FINANCE / LECTURE 1-3
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Equity =
value of an investor's stake in a company.
represented by the value of shares an investor owns.
Liquidity =
the ease with which an asset can be converted into cash without significantly impacting its market value.
it essentially describes how readily an asset can be bought or sold in the market.
think of it as how quickly you can access cash from an investment without losing a lot of its value
Liquidation =
the process of closing a business and distributing its assets to claimants
Sole proprietorship

Partnerships

Limited partnerships

Limited Liability Companies / Corporations
Owners’ liability is limited to the amount they invested in the firm, they are not required to pay back debts of the firm

Double Taxation
+ C and S corporartions

Board of directors

CEO
the one entitled to run the firm day-to-day
CFO
Goal = maximize wealth of shareholders (maximize share price)
Shareholders who own the company can indirectly control the firm by …
Shareholders who own the company can indirectly control the firm by electing the Board of Directors. The Board of Directors is elected by a voting procedure in which each share counts for one vote.
Agency problem =
when the managers work for their self-interests (e.g., by raising their salary)
Shareholders have three methods to limit/remove agency problem

Stock market is divided into primary market and secondary market

Corporations have to provide information to investors so they know how well the firm is making investments and in which business it is concentrating its activity.
The firm provides information to the investors by … .
This makes it … .
following the reporting standards included in the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and International Report Standard (IRS).
This makes it easy to compare firms from different countries and compare the same firm across time
The most important documents issued by the firm to provide information to the financial markets are:
Income = profitability
Cash flow = liquidity
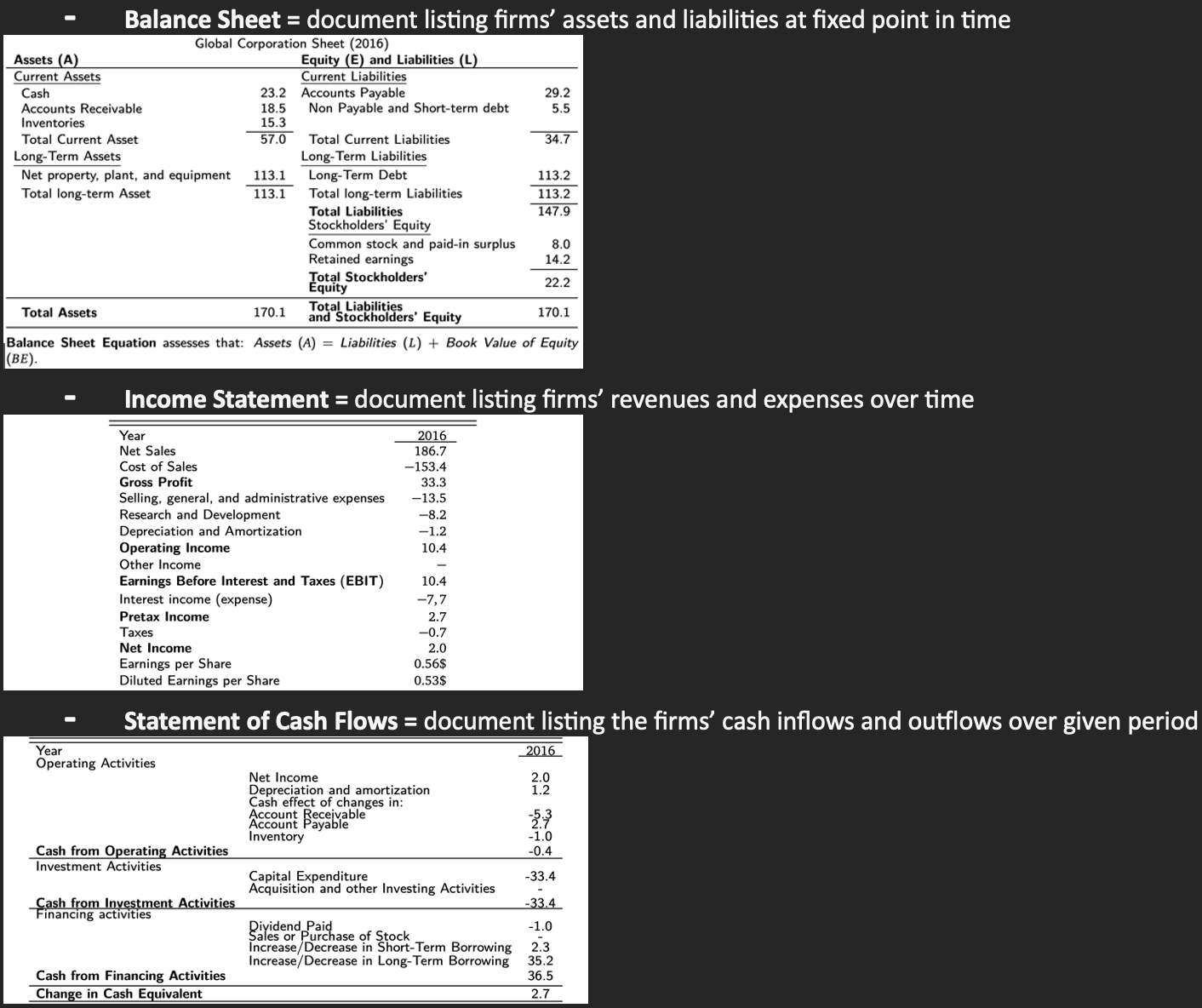
Values that can be calculated from balance sheet
EV represents the total theoretical cost to acquire a company

EPS (earnings per share)
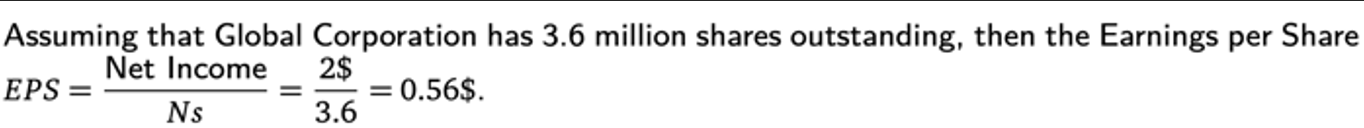
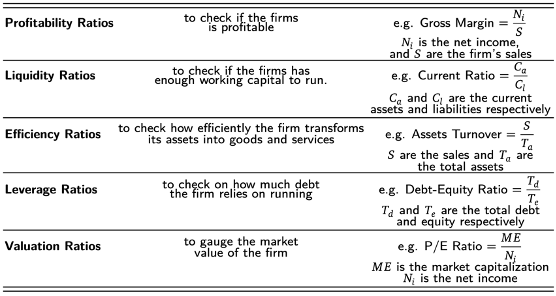
Most used ratios
RE (retained earnings) =
And what does it tell us?
A positive RE suggests that the firm’s management has spotted some good investment opportunities and wants to retain some net income to (re)invest in them

