Chemistry Unit 1 Test September 16th
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Matter
made up of particles, has mass, and volume
atom
particle that makes up matter
mass
amount of matter
volume
how much space matter takes up
2 types of matter
pure substance, mixture
pure substance
has definite composition
2 types of pure substances
element and compound
mixture
made up of 2 or more pure substances PHYSICALLY COMBINED
2 types of mixtures
homogenous mixtures, heterogenous mixtures
homogenous mixture
components are uniformly distributed at the molecular level (mixed uniformly)
special type of homogenous mixture
solution
solution
a liquid mixture in which the solute is uniformly distributed within the solvent
solute
minor component of solution, is being dissolved
solvent
major component of solution, does the dissolving
heterogenous mixture
has a non-uniform composition, meaning its parts are not evenly distributed and are often visible to the naked eye
element
a pure substance containing only one kind of atom
compound
a pure substance containing two or more kinds of elements
Matter that has uniform properties is called a
pure substance
Matter that cannot be decomposed into simpler substances is called an
element
Matter that can be simplified chemically is called a
compound
Matter that does not have uniform properties is called a
mixture
Matter that is uniform throughout is called a
homogenous mixture
Matter that is not uniform throughout is called a
heterogenous mixture
endothermic
absorbs energy
exothermic
releases energy
intensive properties
physical properties that do not depend on amount of matter present
extensive properties
