Microbiology: Antibiotics
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
difference between bactericidal and bacteriostatic?
bactericidal = destroys pathogenic microbes
bacteriostatic = inhibits their growth within the host
what is the difference between disinfectants and antibiotics?
antibiotics are selective against bacteria AT LOW CONCENTRATIONS. antibiotics DIFFERENTIATE between the microbe and the host!!
P-10
penicillin
B10
Bacitracin
S10
streptomycin
GM10
Gentamicin
E15
Erythromycin
CC2
Clindamycin
Te30
Tetracyclines
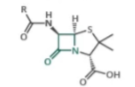
what are B-lactam characteristics and structure and examples?
all beta-lactams contain a beta-lactam ring. they work by interfering with the synthesis of peptidoglycan. most prescribed antibiotic. Beta-lactams inhibit the enzymes called “penicillin-binding” proteins (PBP) whose natural function is to do the transpeptidation reaction at the end of peptidoglycan synthesis. ex: penicillin, amoxicillin (ends in -icillin mostly)
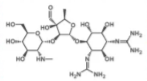
what are aminoglycoside characteristics and structure and examples?
examples include S10 and GM10 (ends in -mycin). these work by inhibiting protein synthesis. only effective against certain gram neg bacteria and some gram pos bacteria. not absorbed during digestion so IT MUST BE INJECTED. they are toxic so their use is limited!!
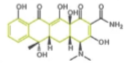
what are tetracycline characteristics, examples, and structure?
examples include: Te30 (ends in cycline). Te30 IS YELLOW. broad-spectrum antibiotic. also inhibits protein sythesis. its use has decreased due to INCREASE IN BACTERIAL RESISTANCE!! is called -cyclin because it has 4 cyclic rings!!
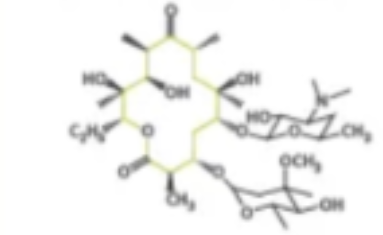
what are the characteristics, structure, and examples of macrolides?
ex: erythromycin (ends in -mycin). act in a BACTERIOSTATIC manner, and INHIBIT protein synthesis. effective against some species that penicillins are not! second most prescribed antibiotic.
what are the characteristics and structure of bacitracin?
disrupt gram pos bacteria by interfering with cell wall and peptidoglycan synthesis. mimic the substrate of the PBP protein. mostly just a topical bc it can cause kidney damage if ingested.
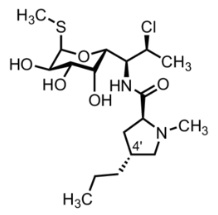
what are the characteristics and structure of clindamycin?
it is bacteriostatic. interferes with the synthesis of proteins. mechanism is similar to macrolides. it is in the lincosamide group. contain amino group and a sulfur group. 2 rings (one 6 sided, the other 5 sided).
what are the side effects of penicillins?
Gi upset, hypersensitivity reactions, Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, neurologic (seizures, ALOC), interstitial nephritis, hepatotoxicity
does penicillin have any drug interactions? when is it used?
no. drug of choice when susceptibility is known.
what are the side effects of tetracyclines? drug interactions? notes?
GI upset, photosensitivity, teeth discoloration, vertigo. caution with cations. highly bioavailable. some cyclines have activity against multidrug resistant organisms.
what can kirby bauer be used for?
it is used by clinician for treatment of patients with bacterial infections. this was the standard test before automation.
what is the difference between selective and differential media?
selective = a medium designed to select for and favor the growth of a specific bacteria
differential = a medium designed to aid the identification of various microorganisms by changing (ex: colors) due to bacteria’s ability to perform chemical reactions.
what kind of bacteria can enteropluri work with?
enteropluri can ONLY work on gram NEGATIVE bacteria!!!
what is MacConkey agar?
(lactose) agar. it is both selective and differential. contains bile salts and crystal violet which select for gram-neg enterics. differentiates lactose fermenters from non-fermenters. red colonies indicate fermentation of lactose, white = no fermentation of lactose.
what is eosin-methylene blue agar (EMB)?
both selective and differential. selective = dye inhibition and precipitation at acid pH. differentiates lactose fermenters from non-fermenters. blue/black = fermentation of lactose. no color or light purple = no fermentation of lactose.
Hekton Agar
both selective and differential. selective = inhibits non-enteric bacteria. differentiates lactose fermenters from non-fermenters. tests for H2S production. yellow or salmon indicate fermentation of lactose. colorless = non-fermenter. black = H2S production.
Mannitol Salt Agar
both selective and differential. selects for staphylococci, which grow at high salt concentrations. differentions staphylococcus aureus from other staphylococci. staph. aureus is yellow (mannitol fermentation). other staphyl are white.