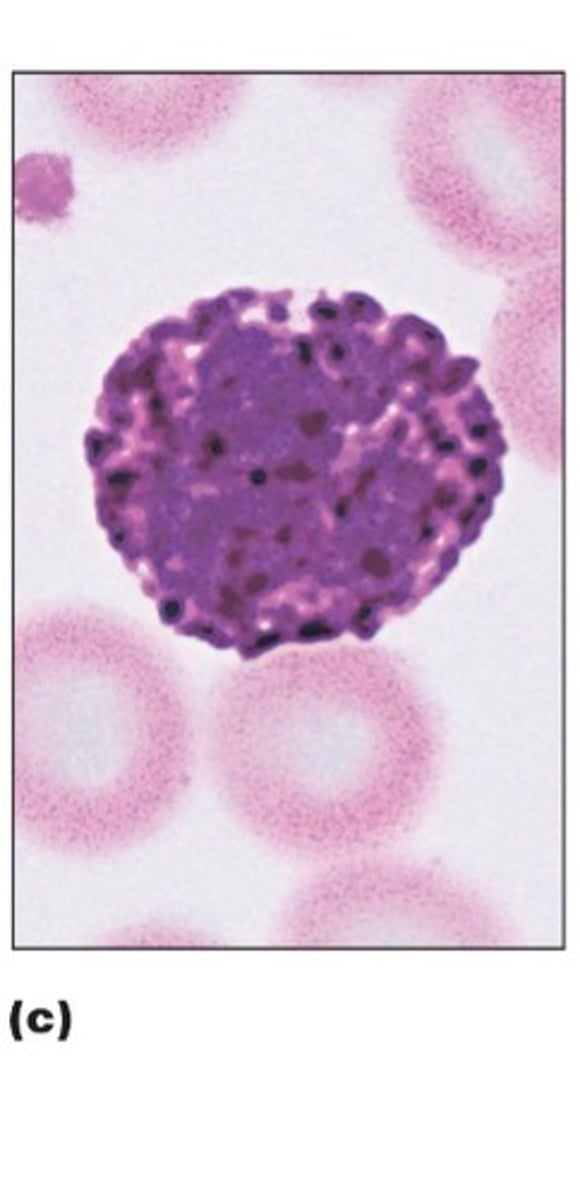
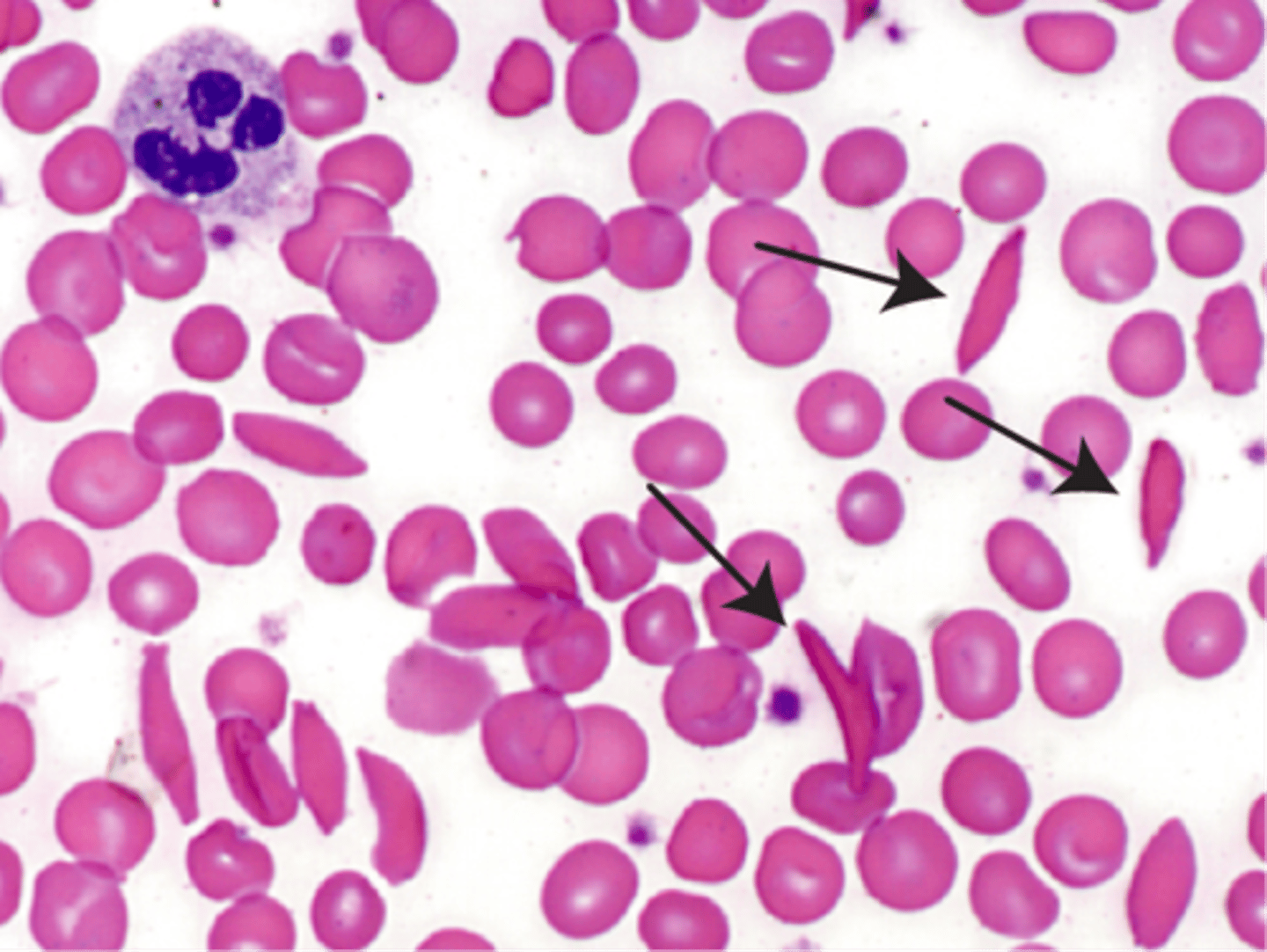
sickle cells
crescent-shaped erythrocytes AKA RBCs saw in a type of anemia, causes pain, RBC destruction and blocks blood flow to tissues
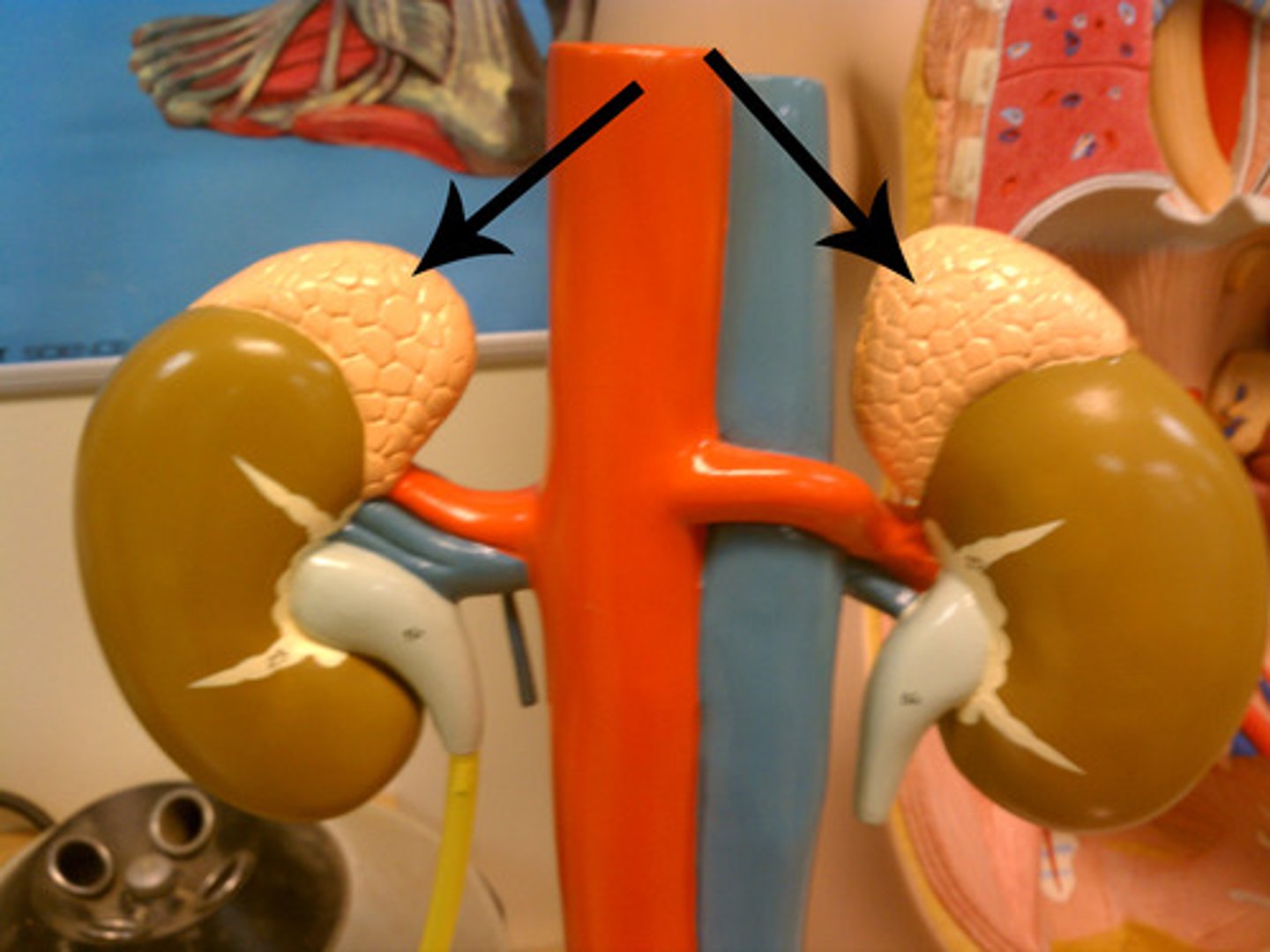
adrenal glands
a pair of endocrine glands that sit just above the kidneys and secrete hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) that help arouse the body in times of stress.
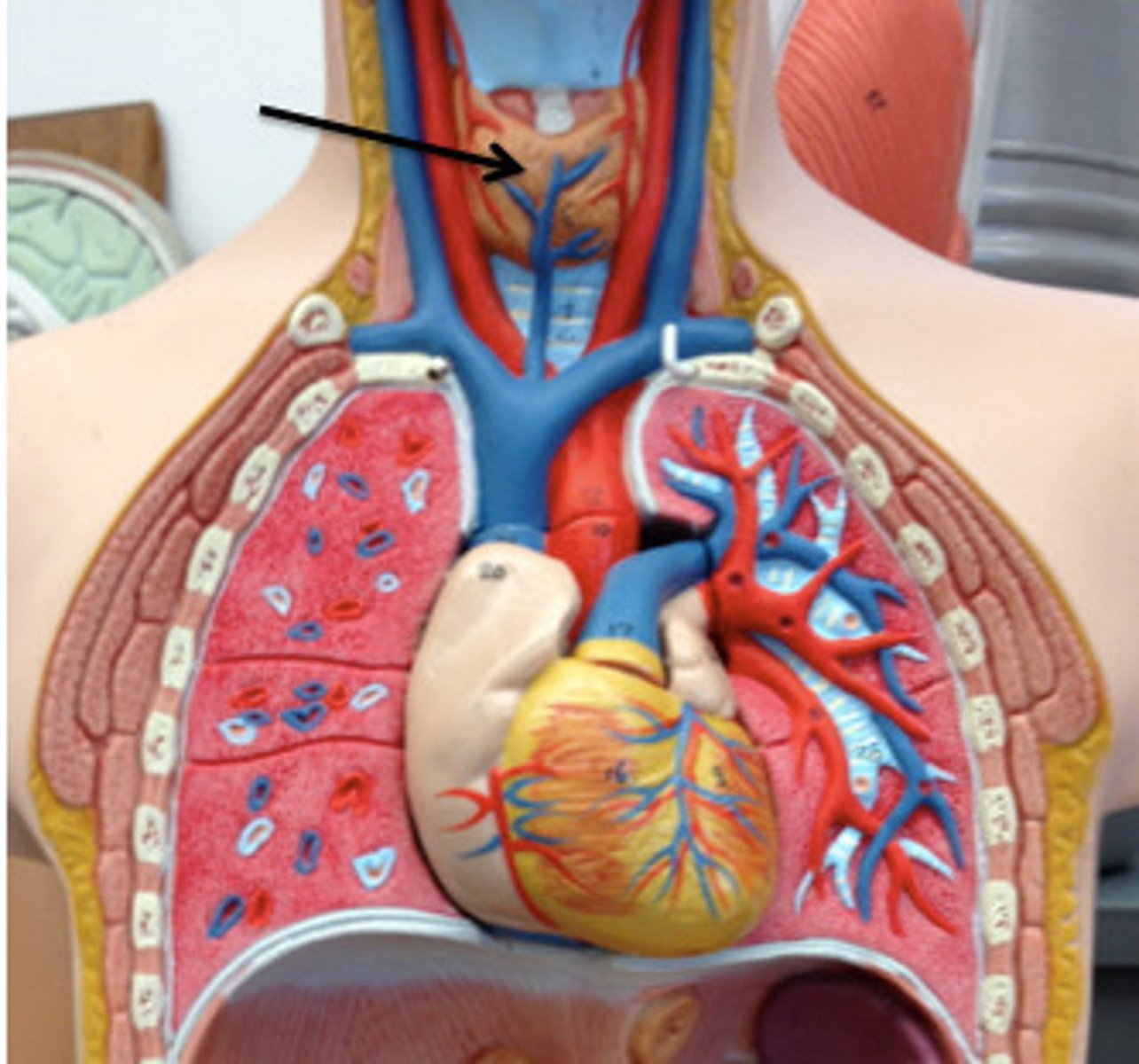
thyroid gland
endocrine gland located in the neck, produces hormones that regulate metabolism, body heat, and bone growth
pancreas
an organ in the abdominal cavity with two roles. The first is an exocrine role: to produce digestive enzymes and bicarbonate, which are delivered to the small intestine. The second is an endocrine role: to secrete insulin and glucagon into the bloodstream to help regulate blood glucose levels.
hypothalamus
a neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.
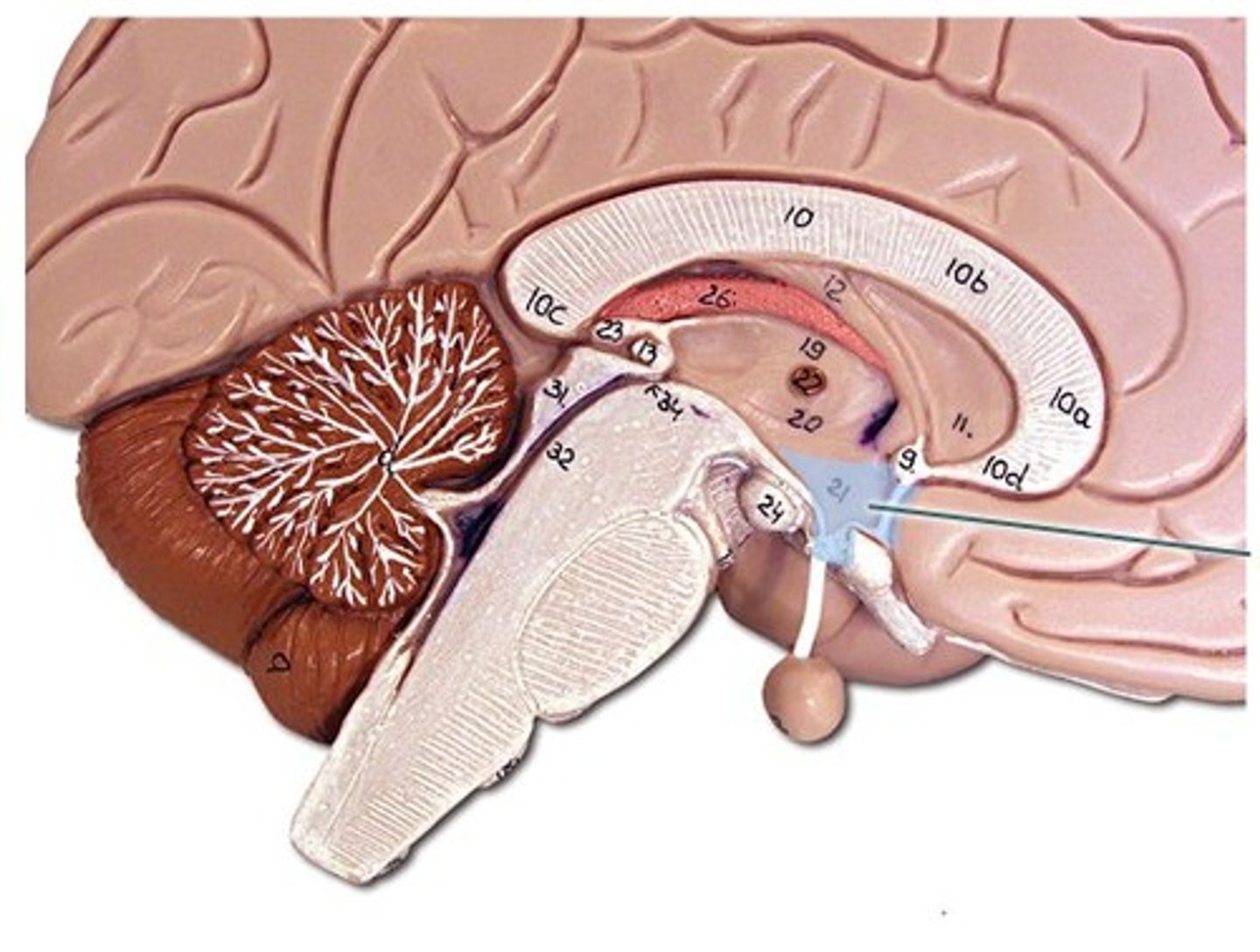
pituitary gland
The endocrine system's most influential gland. Under the influence of the hypothalamus, regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands. Divided into 2 parts anterior and posterior.
