Chapter 1
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Microeconomics
Examines how people, companies, and the government play a part in an economy.
Marketing goods, prices, and production
Small-scale
Macroeconomics
Examines the overall production of a whole economy
Average price, how price and production are related
Large-scale
Resources
Inputs used to produce goods and services
Fallen into four categories
Land
Labor
Capital
Entrepreneurial Ability
Land
Natural resources used in production (farmland, forests, oil, oceans, fish, etc.)
Labor
All physical and mental activity devoted to produce goods and services (plant crops, run machines, teach economics)
Capital
Tools, machinery, infrastructure, and knowledge used to produce goods and services
NOT money
Fallen into two categories:
Physical
Human
Physical
Items that are created to increase productivity (machinery, buildings, trucks, and tools)
Human
Knowledge, skills, and education people acquire to increase productivity
Entrepreneurial Ability
Combining land, labor, and capital to produce goods and services
Involves assuming risk and costs of failure
Scarcity
A condition that results from the inability of limited resources to satisfy unlimited wants
You cannot have everything you want without experiencing some cost
Money
How we allocate resources to save money
Time
Deciding to do this or that to build human capital
Relative Scarcity
Comparison of the scarcity of one good, service, or resource to that of another
Drinkable water compared to water in general
Allocation
Assigning a good, service, or resource to one use instead of another
Allocating public space for recreational use
Opportunity Cost
The value of the next-best forgone alternative
The opportunity that you gave up when you chose one activity or opportunity instead of another
Exists because of scarcity
Marginal Benefit
The additional utility derived from doing something

Marginal Cost
The additional cost associated with expanding an economic activity
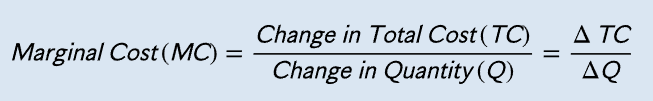
Decreasing (diminishing) Marginal Benefit
As you do more of something in a specific time period, you enjoy each successive unit less
Increasing Marginal Cost
As more of a good is produced in a given time period, the cost of producing each successive unit tends to rise
Optimal Level of Output
The marginal benefit of the last unit produced and consumed is equal to the marginal cost of that unit
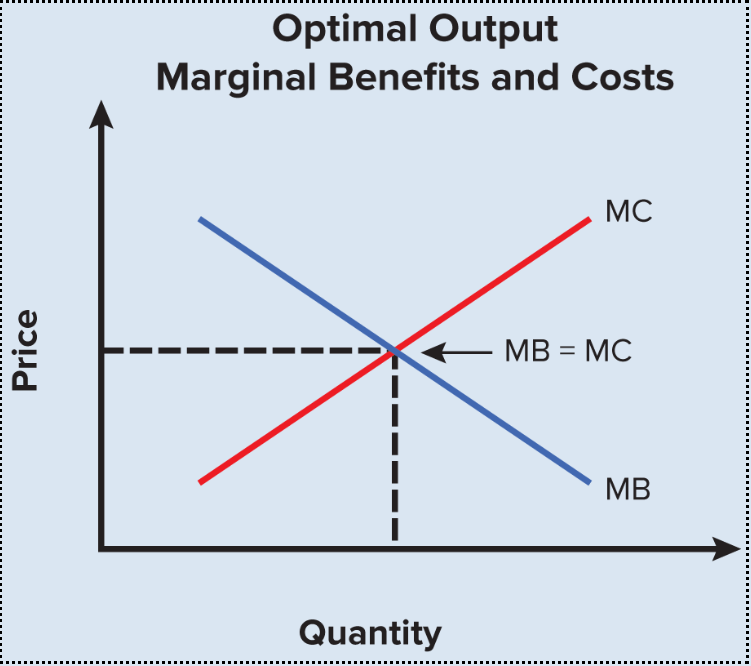
Possible Production Frontier
Shows the production combinations that are attainable and efficient
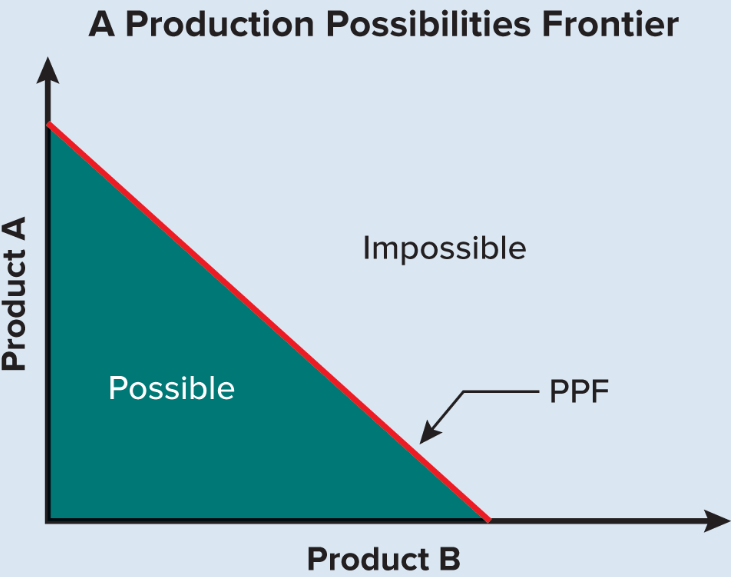
Constant Opportunity Costs
The opportunity cost associated with increasing or decreasing the production of one good of service, in terms of another, is constant at every level of production
Efficient Allocation of Resources
It is possible to increase the production of one good only by decreasing the production of another
Inefficient Allocation of Resources
It is possible to increase the production of one good without decreasing the production of another (going to sleep instead of doing anything)
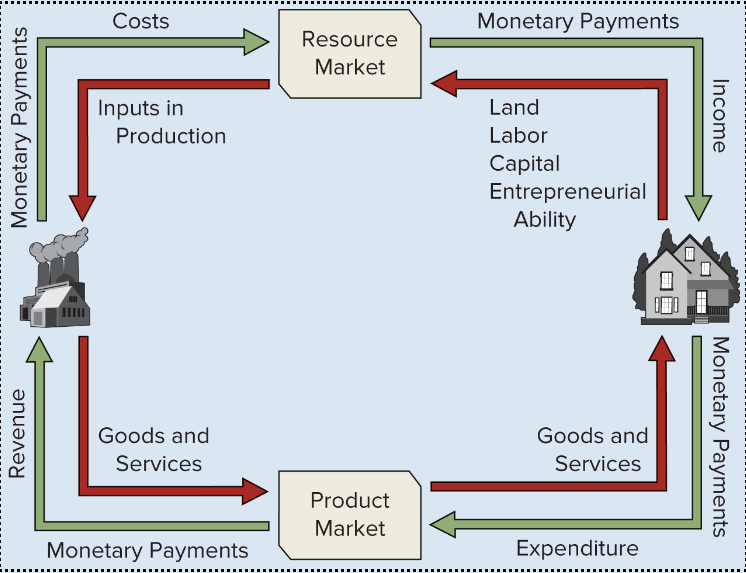
Circular Flow Model
Concisely describes how goods, services, resources, and money flow back and forth in an economy