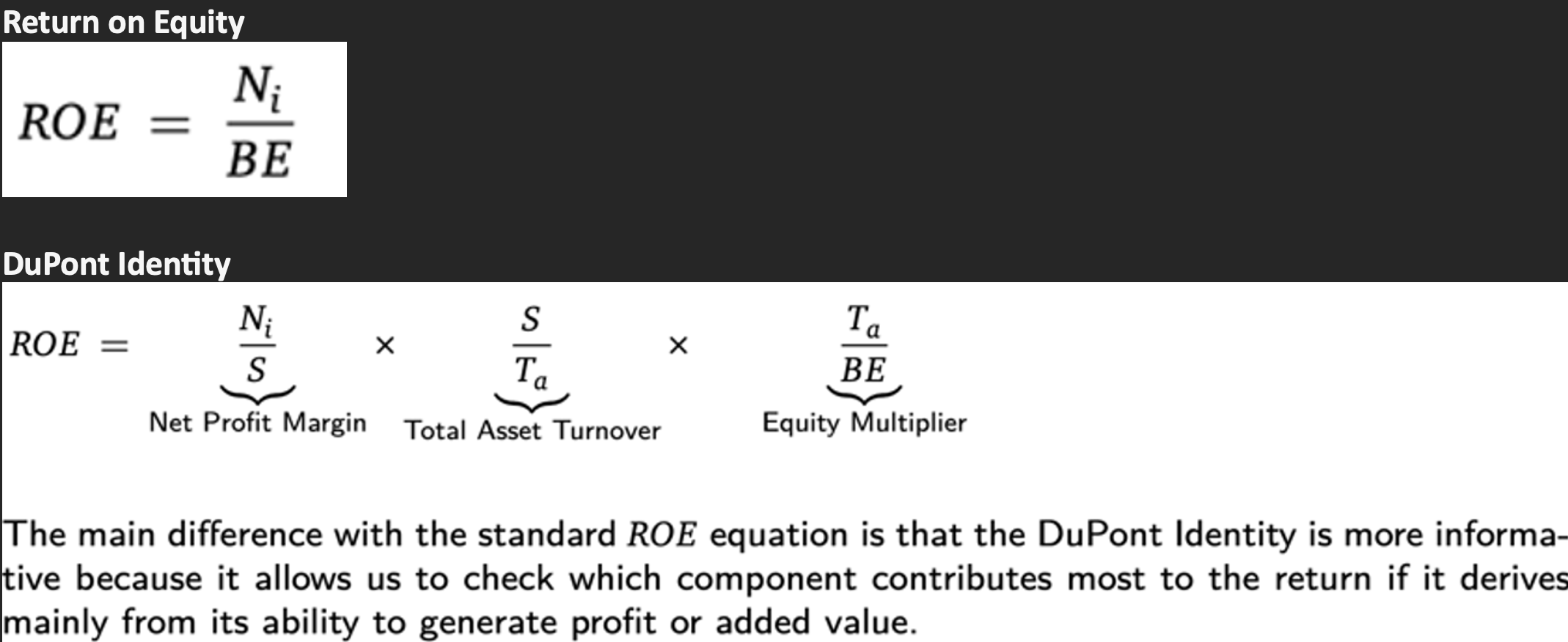
ROE =
DuPont Identity =
What’s the difference?
ROE = powerful tool to assess profitability and management effectiveness. DuPont analysis helps you dig deeper into the sources of that profitability
Time value of money =
the difference between the value of money today and the value of cash tomorrow
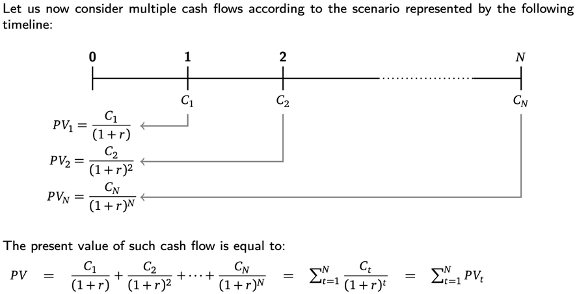
PV of cash flow stream =
4 types of cashflow + examples IRL

Start term and common ratio

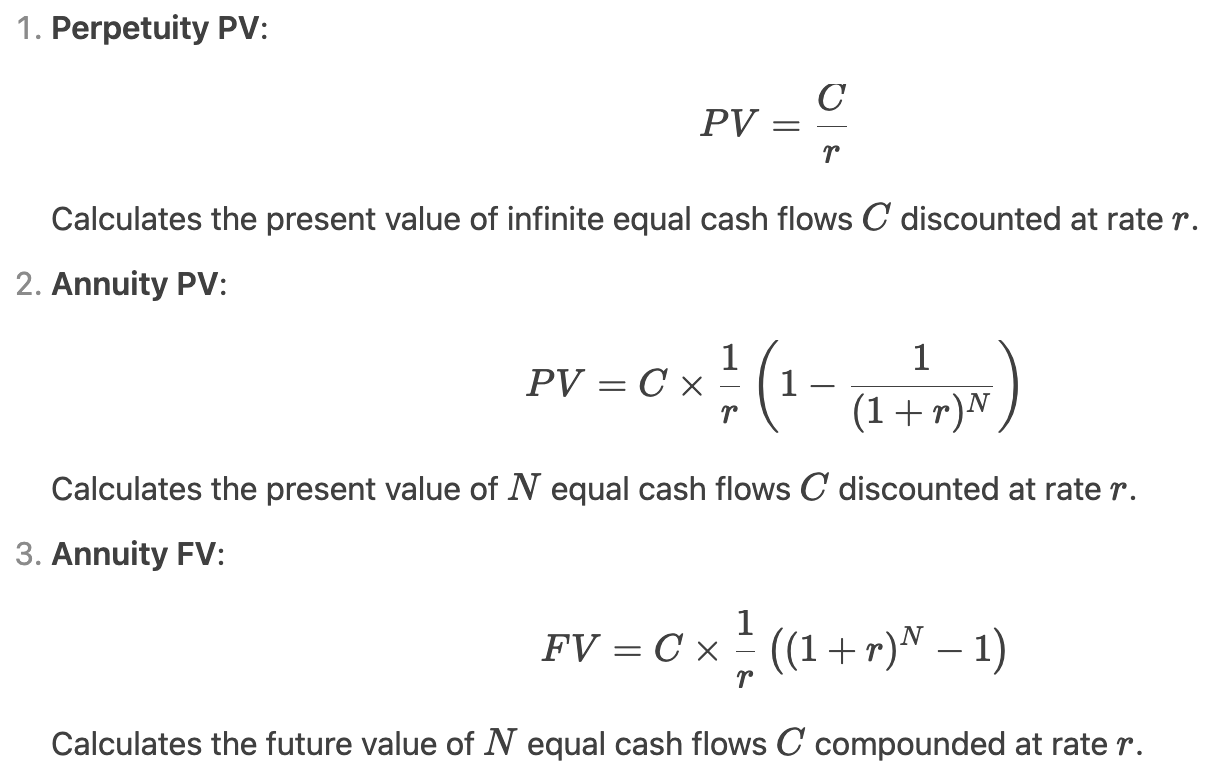
Perpetuity PV =
Annuity PV =
Annuity FV =
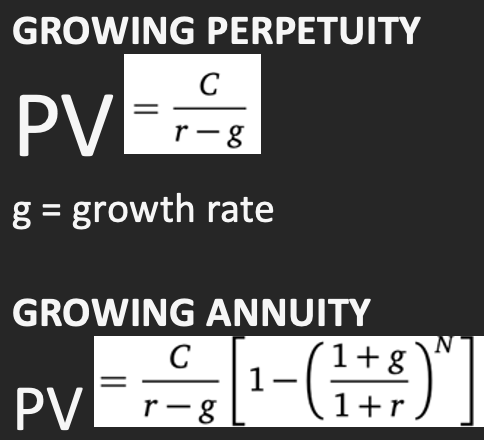
Growing Perpetuity PV =
Growing Annuity PV =
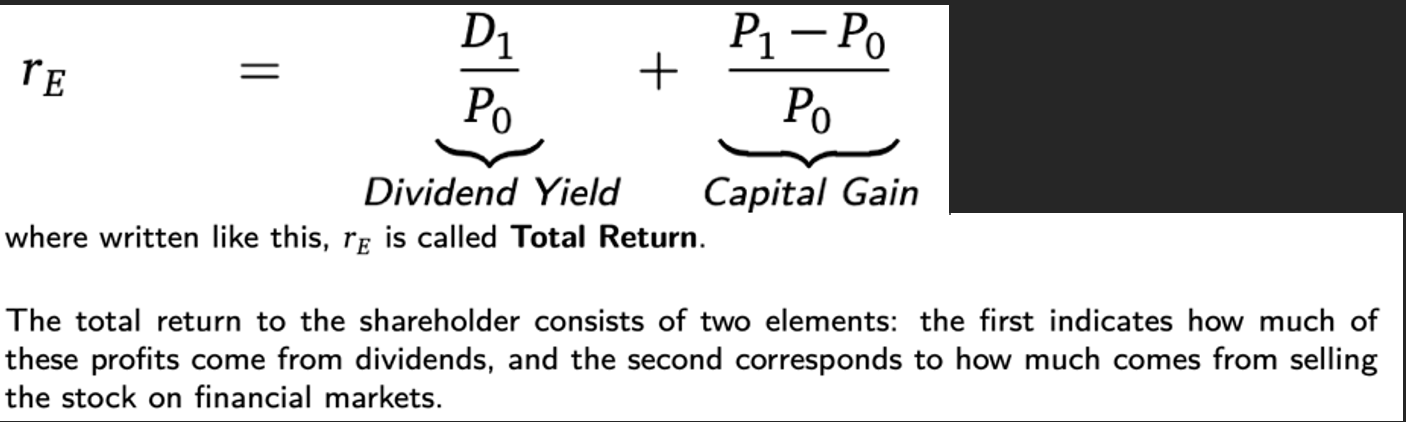
Total Return (investment with dividends) =
Cost of Capital =

