Topic 2: Waves and Optics
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
What is a longitudinal wave?
When the particles' oscillations are parallel to the direction of energy transfer
What is a transverse wave?
When the particles' oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer
What is polarisation?
When oscillations of the transverse wave are in one direction (not all directions) at a right angle to the direction of light.
Can longitudinal waves be polarised?
No, because the particles only oscillate in one direction, so only transverse waves can be polarised.
What is a plane of polarisation?
The plane formed from the vibrations and the direction of wave travel/ energy transfer
What is the structure of an EM wave?
They consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields, which are perpendicular to each other, and the direction of wave travel
What happens when light passes through a Polaroid filter?
Only the light with oscillations in the direction parallel to the plane of the Polaroid filter can pass through
The rest of the light is absorbed
What is reflected light in terms of polarisation?
It is partly plane polarised
What happens if two polarising filters are placed together when they have the same orientation?
All the lights can pass through
What happened if two polarising filters are placed together when they have planes of polarisation that are perpendicular to each other?
The light cannot pass through
What is the proof that light is a transverse wave?
Using polarising filters, we can show this as light cannot pass through both when the planes of polarisation are perpendicular to one another
What are progressive waves?
Ones carried by oscillations particles about an equilibrium position, they transfer energy without transferring matter
What is wave displacement?
The instantaneous distance from the equilibrium position, it is a vector.
What is amplitude?
The maximum displacement of a particle from the equilibrium position.
What is wavelength?
The shortest distance between two particles oscillating in phase.
What is frequency?
The number of ways passing a given point per second. The number of complete oscillations of a particle per second.
What is a period?
The time taken, for one complete wave to pass a point; the time for a particle to make one complete oscillation.
What is the formula for period?
1/frequency
What is the formula for wave speed?
wave speed = frequency x wavelength
What is the phase of an oscillating particle?
A measure of what fraction of a cycle each particle has completed as measured from a chosen, starting point
What can phase be measured in?
Fractions of a wavelength, degrees, or radians
How many radians are there in a circle?
2π
What would the phase 1/2 of a wavelength be if measured in degrees, and in radians?
radians: π
degrees: 180°
What does it mean to be in antiphase?
This is when two points are separated by an odd number of half wavelengths. So for example, they may be half of a wavelength out of phase with one another, or they may be 1.5 wavelengths out of phase with each other.
What will all different types of waves demonstrate?
Reflection, refraction, diffraction, and interference
What is refraction?
When a wave passes across a boundary at which the wave speed changes (the wavelength also changes). The wave changes direction as well as speed.
If a wave slows down in a denser material, will it refract towards, or away from the normal line?
Towards
What is diffraction?
The spreading out of waves as they pass through a narrow gap or around an obstacle.
What makes waves spread out more in diffraction?
if the slit is made narrower or the wavelength is made larger.
What are fringes?
The stripes on a screen when light is diffracted through a slit onto a screen.
What is the relationship between the size of the primary (central) fringe and the outer fringes?
The central fringe is twice as large
What happens to the fringes as you move away on either side from the central fringe?
the light intensity decreases.
What is monochromatic light?
Light of a single frequency/wavelength
What is a point source? Give an example.
a point that produces circular wavefronts
e.g. the sun

What are coherent point sources?
when two point sources produce waves that overlap with each other's, they are coherent if they are ones that produce waves with:
- the same frequency/wavelength (if light then monochromatic is the word)
- similar amplitude
- a constant phase relationship (when the phase difference along two waves is the same for every point along each wave)
What occurs between the waves produced by two coherent point sources?
interference (destructive at some points, constructive at others)
What is path difference? Draw a diagram to help explain.
The difference in distance travelled by the two waves from each of their origins.

When does maximum diffraction occur?