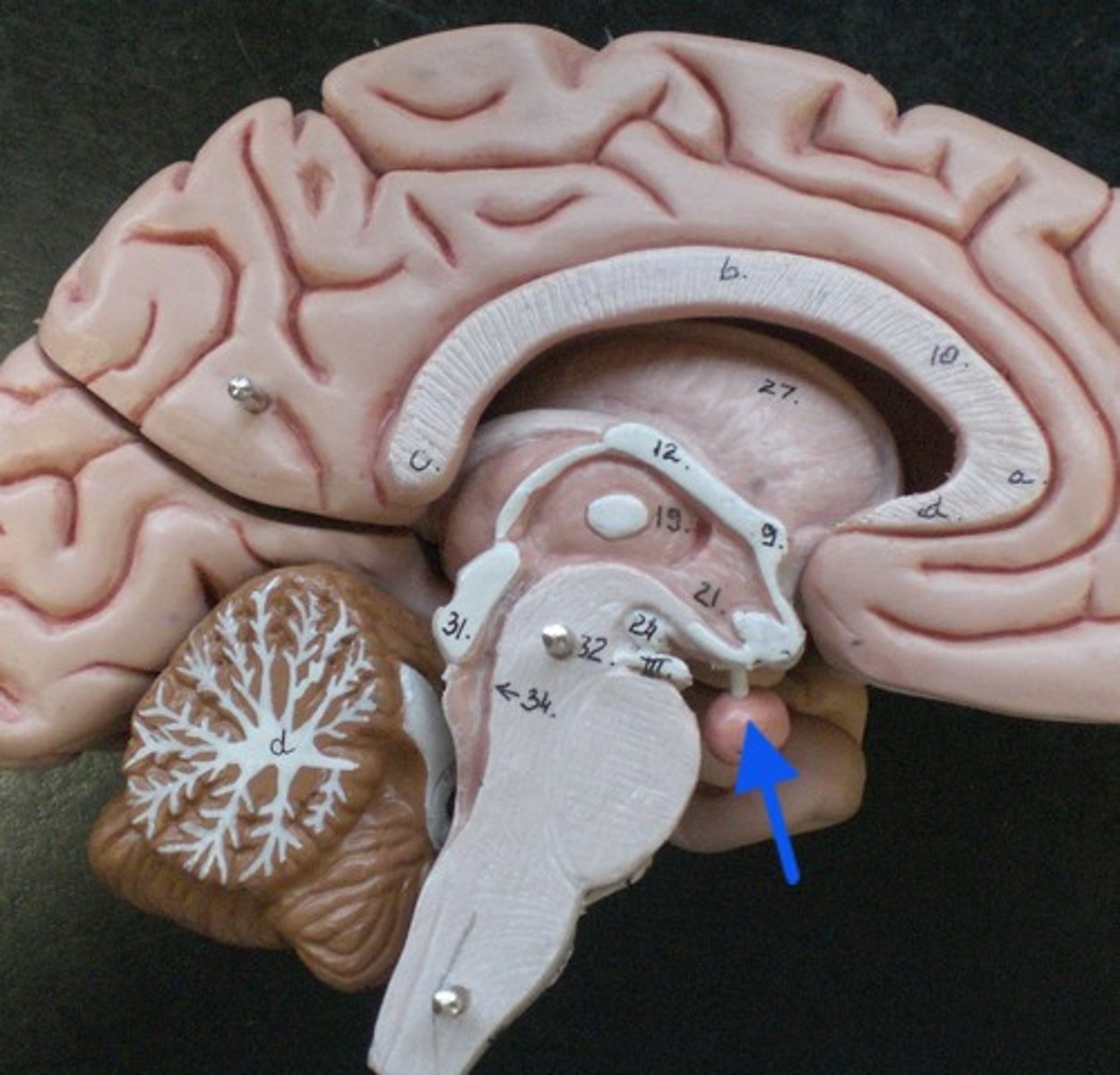
pituitary gland
same gland, different model better showing the 2 parts.
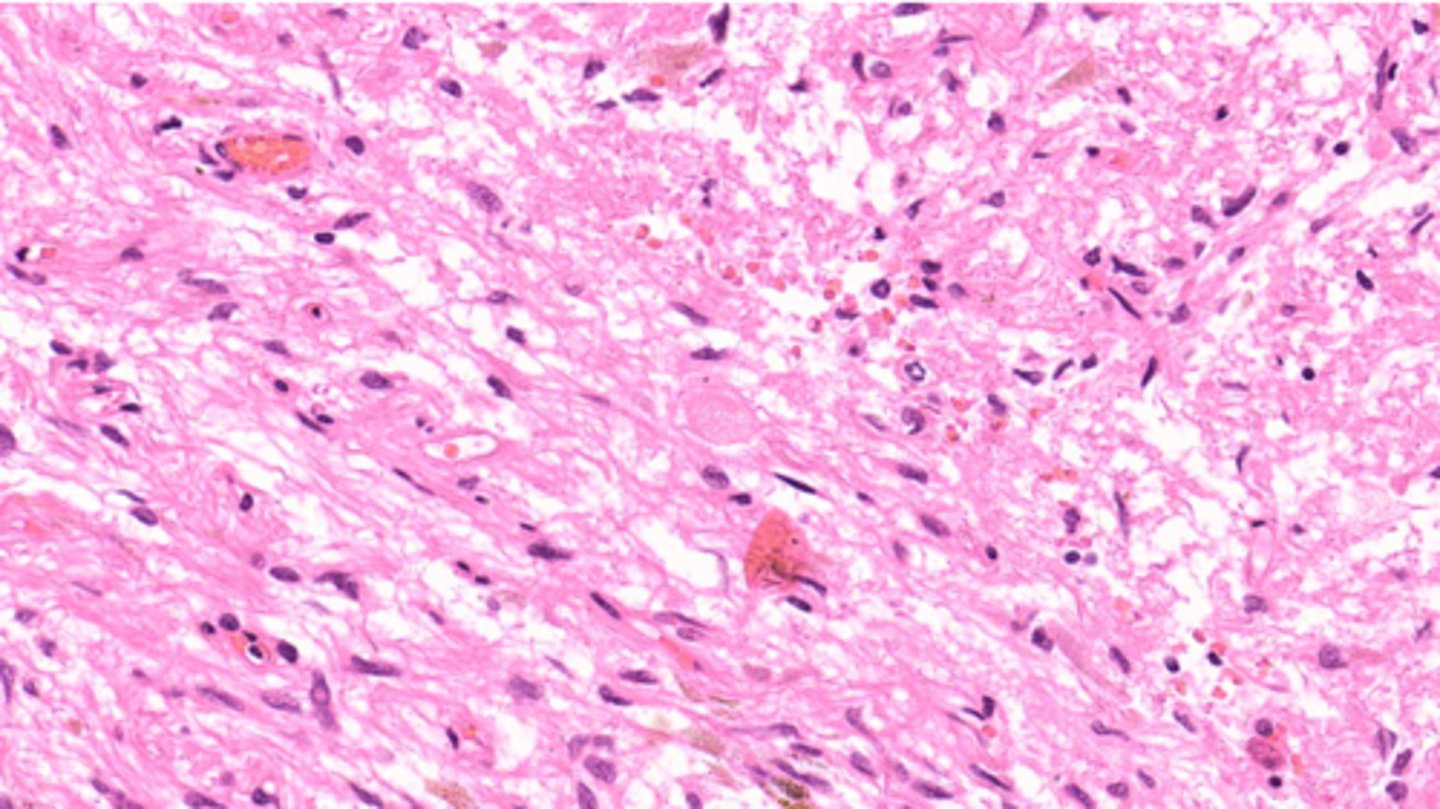
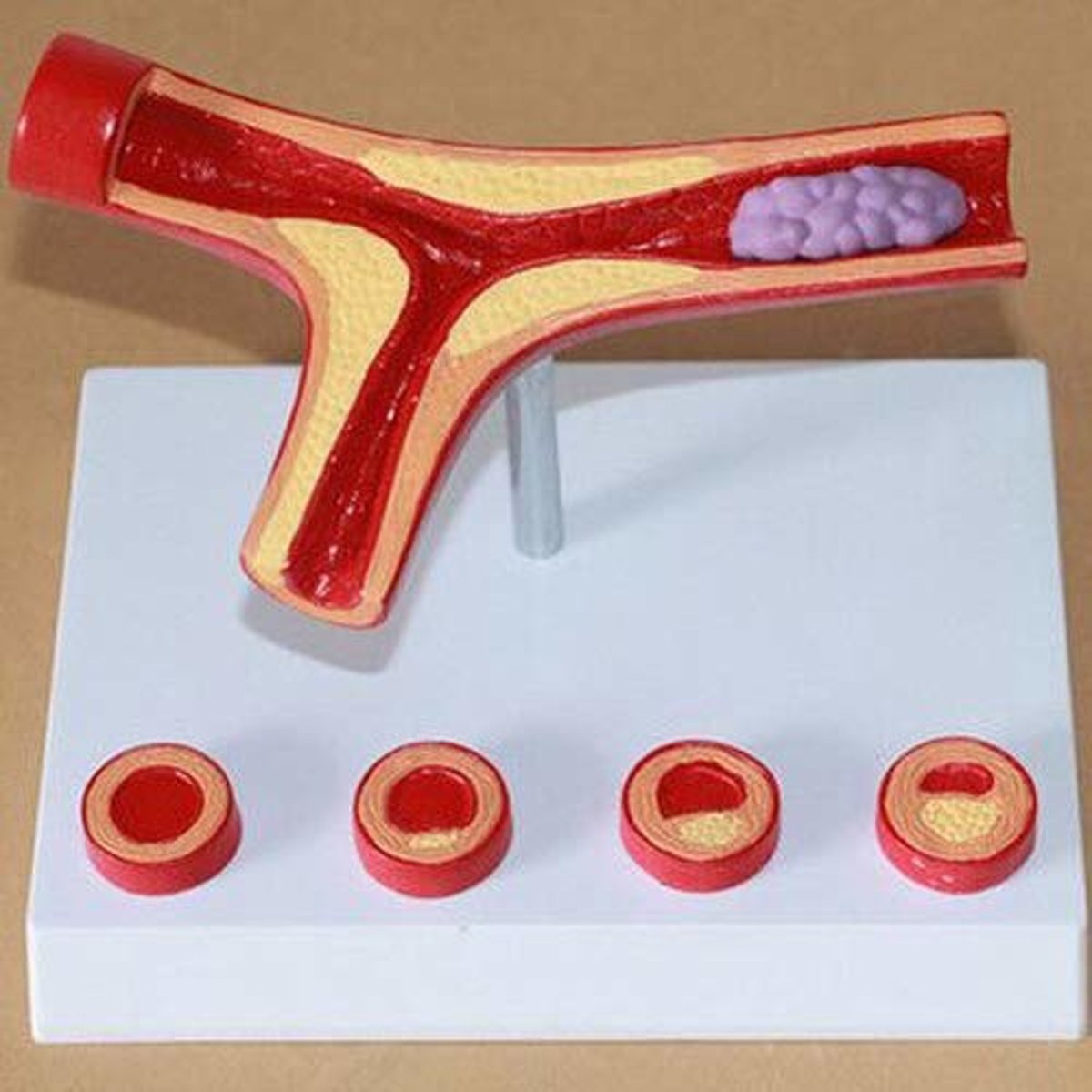
atherosclerosis
condition where fatty deposits (plaques) build up inside the walls of arteries, thickening and stiffening them over time.
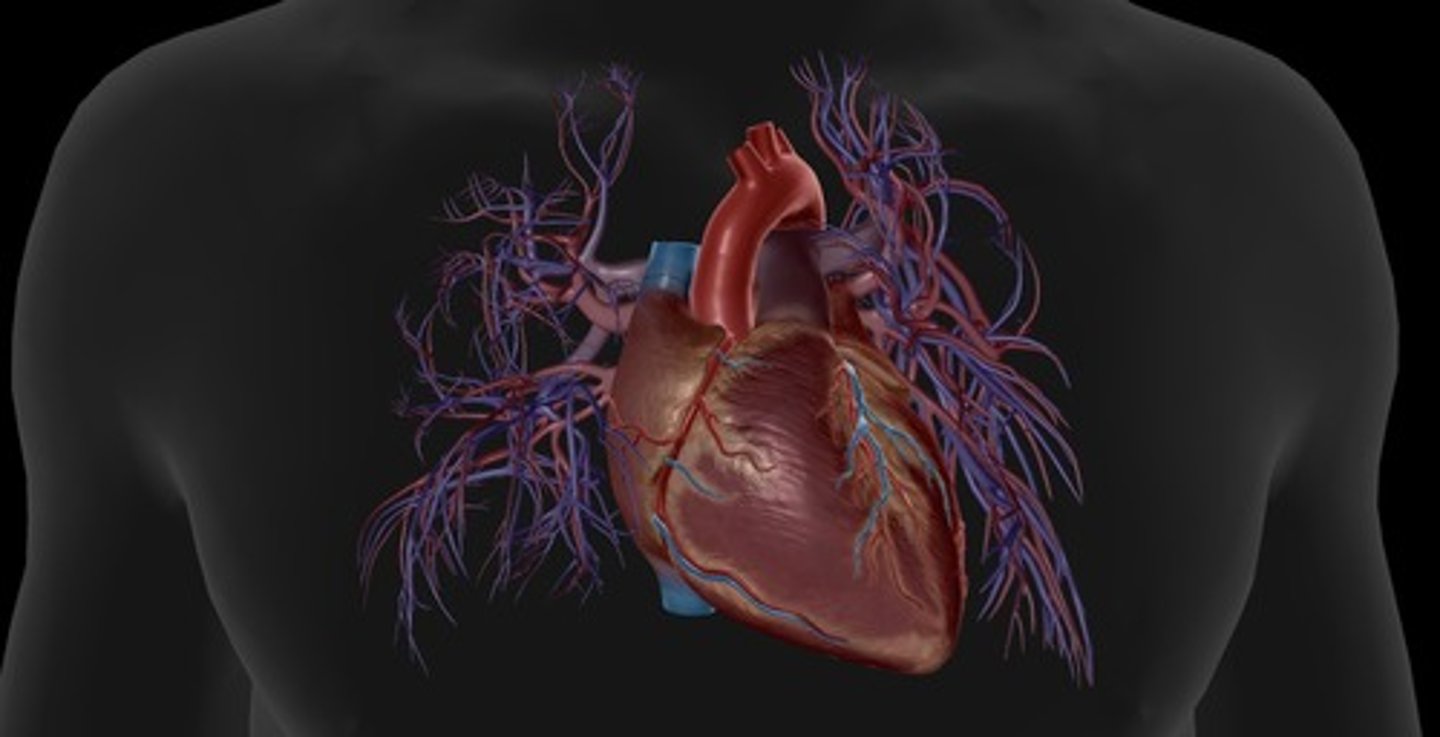
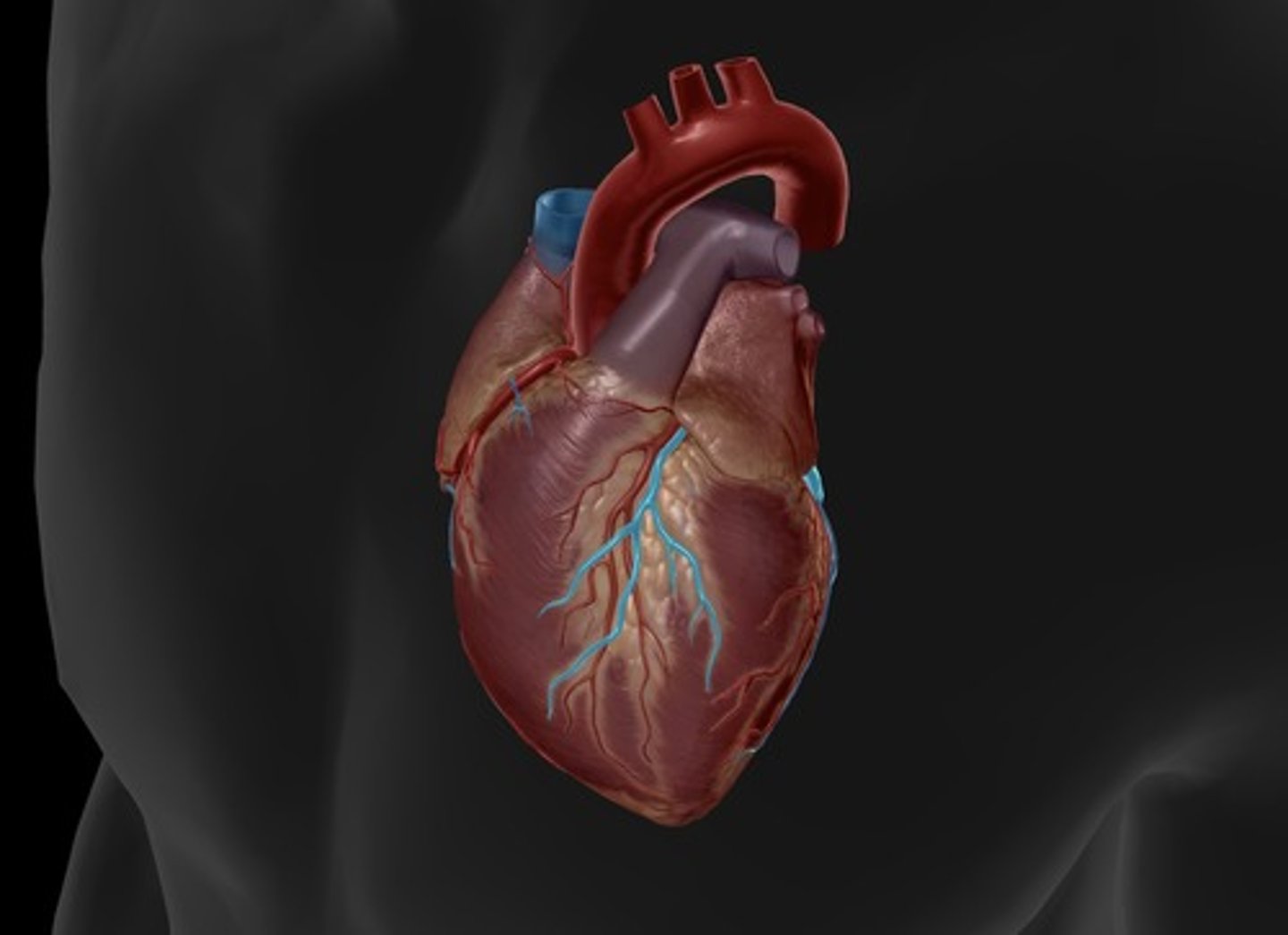
anterior heart
front of heart
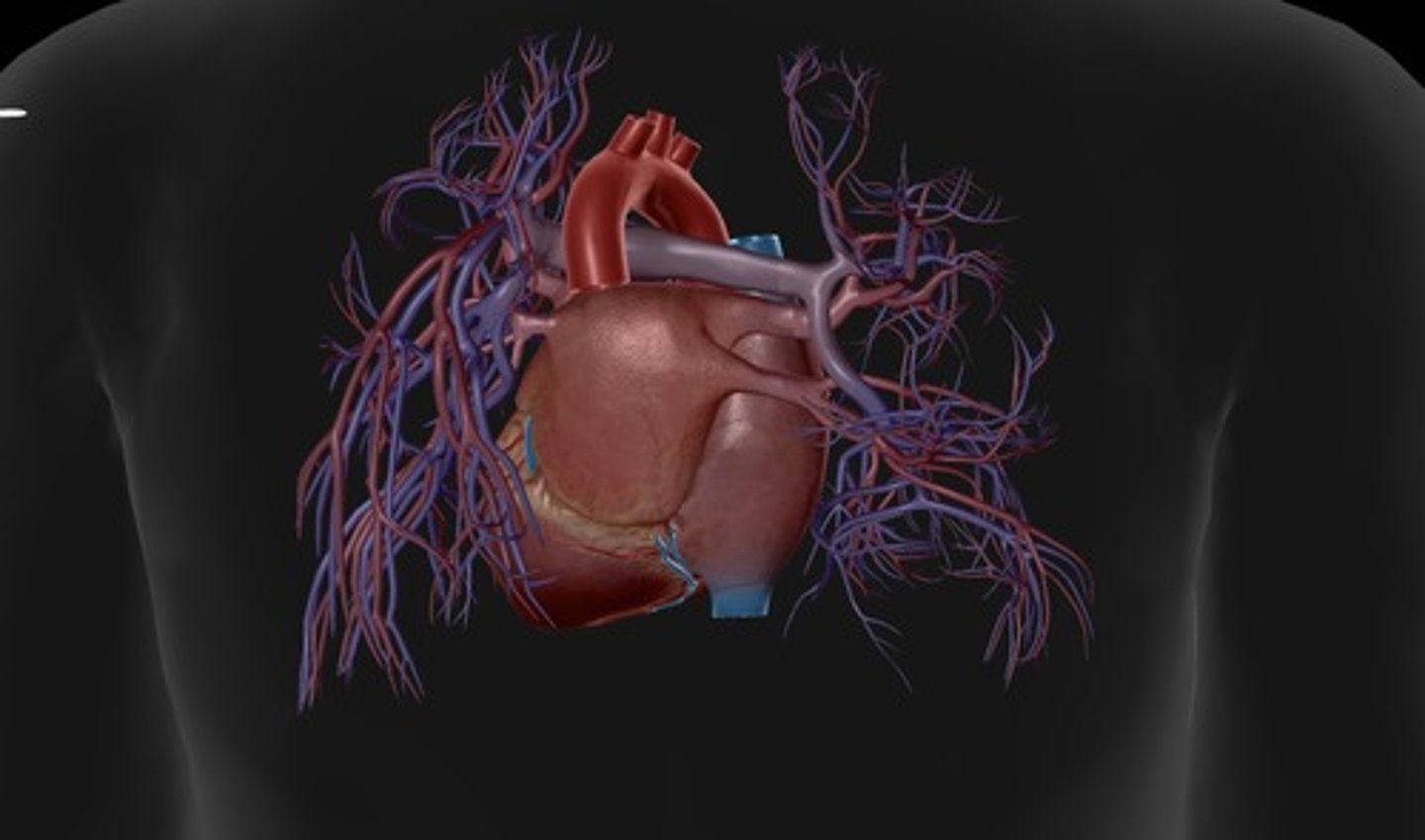
posterior heart
back of heart
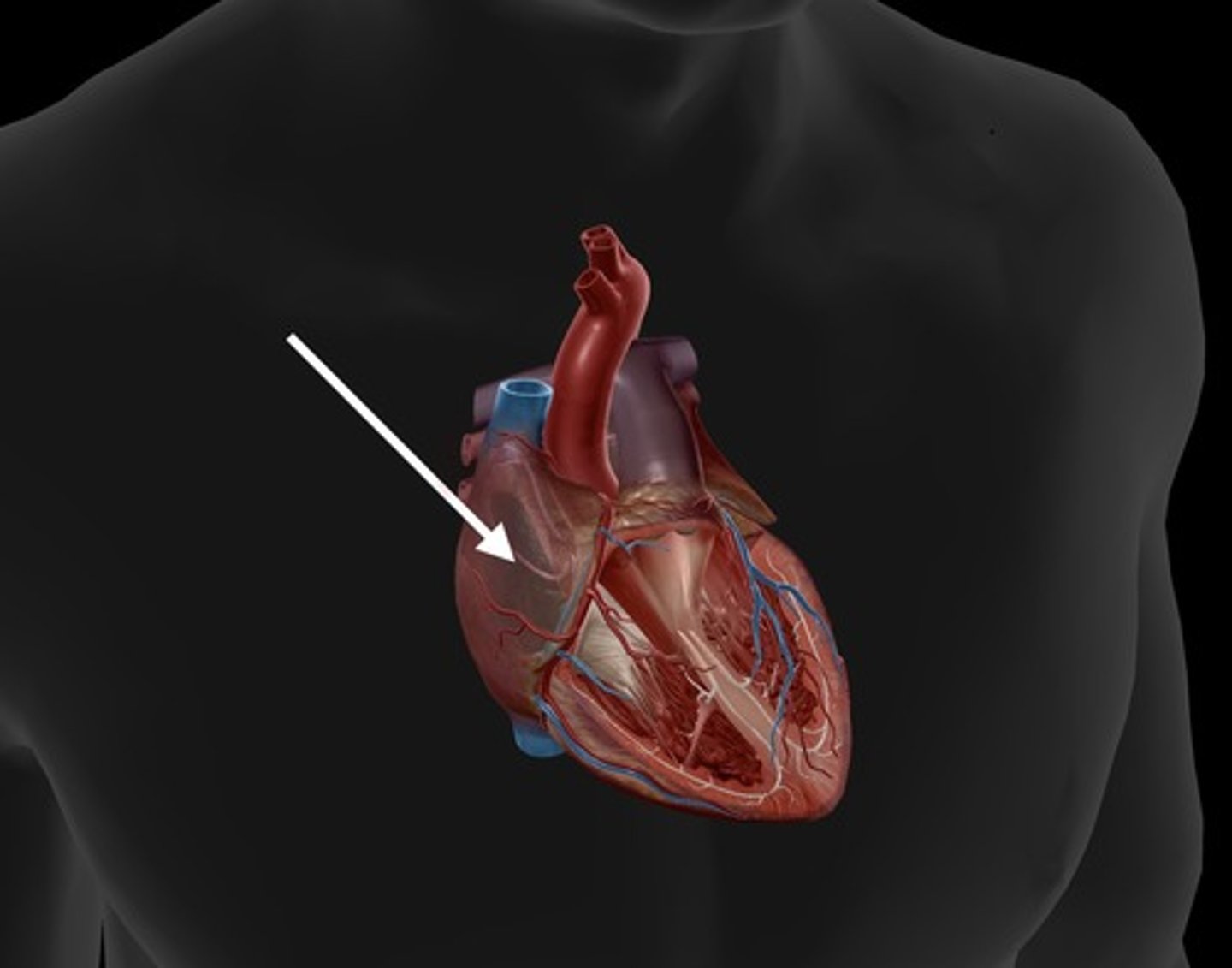
right atrium
receives deoxygenated blood from the body