physical properties that do depend on amount of matter present
Extensive properties examples
Mass, width, height, volume
Physical Change Definition
Change in appearance, change in how it looks
Physical Change Types
Dissolves, phase changes (s, l, g)
Physical Property Definition
Describing, senses
2 Types of Physical Properties
Intensive and Extensive
Physical Property examples
malleable, luster, ductile, color, conductivity, texture, odor, melting point (0C), boiling point (100C)
solid
has definite shape and definite volume
liquid
Has fluidity. Particles touching but allowed to move around.
gas
Particles allowed to move around and is compressible
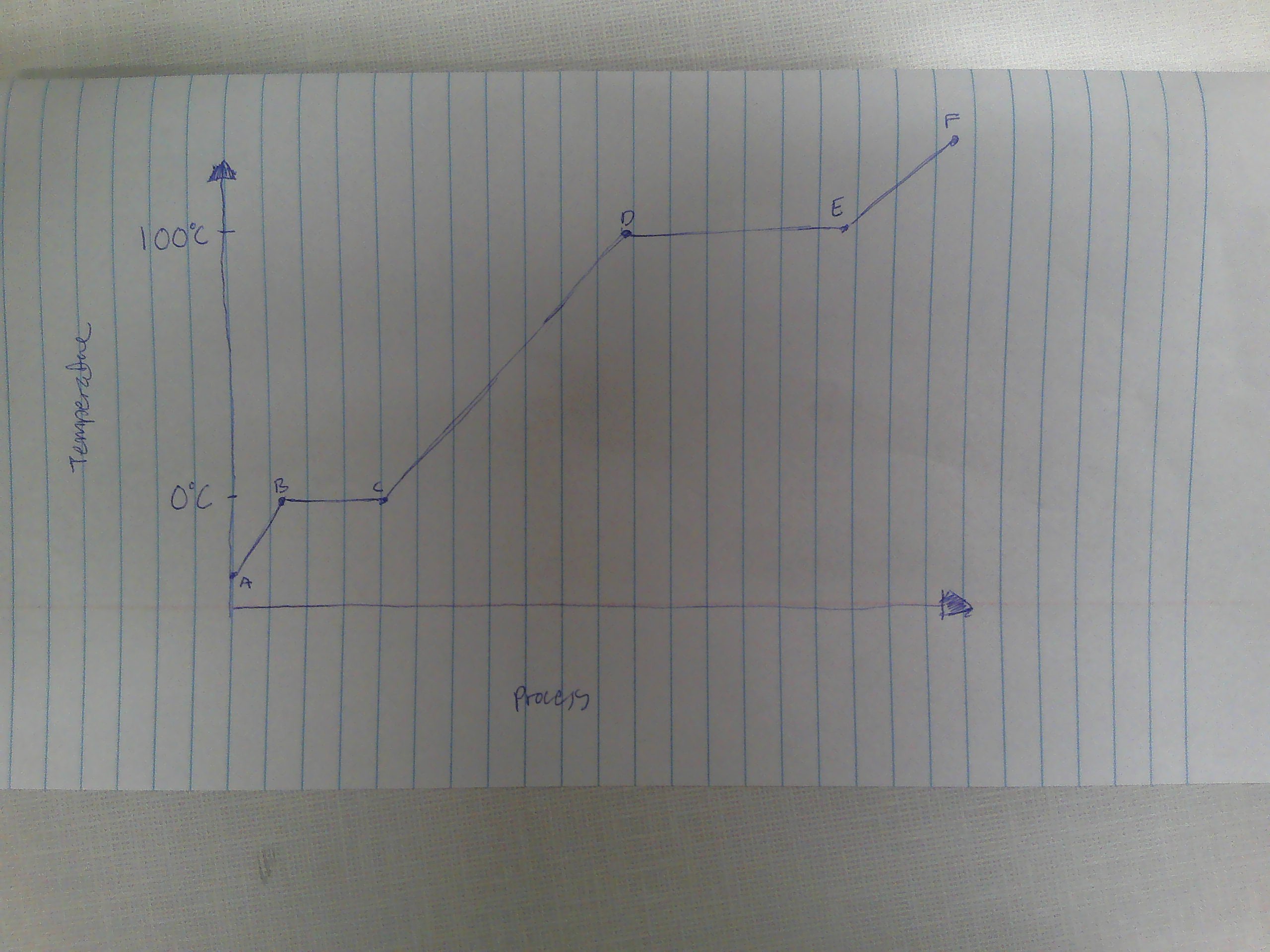
A-B
Solid
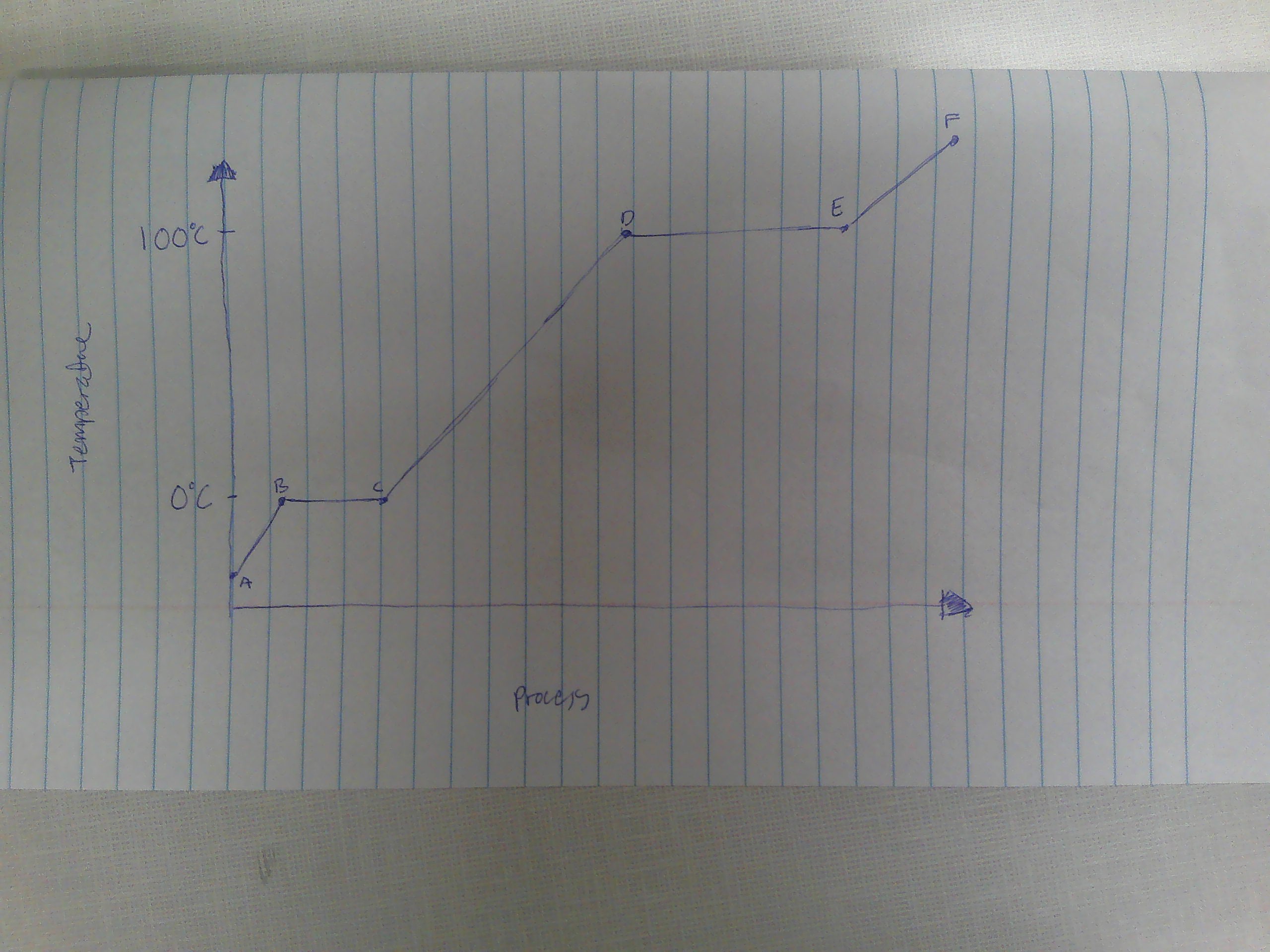
B
melting point (0C)
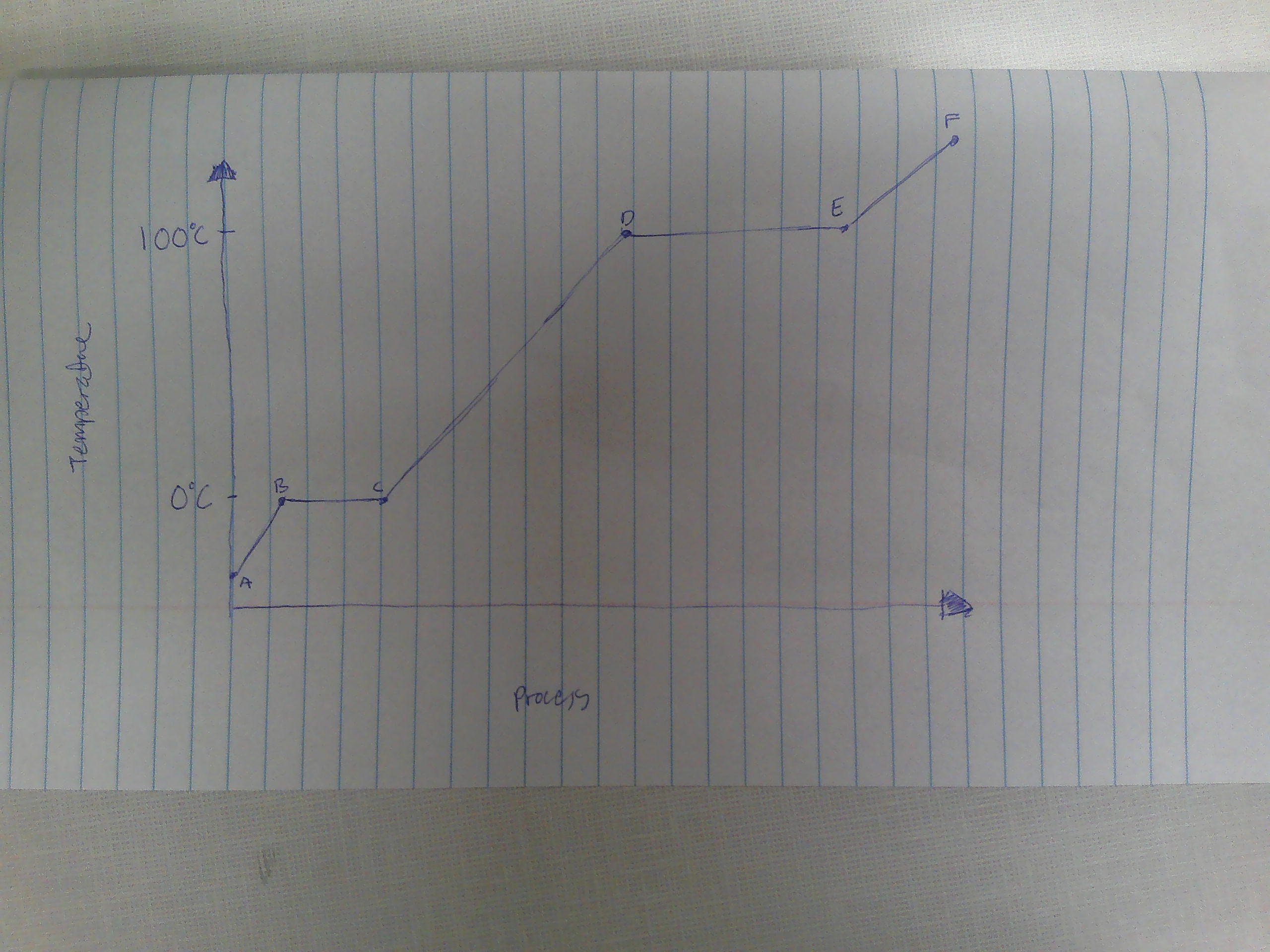
B→C
melting
way to remember melting and freezing points