When the wavelength equals the gap size
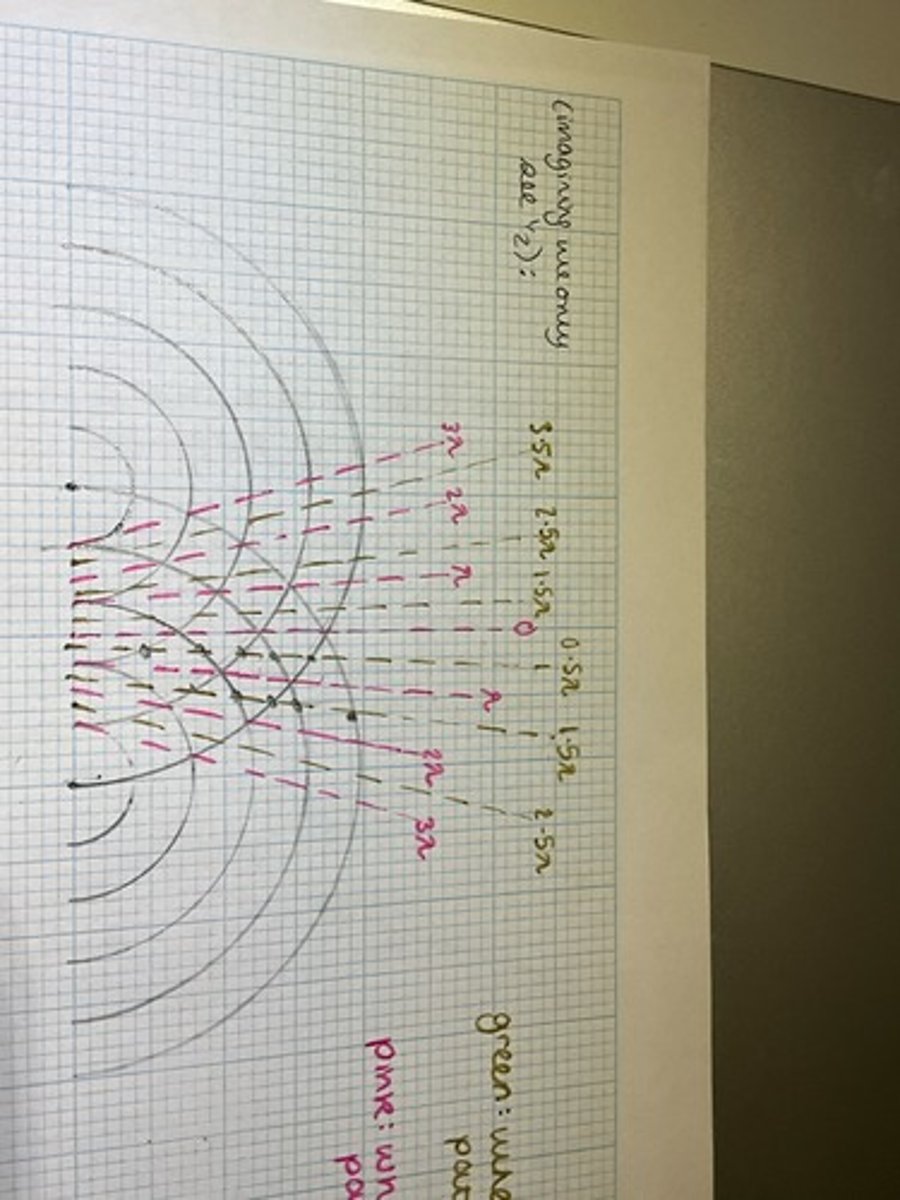
When does constructive interference occur when considering coherent point sources? Draw a diagram to help explain.