right ventricle
pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs
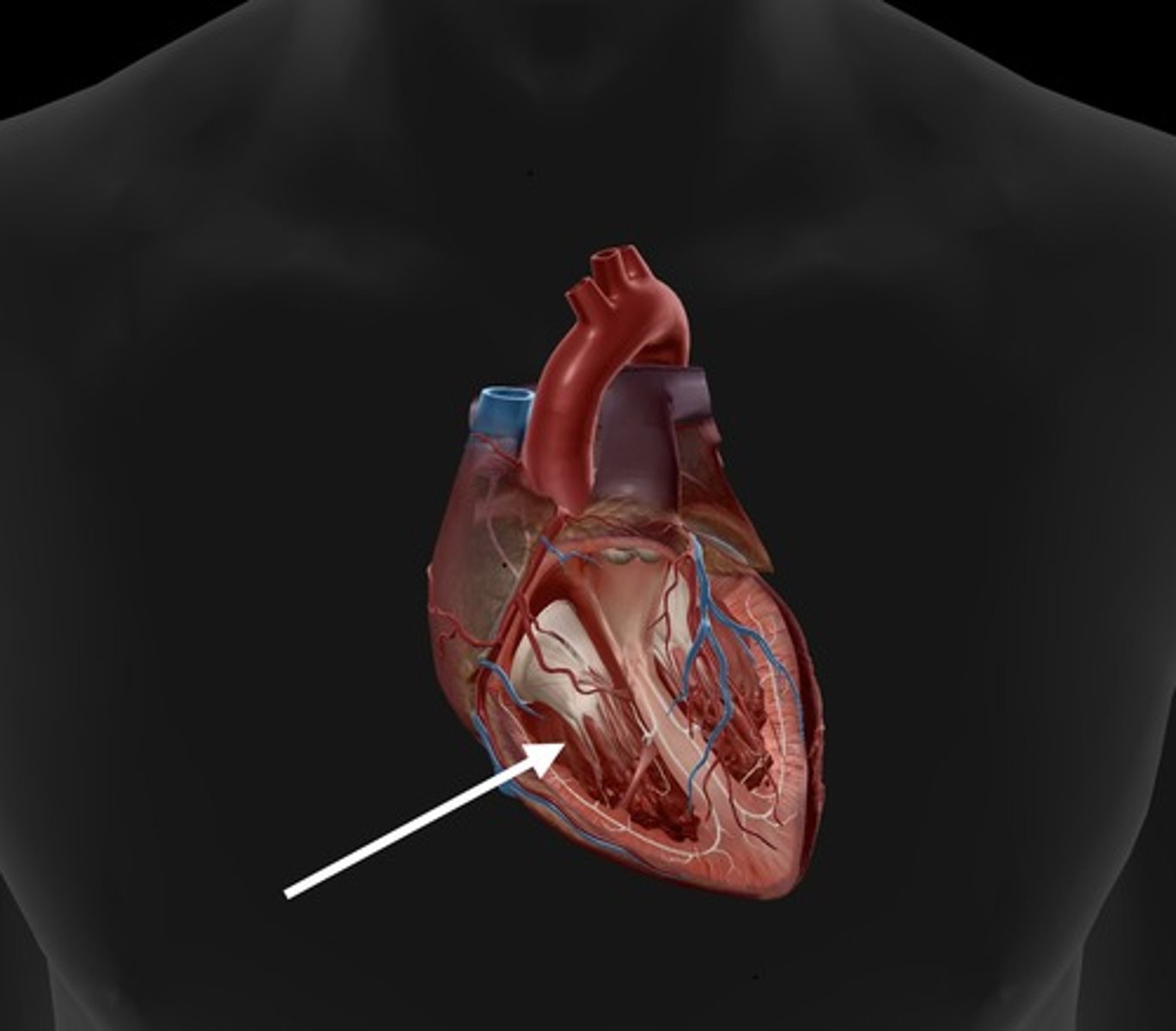
left atrium
receives oxygenated blood from the lungs
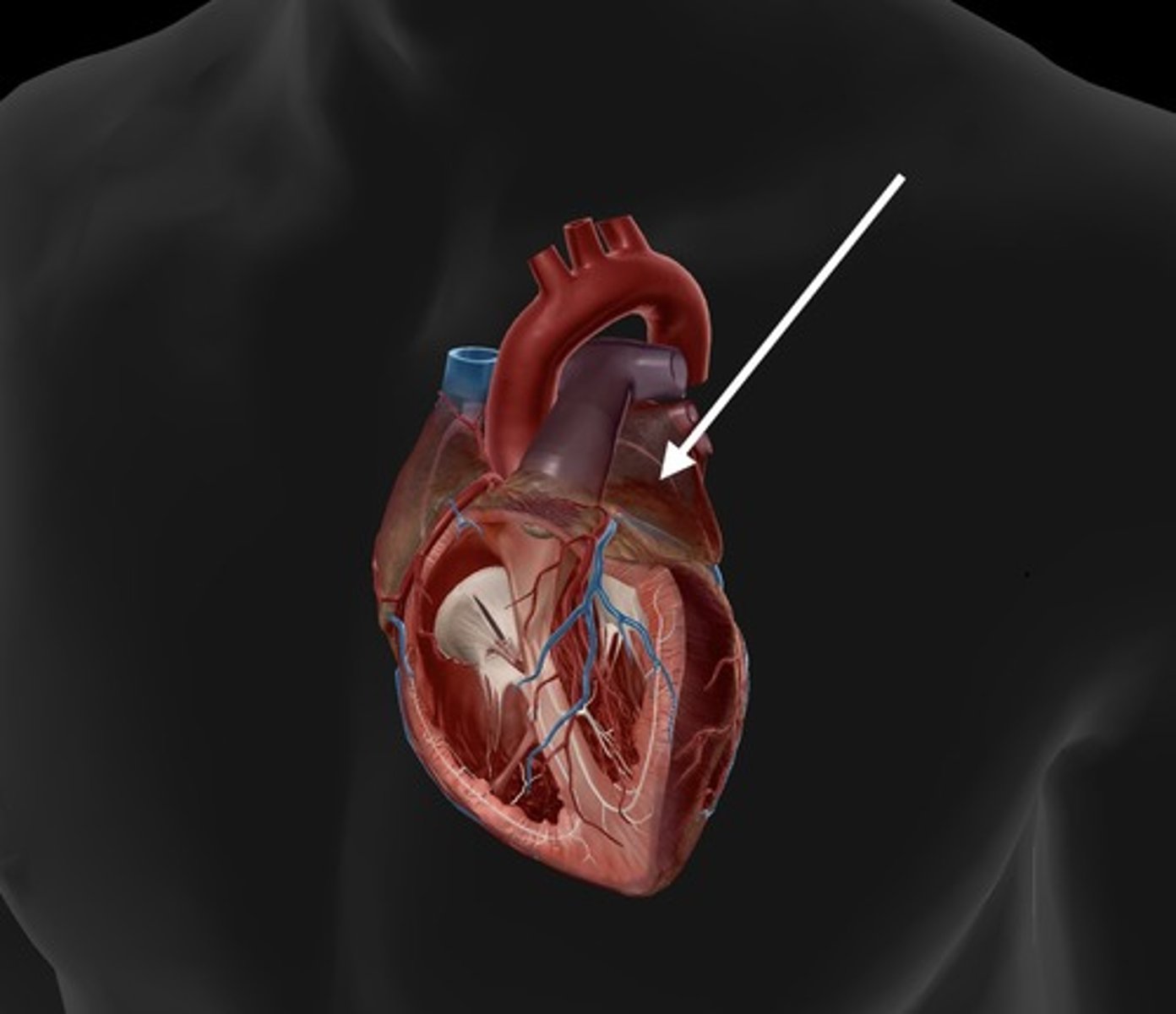
left ventricle
contracts to pump oxygenated blood to the body
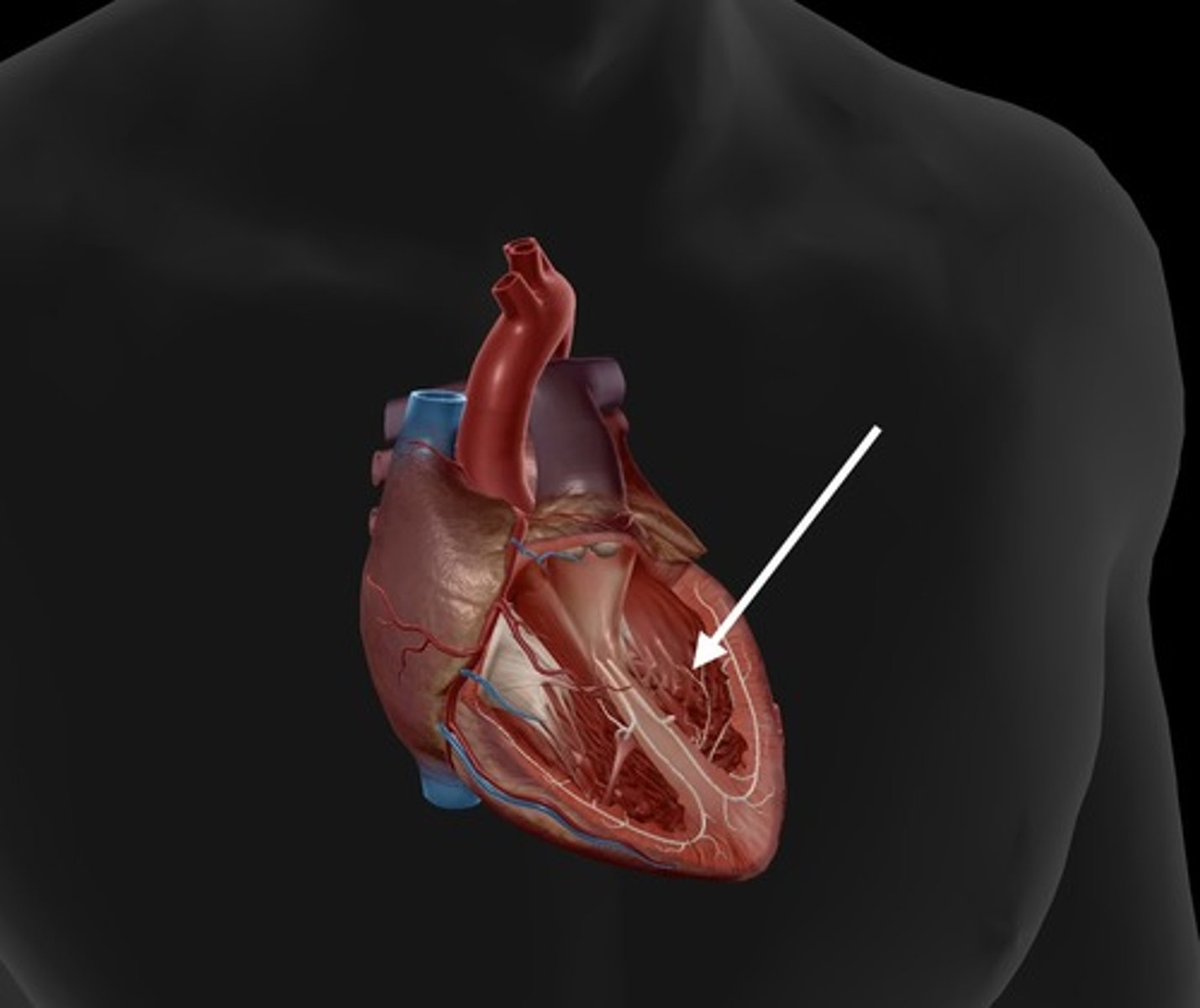
tricuspid valve
valve between the right atrium and the right ventricle
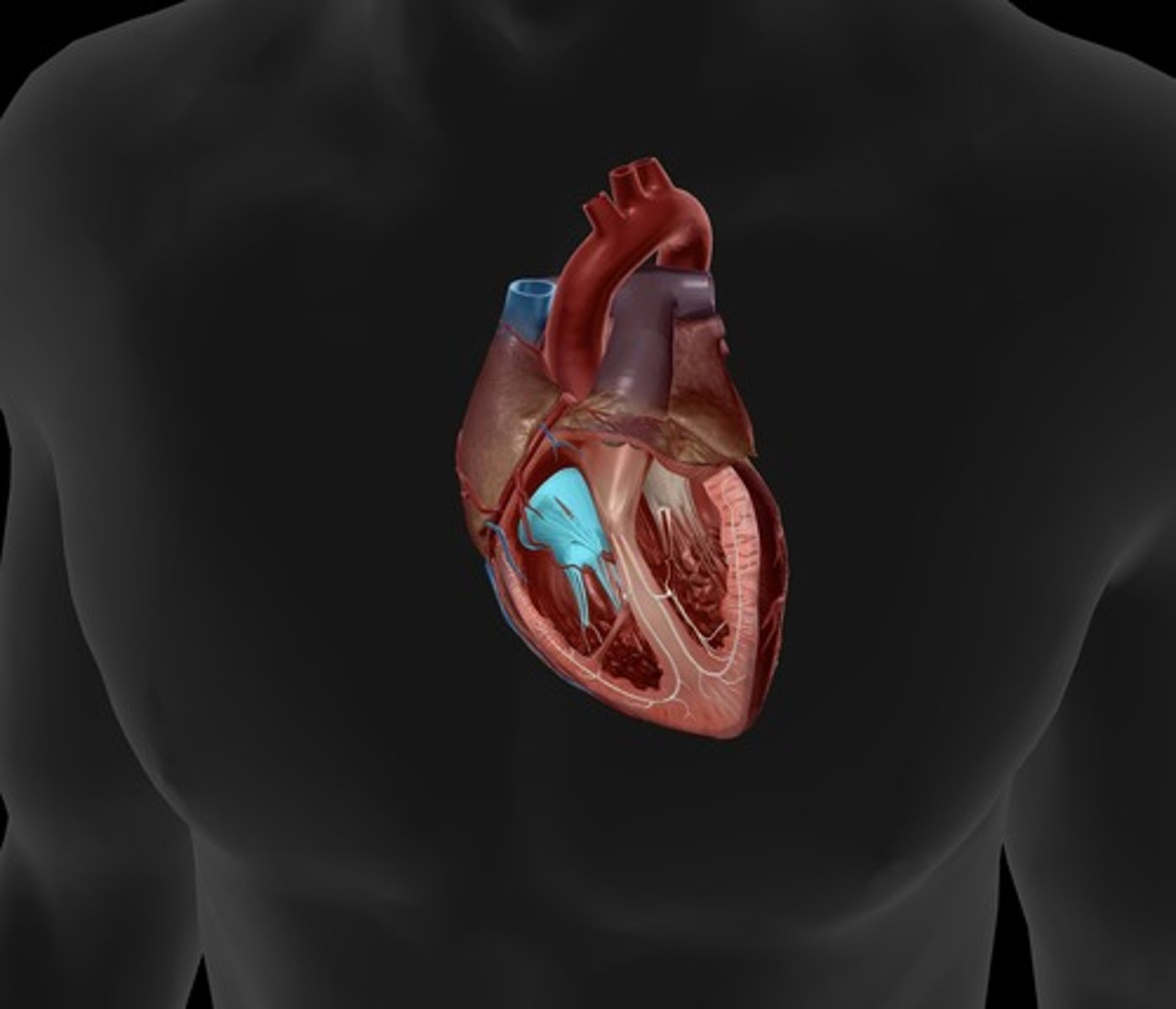
mitral valve
valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle; bicuspid valve
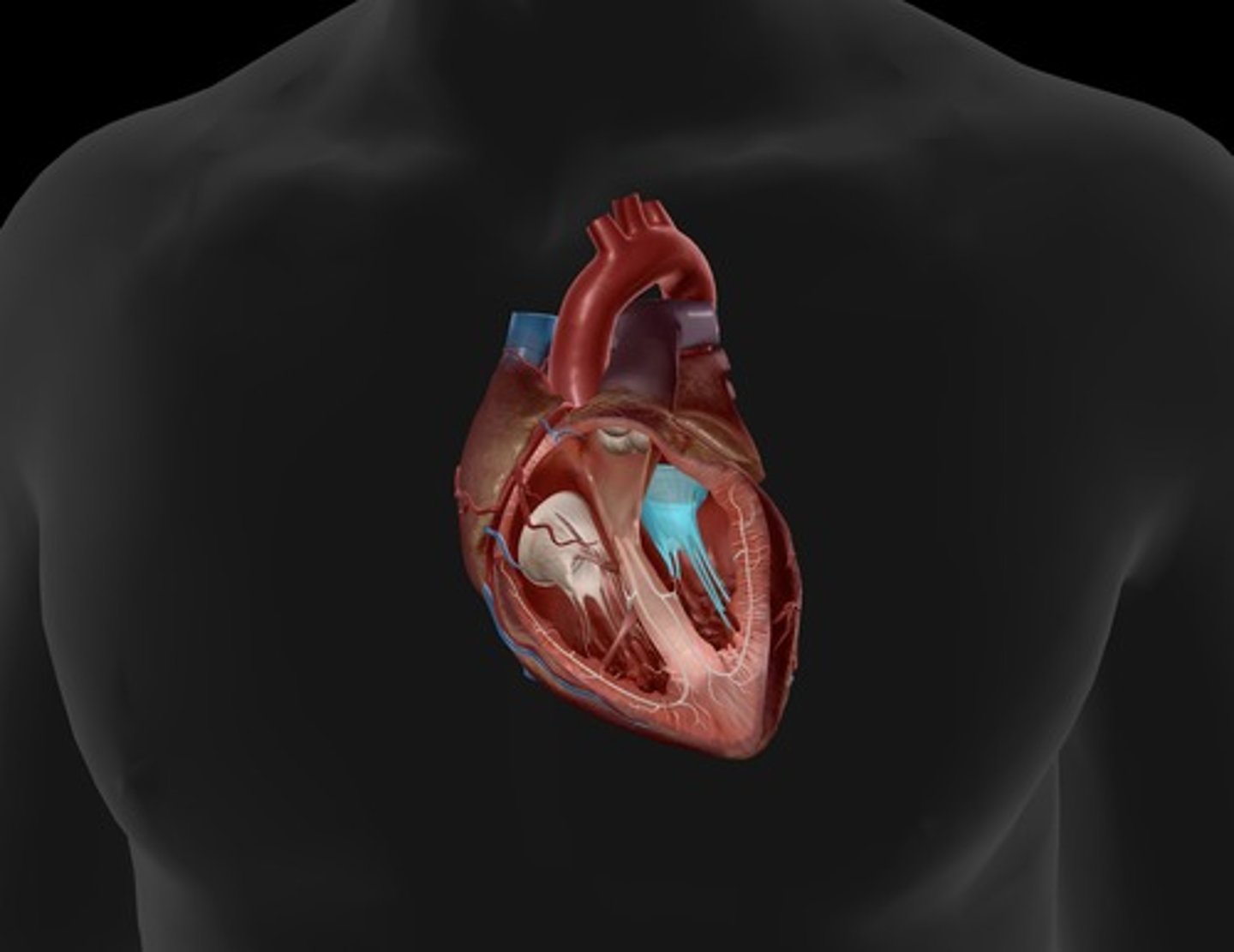
pulmonary semilunar valve
