Heart structure
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
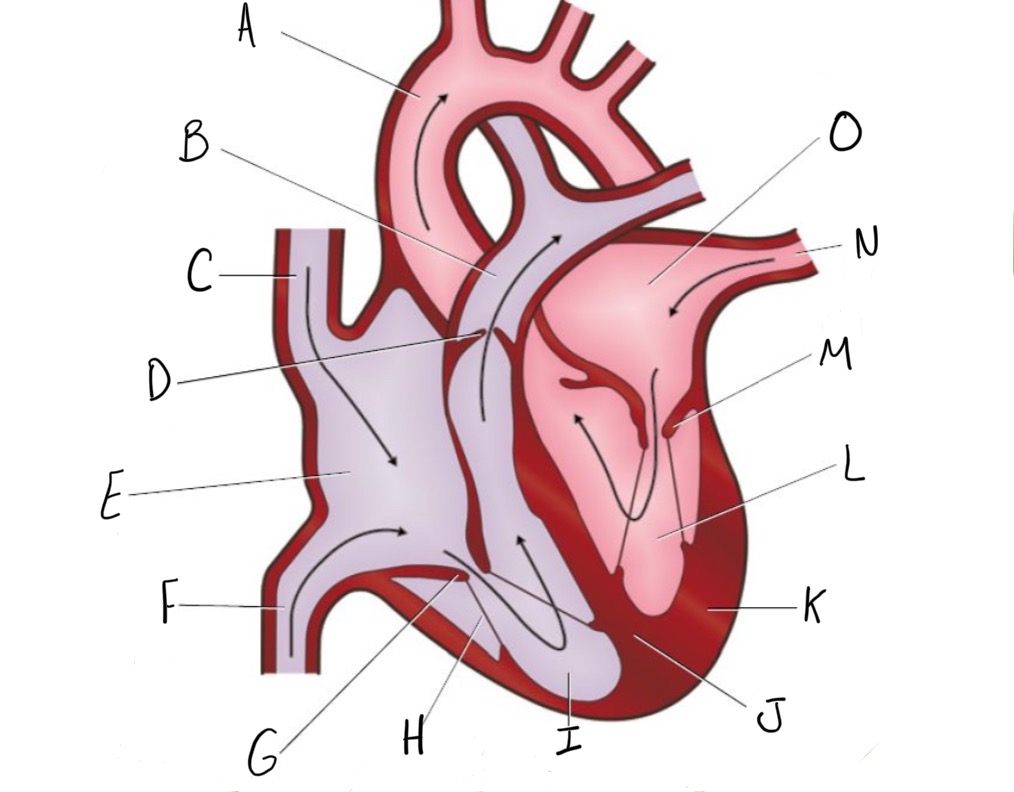
Name the parts of the heart as shown in the diagram.
A) Aorta
B) Pulmonary artery
C) Superior vena cava
D) Semilunar valve
E) Right atrium
F) Inferior vena cava
G) Tricuspid
H) Tendon
I) Right ventricle
J) Septum
K) Thick muscle
L) Left ventricle
M) Bicuspid
N) Pulmonary vein
O) Left atrium
Summarise the journey of blood through the heart and to the body.
Deoxygenated blood is pumped from the heart to the lungs.
The blood receives oxygen and is pumped back to the heart.
The oxygenated blood is then pumped to the rest of the body.
The oxygenated blood leaves the blood to be used for respiration in the body and the blood goes back to the heart.
Simply define what one cardiac cycle represents.
One heartbeat
Summarise what happens in one cardiac cycle.
During a heartbeat, the atria will receive blood from the veins.
The atria will contract and push blood into the ventricles.
The ventricles will contract pushing blood into the arteries.
The atria and ventricles will relax allowing the heart to fill with blood.