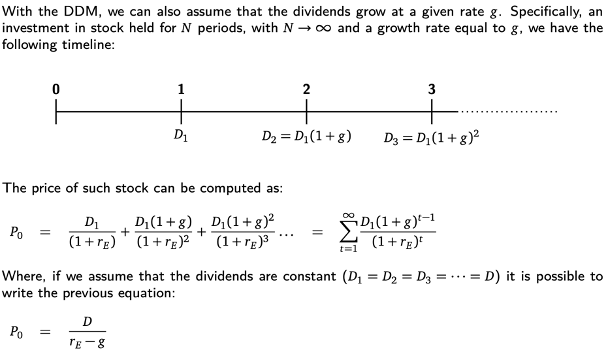
Discount-Dividend Model (DDM) =
if dividends are constant!!!
Limitations of DDM

Growth rate of earnings =

Illiquid asset =
not easily converted into cash
Illiquid market =
few participants and a low volume of activity.
P0 =
^ by looking at funamental value of firm today

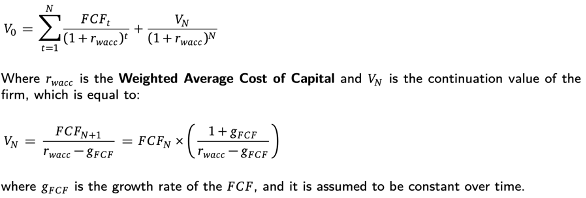
V0 =
V0 = EV
Fundamental value of firm today
FCF =
amount of money generated by the firm’s day-to-day activities

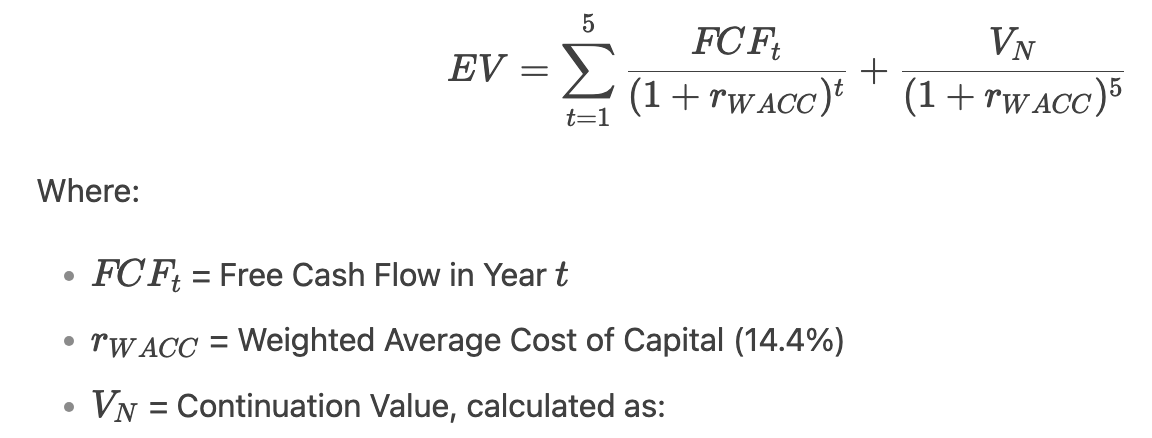
Enterprise Value using Discounted FCF
EMH:
What is it?
Three forms
How can it fail?

Individual Biases and Trading

!!!

Should you use Return Series or Price Series to analyse asset?
Return Series
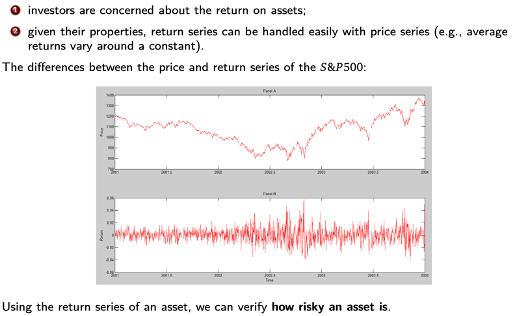
Stochastic process
Brownian Motion

Geometric Brownian Motion (GBM) =
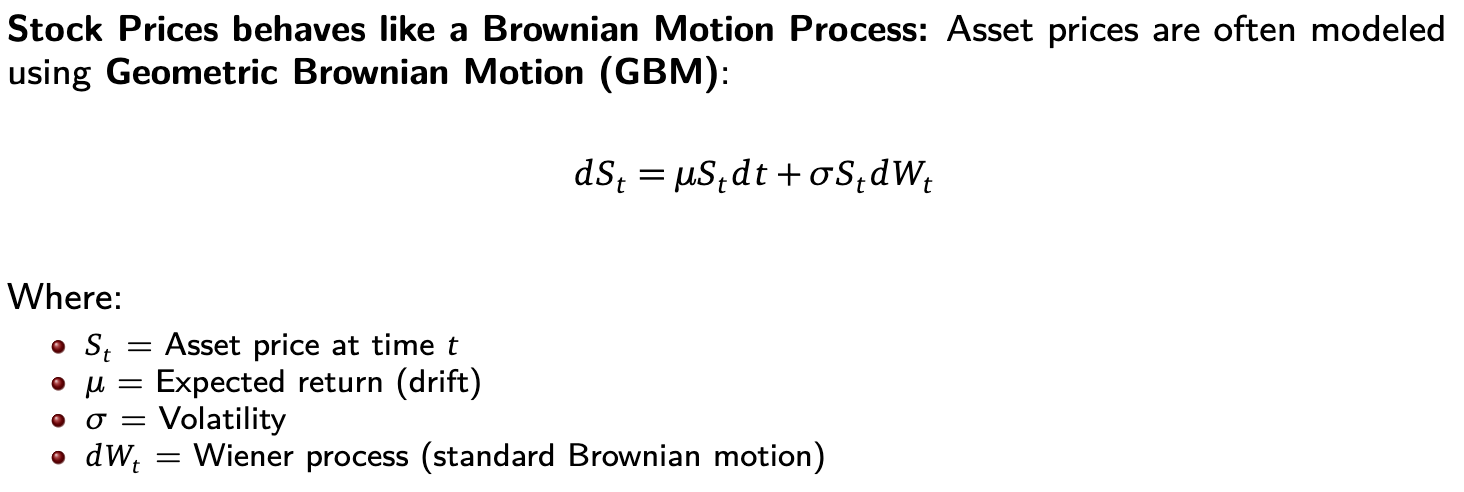
Risk =
broadly defined as uncertainty in future cash flow
financial markets evolve unpredictably, like particles in a chaotic system
Formulas + differences + uses
Arithmetic mean
Geometric mean
The arithmetic mean is useful for forecasting future returns and the geometric mean to evaluate past investment performance

