Miller & Levine Biology - Chapter 13, Miller and Levine Biology Chapter 12
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
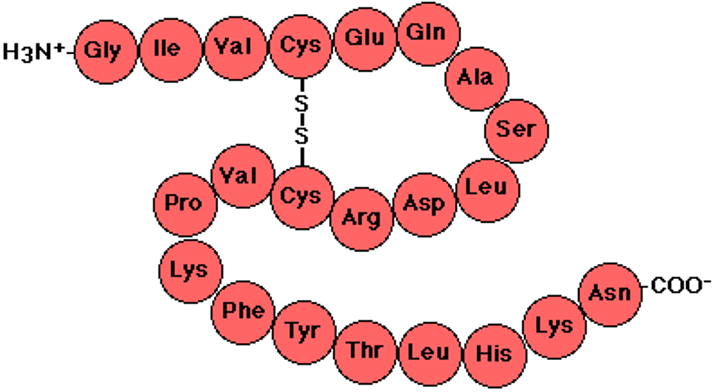
polypeptide
long chain of amino acids that makes proteins
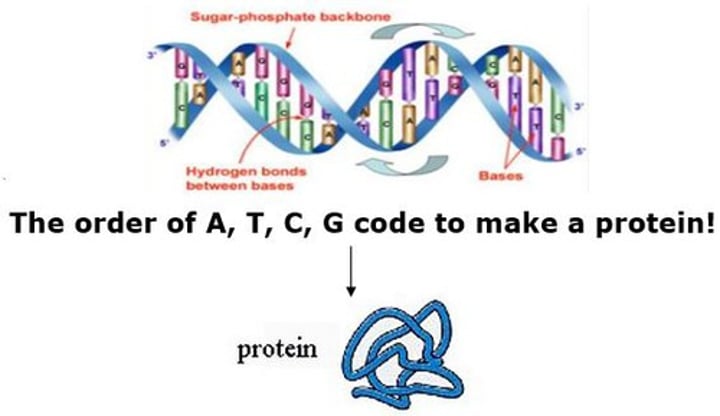
genetic code
The information encoded within the genetic material that can be translated into a protein
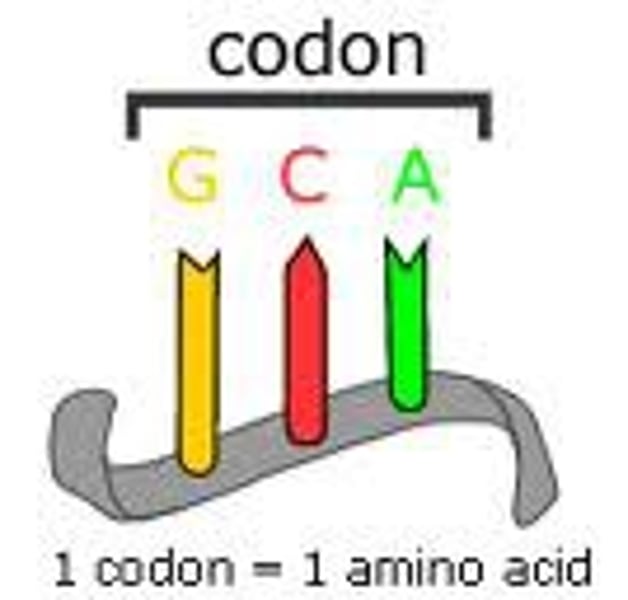
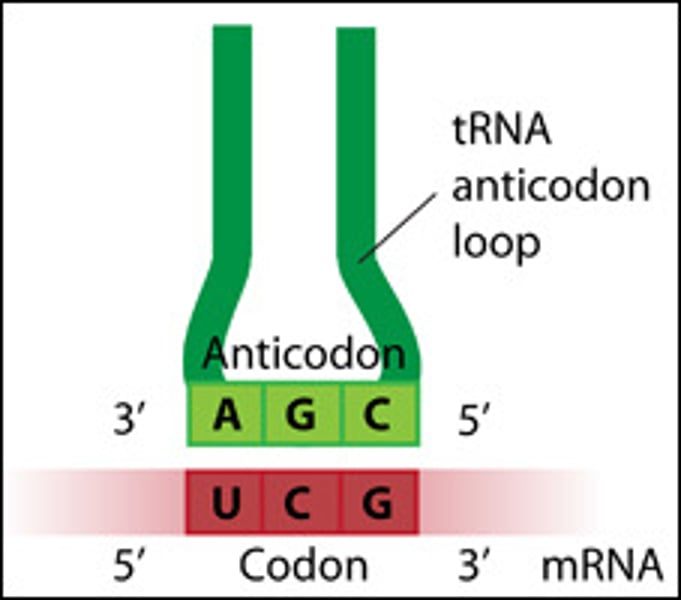
codon
A three-nucleotide sequence of DNA or mRNA that specifies a particular amino acid or termination signal; the basic unit of the genetic code.