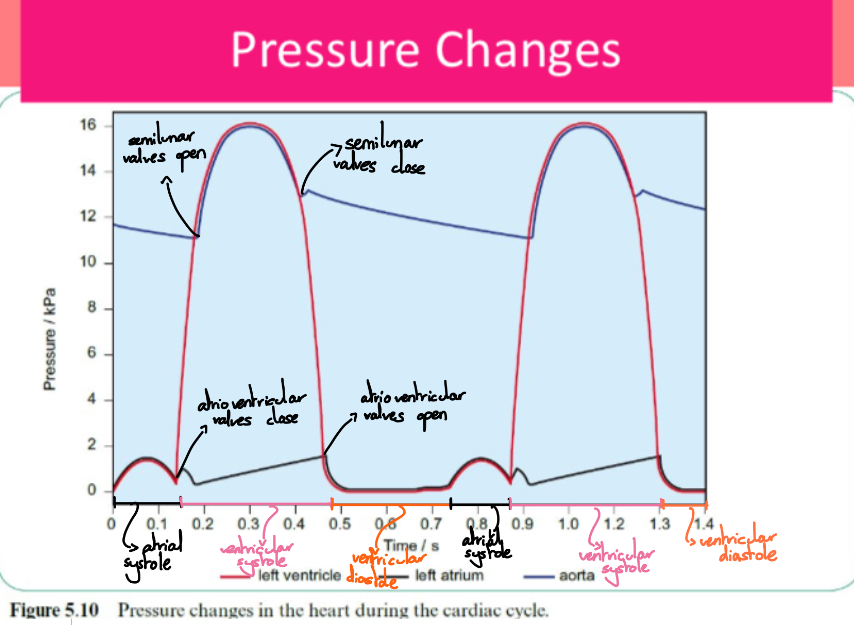
What causes the heart valves to open and close?
Pressure changes in the heart chambers:
High pressure behind the valve forces it to open
High pressure in front of the valve closes it
Name the types of valves that can be found in the heart.
Pocket valves in veins
Atrioventricular valves between atria and ventricles
Semilunar valves in aorta and pulmonary artery
What are the 3 stages of the cardiac cycle?
Atrial systole
Ventricular systole
Diastole
What happens during atrial systole?
The muscles of the atria contract.
The pressure inside of the atria increases as the volume decreases.
The semi-lunar valves in the vena cava and the pulmonary vein close as there’s pressure is higher in the atria than the veins.
The tricuspid and bicuspid atrioventricular valves open as there’s an higher pressure inside the atria than the ventricles allowing blood into the ventricles.
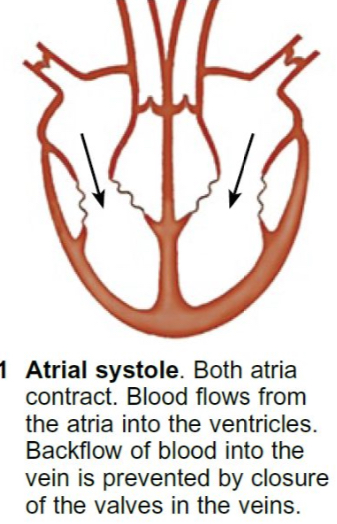
What happens during ventricular systole?
The muscles of the ventricles contract.
The pressure inside the ventricles increase as the volume decreases.
The tricuspid and bicuspid atrioventricular valves close as there’s a higher pressure inside the ventricles than the atria.
The semi-lunar valves in the aorta and pulmonary arteries open as there’s a higher pressure inside the ventricles than the arteries.
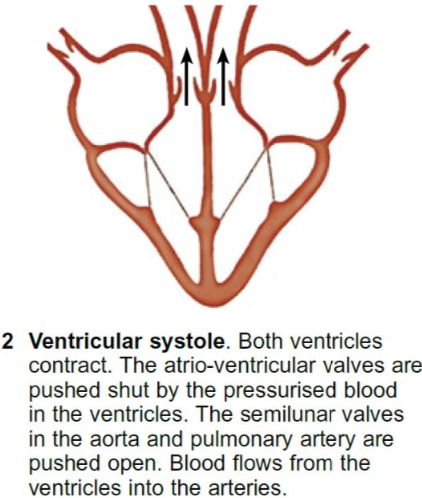
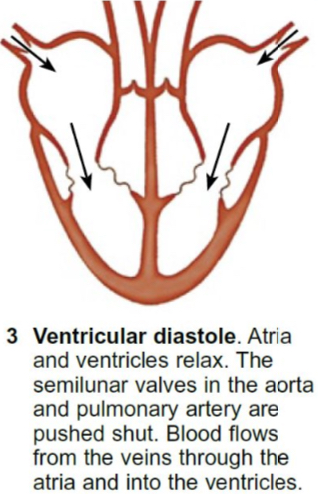
What happens during diastole?