Starting from stock’s price series, there are 2 main tools to “estimate” their expected return and risk:
Average return

Starting from stock’s price series, there are 2 main tools to “estimate” their expected return and risk:
Variance
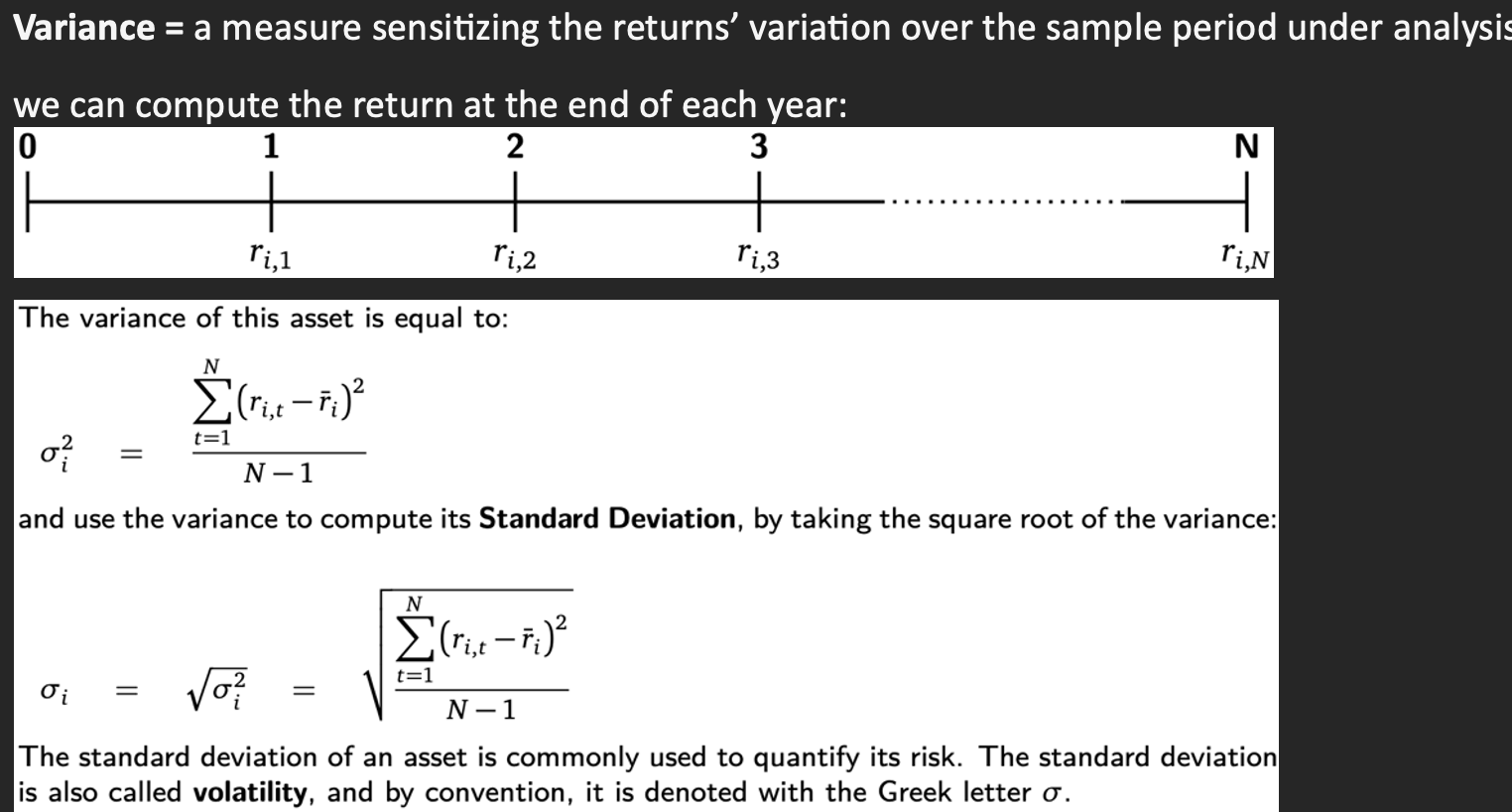
Formula + 3 properties
Volatility
= standard deviation =