heart valve opening from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery
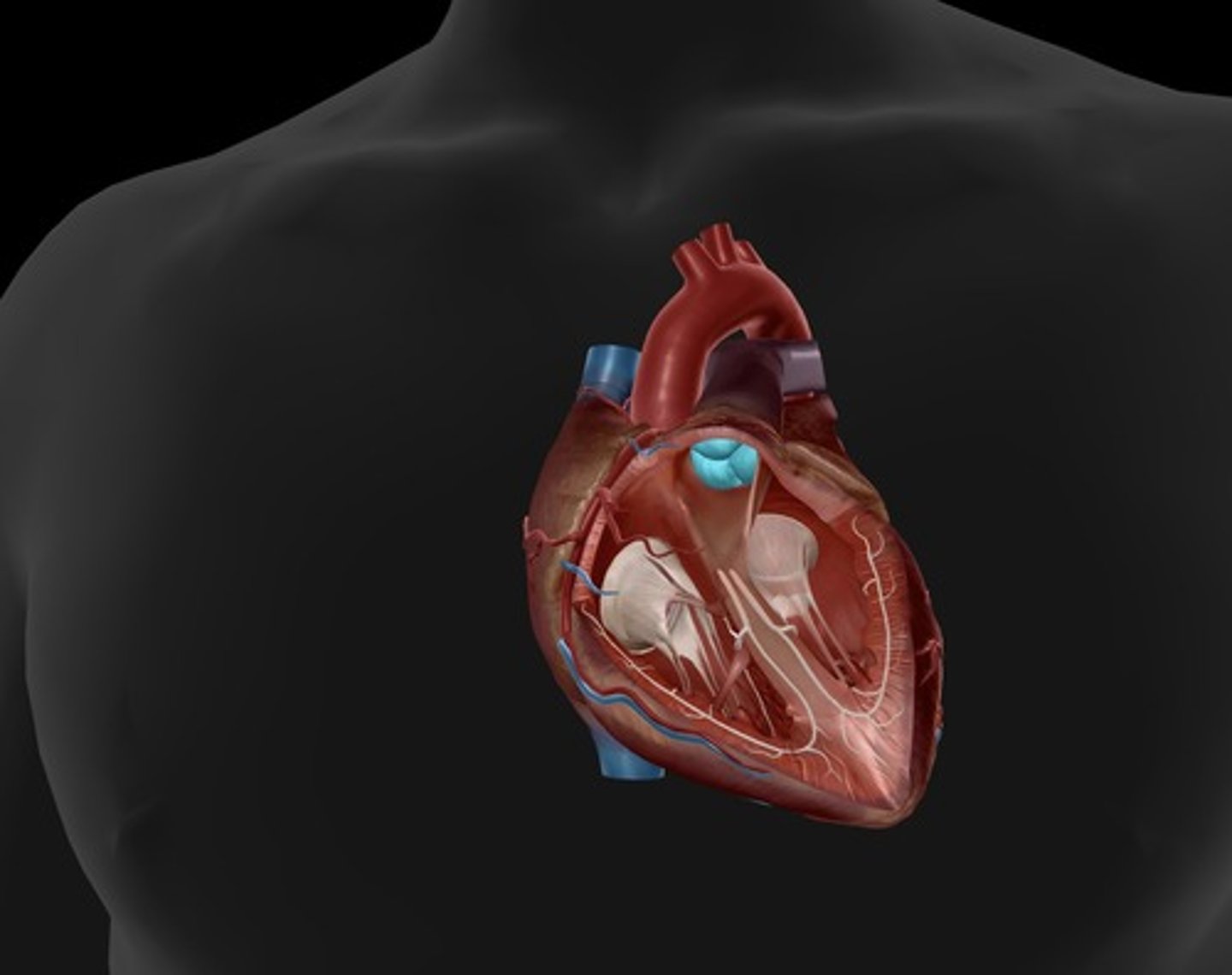
aortic semilunar valve
located between the left ventricle and the aorta
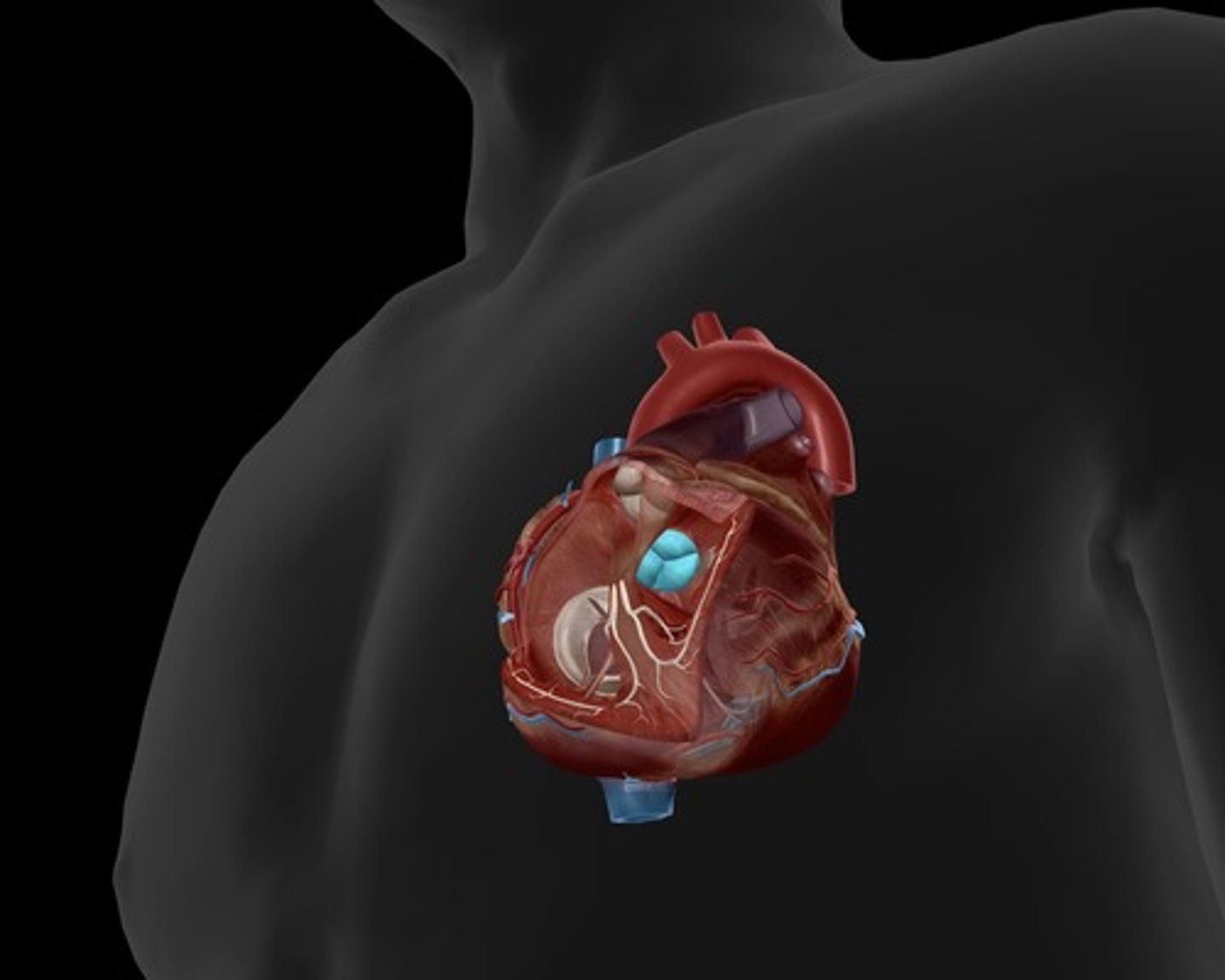
chordae tendineae
thin bands of fibrous tissue that attach to the valves in the heart and prevent them from inverting
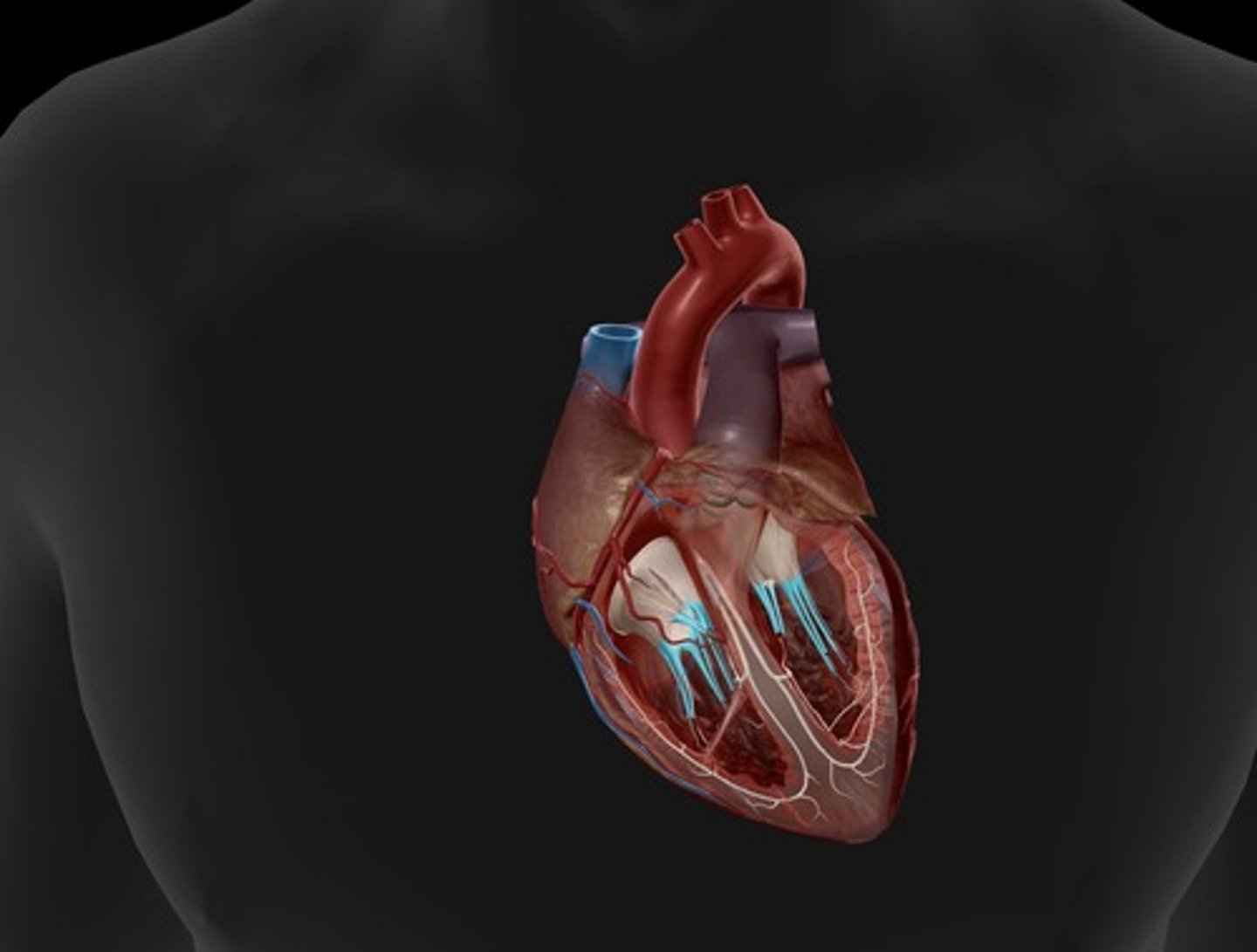
papillary muscles
responsible for pulling the atrioventricular valves closed by means of the chordae tendineae
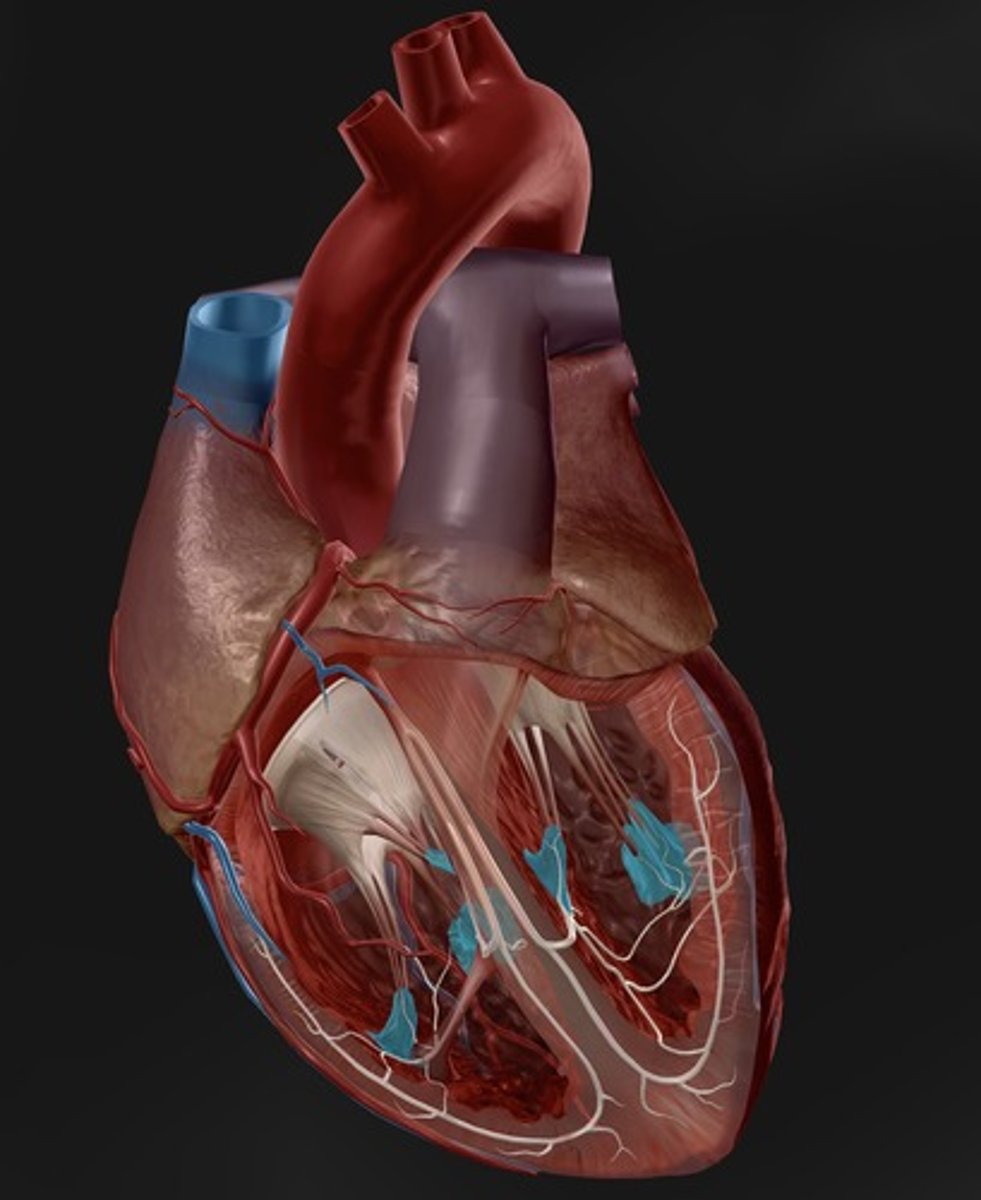
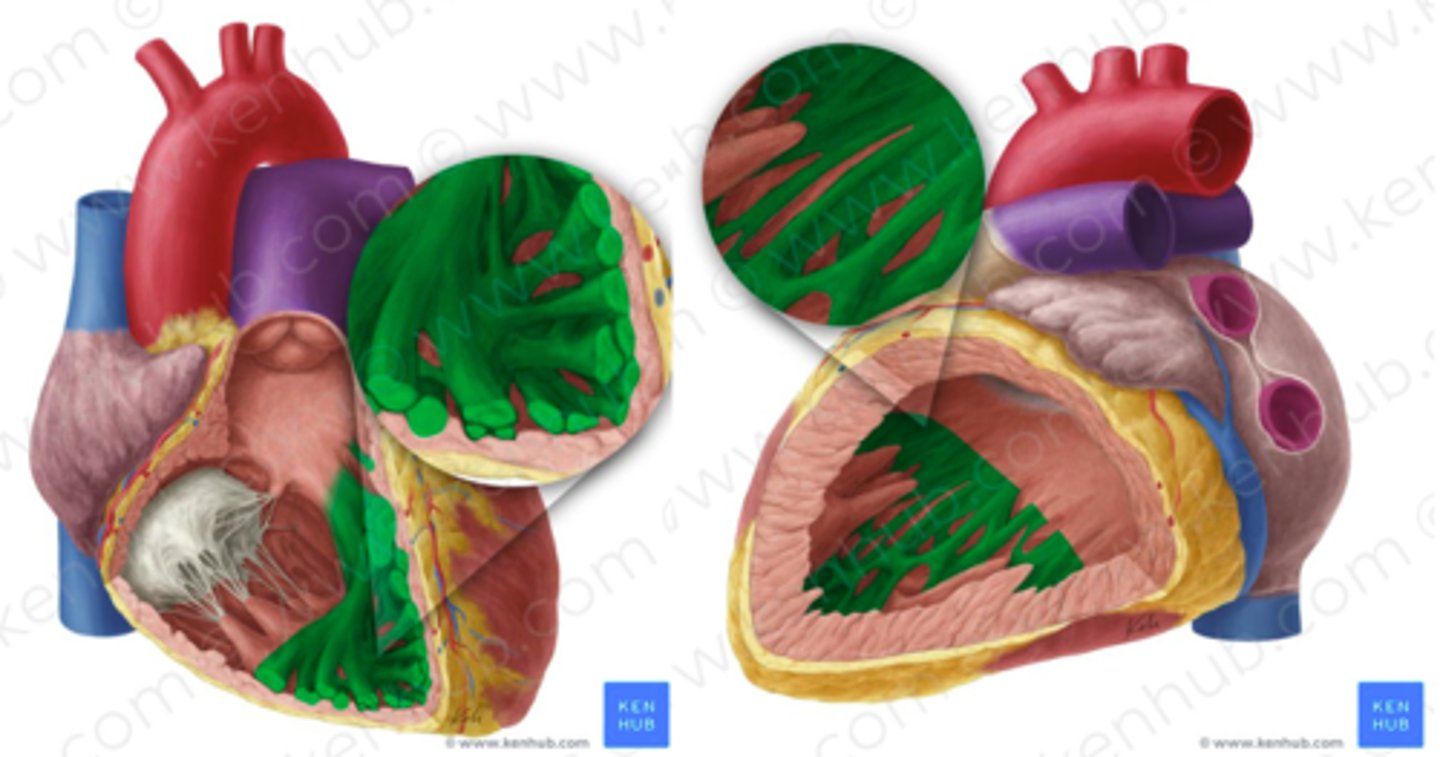
trabeculae carneae