At points when the waves overlap with a path difference of nλ (a whole number of wavelengths), so the waves arrive in phase
It is the points on the pink lines in the diagram
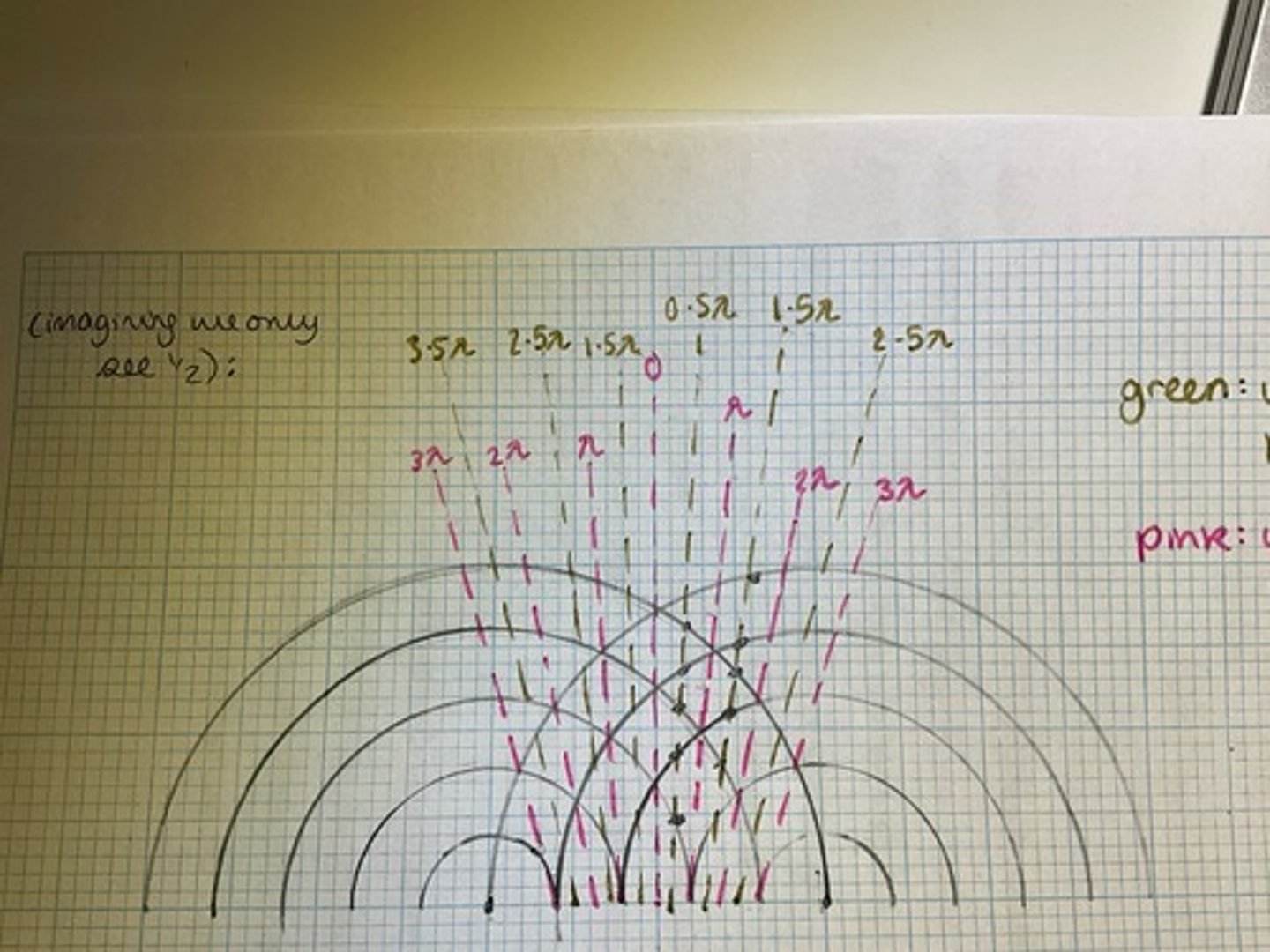
When does destructive interference occur when considering coherent point sources? Draw a diagram to help explain.
At points when the waves overlap with a path difference of (n + 0.5)λ (an odd number of half wavelengths) so the waves arrive in anti-phase
The points on the green lines in the diagram are where this occurs.
What is the wavelength of visible light?
Between 400 and 700 nm
What is interference?
When two waves meet, we can add together the displacement of each wave to find the resultant displacement
Interference be seen?
When two waves have a constant phase relationship
What is constructive interference?
When two waves are in phase with each other, so the resultant displacement is twice as large
What is destructive interference?
When two ways are in antiphase with each other, so they cancel each other out.
What is the principle of superposition?
It states that when two waves meet, the total displacement at a point is equal to the sum of the invidivual displacements at that point (interference).
When are supercrests and supertroughs created?
crest+crest = supercrest
trough + trough = supertrough
What are stationary waves?
Waves where there is no net transfer of energy (there are still oscillations)
When are stationary waves created?
When two progressive waves of equal magnitude travelling in the opposite direction, with similar amplitude and equal frequency and speed are superposed.
This often occurs due to reflection.
What is a node?
Points along a stationary wave where displacement amplitude is at a minimum. (ideally zero)
What is an antinode?
Points of maximum amplitude that occur halfway between each pair of nodes.