Empirical rule
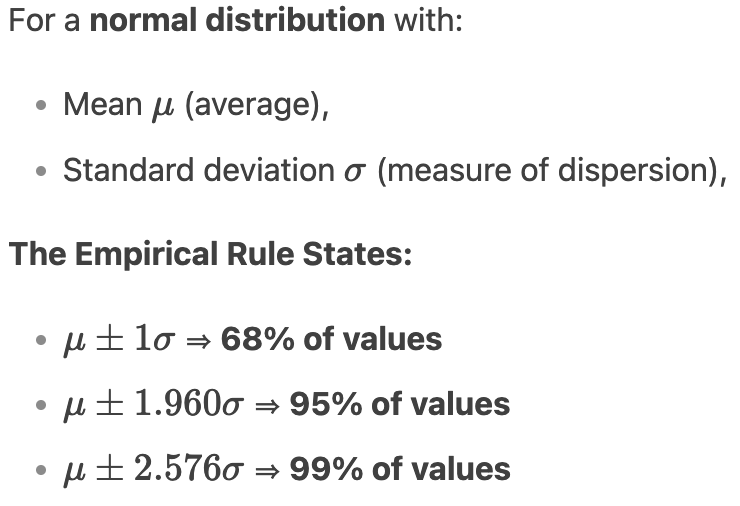
Meaning + formula + how to analyse graph
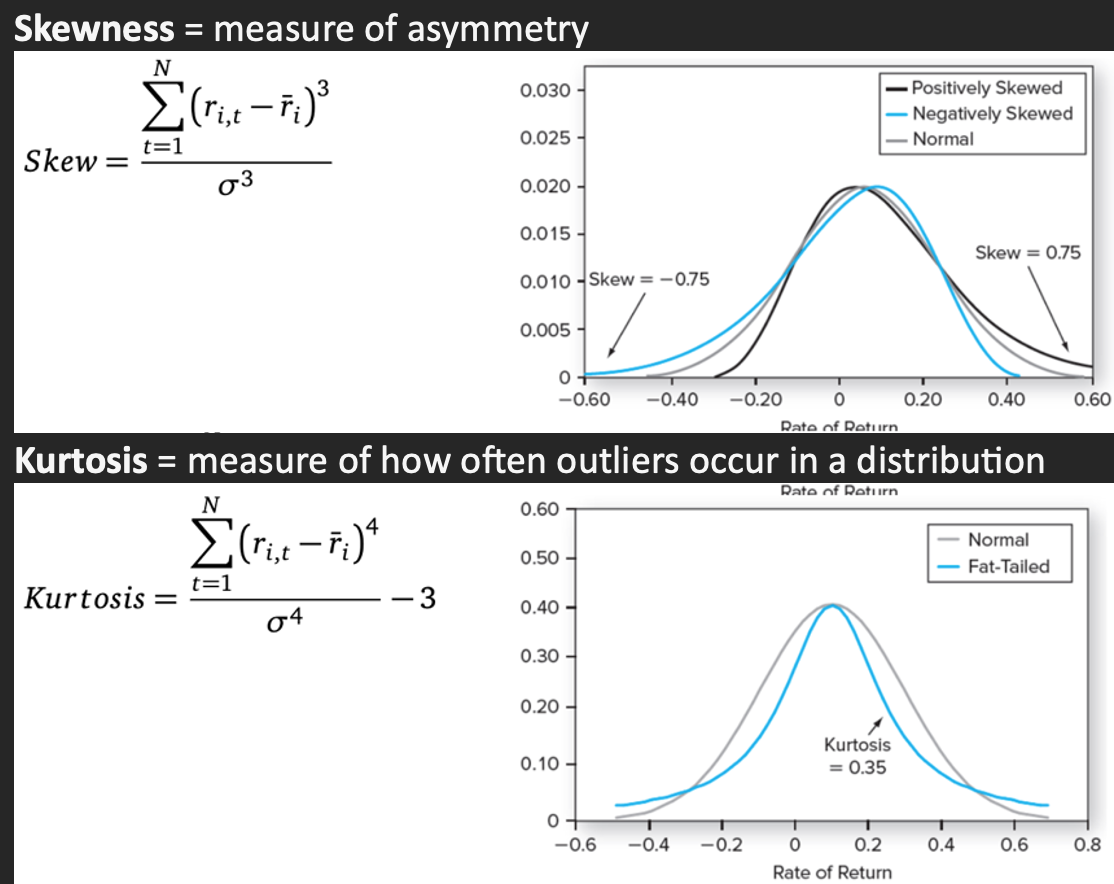
Skewness
Kurtosis
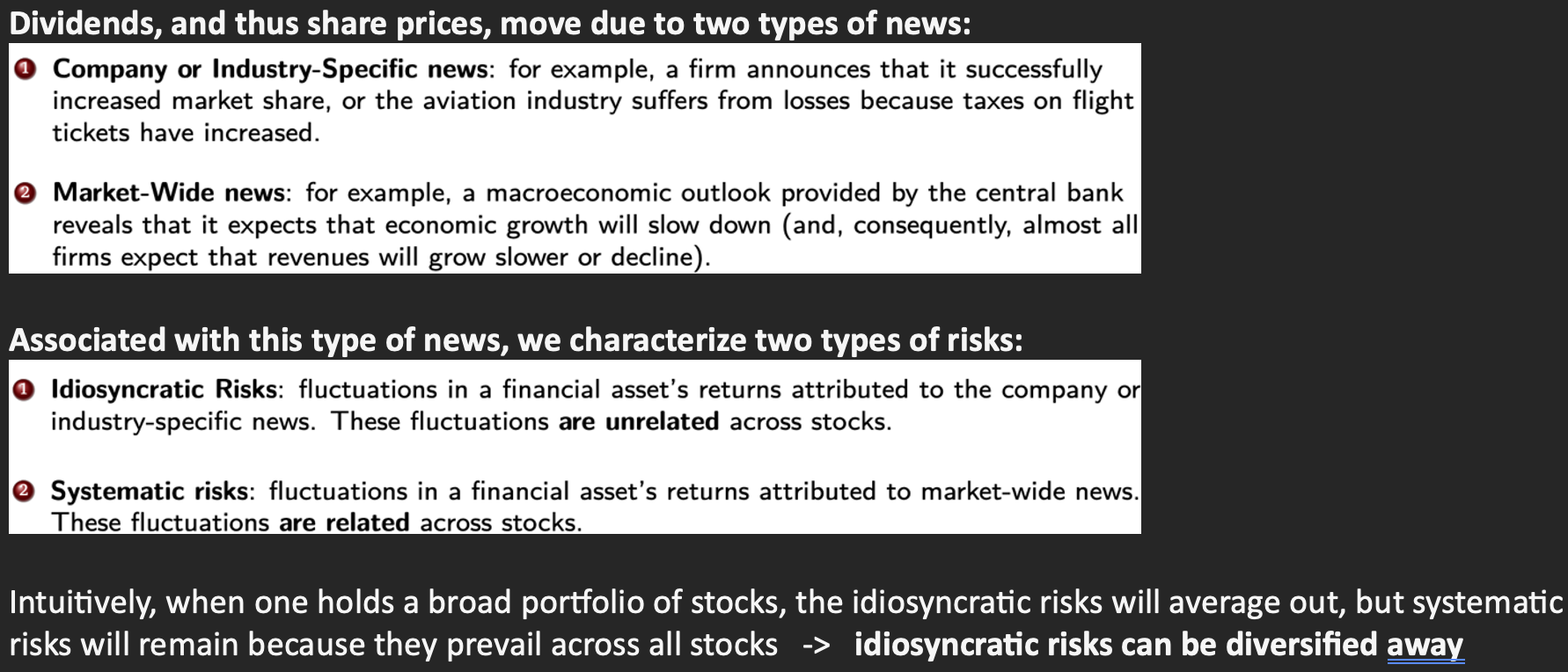
Dividends, and thus share prices, move due to two types of news:
Associated with this type of news, we characterize two types of risks:
The Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) =
Describes the relationship between systematic risk and expected return for assets, particularly stocks.
It is widely used in finance for asset pricing and risk assessment.
CAPM:
E(Ri) =