"meaty ridges"
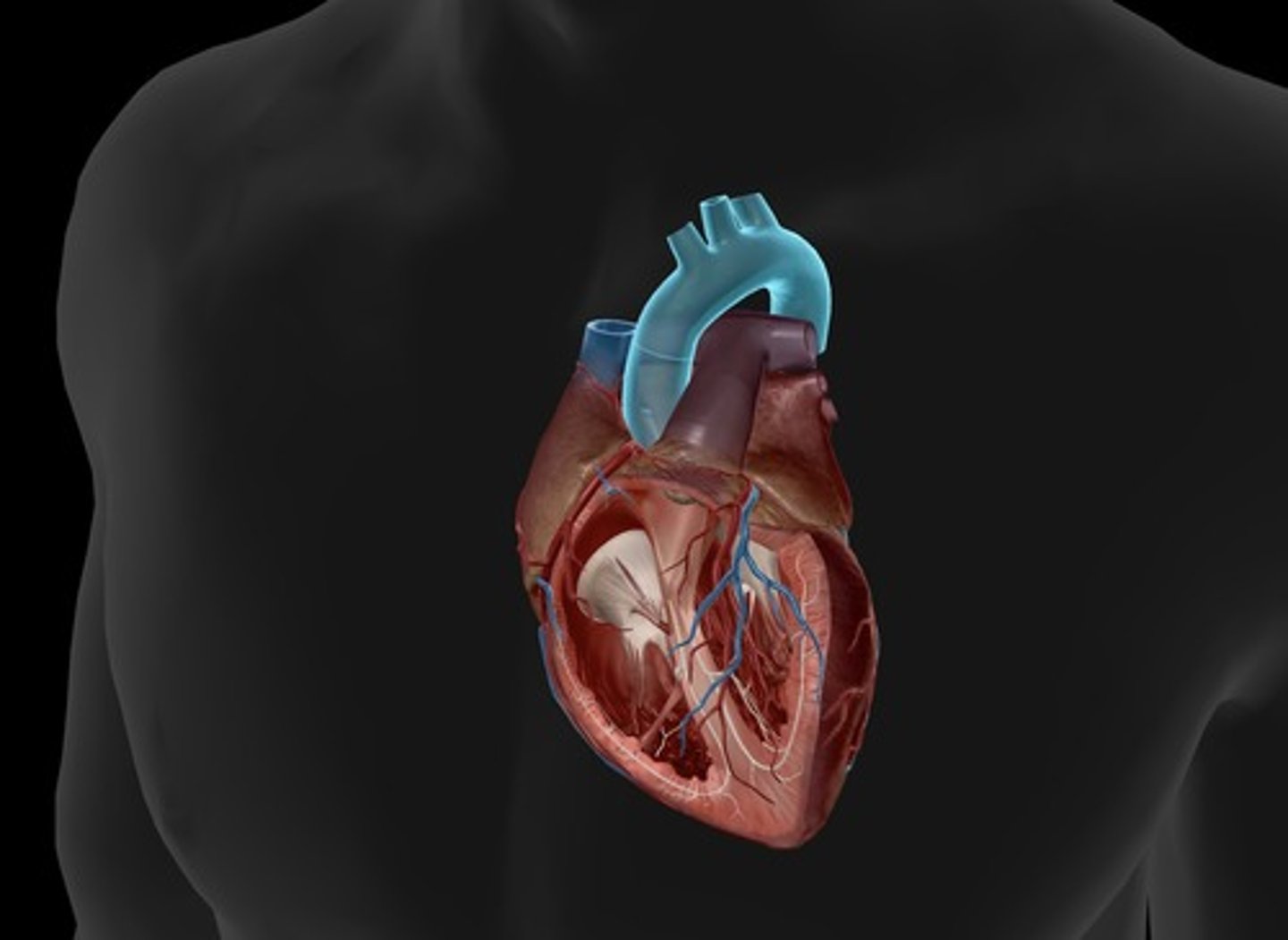
aorta
largest artery in the body, carries oxygenated blood out to tissues/cells from the left ventricle
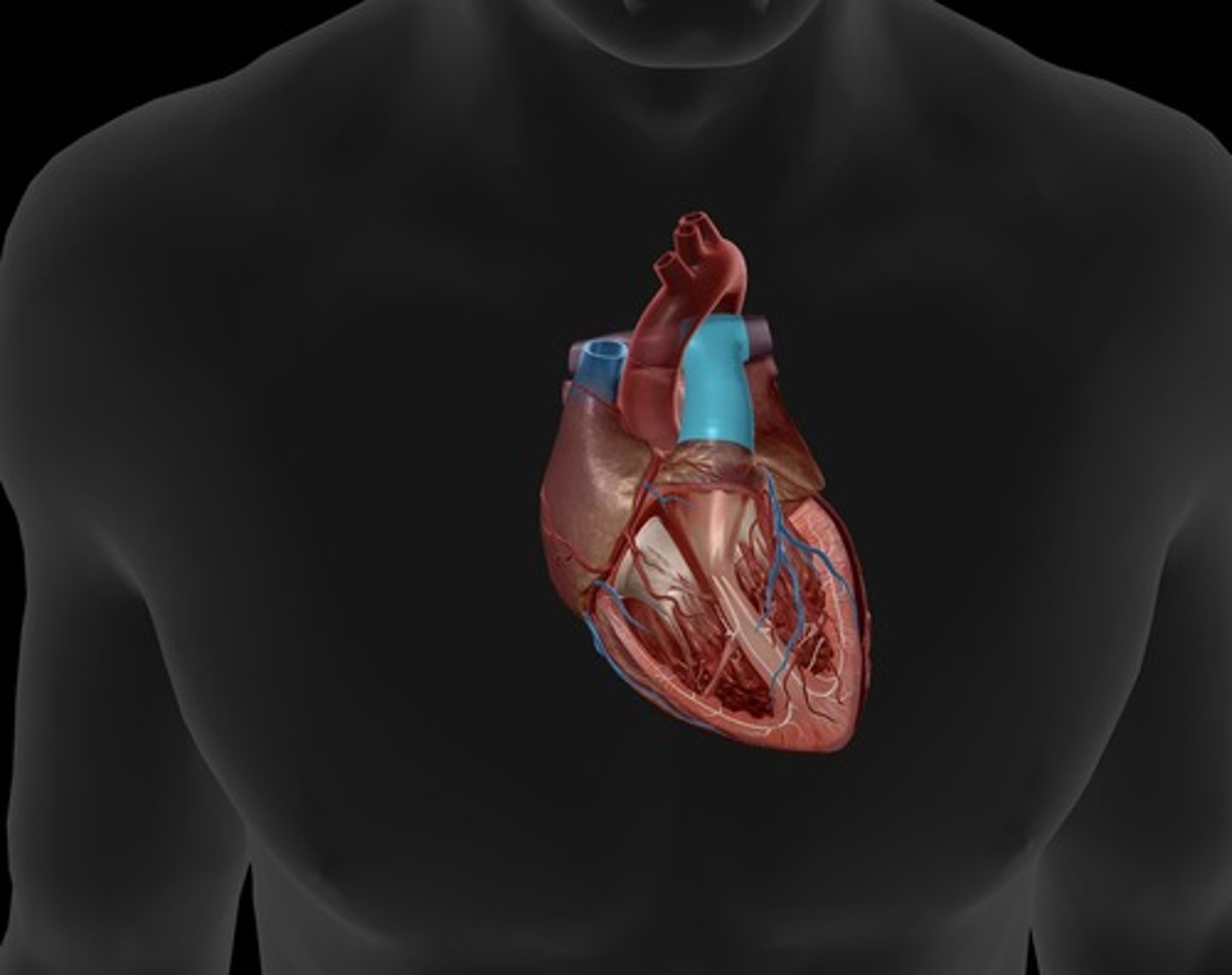
pulmonary trunk
carries blood from right ventricle to pulmonary arteries
pulmonary arteries
carry deoxygenated blood out of the right ventricle and into the lungs (right and left)
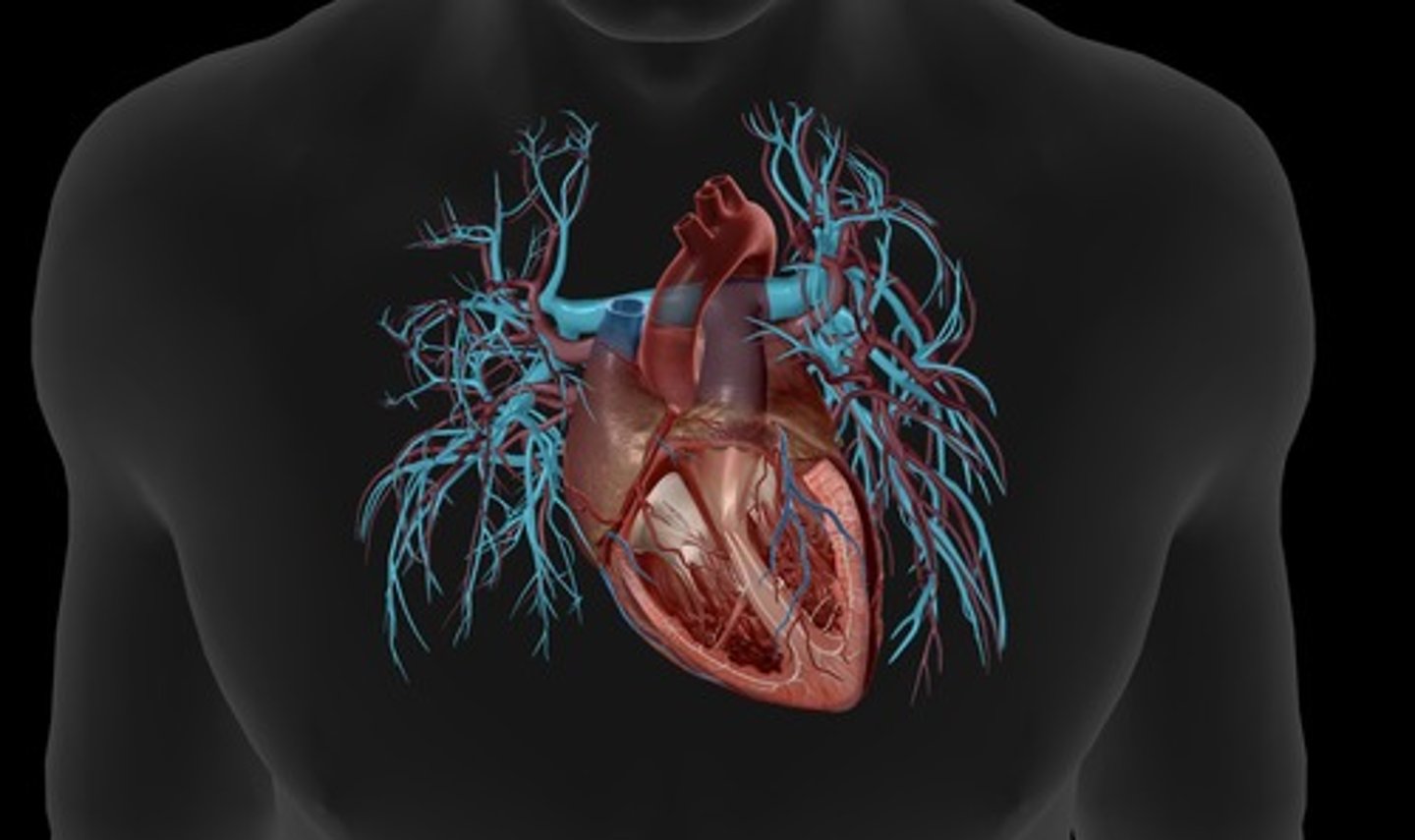
pulmonary veins
deliver oxygen rich blood from the lungs to the left atrium (right and left)
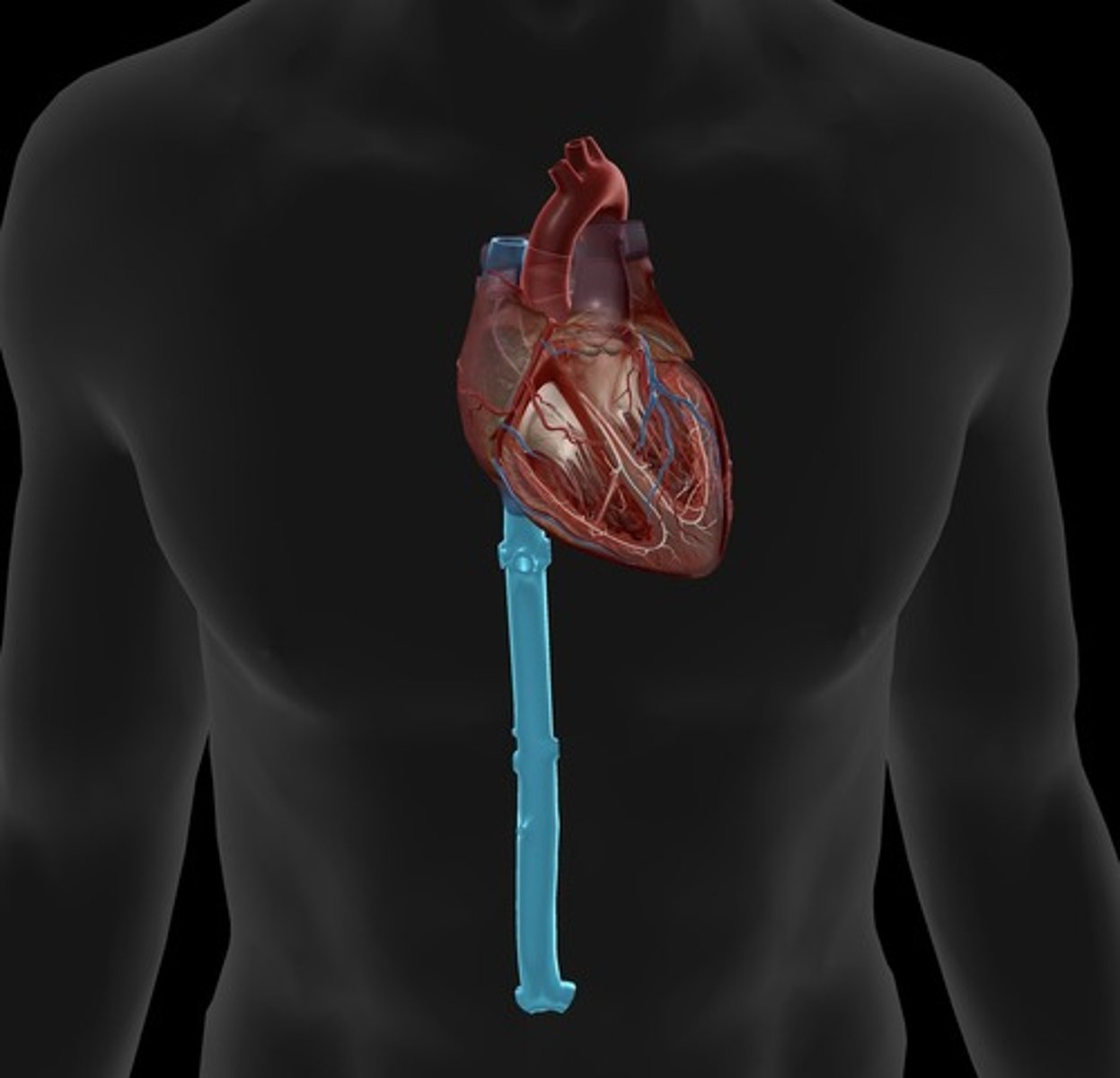
inferior vena cava