All the heart muscles relax.
Pressure inside the ventricles decrease as the volume increases.
The semi-lunar valves in the aorta and the pulmonary arteries close as the pressure inside the arteries are higher than the ventricles.
Pocket valves in the vena cava and pulmonary vein open as there’s a higher pressure inside the veins than atria.
Blood flows into the atria from the vena cava and pulmonary vein allowing the heart to fill with blood.
Blood pressure remains low inside the atria and ventricles.
What’s the equation for cardiac output?
Cardiac output = heart rate x stroke volume
*heart rate = the rate at which the heart beats
*stroke volume = volume of blood pumped out at each beat
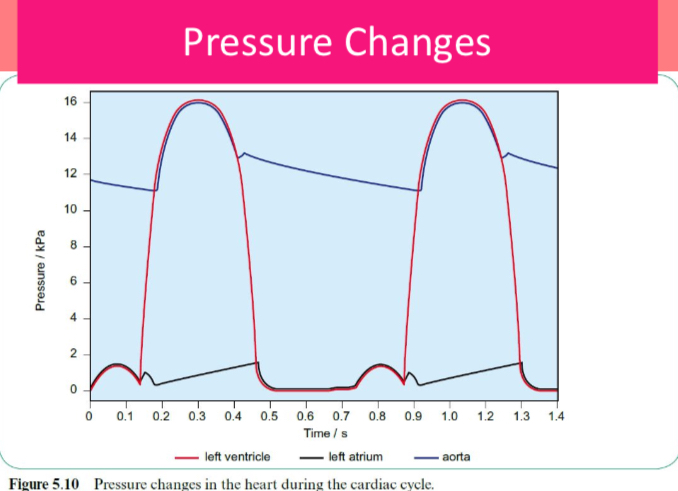
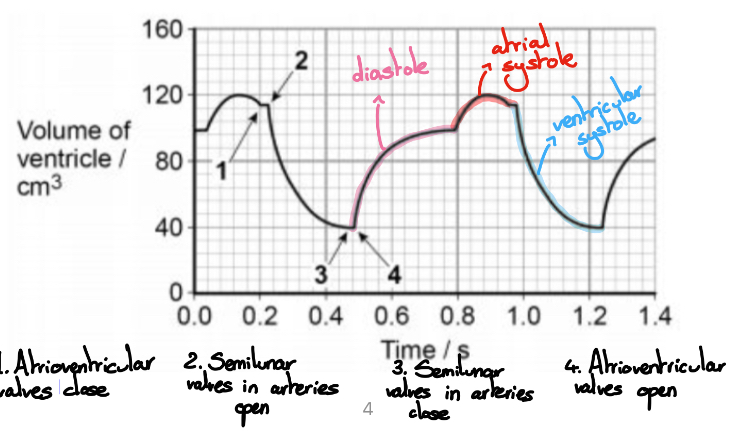
Name when the valves are open and closed and when the stages of the cardiac cycle occur.
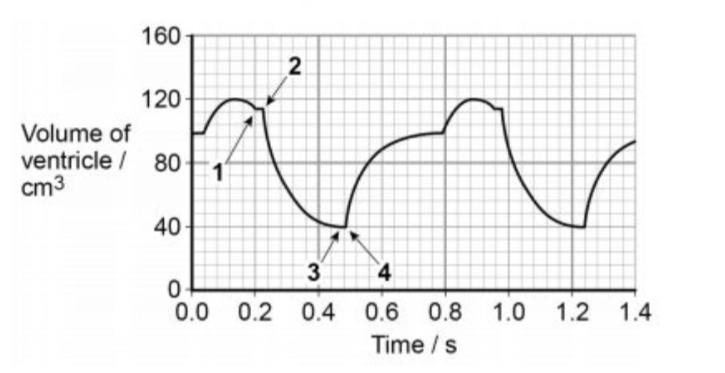
Name when the valves are open and closed and when the stages of the cardiac cycle occur.