Principles of Doppler Echo
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Definition of Doppler Echocardiography
method for detecting the direction and velocity of blood flow
Uses of Doppler echo
to evaluate normal vs abnormal flow states and acquire quantitative data
Laminar blood flow
normal, parabolic blood flow with max velocity <1.5 m/s
Turbulent blood flow
abnormal, disordered direction of flow with many RBC velocities
Frequency
the number of waves that pass a given point in one second (Hertz or unit of cycle/second)
↑ high Frequency =
↓ short wavelength
↓ low Frequency =
↑ long wavelength
What is the sound speed in tissues?
1540 m/s
How does conventional 2D echo work?
The machine calculates distance by timing how long the echo takes to return back from the tissue. This repeats thousands of times per second to create an image
The best images in 2-D are obtained when the target is _____ to the sound waves
perpendicular
How does doppler echo work?
depends on the measurement of relative change in the returned/reflected ultrasound frequency when compared to transmitted frequency
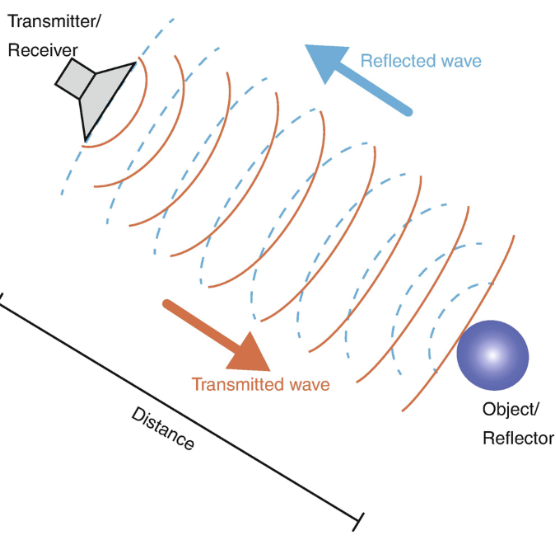
characteristics of disturbed blood flow that doppler echo measures
direction, velocity, turbulence, distinguishes normal and abnormal flow patterns and quantitates them
Red blood cell moves TOWARD the transducer
↑ higher frequency + positive doppler shift
Red blood cell moves AWAY from the transducer
↓ lower frequency - negative doppler shift
The Doppler equation is used to calculate the velocity of blood flow based on
transmitted frequency
Angle of transducer
Velocity of sound in blood (1540m/s)
High pitched sounds
large doppler shifts - presence of high velocities
Low pitched sounds
lesser doppler shifts
Laminar flow audio
smooth, pleasant
Turbulent flow audio
high pitched, whistling, harsh/raspy
A spectral Doppler display
is a graphical representation of blood flow velocity over time, generated by an ultrasound machine
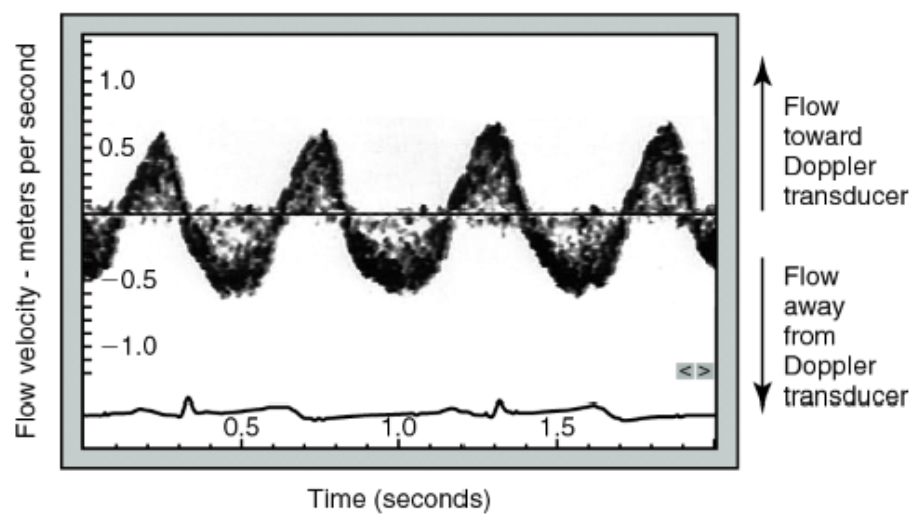
Flow velocity toward the transducer is