What is the distance between adjacent nodes?
Half a wavelength
Give examples of stationary waves
- in a pipe open at one end, there is a node at the closed end and an antinode at the open one
- in a microwave, microwaves are transmitted at metal plates, so they are then reflected back at the same speed and frequency
What is the first harmonic pattern of vibration on a string? Draw it, too.
the lowest possible frequency that gives a pattern
How do you find the wavelength causing the first harmonic pattern of vibration on a string?
2 x length of string (use distance between nodes to calculate this)
Draw the second harmonic pattern of vibration on a string.
lowest possible frequency plus one node
How do you find the wavelength causing the second harmonic pattern of vibration on a string?
1 x length of string (use distance between nodes to calculate this)
Draw the third harmonic pattern of vibration on a string.
lowest possible frequency plus 2 modes
How do you find the wavelength causing the third harmonic pattern of vibration on a string?
2/3 x length of string (use distance between nodes to calculate this)
What three factors aftect the frequency of a standing wave on a string?
- mass of the string
- tension of the string
- length of the string
What is the formula for frequency of a standing wave on a string?
f = (1/(2l)) x (√(T/µ))
What pattern is produced from single slit diffraction? Draw and describe it.
- central fringe is twice as wide as as the outer fringes
- peak intensity decreases rapidly
- outer fringes have a much lower intensity
- each of the other fringes is the same width
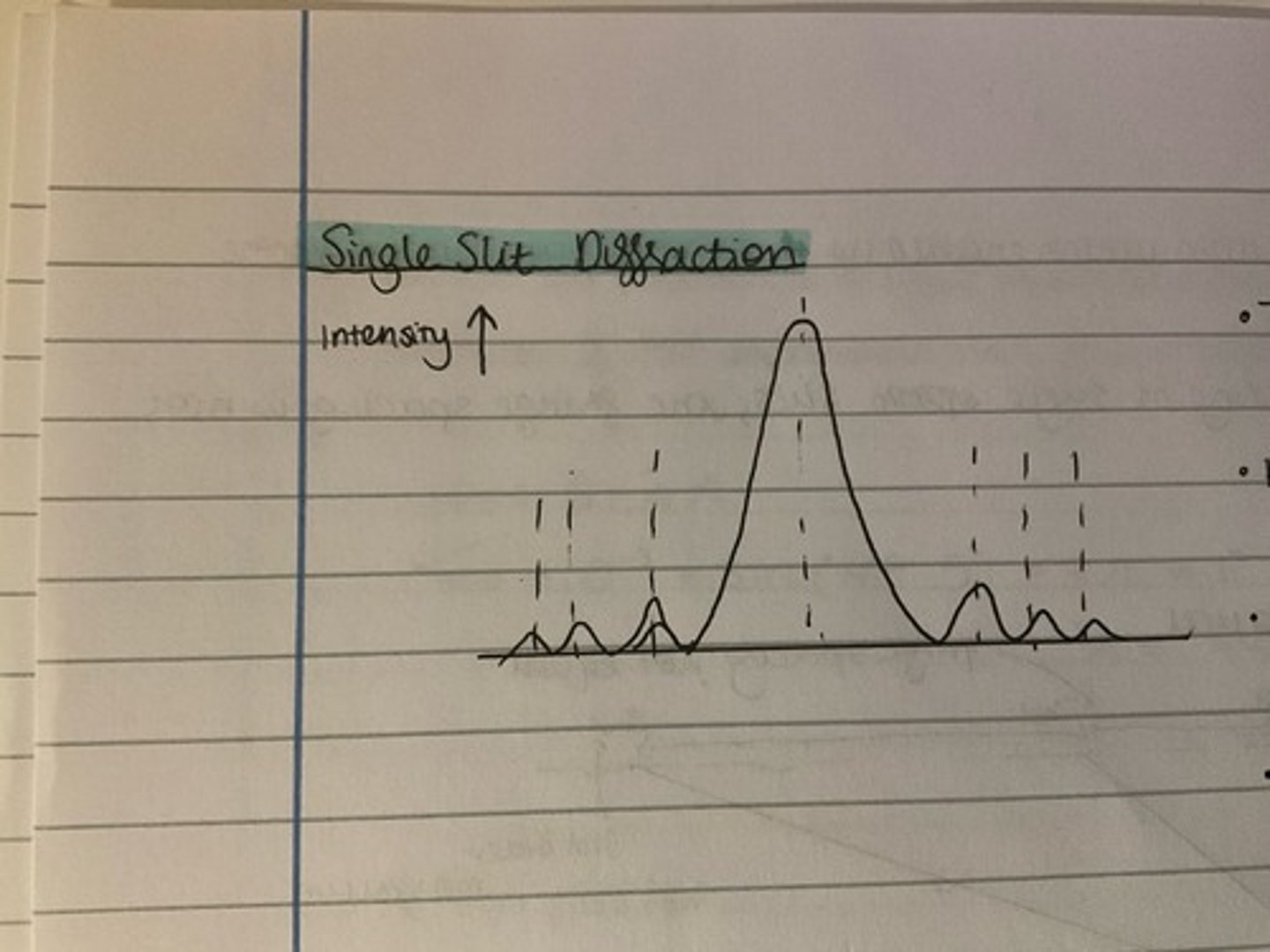
Which factors affect diffraction patterns (single slit)?