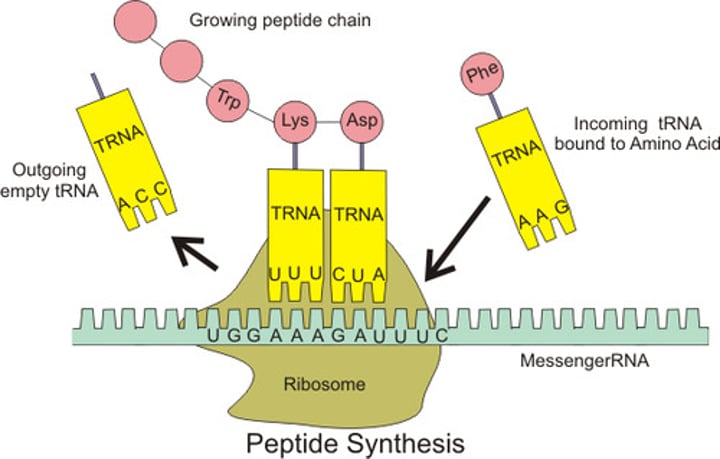
translation
Process by which mRNA is decoded and a protein is produced
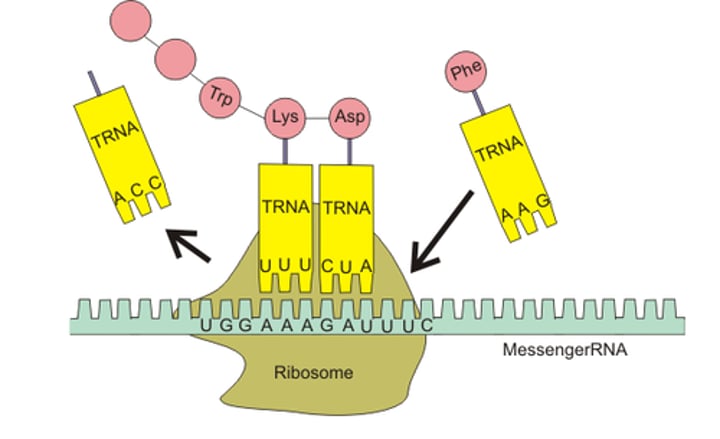
anticodon
group of three bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon
RNA
A type of nucleic acid containing the sugar ribose. Used in protein synthesis.
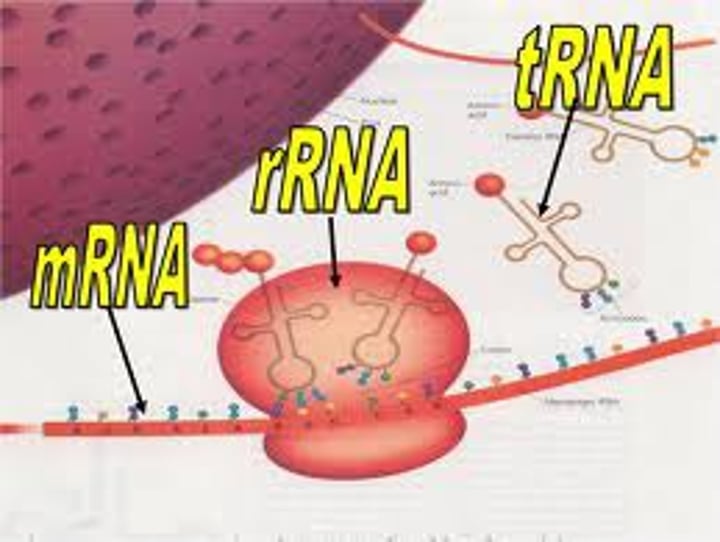
messenger RNA
RNA molecule that carries copies of instructions for the assembly of amino acids into proteins from DNA to the rest of the cell
ribosomal RNA
type of RNA that combines with proteins to form ribosomes