Risk Premium
the additional return an investor expects to earn for taking on higher risk compared to a risk-free investment (such as government bonds).
it compensates investors for the uncertainty and potential loss associated with a risky asset.
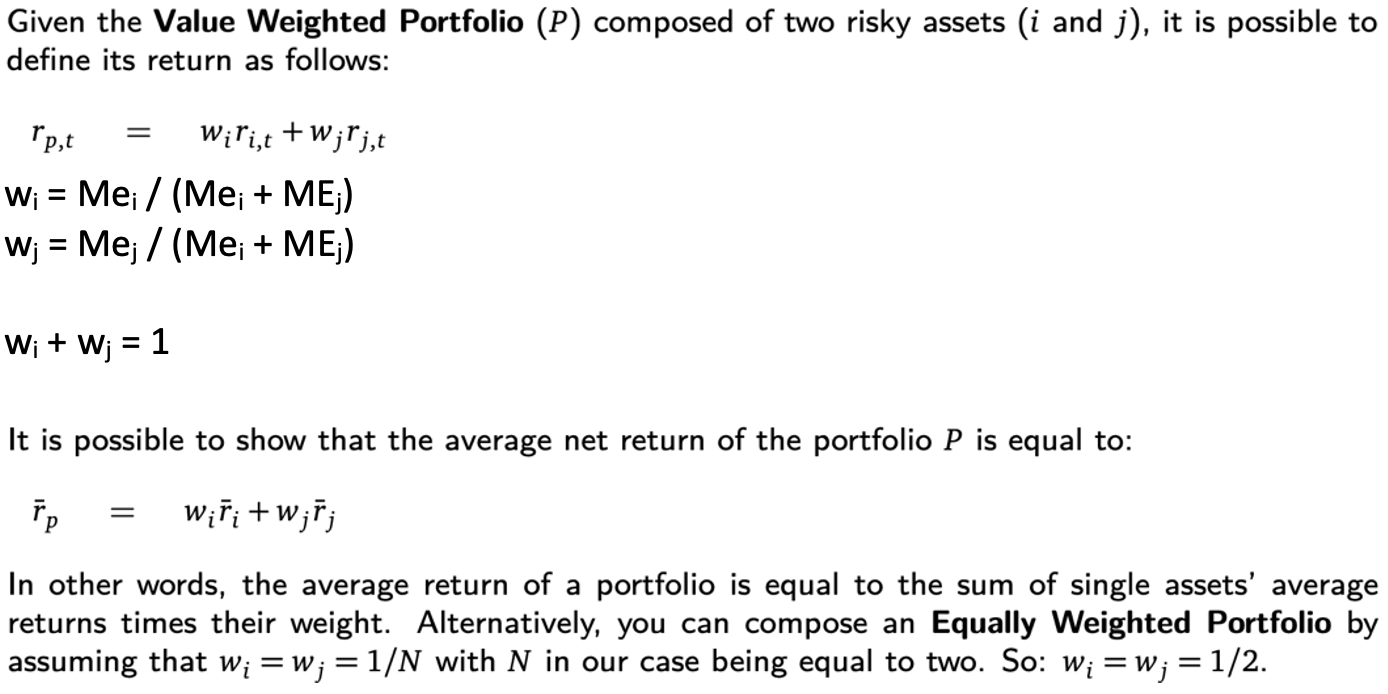
Value Weighted Portfolio Returns:
rp,t =
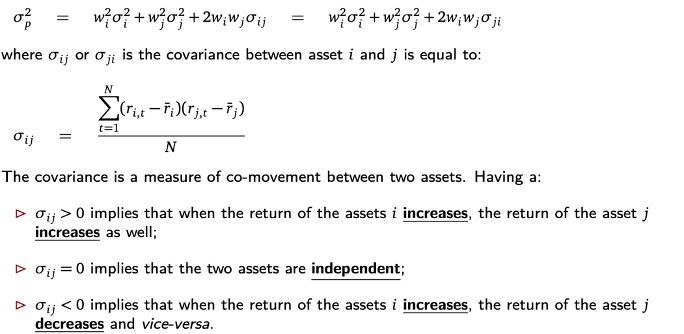
Portfolio variance
Covariance between asset i and j
Correlation
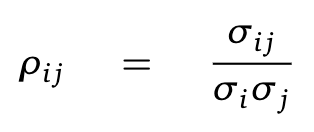
Efficient Frontier definition