carries blood from lower regions of the body to right atrium
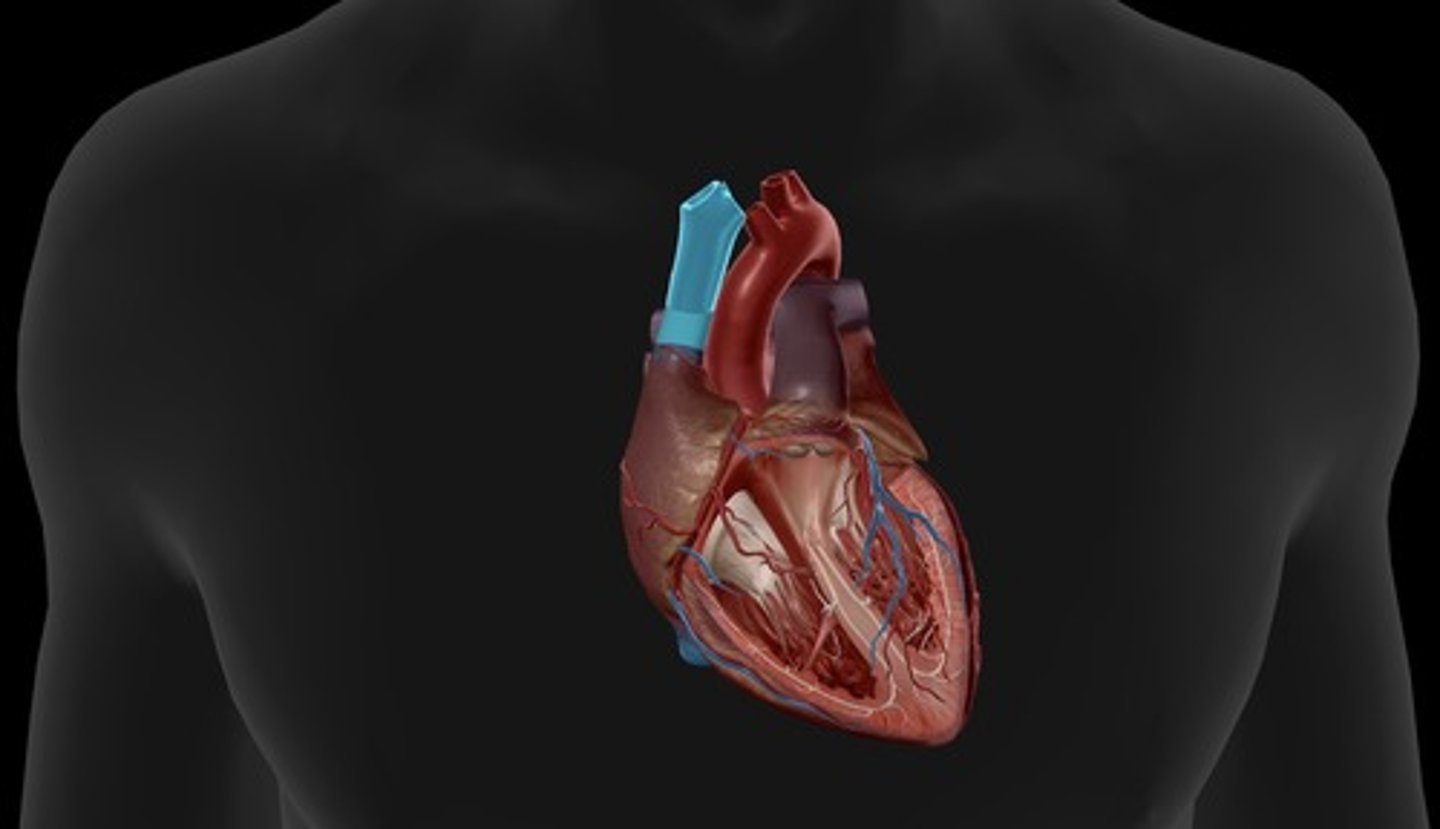
superior vena cava
carries blood from the upper portion of the body to the right atrium
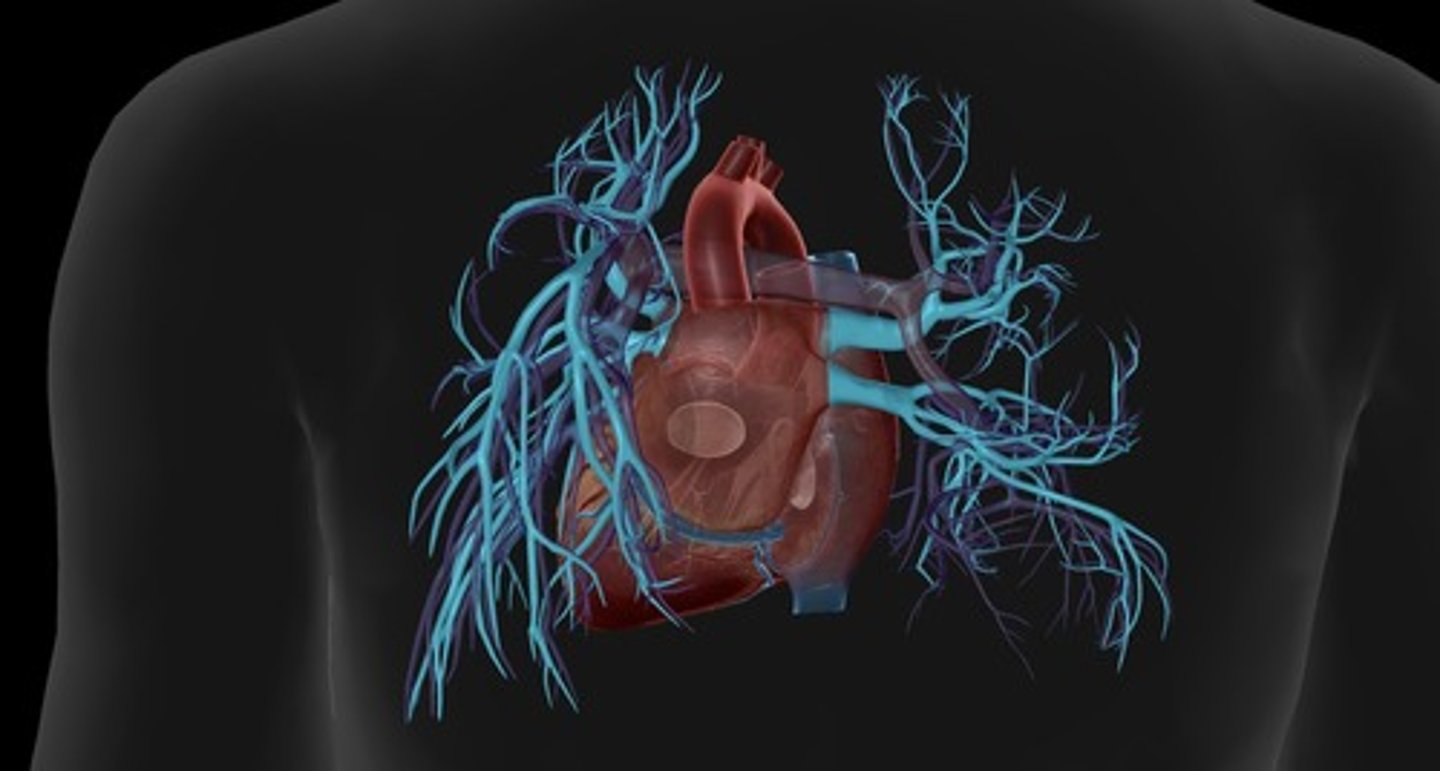
coronary sinus
enlarged vessel on the posterior aspect of the heart that empties blood into the right atrium
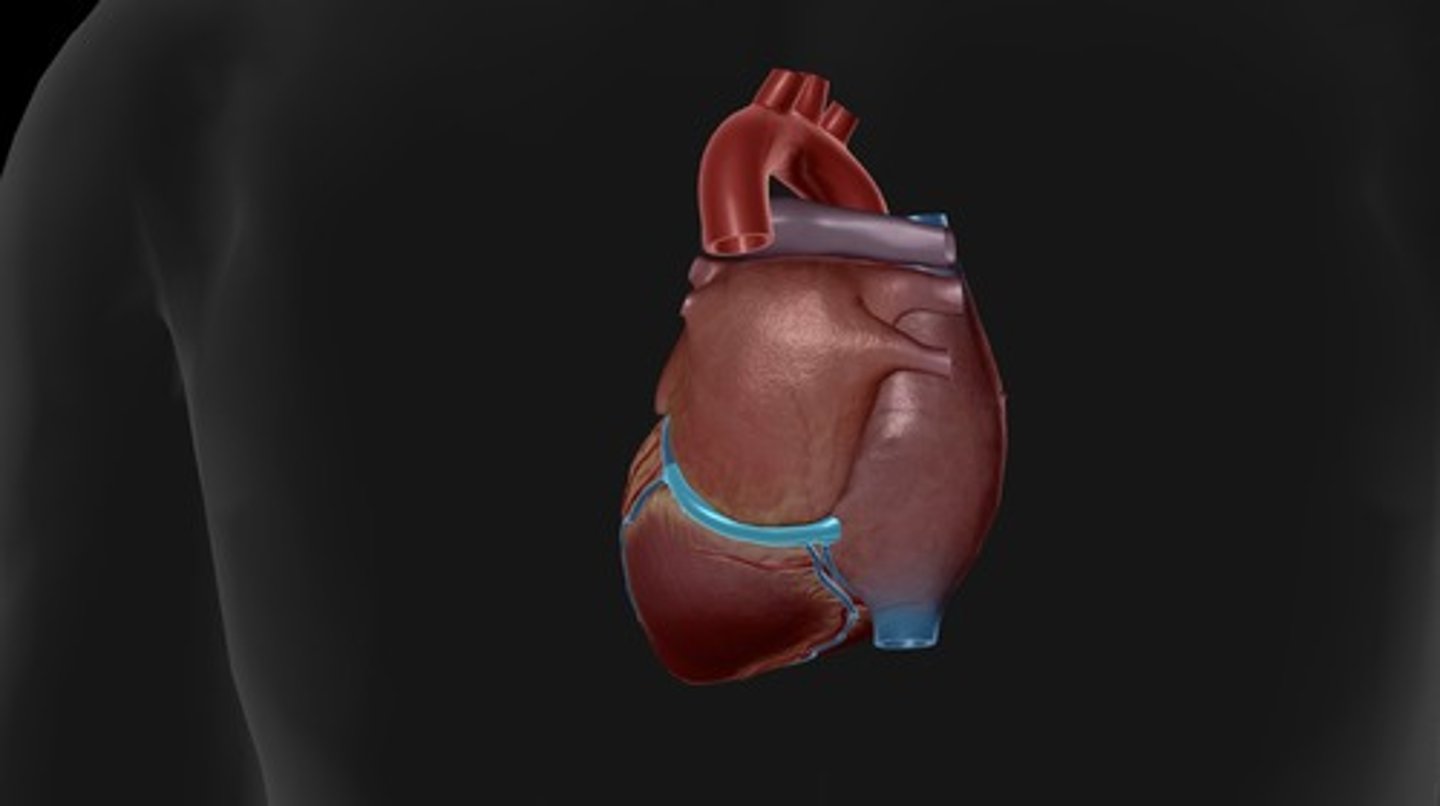
coronary arteries
blood vessels that branch from the aorta and carry oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle (left atrium and pulm trunk dissected to visualize the left) (right and left)
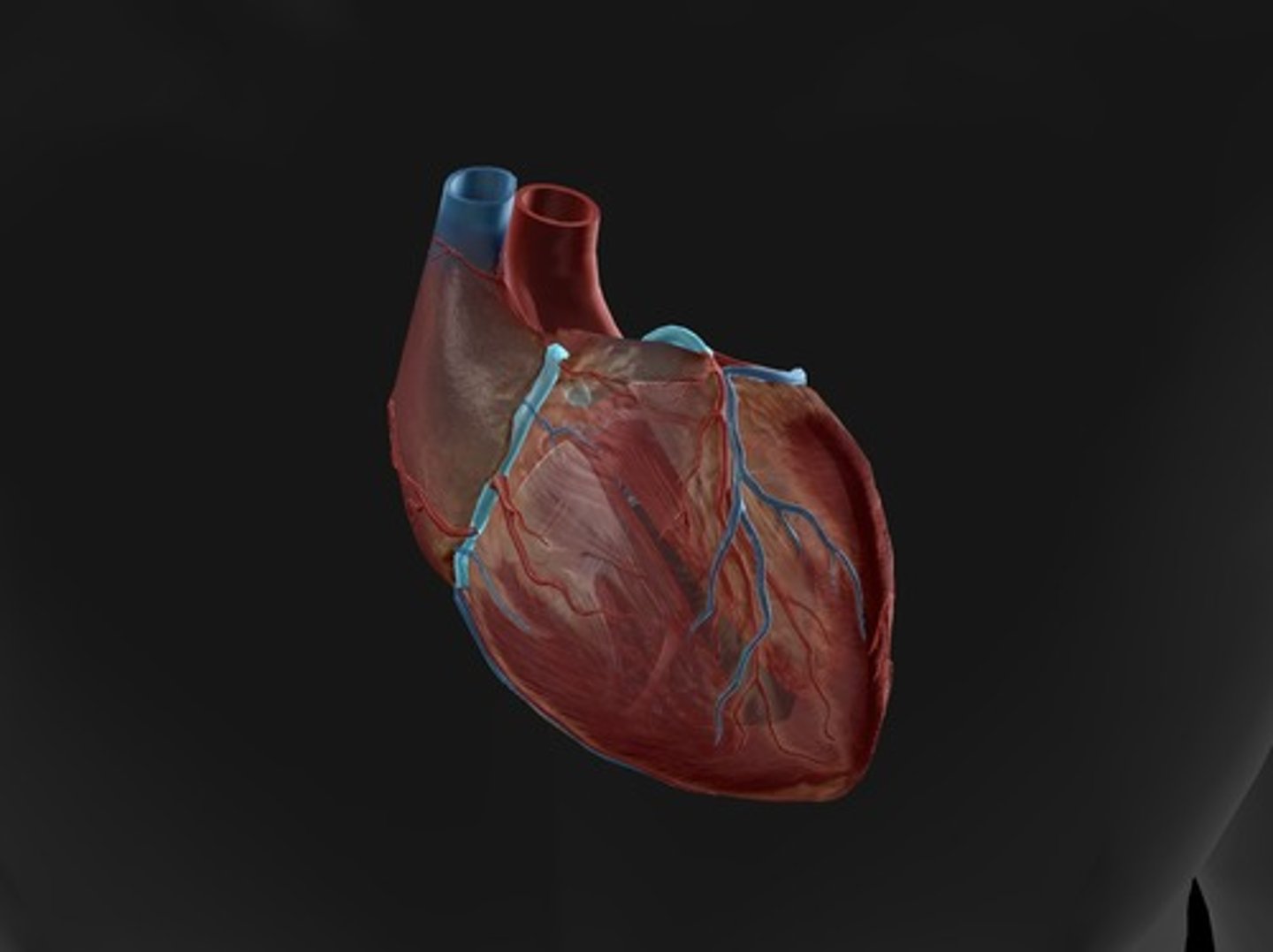