mf
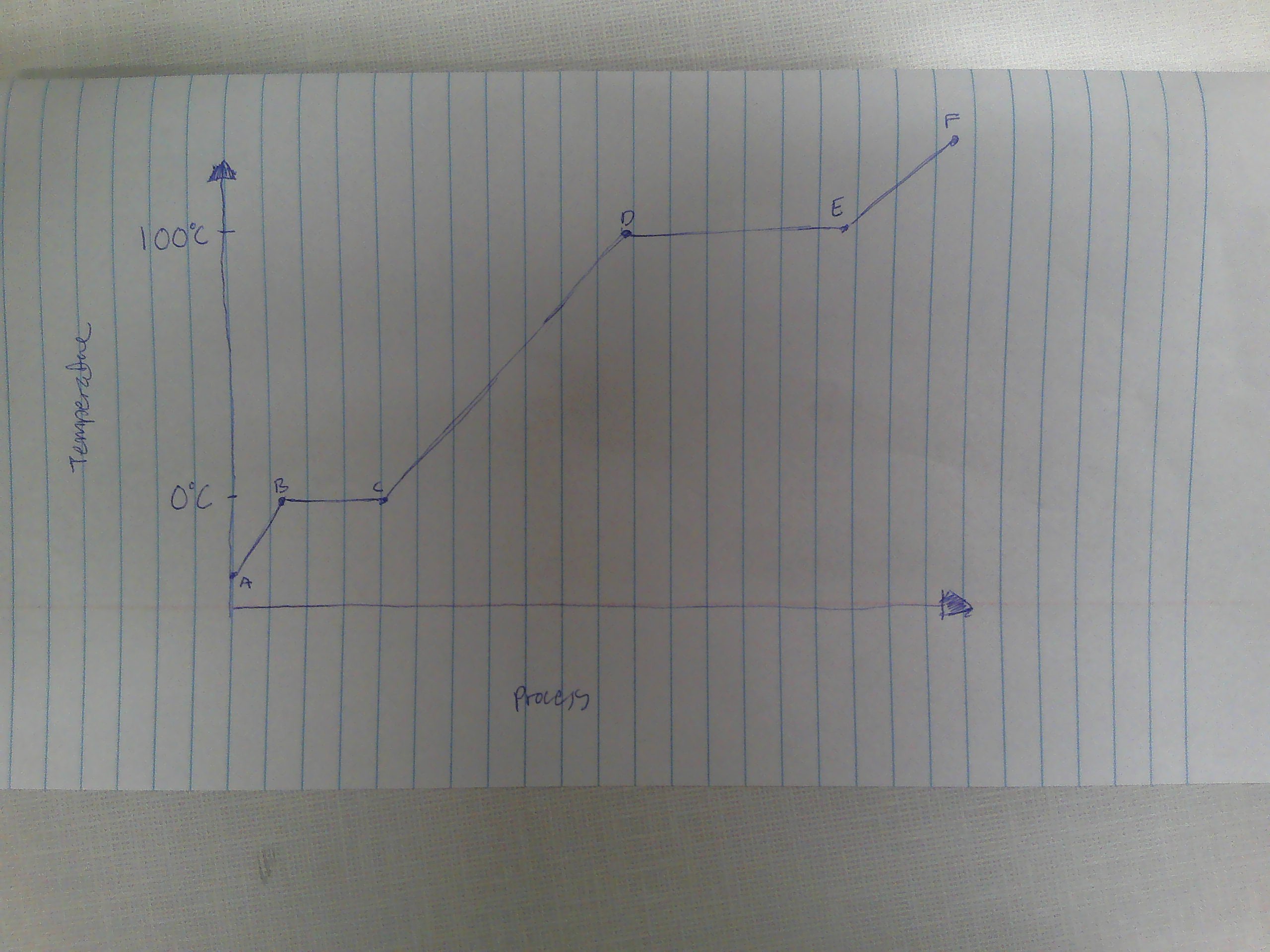
C→B
freezing
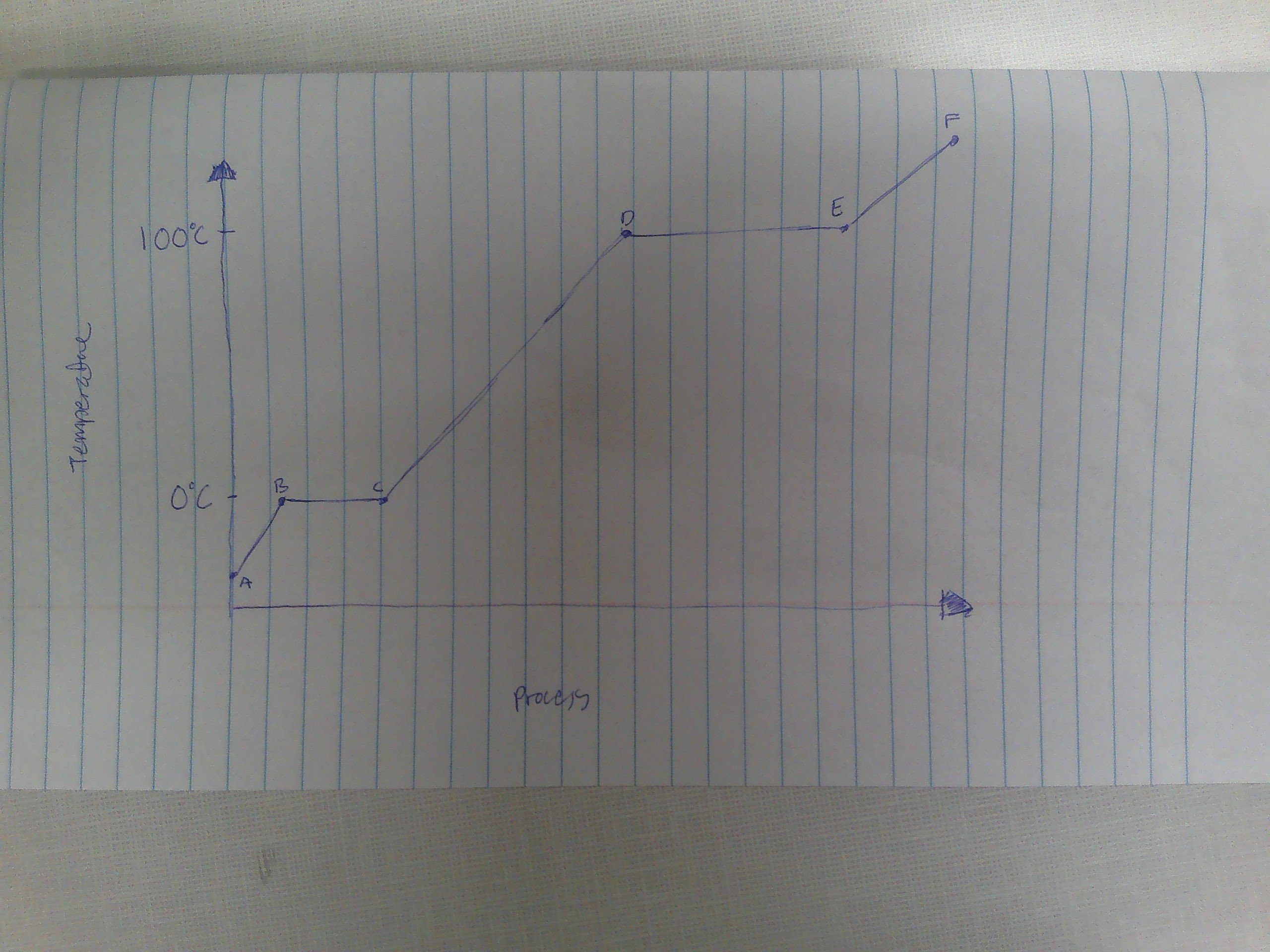
C
freezing point
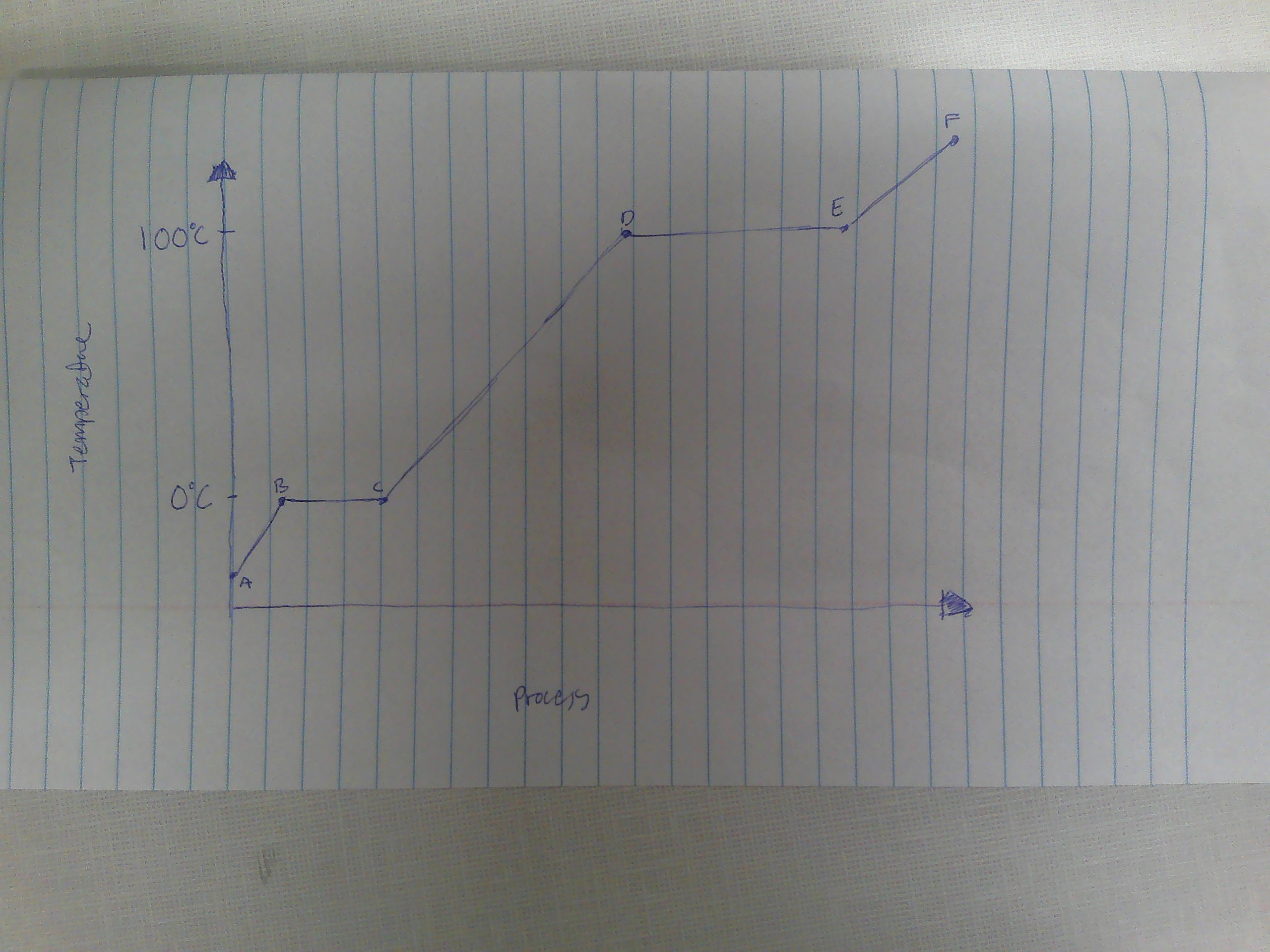
C-D
liquid
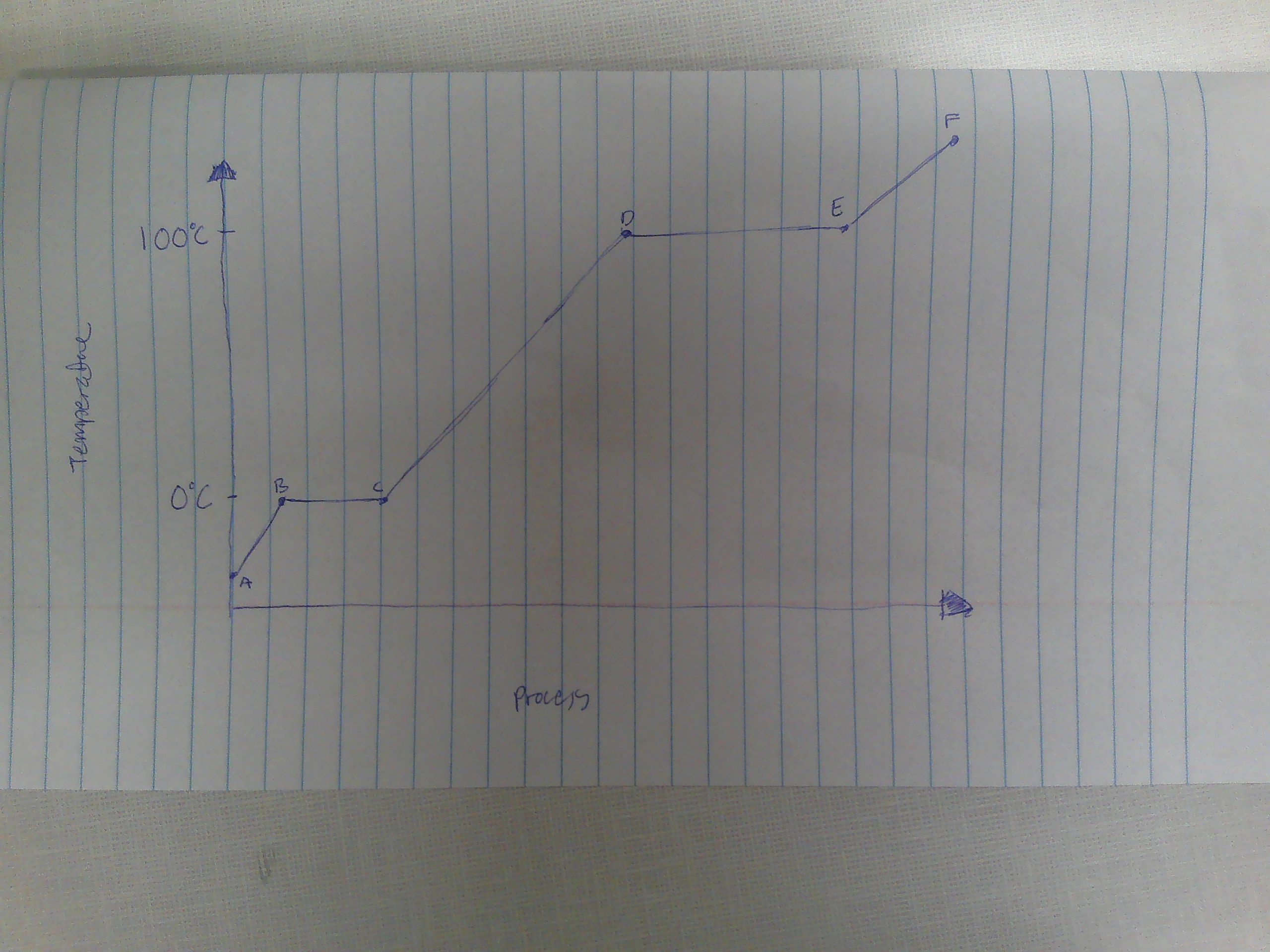
D
boiling point (100C)
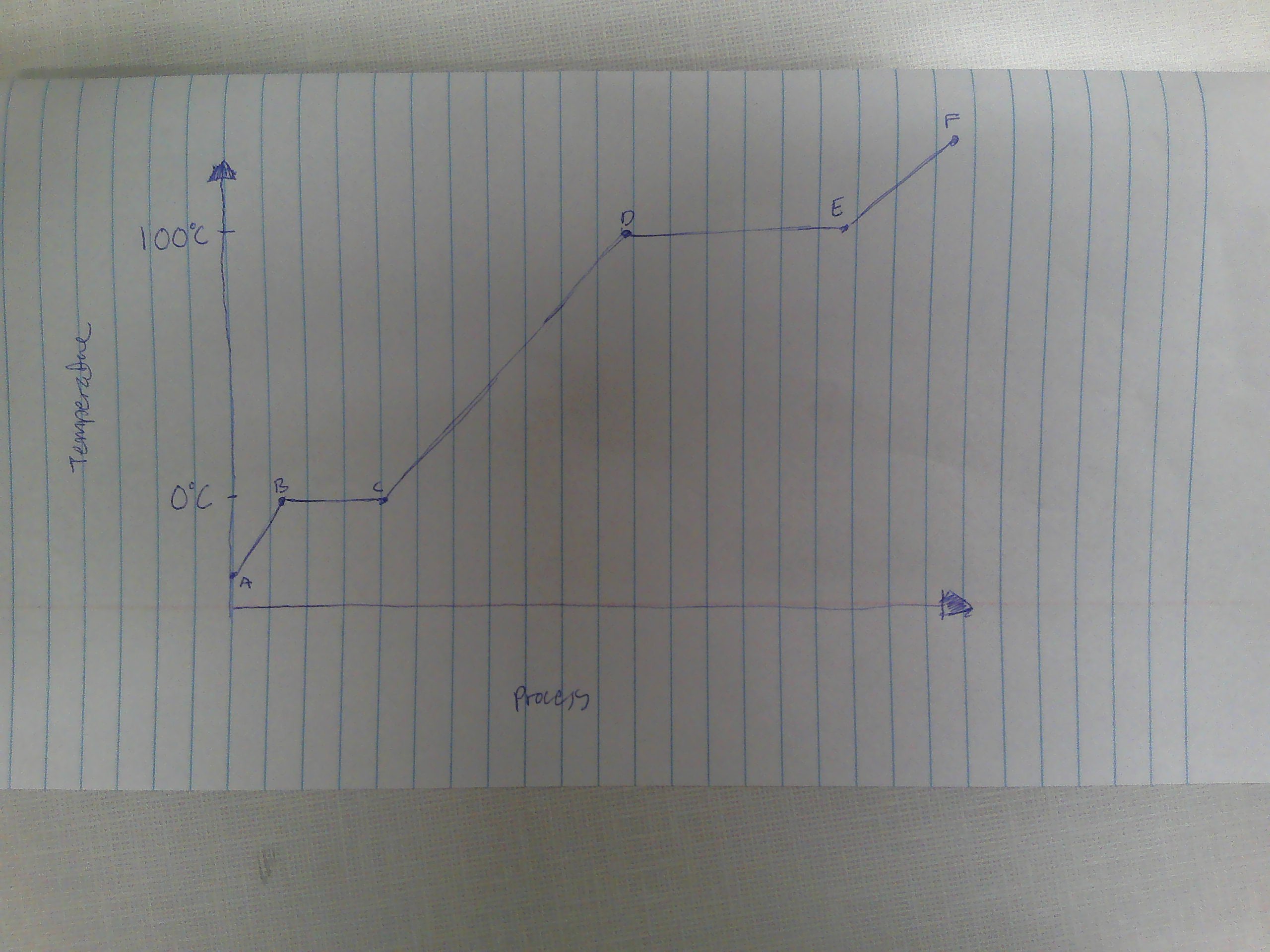
D→E
evaporation
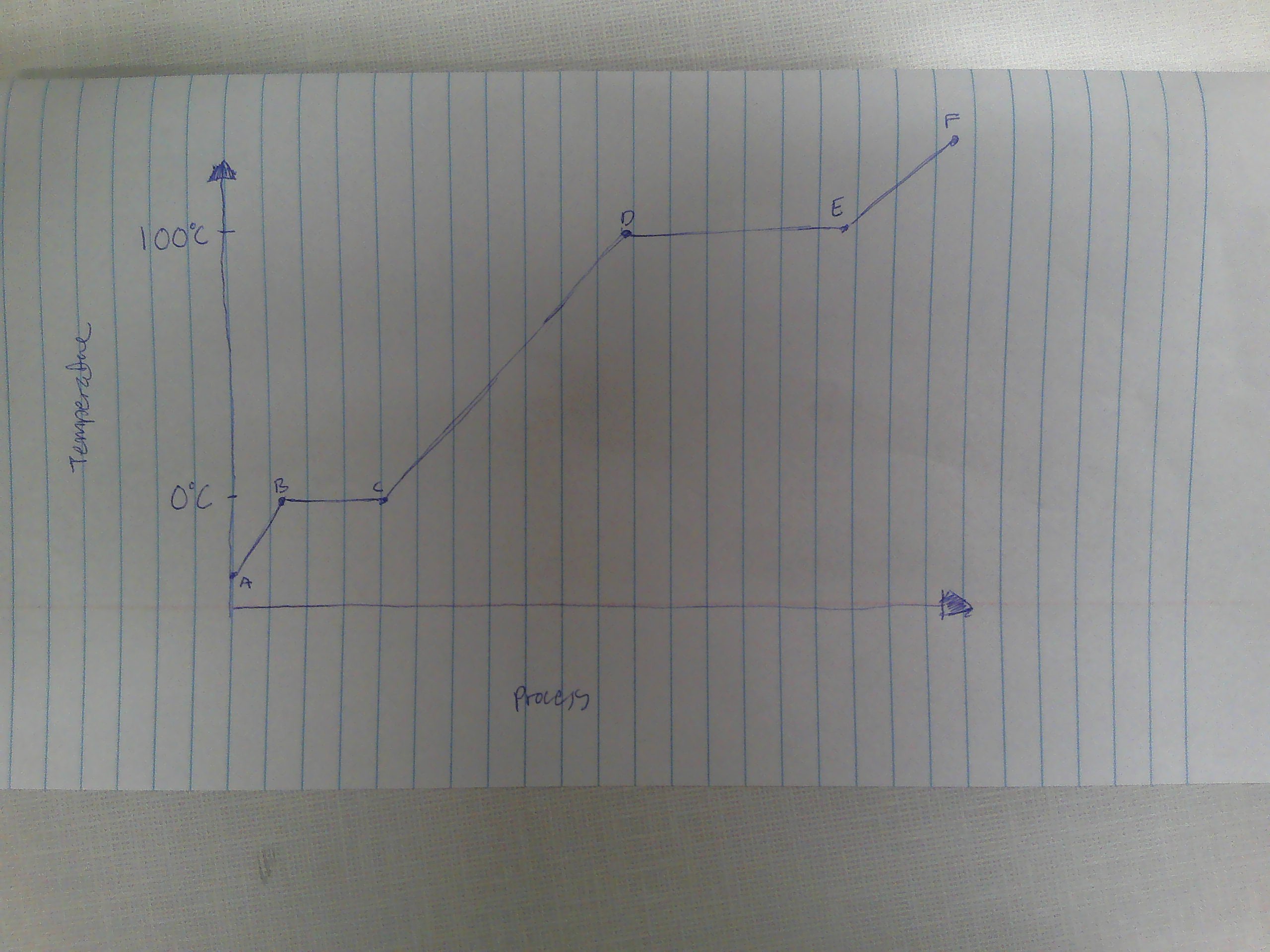
E→D
condensation
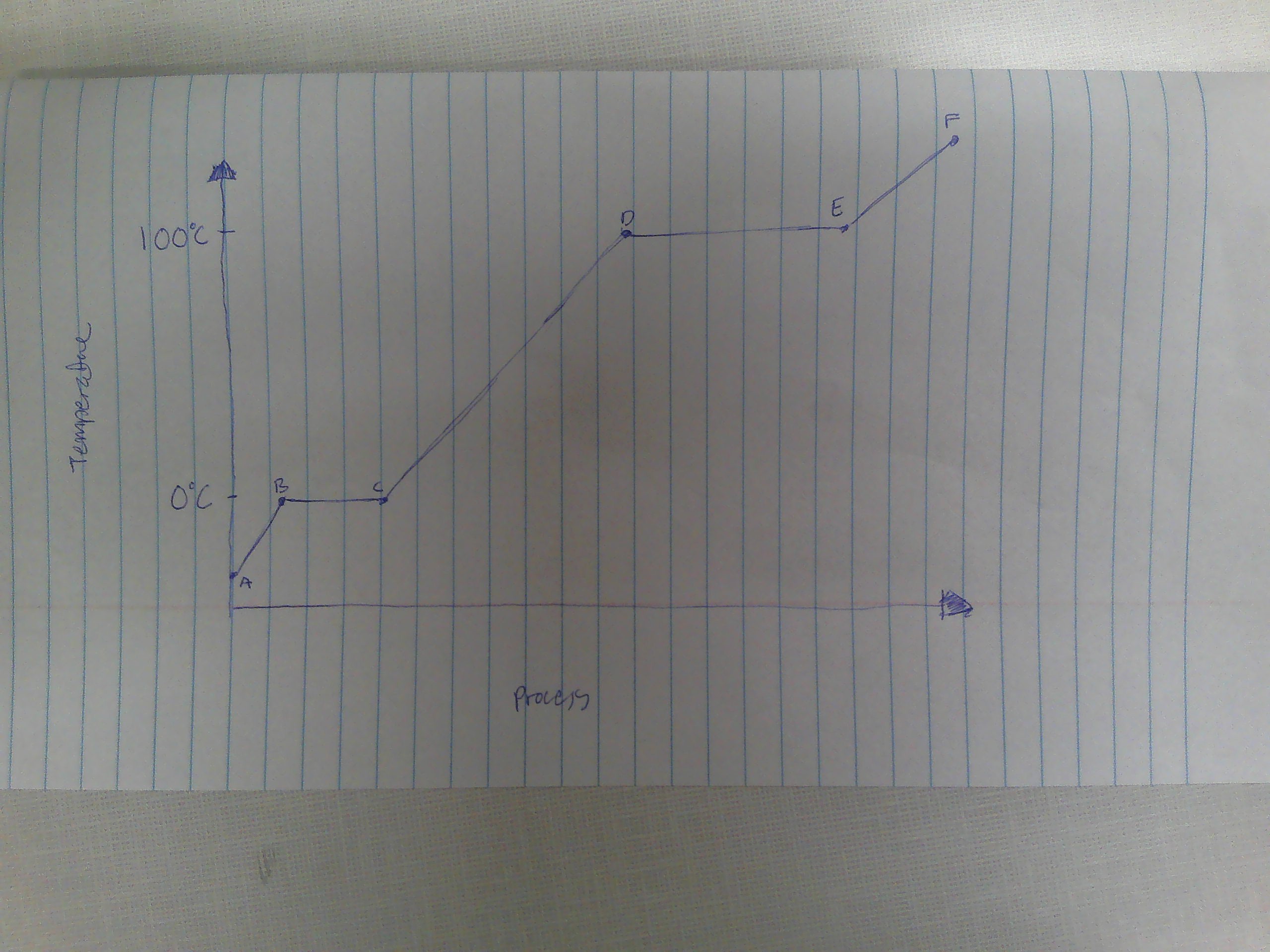
E-F
gas
chemical change definition
change in composition
chemical property
how it reacts
chemical change examples
flash of light, ash, precipitate, producing gas, temperature change
Is density intensive or extensive?
Intensive
chemical property examples
flammability, combustion, corrosion, irritability
density formula
d = m/v
how to read graduated cylinder
volume is higher water level minus lower water level (usually in milliliters, mL)