slit width and wavelength
How does slit width affect diffraction?
- a smaller slit width causes a wider central maximum (due to more diffraction) and a smaller peak (because less light can pass through).
How does wavelength affect diffraction?
- max diffraction is when the slit size is similar to the wavelength
- higher wavelength will to more diffraction (wider maxima and greater spacing)
Which colours of light diffract the most/least?
most = red
least. = violet
What is a diffraction grating?
a large number of equally spaced parallel adjacent slits.
How does adding more slits affect the pattern from a diffraction grating?
- increases intensity of the fringes
- creates narrower fringes
What is the relationship between the spacing of fringes produced from a diffraction grating? How does this compare to that produced by two slits?
The fringe spacing is not equal for a grating, but it is for double slits
For a fringe grating, the angular spacing is equal.
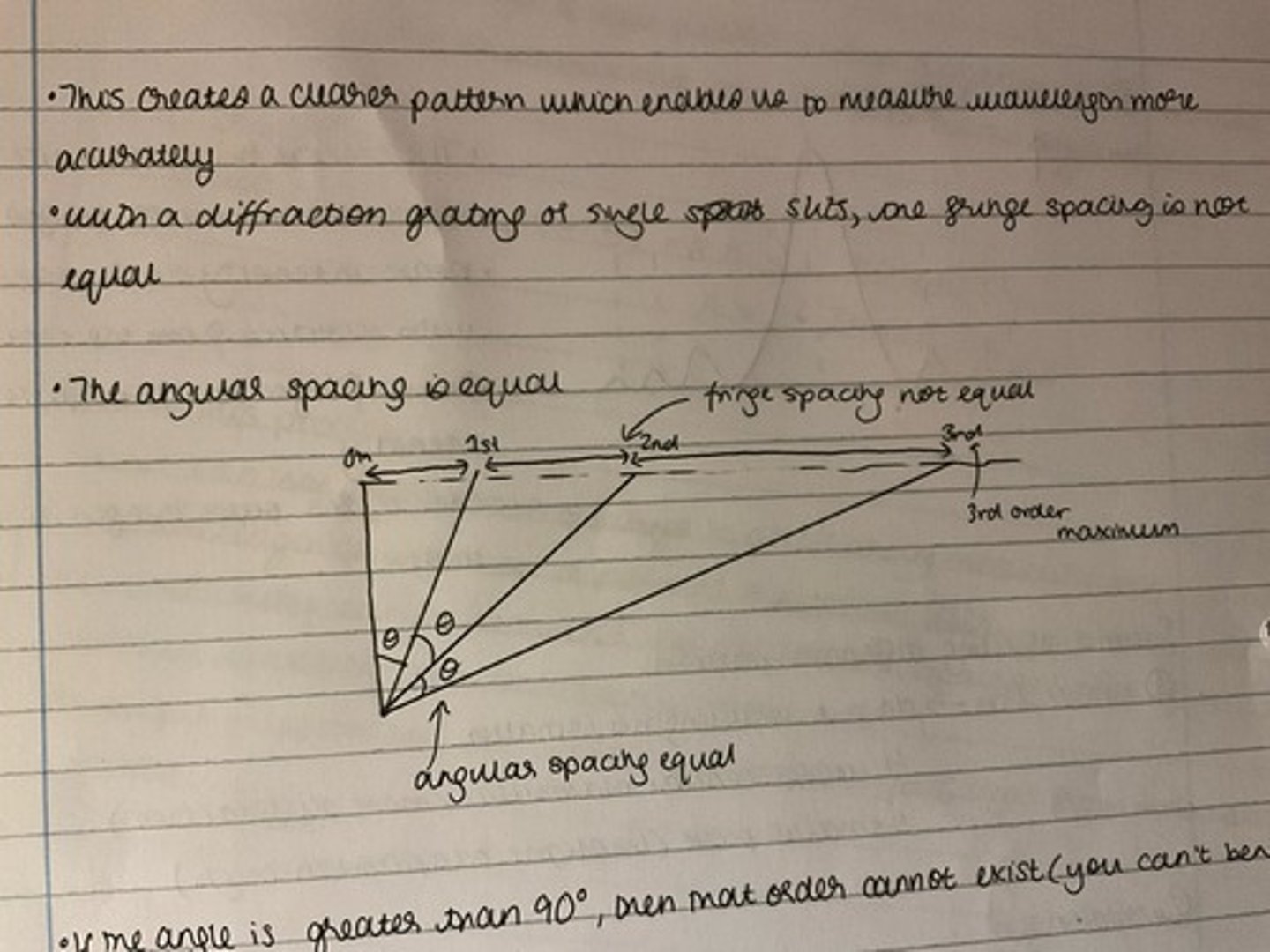
What does each component in the equation dsinθ = nλ stand for?
d = length of a slit
nλ = fringe spacing
- e.g. for secondary maximum, n = 2
Derive the equation dsinθ = nλ.
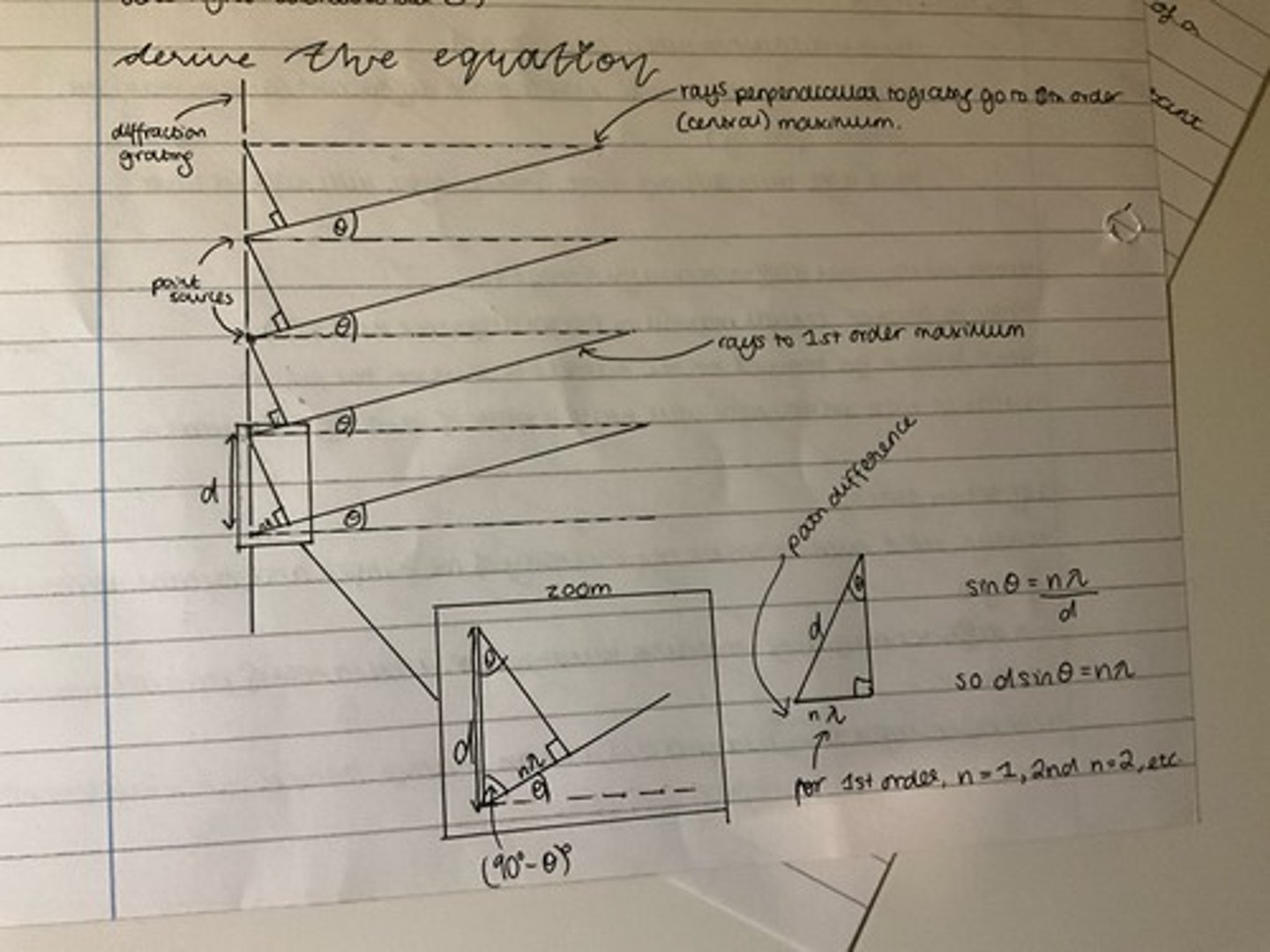
What are the uses of diffraction gratings and the equation?