circumflex artery
supplies the left atrium and the posterior walls of the left ventricle (left atrium dissected to visualize the entire artery)
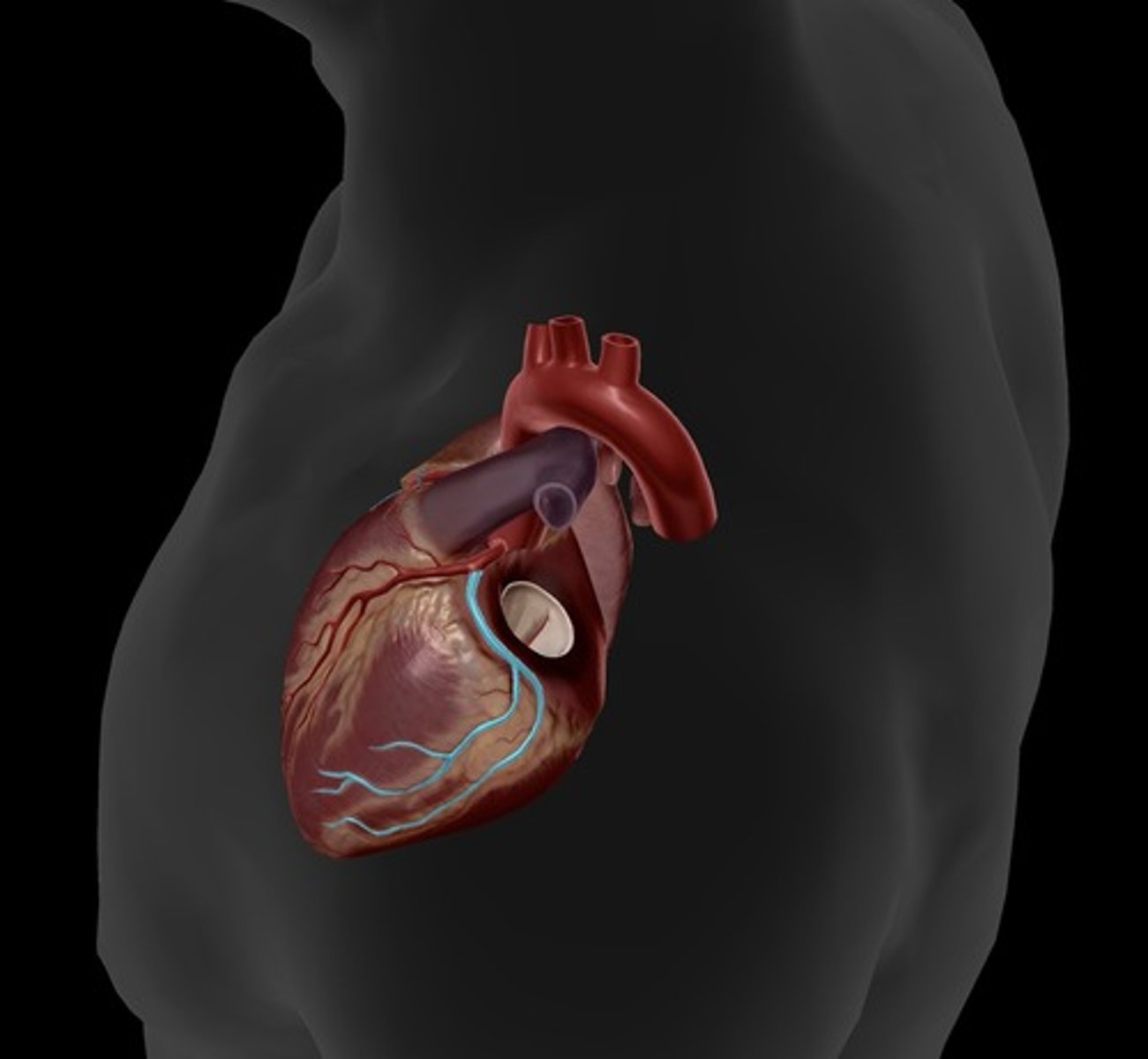
anterior interventricular artery
supplies blood to the interventricular septum and anterior walls of both ventricles
great cardiac vein
runs alongside the anterior interventricular artery
endocardium
inner lining of the heart
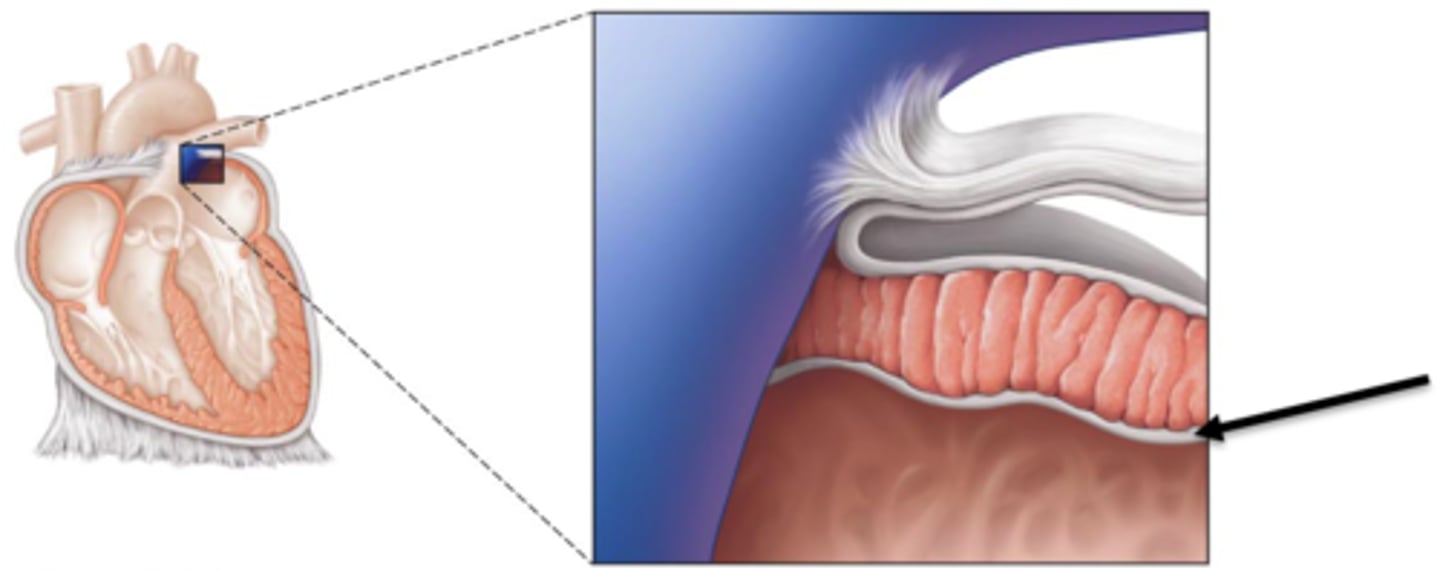
myocardium
thick middle muscle layer of the heart
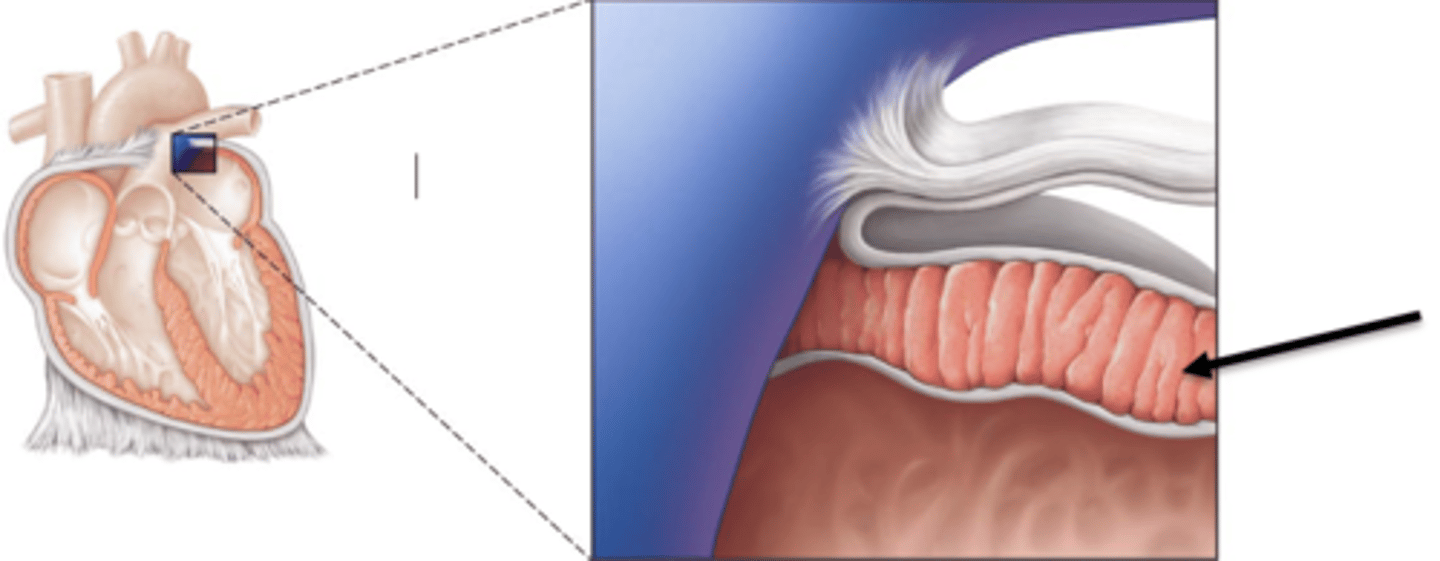
epicardium
outer layer of the heart
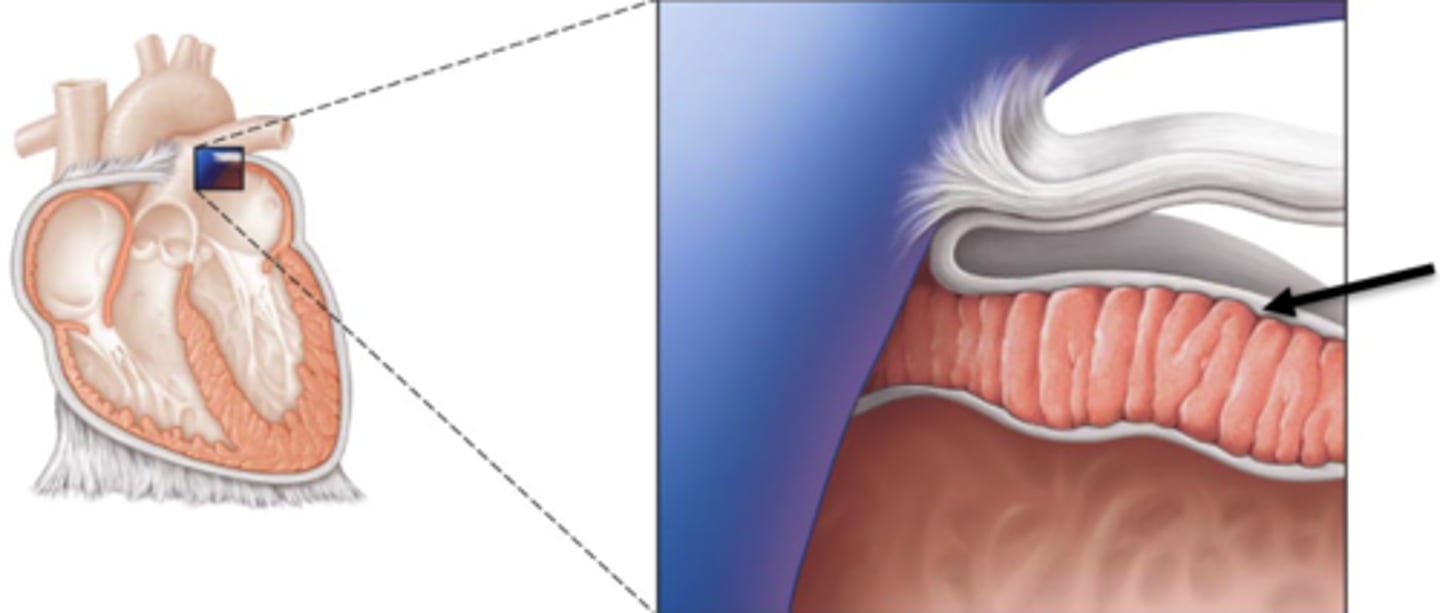