Efficient Frontier
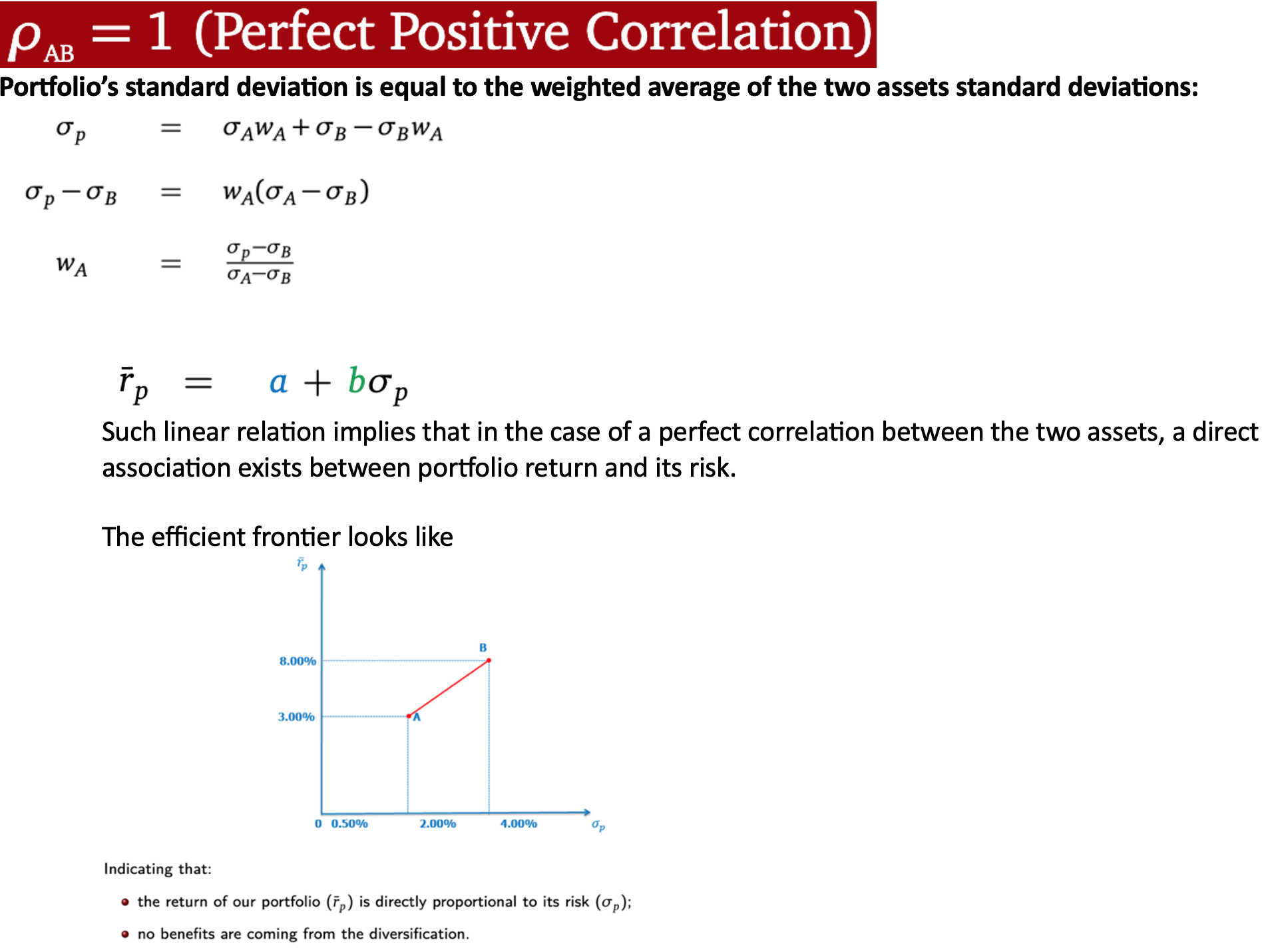
ρAB = 1
Efficient Frontier
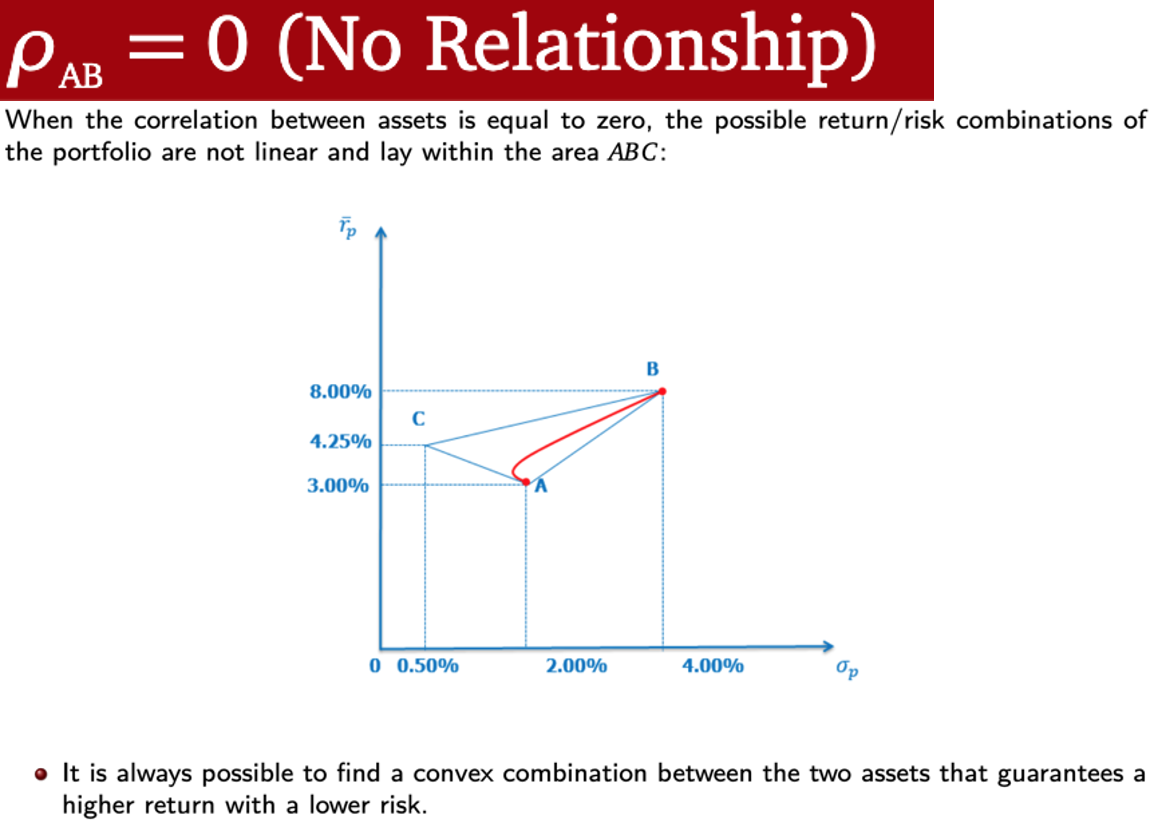
ρAB = 0
Efficient Frontier
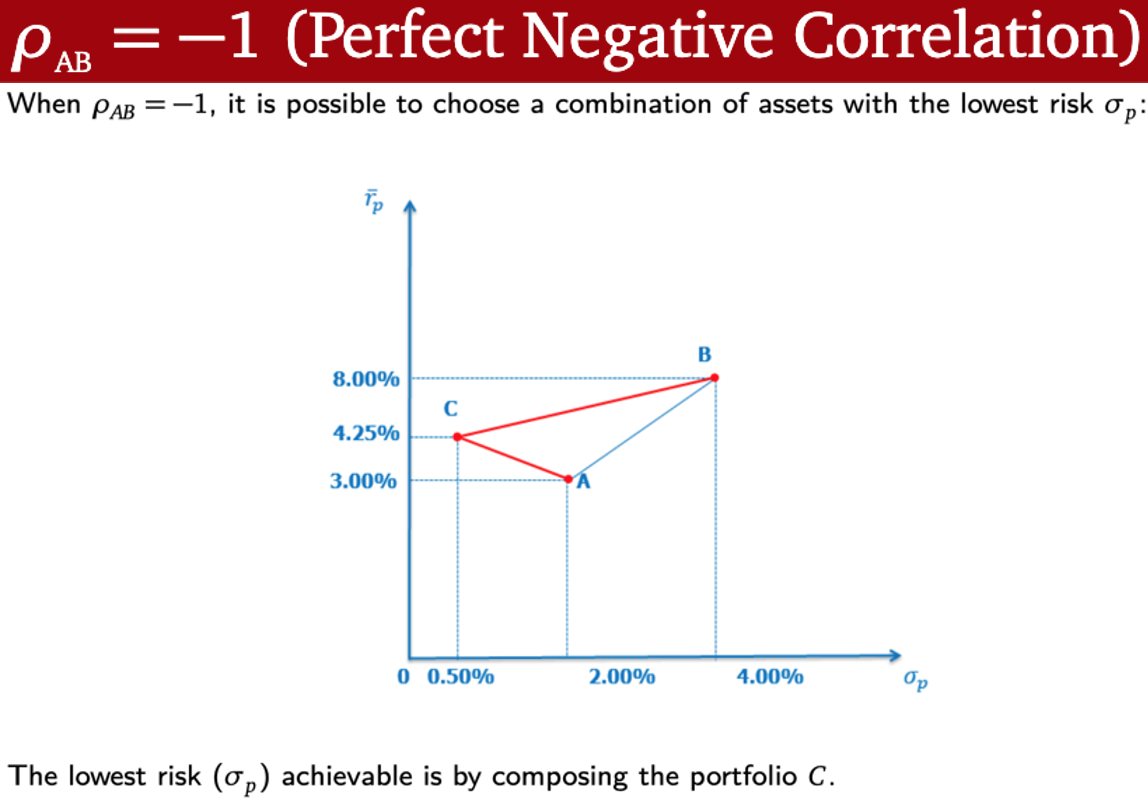
ρAB = -1
Risk-Free Rate =
the return on an investment that carries no risk of financial loss. It represents the minimum return an investor expects for investing in an asset without taking any risk.