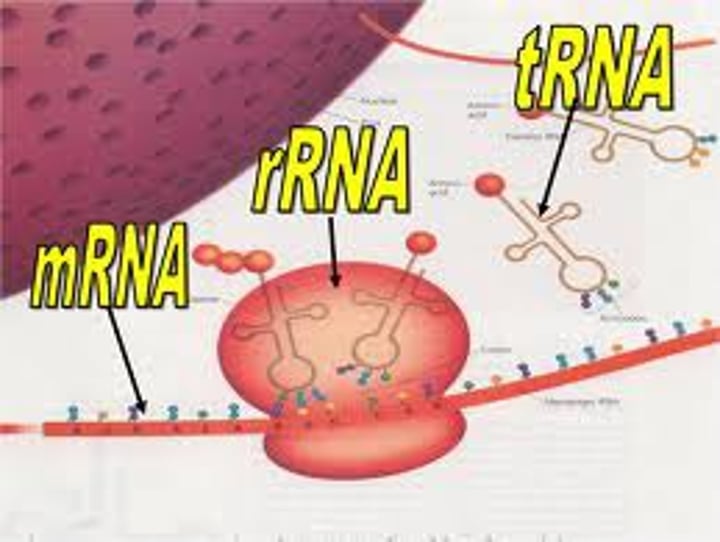
transfer RNA
type of RNA molecule that transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis
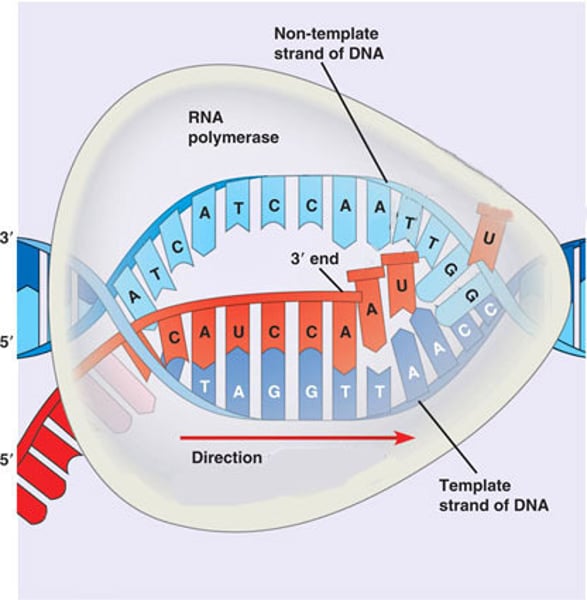
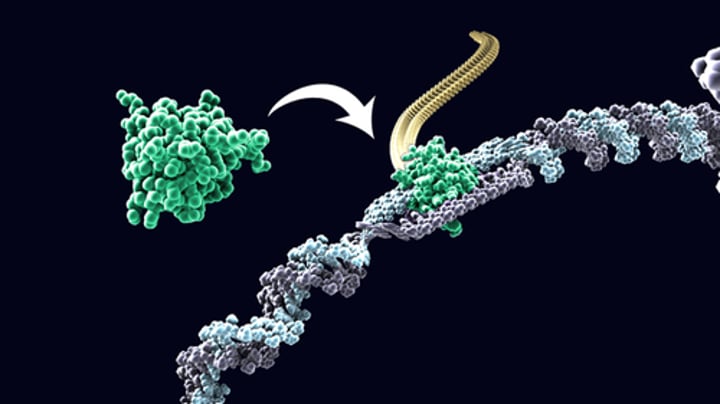
transcription
(genetics) the organic process whereby the DNA sequence in a gene is copied into mRNA
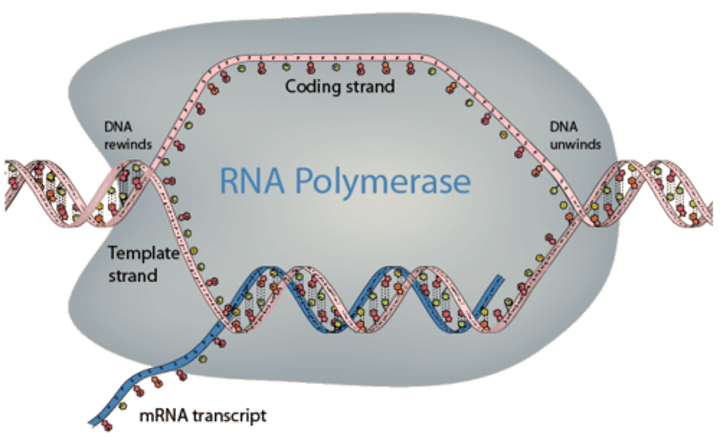
RNA polymerase
Enzyme similar to DNA polymerase that binds to DNA and separates the DNA strands during transcription
mutation
A rare change in the DNA of a gene, ultimately creating genetic diversity.