artery
a blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart
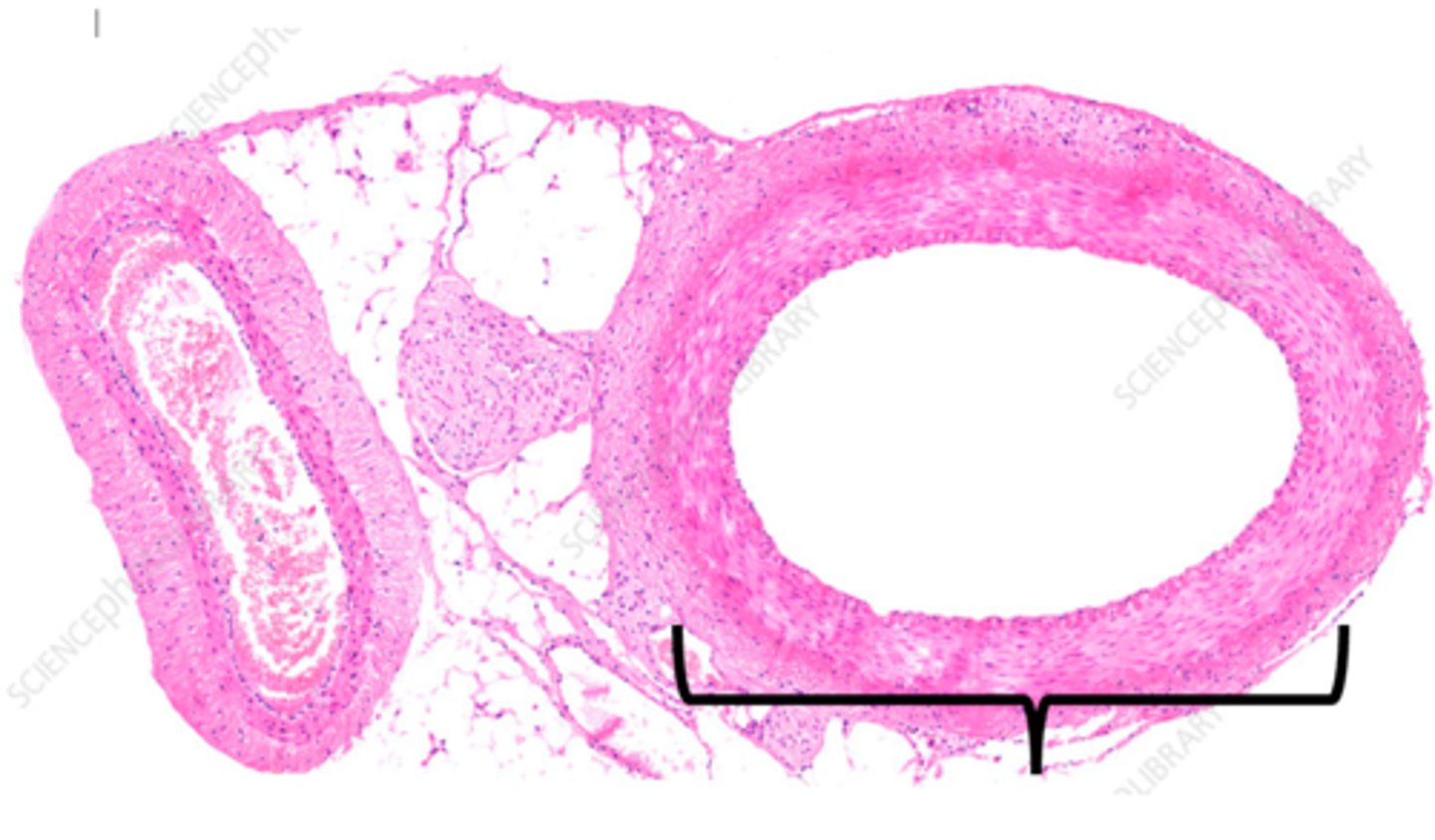
vein
a blood vessel that carries blood back to the heart.
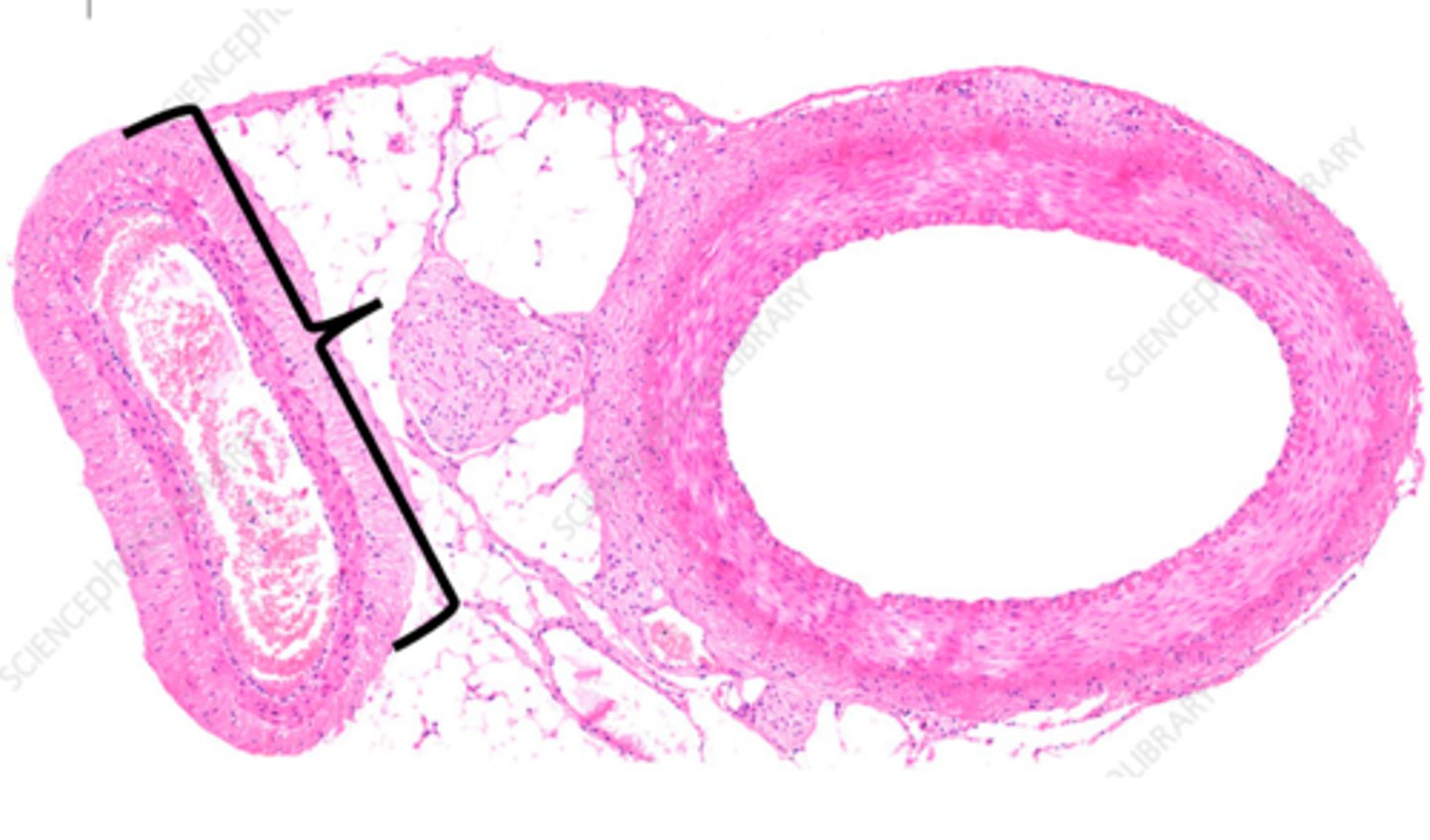
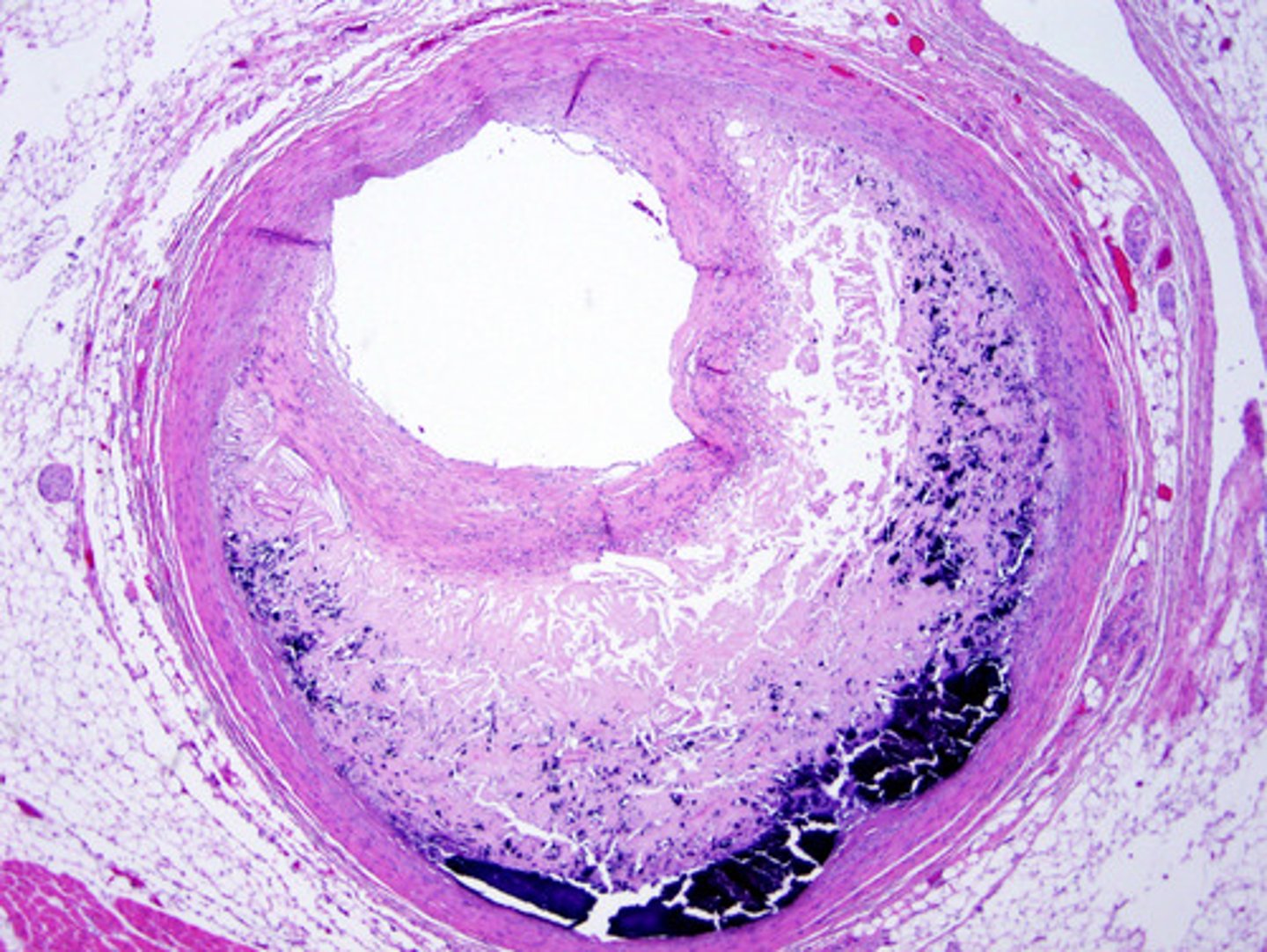
atherosclerosis
condition in which fatty deposits called plaque build up on the inner walls of the arteries (microscopic - the main identifier is the needle-like cholesterol clefts noted within the lumen
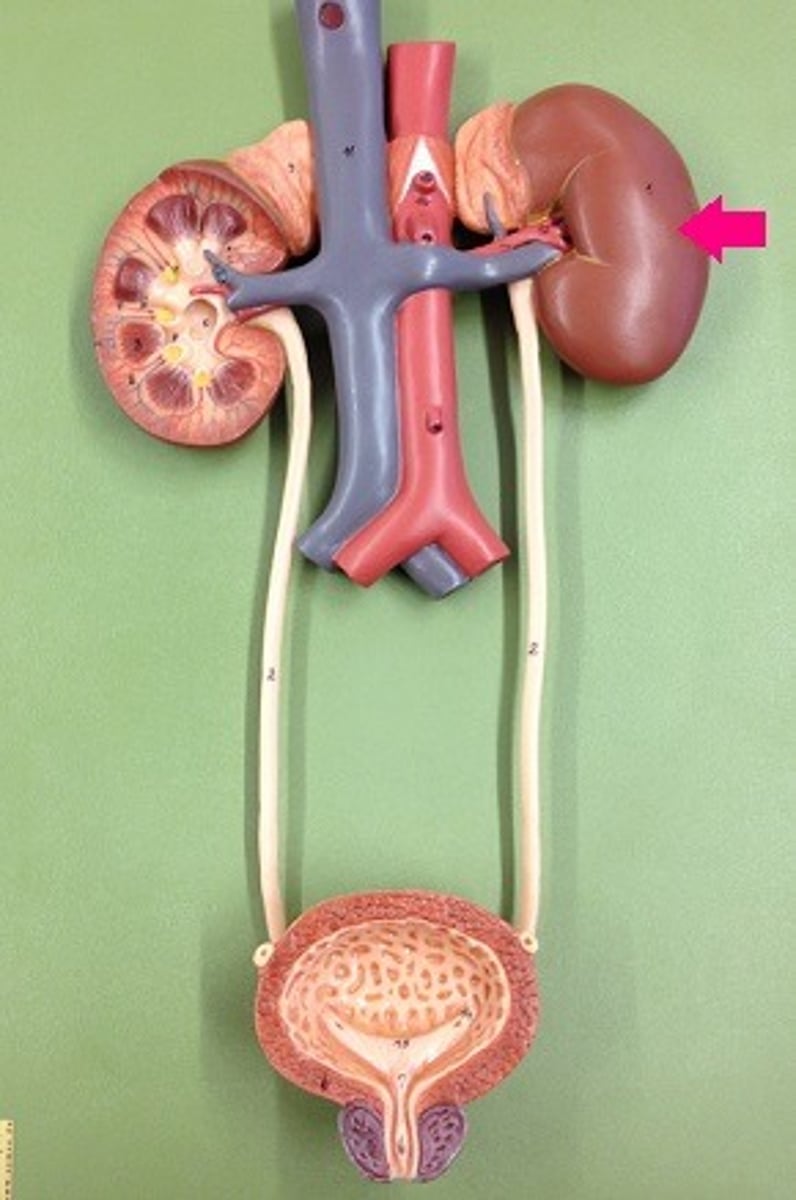
kidney
Filters waste from the blood like urea, water, salt and proteins. (right and left)