instrumentation
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
exam 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Voltage
electrical potential difference
Current
Flow of charge
Resistance
opposition to current
ohm’s law
V = I x R
Formula for power
P= V x I
Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law
The sum of all voltage drops in a closed loop = the supply voltage.
Kirchhoff’s Current Law
The sum of currents in all branches = the total current in the entire circuit
Voltage divider formula
Vout = Vin × (R2 / (R1 + R2))
Current divider formula
I1 = Itotal × (R2 / (R1 + R2))
I2 = Itotal × (R1 / (R1 + R2))
Household power
120 V 60 Hz
Voltage ratio for transformers
Voltage out/voltage in = Turns on secondary coil/ turns on primary coil
Capacitance
ability to store charge in an electric field
Inductance
ability to store energy in a magnetic field
impedance formula
|Z| = √(R² + X²)
Capacitive Reactance formula
Xc = 1 / (2 π f * C)
Phase angle formula
θ = arctan(-X / R)
gain in db formula
20 log (Vout / Vin)
phase shift formula
ϕ = 360 × (Δt / T)
Magnitude transfer formula, low pass
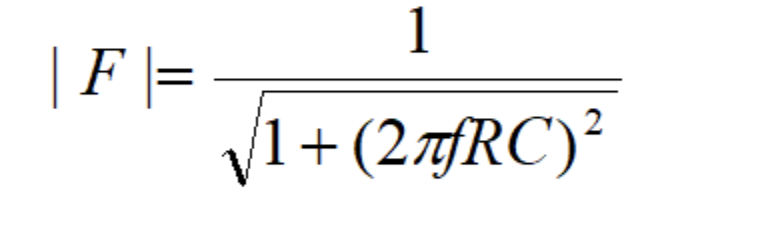
Cut off frequency formula
fc = 1 / (2πRC)
How is Voltage measured?
Across (Parallel)
How is current measured?
through, (in series)
Parallel circuit total resistance formula
1 / Rtotal = 1 / R1 + 1 / R2 + 1 / R3 + …
Phase relation In purely resistive circuits
V and I in phase
Phase relation in purely capacitive circuits
I leads V by 90°
Total reactance formula
X = Xl − Xc
Middle ear resonance
800-1200 hz
Middle ear gain
+34 dB
Main difference in infant ears vs Adult ears
Infant ears are mass dominated
Acoustic reflex
stapedius contraction increases stiffness, decreases admittance
Best voltage transfer:
Z in is greater than Z out
Best Power transfer
Z in = Z out
Stiffness dominant Pathology
Otosclerosis, Fluid in middle ear
Mass dominated pathology
Ossicular discontinuity