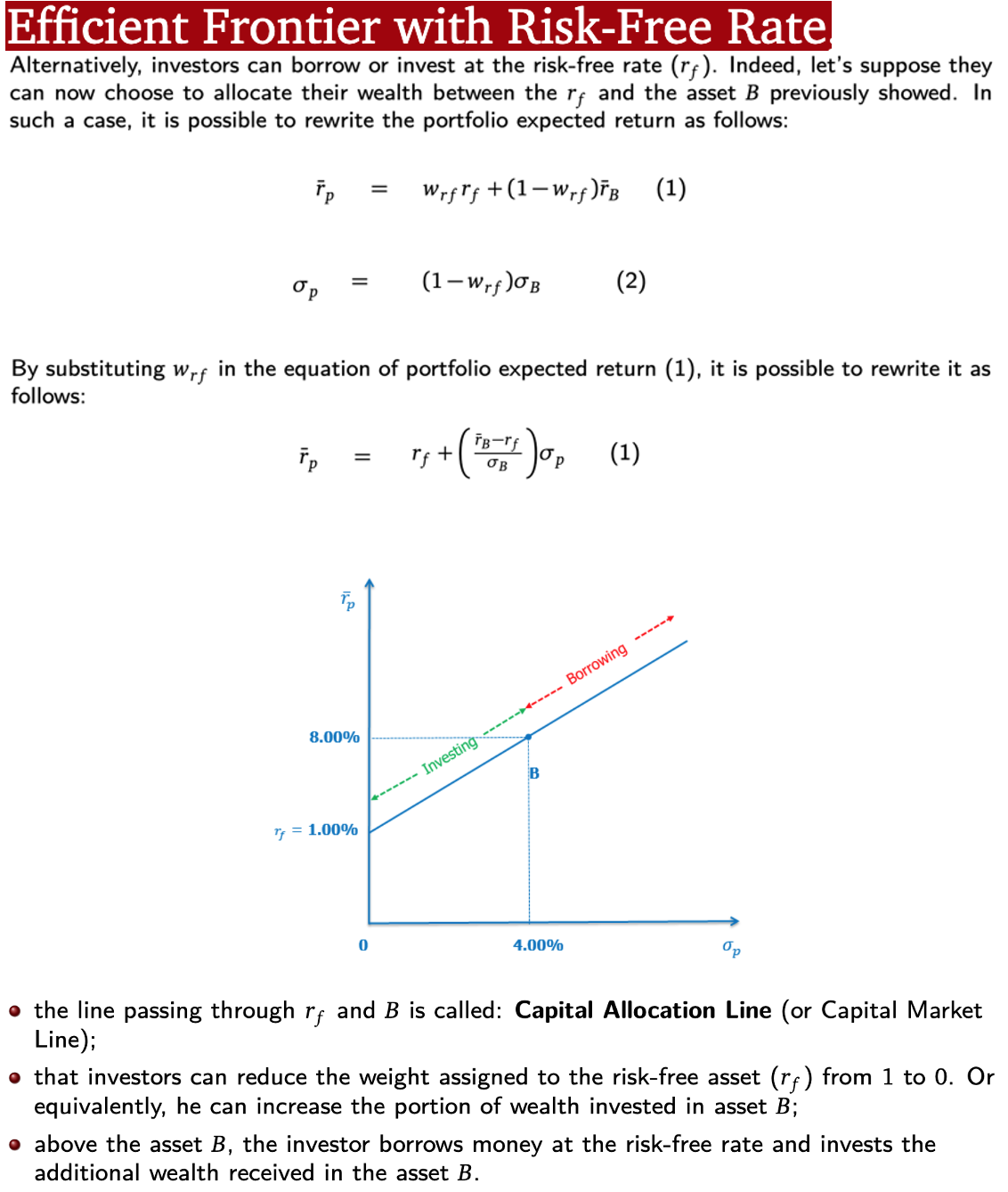
Efficient Frontier:
Risk-Free Rate
Capital Allocation Line
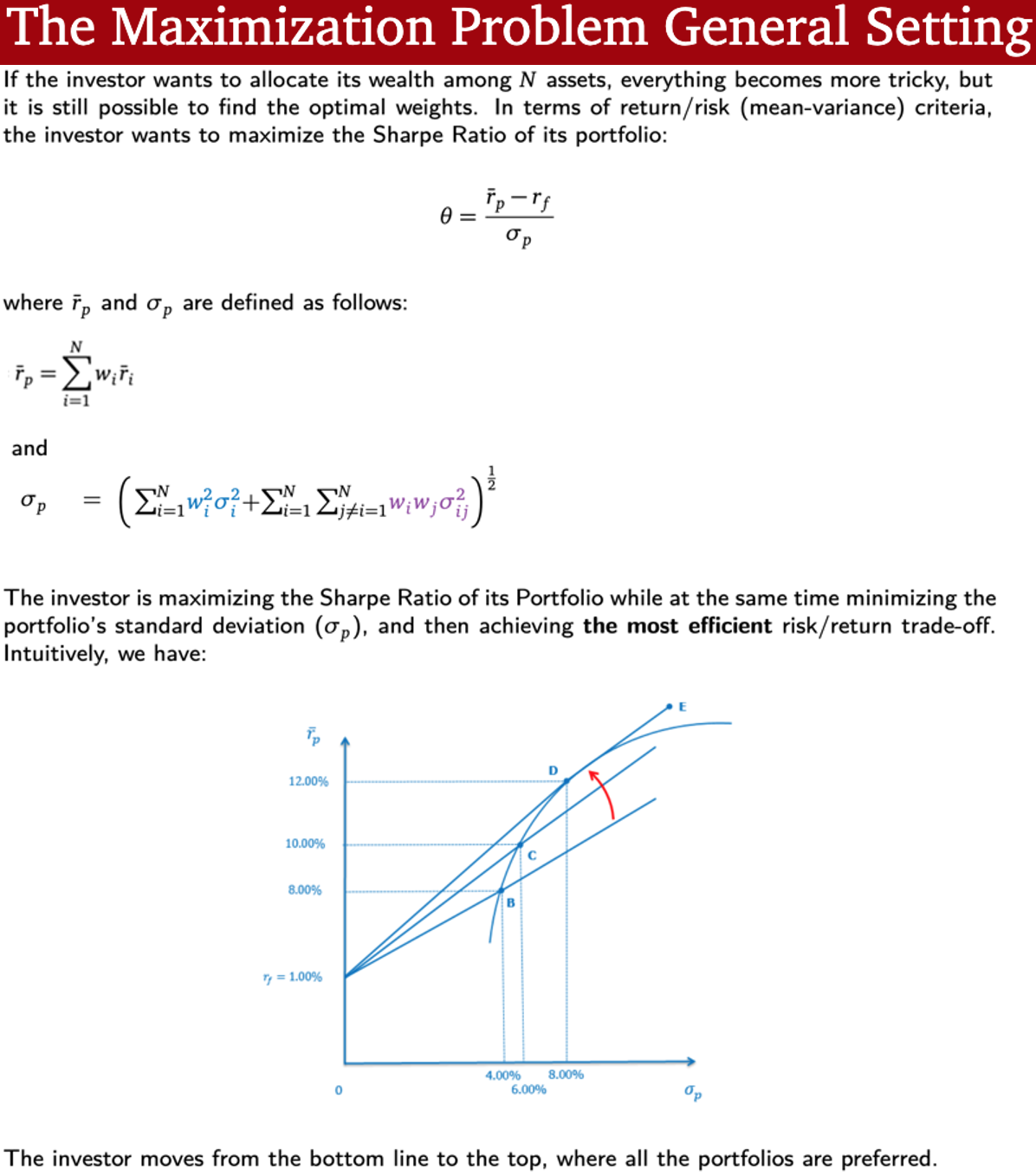
Efficient Frontier:
Maximization Problem General Setting
Sharpe Ratio
Covariance =
Variance portfolio =
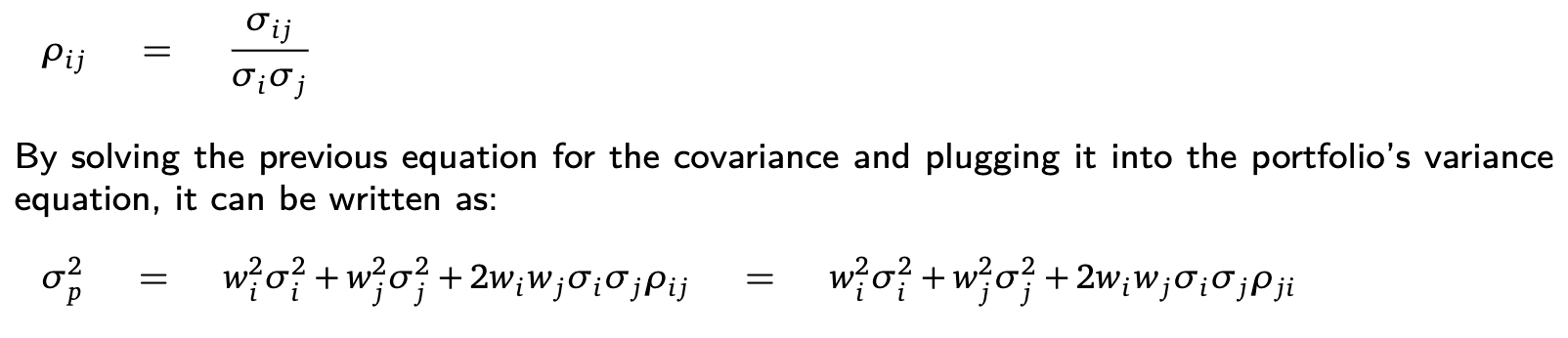
Comparing costs and benefits that occur at different prices
Competitive market =

Common vs Independent Risk