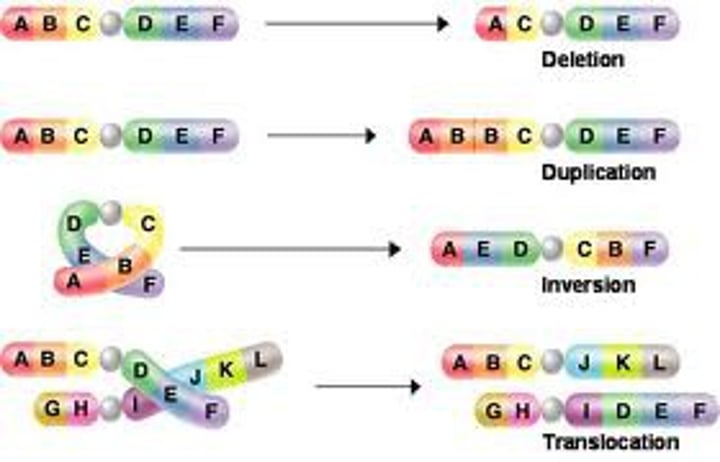
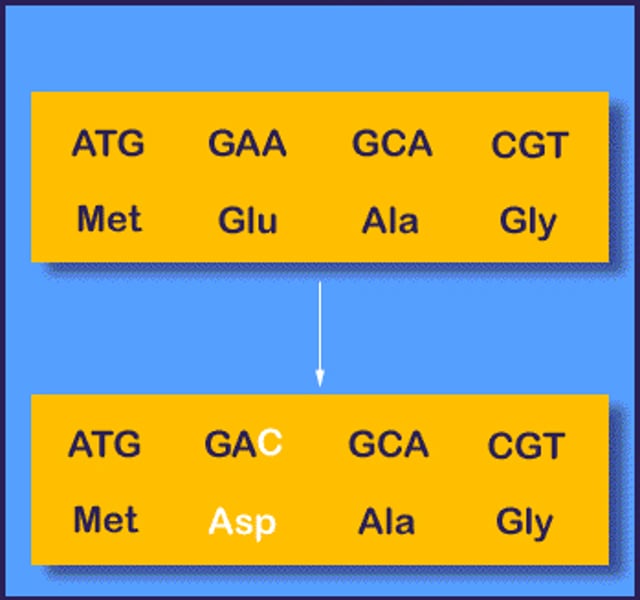
point mutation
Gene mutation involving changes in one or a few nucleotides.
frameshift mutuation
Mutation that shifts the reading frame of the genetic message by inserting or deleting a nucleotide
protein
An organic compound that is made of one or more chains of amino acids and that is a principal component of all cells
What are the four bases of RNA
adenine - uracil : cytosine - guanine
transformation
process where 1 strain of bacteria is changed by genes from another strain of bacteria
to store,
copy, and
transmit genetic information in a cell
DNA's roles (3)
DNA is made of ___
nucleotides joined into long strands/chains by covalent bonds.
Nucleic acids are made of ___
nucleotides
3 basic components of nucleotides
5 carbon sugar
phosphate group
nitrogenous base
DNA's 4 nitrogenous bases
adenine
thymine
cytosine
guanine
double helix
the shape of DNA; 2 DNA molecules twist around each other like a ladder.
anti-parallel strands
2 strands of DNA run in opposite directions
Why is hydrogen bonding in DNA important?
holds 2 strands of the double helix together;
hydrogen bonds form only between certain nitrogenous bases. These weak bonds allow the structure to separate.
What do we call the following:
adenine pairs with thymine
cytosine pairs with guanine
base pairing
replication
a copying process which duplicates the DNA
unzipping
a process (mediated by enzymes) which separates the two strands of DNA, allowing 2 replication forks to form.
role of DNA Helicase enzymes in replication
unzipping the dna
breaking the hydrogen bonds
unwinding 2 strands
DNA polymerase
enzyme that joins individual nucleotides to produce and proofread a new DNA strand.
DNA replication occurs when?
in the S phase
prokaryotic DNA replication
starts in a single spot and goes around in 2 directions until the entire chromosome is copied
eukaryotic DNA replication
begins at many different spots on the DNA molecule and proceeds in 2 directions until the entire chromosome is copied
Single - stranded binding protein
proteins that bind to the freshly split DNA molecule to keep the two strands apart.