positive or upward
Flow away from transducer
negative or downward
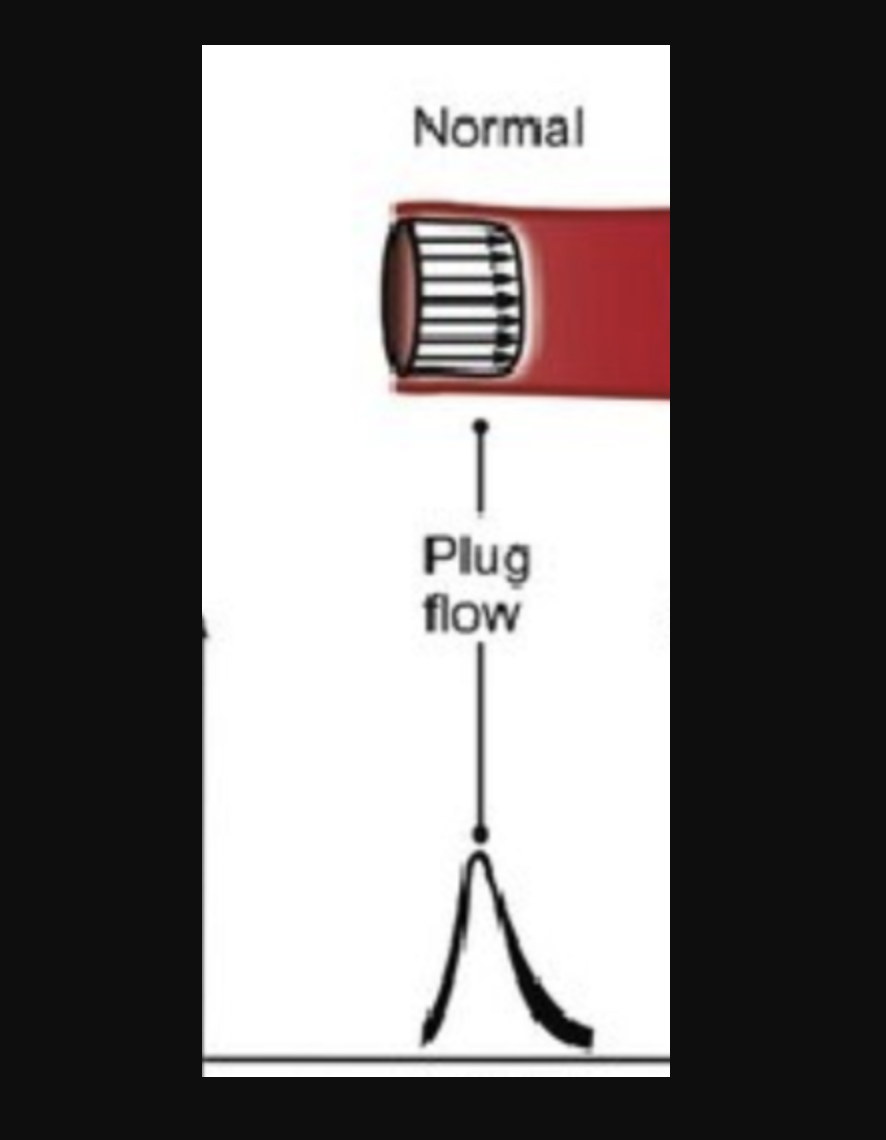
Laminar flow (plug flow) doppler profile
narrow doppler spectrum / Clear frequency window
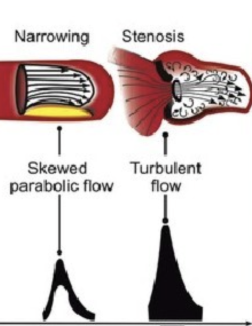
turbulent blood flow doppler profile
Spectral broadening - thicker frequency window that can fill the window depending on grade of narrowing or stenosis
True velocity of blood flow is measured when the angle of Doppler beam direction is
Parallel to the flow
Plug flow
flattened flow during systole - velocity is constant across entire CSA
Continuous Wave Doppler
Continuous generation of ultrasound coupled with continuous ultrasound reception
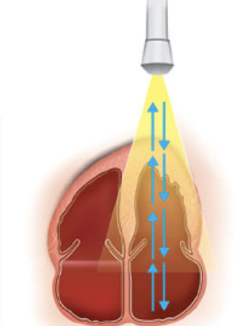
Advantage of CW
measures high velocities accurately
Disadvantage of CW
lack of selectivity or depth discrimination
Pulsed Wave Doppler
alternates transmission and reception of ultrasound
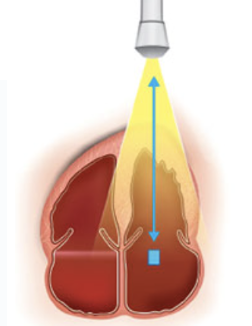
Advantages of PW
provides doppler shift data selectively from a small segment along the ultrasound beam
Sample volume
small, operator defined area within tissue where blood flow velocity is measured
Range gating
transmits short pulses then listens for returning echos only from a specific depth/range
PW mapping
visual map of blood flow
Disadvantage of PW
inability to accurately measure high blood flow velocities over 1.5-2.0 m/s
aliasing
occurs due to sampling rate being too low with respect to Nyquist Rate
Nyquist limit =
PRF/2
Nyquist limit defines…
the maximum velocity that can be measured without aliasing.
PRF
pulse repetition frequency - the number of pulses the ultrasound machine transmits per second
Max PRF is limited by -
The depth of the sample volume from the transducer.
The deeper the sample volume, the longer the ultrasound pulse takes to travel and return, which forces the system to use a lower PRF
The closer the sample volume is located to the transducer-
the higher the max PRF can be used
The Nyquist limit is controlled by 2 factors:
Depth into the tissue and transducer frequency