- accurately measure the wavelength of light as a part of spectrometry
- uncertainties can be reduced by calibration against light of a known wavelength to accurately determine 'd'
- useful in astronomy for measuring the doppler shifts of light from distant stars
When does refraction occur?
when light passes from one transparent medium to another
What happens when light diffracts?
It changes direction because it changes speed. This occurs because one part of the wavefront slows down/speeds up before another.
Which properties change/don't change in refraction?
change: speed, wavelength
doesn't change: frequency
What happens when light goes from an optically less dense to an optically more dense medium?
- slows down
- wavelength decreases
- bends towards the normal
Describe refraction in a triangular prism. (what is the name of the effect produced?)
When white light passes through a triangular prism, the different wavelengths are refracted by different amounts.
this causes the different wavelengths of light to be spread out when refracted through a triangular prism: dispersion
What is a higher refractive index indicative of?
a more optically dense medium (one that slows light down more)
What is refractive index?
The ratio of speed of light in a vacuum to its speed of light in the medium.
What is the formula for refractive index?
n=c/v
c= the speed of light in a vacuum 3x10^8
v= the phase velocity in the medium.
What is snell's law?
n1sinθ1 = n2sinθ2
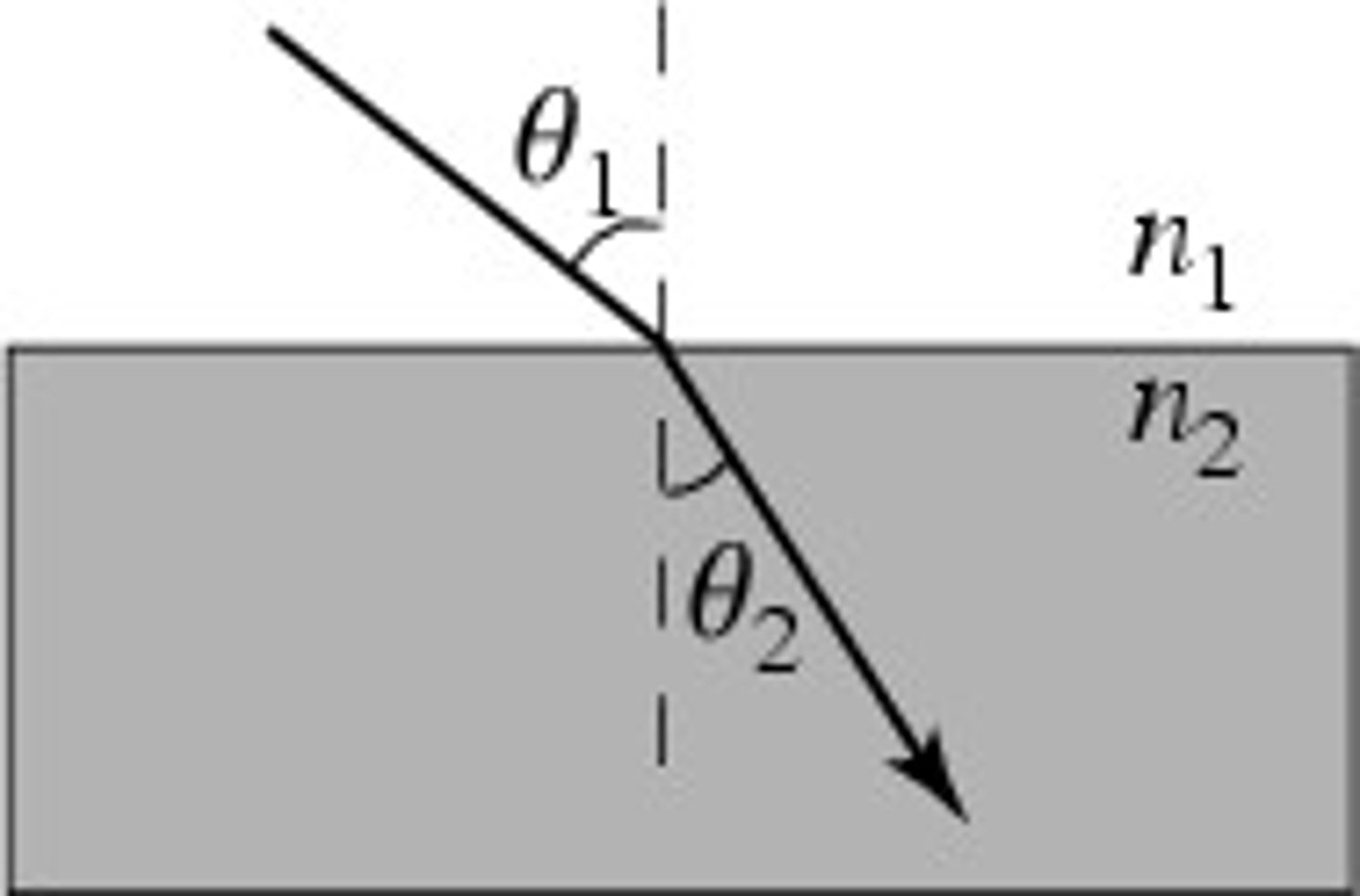
When does total internal reflection occur?
When the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle
Describe why diamonds are ✨sparkly✨?
- small critical angle
- TIR occurs at a very small angle
- high refractive index
- light is "trapped" inside and bounces many times before it can escape through the front of the gem
How to calculate critical angle?
sin c = 1/n
basically, make refractive angle = 90 and apply snell's law, so sin(90) = 11
What are the two parts of an optical fibre?
the core and the cladding
What is the role of the core in an optical fibre?
- acts as transmission medium for EM waves to progress by TIR
- pulses of light carry info at the speed of light in the fibre
What is the role of the cladding in an optical fibre?
- prevents scratching of the core, which could lead to lgiht leading the core, and provides strength
- internal reflection at the core/cladding boundary keeps most of the data/light within the core (refractive index of the cladding is less than in the core)
- reduces "cross-talk" signals crossing from one fibre into another
What is dispersion? (optical fibre)
the broadening of a pulse
What are the two types of dispersion?
Modal and Material
What is modal dispersion?
The spreading of a signal caused by rays taking slightly different paths in the fibre; one longer than the other so that the rays arrive at different times
How to reduce modal dispersion?
Use thinner fibers to reduce the number of possible paths
What is material dispersion?
When light with different wavelengths is used some wavelengths slow down more than others in the fibre so they arrive at different times causing pulse broadening
How to reduce material dispersion?
Use monochromatic light
What are the uses of optical fibres?
- fast: broadband communication (more data more quickly)
- endoscopes in medicine for investigative procedures
- laser light for non-invasive medical treatment
With single slit diffraction, if I use white light where do the blue and red fringes appear?
Blue is on the inside, red is on the outside
With single slit diffraction, if I use a narrower gap, how does using a narrower gap change the appearance of the fringes?
they have a lower intensity because less light can get through
the peaks are wider
When is Young's double slit equation valid?
When the slit-screen distance is considerably greater than the slit separation.