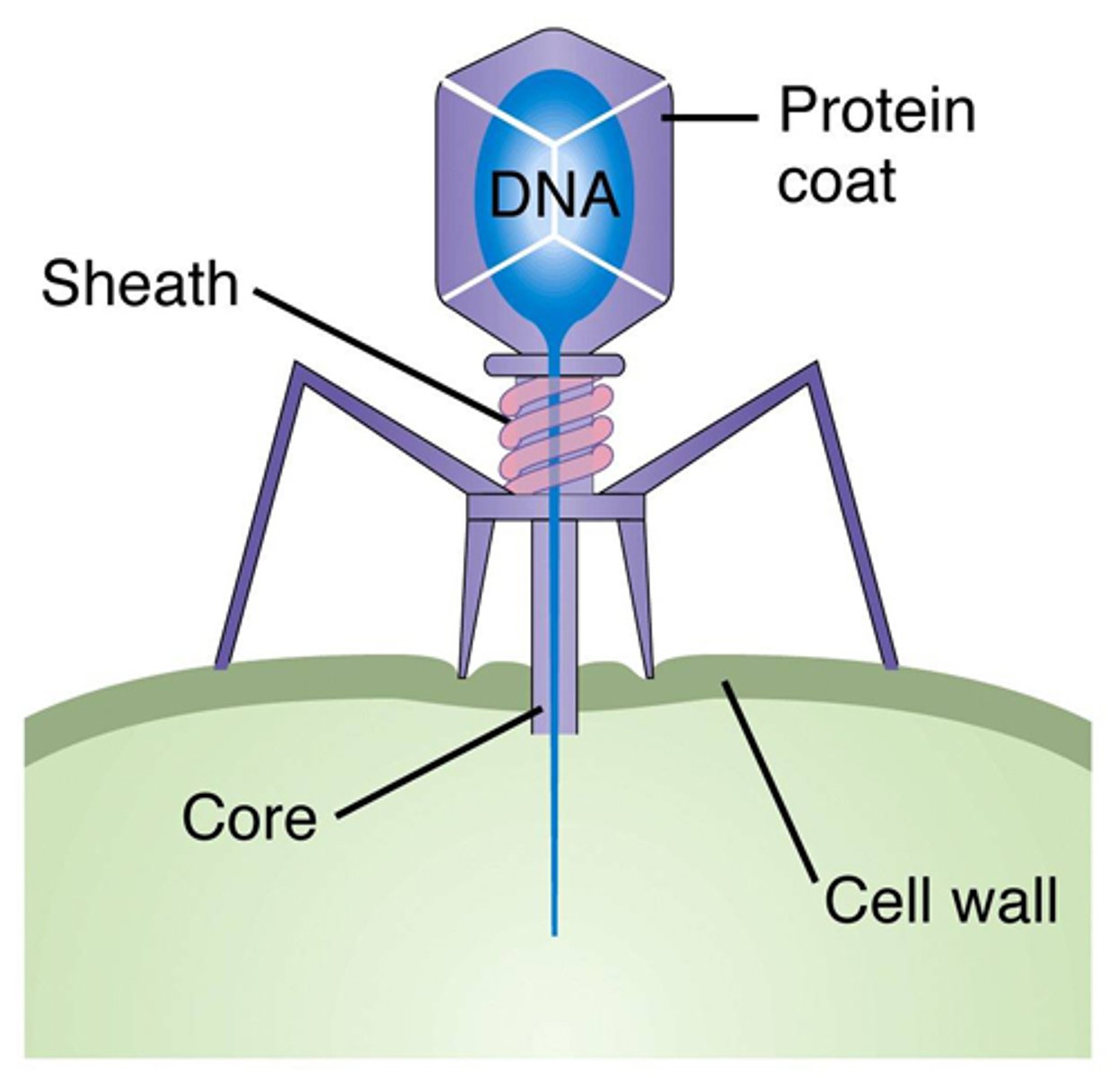
Bacteriophage
What is the image an example of?
GCAT
What would the complementary DNA strand be if the original strand's sequence is CGTA?
Rosalind Franklin
Scientist who conducted x-ray diffraction on DNA to discover it was a double helix shape
Watson and Crick
Scientists who first build a proper model of the DNA molecule
Erwin Chargaff
Scientist who discovered the amount of adenine and thymine are always equal, as well as the amounts of guanine and cytosine.
Circular
The shape of a bacteria cell's DNA
In the cytoplasm
Where a bacteria cell's DNA can be found
in the nucleus
Where a eukaryotic cell's DNA can be found.
Adenine and Guanine
The bases known as the purines.
Thymine and Cytosine
The bases known as the pyrimidines.